Abstract
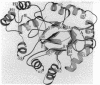
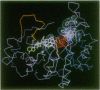
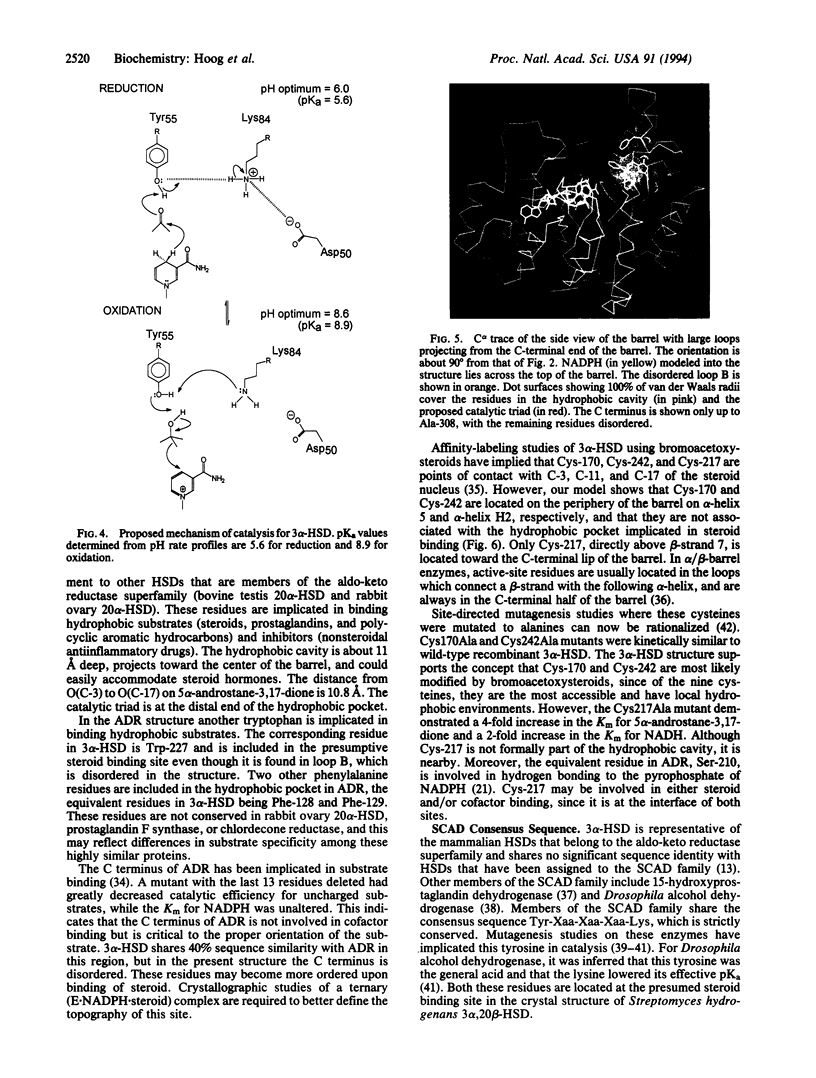
The 3.0-A-resolution x-ray structure of rat liver 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/dihydrodiol dehydrogenase (3 alpha-HSD, EC 1.1.1.50) was determined by molecular replacement using human placental aldose reductase as the search model. The protein folds into an alpha/beta or triose-phosphate isomerase barrel and lacks a canonical Rossmann fold for binding pyridine nucleotide. The structure contains a concentration of hydrophobic amino acids that lie in a cavity near the top of the barrel and that are presumed to be involved in binding hydrophobic substrates (steroids, prostaglandins, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) and inhibitors (nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs). At the distal end of this cavity lie three residues in close proximity that have been implicated in catalysis by site-directed mutagenesis--Tyr-55, Asp-50, and Lys-84. Tyr-55 is postulated to act as the general acid. 3 alpha-HSD shares significant sequence identity with other HSDs that belong to the aldo-keto reductase superfamily and these may show similar architecture. Other members of this family include prostaglandin F synthase and rho-crystallin. By contrast, 3 alpha-HSD shares no sequence identity with HSDs that are members of the short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase family but does contain the Tyr-Xaa-Xaa-Xaa-Lys consensus sequence implicated in catalysis in this family. In the 3 alpha-HSD structure these residues are on the periphery of the barrel and are unlikely to participate in catalysis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal A. K., Monder C., Eckstein B., White P. C. Cloning and expression of rat cDNA encoding corticosteroid 11 beta-dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):18939–18943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askonas L. J., Ricigliano J. W., Penning T. M. The kinetic mechanism catalysed by homogeneous rat liver 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Evidence for binary and ternary dead-end complexes containing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 15;278(Pt 3):835–841. doi: 10.1042/bj2780835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner D. W., Bloomer A. C., Petsko G. A., Phillips D. C., Pogson C. I., Wilson I. A., Corran P. H., Furth A. J., Milman J. D., Offord R. E. Structure of chicken muscle triose phosphate isomerase determined crystallographically at 2.5 angstrom resolution using amino acid sequence data. Nature. 1975 Jun 19;255(5510):609–614. doi: 10.1038/255609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohren K. M., Bullock B., Wermuth B., Gabbay K. H. The aldo-keto reductase superfamily. cDNAs and deduced amino acid sequences of human aldehyde and aldose reductases. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9547–9551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohren K. M., Grimshaw C. E., Gabbay K. H. Catalytic effectiveness of human aldose reductase. Critical role of C-terminal domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20965–20970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borhani D. W., Harter T. M., Petrash J. M. The crystal structure of the aldose reductase.NADPH binary complex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24841–24847. doi: 10.2210/pdb1abn/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Jiang J. C., Lin Z. G., Lee W. R., Baker M. E., Chang S. H. Site-specific mutagenesis of Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase: evidence for involvement of tyrosine-152 and lysine-156 in catalysis. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3342–3346. doi: 10.1021/bi00064a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensor C. M., Tai H. H. Site-directed mutagenesis of the conserved tyrosine 151 of human placental NAD(+)-dependent 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase yields a catalytically inactive enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 30;176(2):840–845. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80262-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber G. K., Petsko G. A. The evolution of alpha/beta barrel enzymes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jun;15(6):228–234. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90035-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh D., Weeks C. M., Grochulski P., Duax W. L., Erman M., Rimsay R. L., Orr J. C. Three-dimensional structure of holo 3 alpha,20 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: a member of a short-chain dehydrogenase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10064–10068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph D., Petsko G. A., Karplus M. Anatomy of a conformational change: hinged "lid" motion of the triosephosphate isomerase loop. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1425–1428. doi: 10.1126/science.2402636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krook M., Marekov L., Jörnvall H. Purification and structural characterization of placental NAD(+)-linked 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase. The primary structure reveals the enzyme to belong to the short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase family. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 23;29(3):738–743. doi: 10.1021/bi00455a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krozowski Z. 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and the short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase (SCAD) superfamily. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1992 Mar;84(1-2):C25–C31. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(92)90064-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy W. R., Washenick K. J., Cook R. G., Dunbar B. S. Molecular cloning and expression of an abundant rabbit ovarian protein with 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Jan;7(1):58–66. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.1.8446108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. K., Kuliopulos A., Mildvan A. S., Talalay P. Environments and mechanistic roles of the tyrosine residues of delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 23;32(7):1816–1824. doi: 10.1021/bi00058a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luu The V., Labrie C., Zhao H. F., Couët J., Lachance Y., Simard J., Leblanc G., Côté J., Bérubé D., Gagné R. Characterization of cDNAs for human estradiol 17 beta-dehydrogenase and assignment of the gene to chromosome 17: evidence of two mRNA species with distinct 5'-termini in human placenta. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1301–1309. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-8-1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marekov L., Krook M., Jörnvall H. Prokaryotic 20 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase is an enzyme of the 'short-chain, non-metalloenzyme' alcohol dehydrogenase type. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):51–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81504-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obeid J., White P. C. Tyr-179 and Lys-183 are essential for enzymatic activity of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Oct 15;188(1):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92373-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowski J. E., Huizinga M., Penning T. M. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA for rat liver 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid/dihydrodiol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8820–8825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penning T. M., Abrams W. R., Pawlowski J. E. Affinity labeling of 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase with 3 alpha-bromoacetoxyandrosterone and 11 alpha-bromoacetoxyprogesterone. Isolation and sequence of active site peptides containing reactive cysteines; sequence confirmation using nucleotide sequence from a cDNA clone. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8826–8834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penning T. M., Mukharji I., Barrows S., Talalay P. Purification and properties of a 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase of rat liver cytosol and its inhibition by anti-inflammatory drugs. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 15;222(3):601–611. doi: 10.1042/bj2220601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penning T. M., Sharp R. B. Prostaglandin dehydrogenase activity of purified rat liver 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):646–652. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90925-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penning T. M., Talalay P. Inhibition of a major NAD(P)-linked oxidoreductase from rat liver cytosol by steroidal and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents and by prostaglandins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4504–4508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricigliano J. W., Penning T. M. Evidence that enzyme-generated aromatic Michael acceptors covalently modify the nucleotide-binding site of 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 1;269(3):749–755. doi: 10.1042/bj2690749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrutton N. S., Berry A., Perham R. N. Redesign of the coenzyme specificity of a dehydrogenase by protein engineering. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):38–43. doi: 10.1038/343038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithgall T. E., Harvey R. G., Penning T. M. Regio- and stereospecificity of homogeneous 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid-dihydrodiol dehydrogenase for trans-dihydrodiol metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6184–6191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takikawa H., Ookhtens M., Stolz A., Kaplowitz N. Cyclical oxidation-reduction of the C3 position on bile acids catalyzed by 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. II. Studies in the prograde and retrograde single-pass, perfused rat liver and inhibition by indomethacin. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):861–866. doi: 10.1172/JCI113144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thatcher D. R., Sawyer L. Secondary-structure prediction from the sequence of Drosophila melanogaster (fruitfly) alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):884–886. doi: 10.1042/bj1870884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrielink A., Lloyd L. F., Blow D. M. Crystal structure of cholesterol oxidase from Brevibacterium sterolicum refined at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jun 5;219(3):533–554. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. C., Murdock G. L., Ma Y., Goodman S. R., Zimmer W. E. Molecular cloning of testicular 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: identity with aldose reductase. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 16;32(6):1401–1406. doi: 10.1021/bi00057a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westbrook E. M., Piro O. E., Sigler P. B. The 6-A crystal structure of delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Architecture and location of the active center. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9096–9103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. K., Bohren K. M., Gabbay K. H., Quiocho F. A. An unlikely sugar substrate site in the 1.65 A structure of the human aldose reductase holoenzyme implicated in diabetic complications. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):81–84. doi: 10.1126/science.1621098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]