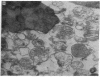
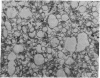
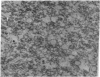
Abstract
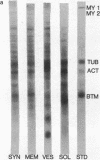
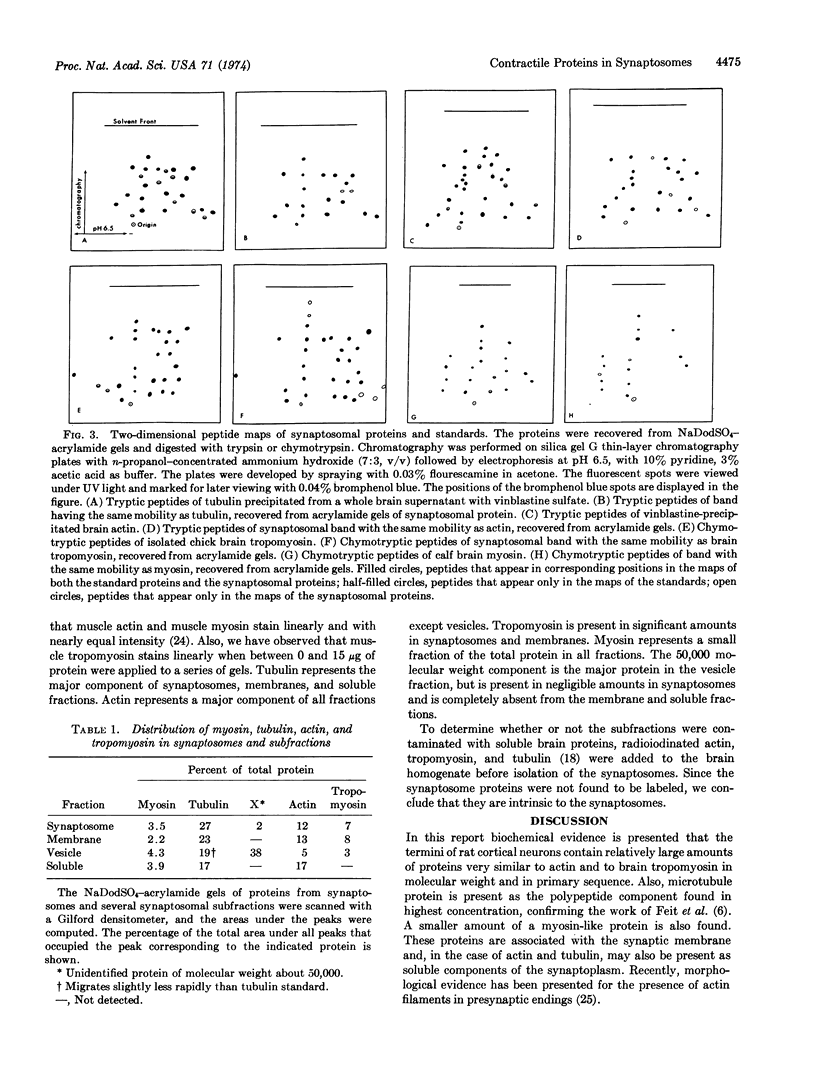
Material in major bands with molecular weights corresponding to those of actin, brain tropomyosin, and myosin is present in purified rat synaptosomes dissolved in sodium dodecyl sulfate and subjected to electrophoresis on dodecyl sulfate-acrylamide gels. A band corresponding to tubulin appears to be the major constituent of synaptosomes, confirming the work of Feit and his coworkers. We have demonstrated by peptide mapping that the proteins in these bands have strong chemical similarities to actin, brain tropomyosin, myosin, and tubulin. We have prepared synaptic membrane, vesicle, and soluble fractions from synaptosomes. The polypeptide composition of synaptic membranes, as determined by dodecyl sulfate-acrylamide gel electrophoresis, is similar to that of synaptosomes, with tubulin, actin, and tropomyosin being major constituents. Synaptic vesicles have as their major polypeptide an unidentified protein with a molecular weight of 50,000; they also have many bands in common with synaptosomes. The soluble fraction predominantly contains actin and tubulin. The possibility that the muscle-like contractile proteins and tubulin are membrane-associated in various cell types is discussed, as is their possible role in neurotransmitter release.
Keywords: brain; peptide mapping; actin, myosin, tropomyosin; membrane-associated protein
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Conti M. A., Johnson G. S., Pastan I., Pollard T. D. Isolation and characterization of myosin from cloned mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3693–3697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adelstein R. S., Pollard T. D., Kuehl W. M. Isolation and characterization of myosin and two myosin fragments from human blood platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2703–2707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berl S., Puszkin S., Nicklas W. J. Actomyosin-like protein in brain. Science. 1973 Feb 2;179(4072):441–446. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4072.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisy G. G., Taylor E. W. The mechanism of action of colchicine. Binding of colchincine-3H to cellular protein. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):525–533. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D., Brownlee S. M. Peptide mapping of proteins from acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1973 Sep;55(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90306-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison P. F., Winslow B. The protein subunit of calf brain neurofilament. J Neurobiol. 1974;5(2):119–133. doi: 10.1002/neu.480050204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton G. R., Barondes S. Microtubular protein: synthesis and metabolism in developing brain. Science. 1969 Dec 26;166(3913):1637–1638. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3913.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M. Calcium ion and muscle contraction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1968;18:123–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(68)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feit H., Dutton G. R., Barondes S. H., Shelanski M. L. Microtubule protein. Identification in and transport to nerve endings. J Cell Biol. 1971 Oct;51(1):138–147. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine R. E., Blitz A. L., Hitchcock S. E., Kaminer B. Tropomyosin in brain and growing neurones. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 10;245(145):182–186. doi: 10.1038/newbio245182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine R. E., Bray D. Actin in growing nerve cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 24;234(47):115–118. doi: 10.1038/newbio234115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G., WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg C. S., Glick M. C. Electrophoretic study of the polypeptides from surface membranes of mammalian cells. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 26;11(20):3680–3685. doi: 10.1021/bi00770a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grefrath S. P., Reynolds J. A. Polypeptide components of an excitable plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6091–6094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurd J. W., Jones L. R., Mahler H. R., Moore W. J. Isolation and partial characterization of rat brain synaptic plasma membranes. J Neurochem. 1974 Feb;22(2):281–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb11591.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE EFFECT OF CALCIUM ON ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE FROM MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:496–503. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUROKAWA M., SAKAMOTO T., KATO M. A RAPID ISOLATION OF NERVE-ENDING PARTICLES FROM BRAIN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 25;94:307–309. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadota K., Kadota T. Isolation of coated vesicles, plain synaptic vesicles, and flocculent material from a crude synaptosome fraction of guinea pig whole brain. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jul;58(1):135–151. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Soto E. F., de Robertis E. Gangliosides and acetylcholinesterase in isolated membranes of the rat-brain cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 1;135(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metuzals J., Mushynski W. E. Electron microscope and experimental investigations of the neurofilamentous network in Deiters' neurons. Relationship with the cell surface and nuclear pores. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jun;61(3):701–722. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto K., Harrington W. F. Substructure of the thick filament of vertebrate striated muscle. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 15;83(1):83–97. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas W. J., Berl S. Effects of cytochalasin B on uptake and release of putative transmitters by synaptosomes and on brain actomyosin-like protein. Nature. 1974 Feb 15;247(5441):471–473. doi: 10.1038/247471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas W. J., Puszkin S., Berl S. Effect of vinblastine and colchicine on uptake and release of putative transmitters by synaptosomes and on brain actomyosin-like protein. J Neurochem. 1973 Jan;20(1):109–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. T., Poduslo S. E. Myelination in rat brain: method of myelin isolation. J Neurochem. 1973 Oct;21(4):749–757. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb07519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdue J. F. The distribution, ultrastructure, and chemistry of microfilaments in cultured chick embryo fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):265–283. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Korn E. D. Electron microscopic identification of actin associated with isolated amoeba plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):448–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puszkin S., Berl S., Puszkin E., Clarke D. D. Actomyosin-like protein isolated from mammalian brain. Science. 1968 Jul 12;161(3837):170–171. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3837.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raiteri M., Levi G. Stereochemical interpretation of high oxygen affinity of haemoglobin Little Rock alpha-2beta-2 143His-Gln. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 6;243(127):180–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoa N. B., Wooten G. F., Axelrod J., Kopin I. J. Inhibition of release of dopamine- -hydroxylase and norepinephrine from sympathetic nerves by colchicine, vinblastine, or cytochalasin-B (hypogastric nerve stimulation-exocytosis-microtubules-microfilaments-guinea pig). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):520–522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAKER V. P., SHERIDAN M. N. THE MORPHOLOGY AND ACETYLCHOLINE CONTENT OF ISOLATED CEREBRAL CORTICAL SYNAPTIC VESICLES. J Neurochem. 1965 May;12:363–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb04237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenberg R. C. Microtubule formation in vitro in solutions containing low calcium concentrations. Science. 1972 Sep 22;177(4054):1104–1105. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4054.1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P., Essman W. B., Dowe G. H. The isolation of pure cholinergic synaptic vesicles from the electric organs of elasmobranch fish of the family Torpedinidae. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(4):833–845. doi: 10.1042/bj1280833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]