Abstract
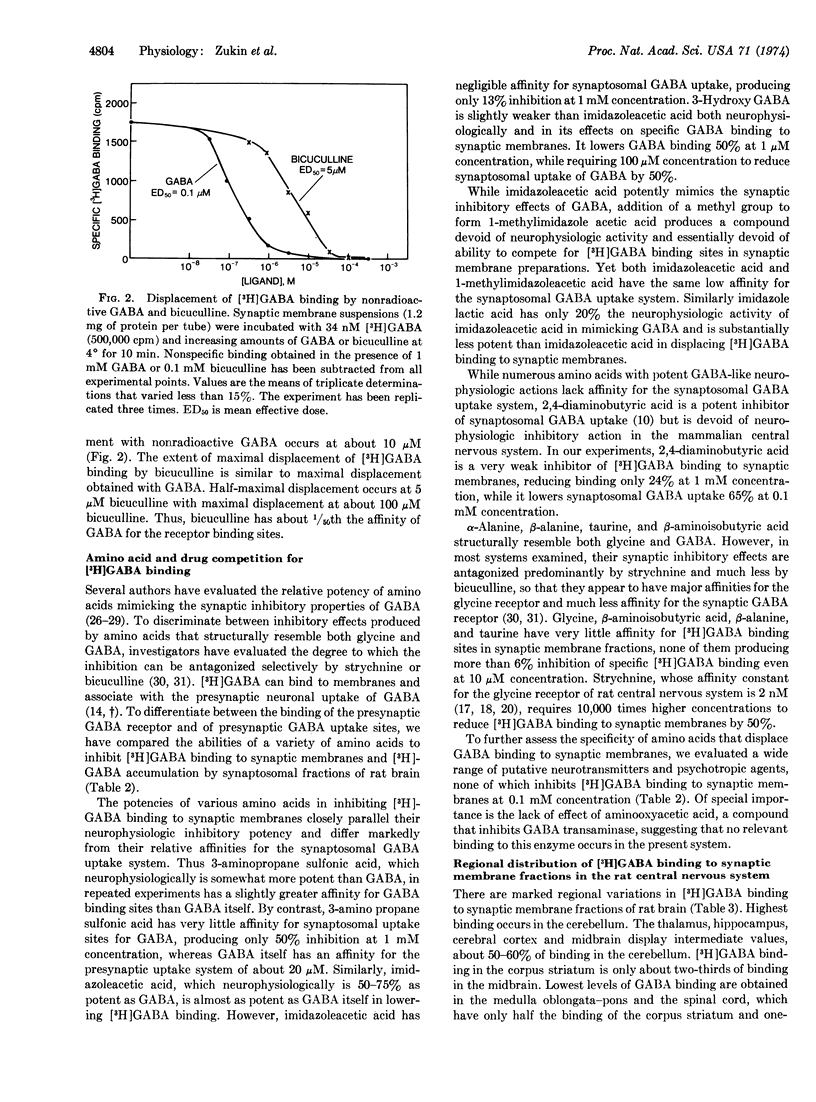
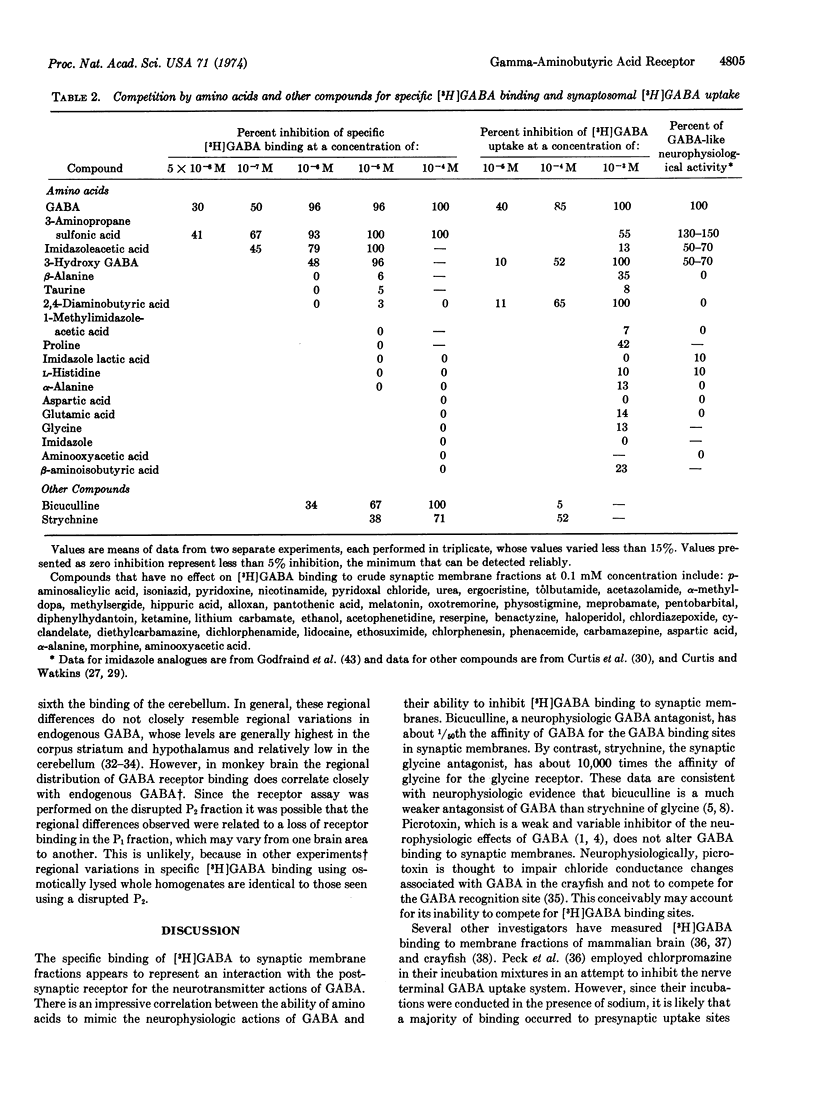
[3H]Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) binds to synaptic membrane fractions of rat brain in a selective fashion representing an interaction with postsynaptic GABA receptors. Inhibition of [3H]GABA binding by a variety of amino acids closely parallels their ability to mimic the synaptic inhibitory actions of GABA and does not correlate with their relative affinity for the presynaptic synaptosomal GABA uptake system. [3H]GABA binding is saturable with an affinity constant of about 0.1 μM. The GABA antagonist bicuculline inhibits [3H]GABA binding with half maximal effects at 5 μM, whereas it requires a concentration of 0.5 mM to reduce synaptosomal GABA uptake by 50%. In subcellular fractionation experiments [3H]GABA binding is most enriched in crude synaptic membranes. [3H]GABA binding is greatest in the cerebellum, least in the spinal cord and medulla oblongatapons, with intermediate values in the thalamus, hippocampus, hypothalamus, cerebral cortex, midbrain, and corpus striatum.
Keywords: neurotransmitter, bicuculline, synaptic membranes, glycine, strychnine
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERL S., WAELSCH H. Determination of glutamic acid, glutamine, glutathione and gamma-aminobutyric acid and their distribution in brain tissue. J Neurochem. 1958 Dec;3(2):161–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. P., Jr, Logan W. J., Snyder S. H. Amino acids as central nervous transmitters: the influence of ions, amino acid analogues, and ontogeny on transport systems for L-glutamic and L-aspartic acids and glycine into central nervous synaptosomes of the rat. J Neurochem. 1973 Dec;21(6):1533–1550. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb06037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Brown D. A. -Aminobutyric acid uptake by sympathetic ganglia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 19;238(81):89–91. doi: 10.1038/newbio238089a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD J. M., CURTIS D. R. THE EXCITATION AND DEPRESSION OF MAMMALIAN CORTICAL NEURONES BY AMINO ACIDS. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Oct;23:313–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PHILLIS J. W., WATKINS J. C. The depression of spinal neurones by gamma-amino-n-butyric acid and beta-alanine. J Physiol. 1959 Apr 23;146(1):185–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., WATKINS J. C. The excitation and depression of spinal neurones by structurally related amino acids. J Neurochem. 1960 Sep;6:117–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1960.tb13458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Felix D., Johnston G. A. Bicuculline, an antagonist of GABA and synaptic inhibition in the spinal cord of the cat. Brain Res. 1971 Sep 10;32(1):69–96. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Felix D., Johnston G. A., McLennan H. Antagonism between bicuculline and GABA in the cat brain. Brain Res. 1971 Oct 8;33(1):57–73. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Johnston G. A. The inactivation of extracellularly administered amino acids in the feline spinal cord. Exp Brain Res. 1970 Jun 25;10(5):447–462. doi: 10.1007/BF00234262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Hösli L., Johnston G. A. A pharmacological study of the depression of spinal neurones by glycine and related amino acids. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00235443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Watkins J. C. The pharmacology of amino acids related to gamma-aminobutyric acid. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Dec;17(4):347–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. Molecular biology of synaptic receptors. Science. 1971 Mar 12;171(3975):963–971. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3975.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeudis F. V. Sodium dependency of gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to particulate fractions of mouse brain. Exp Neurol. 1973 Oct;41(1):54–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(73)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT K. A., VAN GELDER N. M. Occlusion and metabolism of gamma-aminobutyric acid by brain tissue. J Neurochem. 1958 Oct;3(1):28–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahn S., Côté L. J. Regional distribution of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in brain of the rhesus monkey. J Neurochem. 1968 Mar;15(3):209–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb06198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Iversen L. L. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):655–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind J. M., Krnjević K., Maretić H., Pumain R. Inhibition of cortical neurones by imidazole and some derivatives. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1973 Nov;51(11):790–797. doi: 10.1139/y73-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henn F. A., Hamberger A. Glial cell function: uptake of transmitter substances. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2686–2690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiley C. R., Burgen A. S. The distribution of muscarinic receptor sites in the nervous system of the dog. J Neurochem. 1974 Jan;22(1):159–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb12192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Neal M. J. The uptake of [3H]GABA by slices of rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1968 Oct;15(10):1141–1149. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb06831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan W. J., Snyder S. H. High affinity uptake systems for glycine, glutamic and aspaspartic acids in synaptosomes of rat central nervous tissues. Brain Res. 1972 Jul 20;42(2):413–431. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90540-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. J., Iversen L. L. Autoradiographic localization of 3 H-GABA in rat retina. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 16;235(59):217–218. doi: 10.1038/newbio235217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck E. J., Jr, Schaeffer J. M., Clark J. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid, bicuculline, and post-synaptic binding sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):394–400. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90724-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts E., Kuriyama K. Biochemical-physiological correlations in studies of the gamma-aminobutyric acid system. Brain Res. 1968 Apr;8(1):1–35. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Young A. B., Bennett J. P., Mulder A. H. Synaptic biochemistry of amino acids. Fed Proc. 1973 Oct;32(10):2039–2047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Takeuchi N. A study of the action of picrotoxin on the inhibitory neuromuscular junction of the crayfish. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(2):377–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINSTEIN H., VARON S., MUHLEMAN D. R., ROBERTS E. A CARRIER-MEDIATED TRANSFER MODEL FOR THE ACCUMULATION OF 14-C-GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID BY SUBCELLULAR BRAIN PARTICLES. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 Mar;14:273–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werman R. CNS cellular level: membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1972;34:337–374. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.34.030172.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werman R., Davidoff R. A., Aprison M. H. Inhibitory of glycine on spinal neurons in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Jan;31(1):81–95. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. B., Oster-Granite M. L., Herndon R. M., Snyder S. H. Glutamic acid: selective depletion by viral induced granule cell loss in hamster cerebellum. Brain Res. 1974 Jun 14;73(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)91002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Strychnine binding associated with glycine receptors of the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2832–2836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. B., Zukin S. R., Snyder S. H. Interaction of benzodiazepines with central nervous glycine receptors: possible mechanism of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2246–2250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



