Abstract
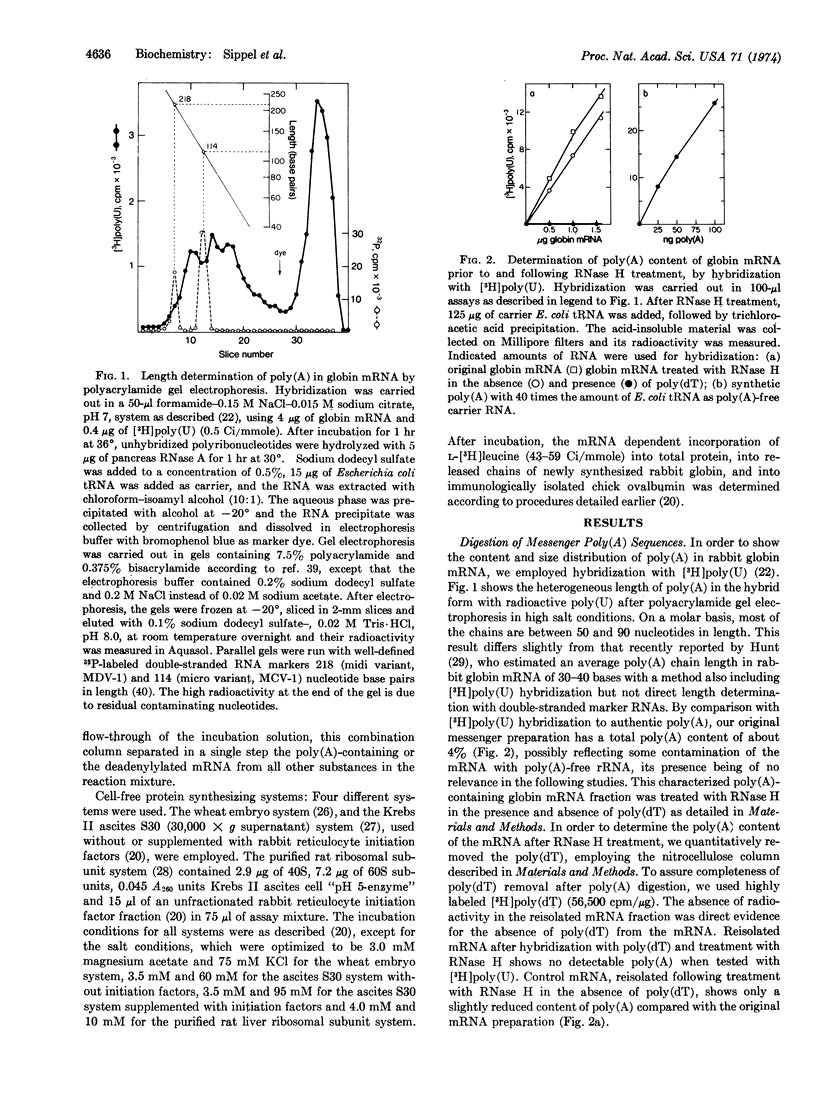
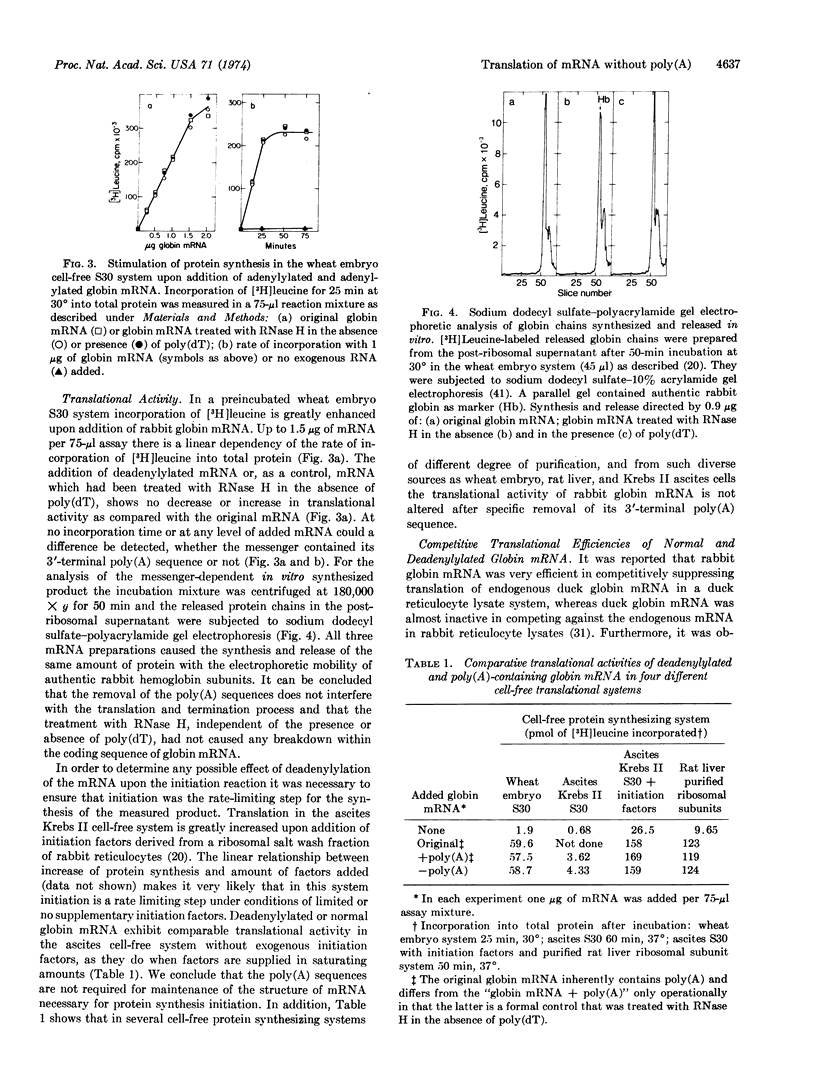
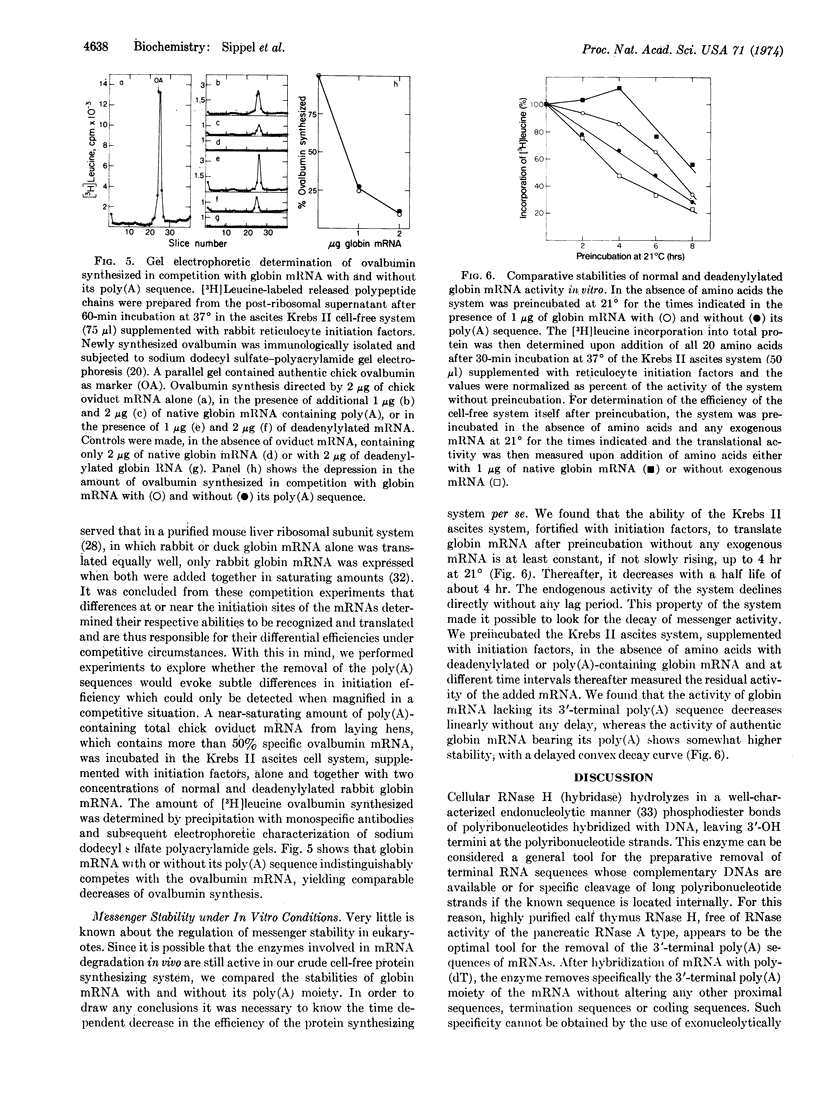
Highly purified RNase H (RNA·DNA hybrid ribonucleotidohydrolase, EC 3.1.4.34) from calf thymus was used to specifically remove the poly(A) sequences of purified rabbit globin mRNA after its hybridization with poly(dT). The deadenylylated globin mRNA was repurified by a one-step procedure including a nitrocellulose column. The poly(A) size and the content of unmodified mRNA were determined by hybridization with [3H]-poly(U), and it could be shown that the RNase H digestion method effectively removes this terminal poly(A) sequence. No difference in activity was found between mRNAs with and without poly(A) to initiate, elongate, terminate, and release newly synthesized globin chains in exogenous-mRNA-dependent, cell-free, protein-synthesizing systems from wheat embryo, ascites Krebs II cells, and rat liver. Furthermore, poly(A)-free globin mRNA competed with the same efficiency as authentic globin mRNA against chick ovalbumin mRNA when translated under total mRNA saturation conditions. It is apparent that the 3′-terminal poly(A) sequence is not necessary to maintain the translationally active secondary and tertiary configuration of the globin mRNA molecule. Preincubation of intact and deadenylylated globin mRNA in the Krebs II ascites translational system indicates that the presence of the poly(A) sequence may stabilize the translationally active mRNA molecule.
Keywords: poly(dT), nitrocellulose column, cell-free protein synthesis systems, mRNA competition, mRNA stability
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adesnik M., Darnell J. E. Biogenesis and characterization of histone messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Claybrook J. R., Spiegelman S. Electrophoretic separation of viral nucleic acids on polyacrylamide gels. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):373–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. A protein of molecular weight 78,000 bound to the polyadenylate region of eukaryotic messenger RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):924–928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunitzer G., Best J. S., Flamm U., Schrank B. Zur Phylogenie des Hämoglobins: Untersuchungen am Hämoglobin des Kaninchens (Caniculus) Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1966;347(4):207–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. M., Bollum F. J. Deoxynucleotide-polymerizing enzymes of calf thymus gland. V. Homogeneous terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):909–916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Wall R., Tushinski R. J. An adenylic acid-rich sequence in messenger RNA of HeLa cells and its possible relationship to reiterated sites in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1321–1325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds M., Vaughan M. H., Jr, Nakazato H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the heterogeneous nuclear RNA and rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA of HeLa cells: possible evidence for a precursor relationship. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1336–1340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskill P., Kabat D. Unexpectedly large size of globin messenger ribonucleic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):72–75. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. A. Interaction between polyuridylic acid and rabbit globin messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):327–333. doi: 10.1042/bj1310327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. E., Bose H. R. Correlation of messenger RNA function with adenylate-rich segments in the genomes of single-stranded RNA viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1514–1516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K. I., Gonçalves J. M., Houts G. E., Bollum F. J. Deoxynucleotide-polymerizing enzymes of calf thymus gland. II. Properties of the terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 10;242(11):2780–2789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W., Crouch R. Degradation of DNA RNA hybrids by ribonuclease H and DNA polymerases of cellular and viral origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3360–3364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan S. W., Brawerman G. A particle associated with the polyadenylate segment in mammalian messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3247–3250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Mendecki J., Brawerman G. A polynucleotide segment rich in adenylic acid in the rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA component of mouse sarcoma 180 ascites cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1331–1335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L., Canellakis E. S. Adenine-rich polymer associated with rabbit reticulocyte messenger RNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):710–712. doi: 10.1038/227710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M., Korner A. Mammalian cell-free protein synthesis directed by viral ribonucleic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):328–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Kramer F. R., Spiegelman S. Complete nucleotide sequence of a replicating RNA molecule. Science. 1973 Jun 1;180(4089):916–927. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4089.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W., Rosenfeld G. C., Comstock J. P., Means A. R. Steroid hormone induction of a specific translatable messenger RNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 8;240(97):45–48. doi: 10.1038/newbio240045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman S., Abelson H. T., Penman S. Mitochondrial protein synthesis: RNA with the properties of Eukaryotic messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):350–353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Wall R., Glickman G., Darnell J. E. Addition of polyadenylate sequences to virus-specific RNA during adenovirus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2806–2809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E., McKnight G. S., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of ovalbumin in a rabbit reticulocyte cell-free system programmed with hen oviduct ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7407–7410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis: the importance of ribosome and initiation factor quality for the efficiency of in vitro systems. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 19;73(3):329–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Translation of duck-globin messenger RNA in a partially purified mammalian cell-free system. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr;34(2):213–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutz G., Beato M., Feigelson P. Messenger RNA for hepatic tryptophan oxygenase: its partial purification, its translation in a heterologous cell-free system, and its control by glucocorticoid hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1218–1221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Darnell J. E. Polyadenylic acid segment in mRNA becomes shorter with age. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 28;241(113):265–268. doi: 10.1038/newbio241265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater D. W., Slater I., Gillespie D. Post-fertilization synthesis of polyadenylic acid in sea urchin embryos. Nature. 1972 Dec 8;240(5380):333–337. doi: 10.1038/240333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater I., Gillespie D., Slater D. W. Cytoplasmic adenylylation and processing of maternal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):406–411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrianopoulos J. G., Chargaff E. Purification and properties of ribonuclease H of calf thymus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1959–1963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. G., Gander E. S., Morel C., Luppis B., Scherrer K. Differential translation of duck- and rabbit-globin messenger RNAs in reticulocyte-lysate systems. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr;34(2):205–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb21105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiapalis C. M., Dorson J. W., De Sante D. M., Bollum F. J. Terminal riboadenylate transferase: a polyadenylate polymerase from calf thymus gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 5;50(3):737–743. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91306-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Crossley J., Humphries S. Translation of mouse globin messenger ribonucleic acid from which the poly(adenylic acid) sequence has been removed. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):703–707. doi: 10.1021/bi00701a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilt F. H. Polyadenylation of maternal RNA of sea urchin eggs after fertilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2345–2349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



