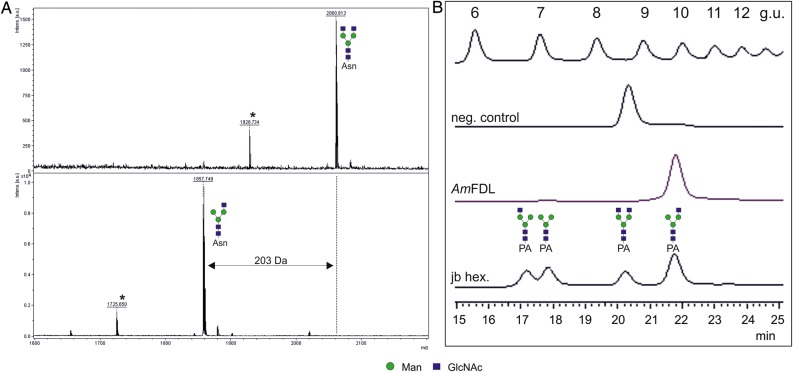
Fig. 4.
Apis mellifera hexosaminidase is a true FDL enzyme. The recombinantly expressed, affinity-purified A. mellifera hexosaminidase removes only one of the two terminal β-GlcNAc residues from a glycopeptide carrying typical biantennary N-glycan (structures were detected in [M+H+] form) (A). To confirm whether the recombinant enzyme shows any preference to one or the other terminal β-linked GlcNAc of a biantennary N-glycan, the activity of the recombinant enzyme was measured using a 2-aminopyridine modified biantennary N-glycan containing two terminal, β-linked GlcNAc residues. For comparison, the same N-glycan structure was partially digested in the presence of jack bean hexosaminidase (jb hex.) generating three different products, as described previously (Léonard et al. 2006) (B). Asterisk indicates the peaks derived from the laser-induced removal of the dabsyl group from the dabsylated glycopeptides. The glycans are depicted following the glycan nomenclature of the Consortium for Functional Glycomics (http://www.functionalglycomics.org). g.u., glucose units.