Abstract
A cell separation technique was designed based on the interaction between cell-surface-bound IgG and protein A of Staphylococcus aureus. The density of lymphoid cells coated with IgG antibodies against one of the surface markers was increased by adherence of staphylococci. Cells with adhering bacteria were separated from cells without bacteria by density gradient centrifugation in 11.5% sodium metrizoate. Bacteria were removed from the lymphoid cells by lysostaphin digestion.
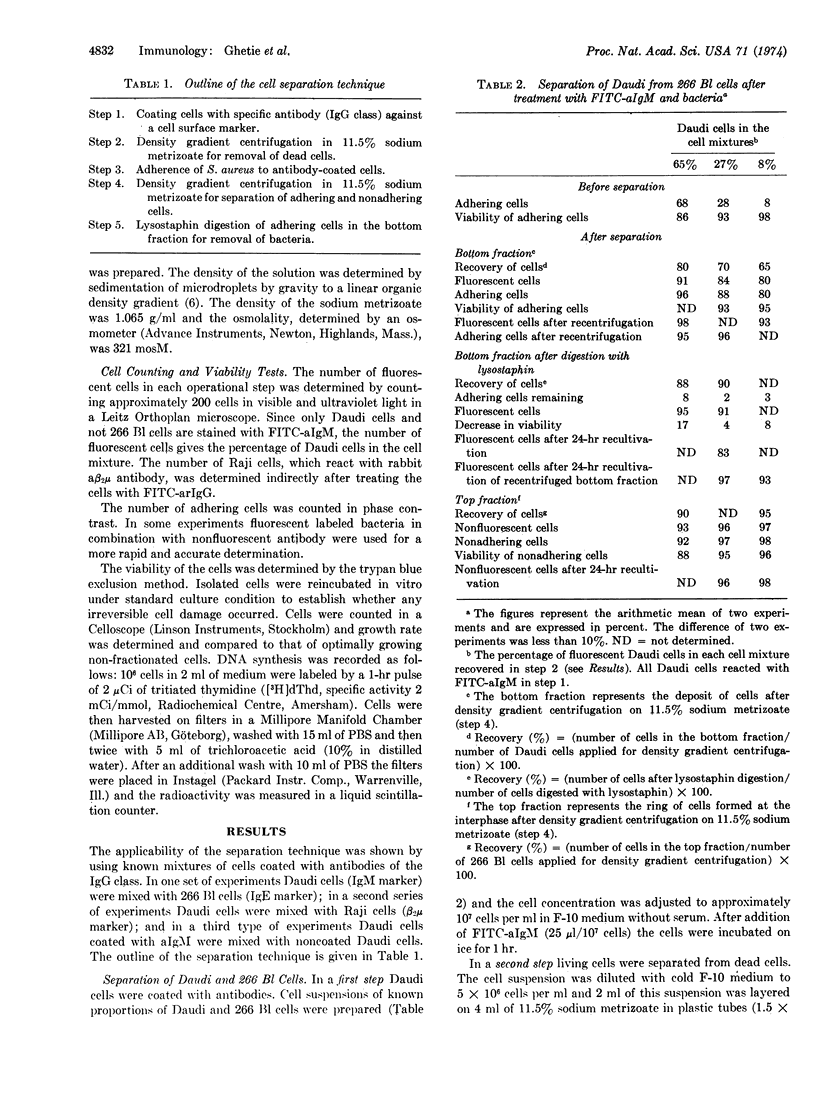
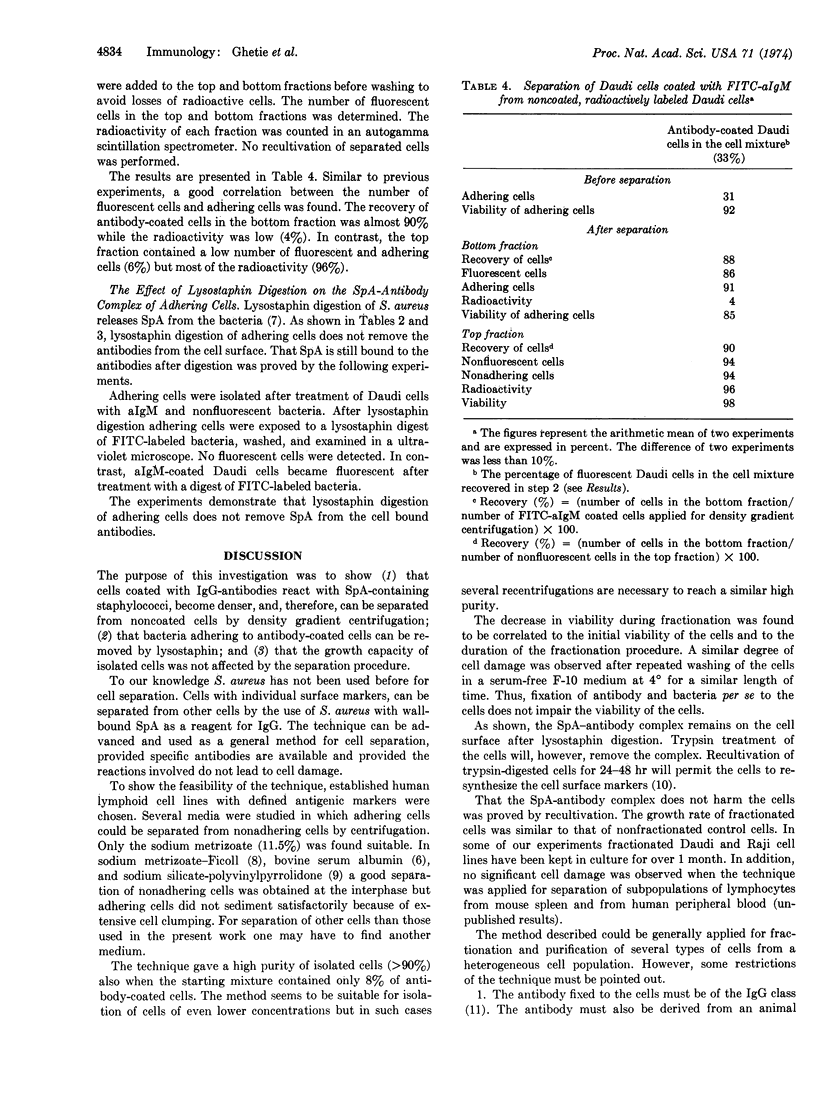
The purity of separated cells was approximately 95% even when the proportion of a specific cell population was below 10% in the initial mixture. The viability and the ability of cells to multiply in vitro were not significantly impaired by the fractionating procedure.
The technique can generally be applied for cell separation, provided antibodies of the IgG class against specific surface markers are available.
Keywords: surface-bound IgG, sodium metrizoate, lysostaphin
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghetie V., Nilsson K., Sjöquist J. Detection and quantitation of IgG on the surface of human lymphoid cells by rosette formation with protein A-coated sheep red blood cells. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Jul;4(7):500–505. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghetie V., Nilsson K., Sjöquist J. Identification of cell surface immunoglobulin markers by protein A-containing fluorescent staphylococci. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(4):397–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1300–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Bennich H., Johansson S. G., Pontén J. Established immunoglobulin producing myeloma (IgE) and lymphoblastoid (IgG) cell lines from an IgE myeloma patient. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Oct;7(4):477–489. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortman K. The separation of different cell classes from lymphoid organs. II. The purification and analysis of lymphocyte populations by equilibrium density gradient centrifugation. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Aug;46(4):375–396. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist J., Meloun B., Hjelm H. Protein A isolated from Staphylococcus aureus after digestion with lysostaphin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 25;29(3):572–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Baur S., Uhr J. W. Cell surface immunoglobulin. II. Isolation and characterization of immunoglobulin from mouse splenic lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):242–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


