Abstract
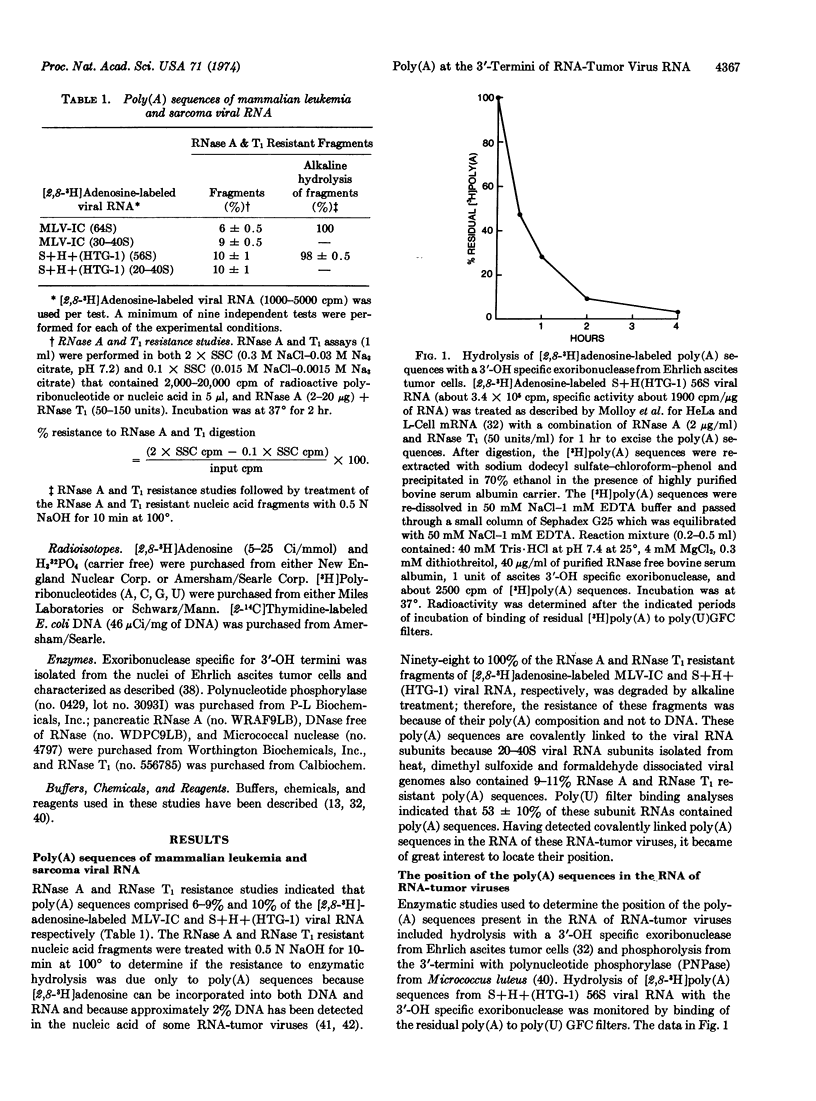
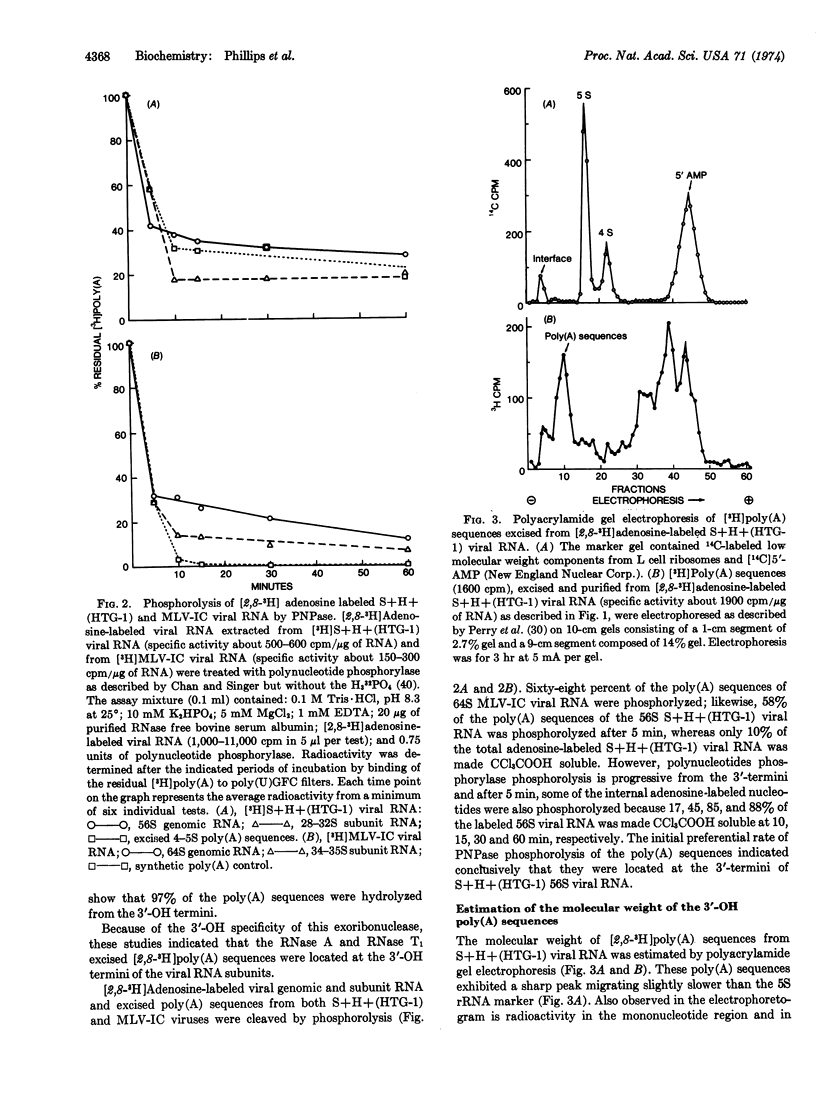
The location of poly(A) sequences in the RNA of mammalian RNA-tumor viruses was determined by enzymatic analyses. The 56-64S viral genomic RNAs, the 20-40S viral subunit RNAs, and the 4-5S poly(A) sequences excised from these viral RNAs were subjected to either hydrolysis with a 3′-OH specific exoribonuclease from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells or phosphorolysis from the 3′-termini with polynucleotide phosphorylase from Micrococcus luteus. Purified adenosine-labeled poly(A) fragments, excised from genomic viral RNAs by RNase A and T1 digestion, were hydrolyzed with the 3′-OH specific exoribonuclease for various periods of time. Poly(U) filter binding studies of the residual poly(A) indicated that 97% of the poly(A) fragments were hydrolyzed. Adenosine-labeled genomic and subunit viral RNAs and excised poly(A) fragments were phosphorolyzed from their 3′-termini for various periods of time with polynucleotide phosphorylase. The degree of phosphorolysis was monitored by poly(U) filter binding studies, and CCl3COOH insolubility and solubility determinations. There was an initial preferential rate of phosphorolysis of the poly(A) sequences of genomic and subunit viral RNAs as compared to the total adenosine-labeled viral RNAs. The data from these two different enzymatic mechanisms of action indicated conclusively that the poly(A) sequences were located at the 3′-termini of genomic and subunit viral RNAs.
Keywords: RNA-tumor viral RNA, poly(A) detection and location, 3′-OH exoribonuclease hydrolysis, polynucleotide phosphorylase phosphorolysis
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A., Edmonds M., Nakazato H., Phillips B. A., Vaughn M. H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the virion RNA of poliovirus and Eastern Equine Encephalitis virus. Science. 1972 May 5;176(4034):526–528. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4034.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEERS R. F., Jr Hydrolysis of polyadenylic acid by pancreatic ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2393–2398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachenheimer S. L., Roizman B. Ribonucleic acid synthesis in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. VI. Polyadenylic acid sequences in viral messenger ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):875–879. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.875-879.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswal N., McCain B., Maccain B., Benyeshh-Melnick M. The DNA of murine sarcoma-leukemia virus. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):697–706. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Singer M. F. Kinetic analysis of the phosphorolysis of oligonucleotides by polynucleotide phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):995–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jelinek W. R., Molloy G. R. Biogenesis of mRNA: genetic regulation in mammalian cells. Science. 1973 Sep 28;181(4106):1215–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4106.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaghue T. P., Faulkner P. Characterisation of the 3'-terminus of Sindbis virion RNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 12;246(154):168–170. doi: 10.1038/newbio246168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton B. T., Faulkner P. Heterogeneity in the poly(A) content of the genome of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):865–873. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90440-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds M., Vaughan M. H., Jr, Nakazato H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the heterogeneous nuclear RNA and rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA of HeLa cells: possible evidence for a precursor relationship. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1336–1340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Summers D. F. Adenylate-rich sequences in vesicular stomatitis virus messenger ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):683–688. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.683-688.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Takemoto K., Robert M., Gallo R. C. Polyadenylic acid in Visna virus RNA. Science. 1973 Mar 30;179(4080):1328–1330. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4080.1328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Cartas M. The genome of RNA tumor viruses contains polyadenylic acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):791–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R., Perry R. P. Relative occurrence of polyadenylic acid sequences in messenger and heterogeneous nuclear RNA of L cells as determined by poly (U)-hydroxylapatite chromatography. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 14;72(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. A. Terminal-sequence studies of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid. The 3'-termini of rabbit reticulocyte ribosomal RNA. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(2):353–363. doi: 10.1042/bj1200353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W., Adesnik M., Salditt M., Sheiness D., Wall R., Molloy G., Philipson L., Darnell J. E. Further evidence on the nuclear origin and transfer to the cytoplasm of polyadenylic acid sequences in mammalian cell RNA. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 15;75(3):515–532. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90458-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. E., Bose H. R. An adenylate-rich segment in the virion RNA of Sindbis virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):712–718. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80198-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. E., Bose H. R. Correlation of messenger RNA function with adenylate-rich segments in the genomes of single-stranded RNA viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1514–1516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Duesberg P. H. Adenylic acid-rich sequence in RNAs of Rous sarcoma virus and Rauscher mouse leukaemia virus. Nature. 1972 Feb 18;235(5338):383–386. doi: 10.1038/235383c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Mendecki J., Brawerman G. A polynucleotide segment rich in adenylic acid in the rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA component of mouse sarcoma 180 ascites cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1331–1335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson W., Bishop J. M., Quintrell N., Jackson J. Presence of DNA in Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1970 Sep 5;227(5262):1023–1025. doi: 10.1038/2271023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Gillespie D. Poly U tracts absent from viral RNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 8;240(97):43–45. doi: 10.1038/newbio240043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin C. S., Warner J. R., Edmonds M., Nakazato H., Vaughan M. H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in yeast messenger ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1466–1471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy G. R., Sporn M. B., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Localization of polyadenylic acid sequences in messenger ribonucleic acid of mammalian cells. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 15;11(17):3256–3260. doi: 10.1021/bi00767a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E., LaTorre J. Lack of polyadenylic acid sequences in the messenger RNA of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 26;48(6):1593–1600. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90896-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., La Torre J., Kelley D. E., Greenberg J. R. On the lability of poly(A) sequences during extraction of messenger RNA from polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Wall R., Glickman G., Darnell J. E. Addition of polyadenylate sequences to virus-specific RNA during adenovirus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2806–2809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. A., Hollis V. W., Jr, Bassin R. H., Fischinger P. J. Characterization of RNA from noninfectious virions produced by sarcoma positive-leukemia negative transformed 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):3002–3006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.3002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskas H. J., Bhaduri S. Poly(adenylic acid) sequences in adenovirus ribonucleic acid released from isolated nuclei. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb 27;12(5):920–925. doi: 10.1021/bi00729a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz M., Gillespie D., Saxinger W. C., Robert M., Gallo R. C. Poly (rA) tracts of tumor virus 70S RNA are not transcribed in endogenous or reconstituted reactions of viral reverse transcriptase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Dec 4;49(5):1216–1224. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90598-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rho H. M., Green M. The homopolyadenylate and adjacent nucleotides at the 3'-terminus of 30-40s RNA subunits in the genome of murine sarcoma-leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2386–2390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Tronick S. R., Scolnick E. M. Polyadenylate rich RNA in the 70 S RNA of murine leukemia-sarcoma virus. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):230–235. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríman J. Evidence for uracil nucleotide-rich segments in the RNA molecule of the virus BAI strain A (avian myeloblastosis). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Nov 22;25(4):447–453. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90226-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon R., Jurale C., Kates J. Detection of polyadenylic acid sequences in viral and eukaryotic RNA(polu(U)-cellulose columns-poly(U) filters-fiberglass-HeLa cells-bacteriophage T4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):417–421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon R., Kates J., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Polyadenylic acid sequences on 3' termini of vaccinia messenger ribonucleic acid and mammalian nuclear and messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 26;11(20):3829–3834. doi: 10.1021/bi00770a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S., Bachenheimer S. L., Frenkel N., Roizman B. Relationship between post-transcriptional adenylation of herpes virus RNA and messenger RNA abundance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2101–2104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Lazarus H. M., Smith J. M., Henderson W. R. Studies on nuclear exoribonucleases. 3. Isolation and properties of the enzyme from normal and malignant tissues of the mouse. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1698–1706. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson M. L., Scott J. F., Zamecnik P. C. Evidence that the polyadenylic acid segment of "35S" RNA of avian myeloblastosis virus is located at the 3'-OH terminus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 1;55(1):8–16. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80052-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Banerjee A. K. Two oligonucleotide classes of single-stranded ribopolymers in reovirus A-rich RNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Oct;152(2):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90269-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R., Banerjee A. K., LaFiandra A., Shatkin A. J. Reovirus-specific ribonucleic acid from polysomes of infected L cells. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):61–69. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.61-69.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Ben-Ishai Z., Newbold J. E. Poly A associated with SV40 messenger RNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):111–113. doi: 10.1038/newbio238111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Poly (A) and poly (U) in poliovirus double stranded RNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 11;242(119):171–174. doi: 10.1038/newbio242171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



