Abstract
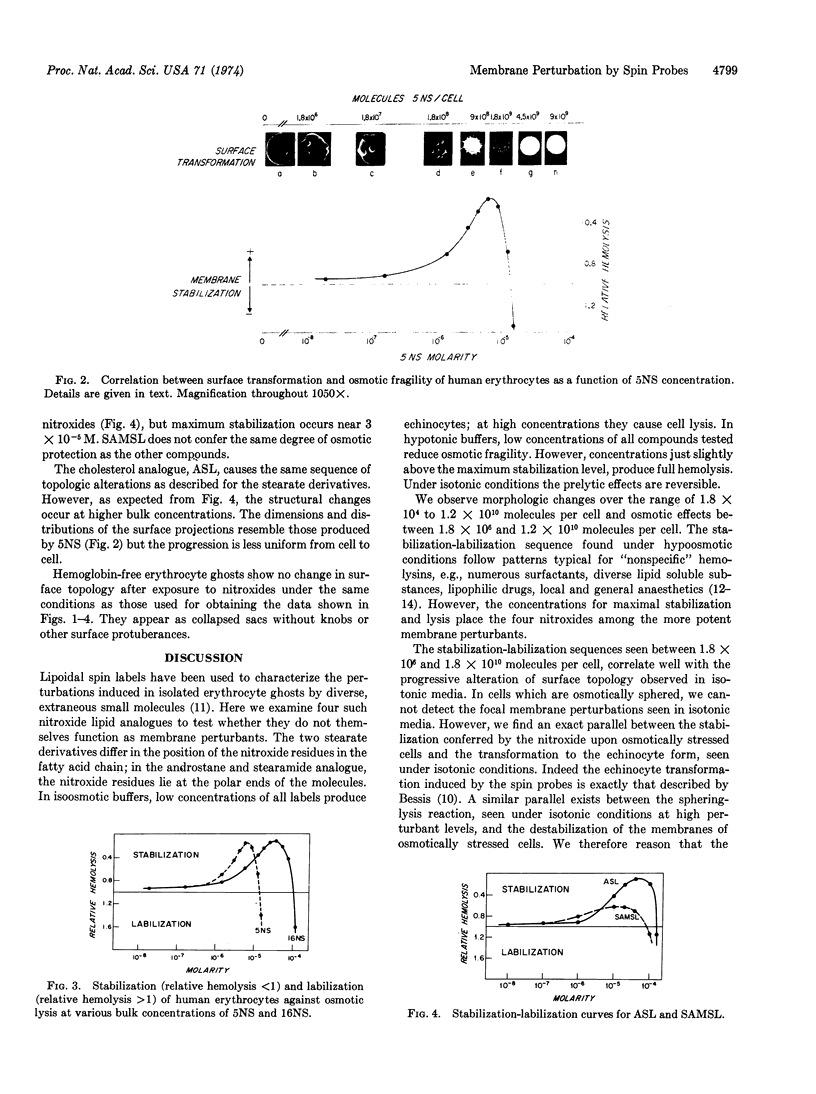
Three classes of lipoidal nitroxide spin probes reversibly perturb erythrocyte membranes at low concentrations (10-10-10-5 M). This is manifest in (a) decreased osmotic fragility and (b) alterations of surface topology. At bulk phase nitroxide concentrations providing maximal osmotic stabilization, the erythrocytes exhibit a classic echinocyte morphology. At nitroxide concentrations very slightly higher than those yielding minimal osmotic fragility (10-5-10-4 M), the cellus undergo a sphering reaction and lyse. The morphologic sequence seen in intact cells is not observed in erythrocyte ghosts. We suggest that the spin probes initially concentrate in focal domains, which expand into echinocytic protrusions primarily due to localized weakening of membrane cohesion. We propose that cell lysis involves an irreversible breakdown in membrane domain structure.
Keywords: scanning electron microscopy, osmotic fragility, echinocytes, membrane domains, paramagnetic probes
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cadenhead D. A., Katti S. S. A comparative study of cholesterol and a cholesterol-like ESR probe in pure and mixed monomolecular films. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):709–712. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley C. M., Metcalfe S. M., Turner B., Burgen A. S., Metcalfe J. C. The binding of benzyl alcohol to erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 1;233(3):720–729. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii T., Sato T., Nakanishi K. In vitro shape changes of human erythrocyte membranes. Physiol Chem Phys. 1973;5(5):423–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Spin-label studies of the excitable membranes of nerve and muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):12–16. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., Metcalfe J. C., Metcalfe S. M., McConnell H. M. The interaction of small molecules with spin-labelled erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 1;219(2):415–427. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith A. D., Sharnoff M., Cohn G. E. A summary and evaluation of spin labels used as probes for biological membrane structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 28;300(4):379–419. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlhorn R., Snipes W., Keith A. Spin label motion in fatty acids. Biophys J. 1973 Nov;13(11):1223–1231. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)86057-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe J. C., Burgen A. S. Relaxation of anaesthetics in the presence of cyto-membranes. Nature. 1968 Nov 9;220(5167):587–588. doi: 10.1038/220587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe J. C., Seeman P., Burgen A. S. The proton relaxation of benzyl alcohol in erythrocyte membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1968 Jan;4(1):87–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Seeman P. Anesthetics expand erythrocyte membranes without causing loss of K + . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):190–198. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Fujii T. Changes in shape and osmotic resistance of human erythrocytes resulted from changes in the lysolecithin content of the membranes. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1974 Jan;22(1):152–156. doi: 10.1248/cpb.22.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. Erythrocyte membrane stabilization by steroids and alcohols; a possible model for anesthesia. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Oct;15(10):1632–1637. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90214-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Kwant W. O., Sauks T., Argent W. Membrane expansion of intact erythrocytes by anesthetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;183(3):490–498. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90163-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco J., Ghosh D., Keith A. D. Interactions of spin-labeled lipid molecules with natural lipids in monolayers at the air-water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):279–285. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D. F., Verma S. P., Weidekamm E., Bieri V. Hydrophobic binding sites in bovine serum albumin and erythrocyte ghost proteins. Study by spin-labelling, paramagnetic fluorescence quenching and chemical modification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):68–81. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90294-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]