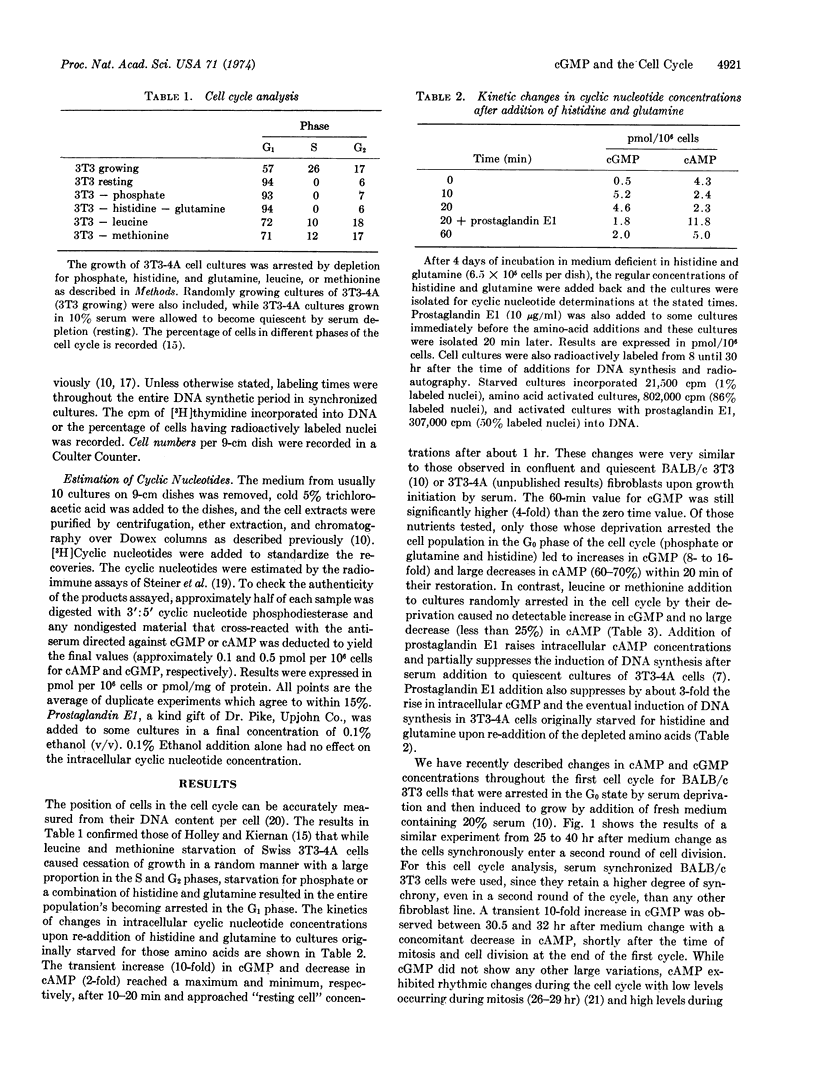
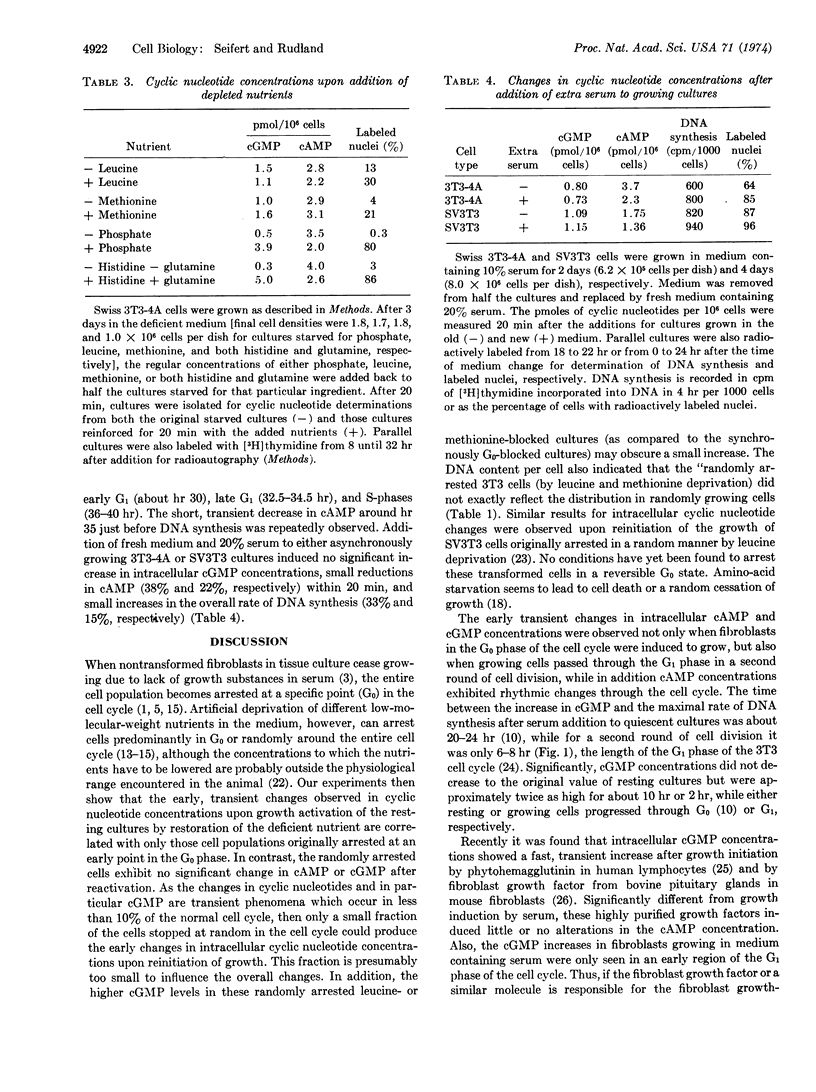
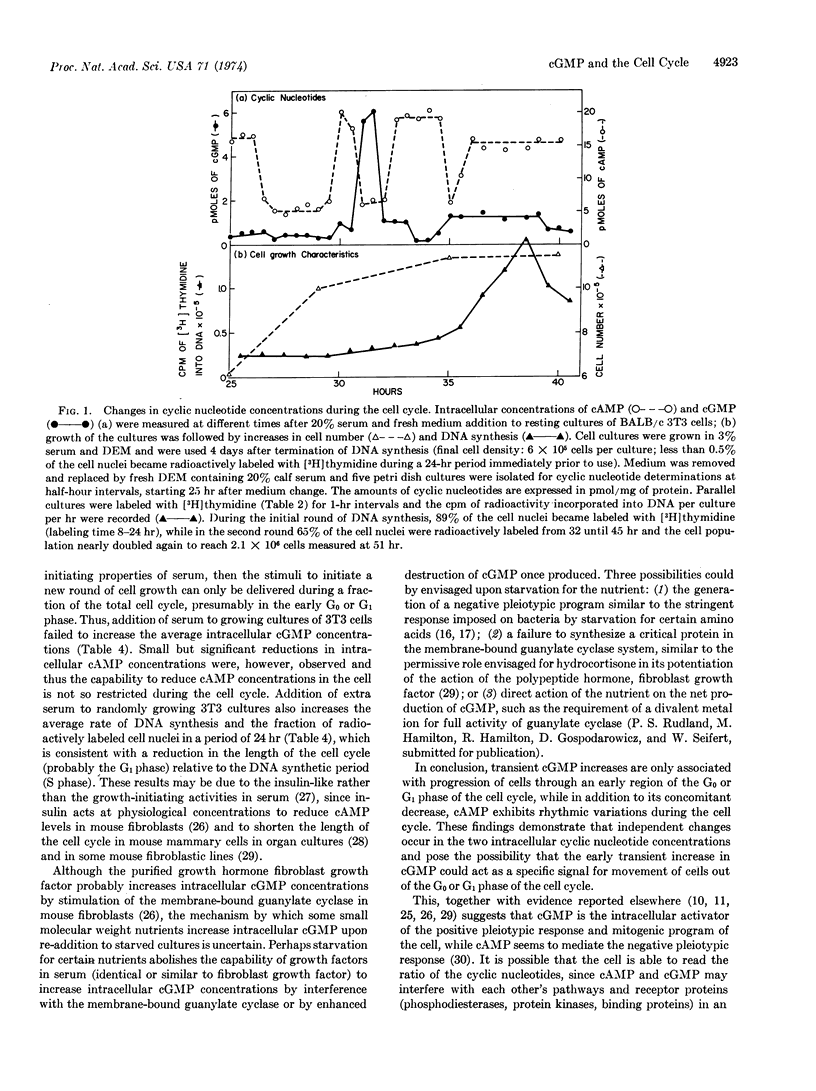
Abstract
The commencement of cell growth following serum addition to quiescent cultures of mouse fibroblasts is preceded by transient changes in intracellular concentrations of cAMP and cGMP. By artificial depletion of the culture medium for different nutrients, cell growth can be reversibly arrested in various phases of the cell cycle. Here it is shown that the major cGMP increases are only observed when cultures which are arrested in the G0 phase are stimulated to grow or when synchronized growing cells pass through the G1 phase. In addition to its concomitant decrease, cAMP exhibits rhythmic changes during the cell cycle. This suggests that the increase in cGMP could act as a specific signal for movement of cells out of the G0 or G1 phase of the cell cycle by activating the pleiotypic and mitogenic program of the cell.
Keywords: cAMP, nutrient starvation, G0 arrest, DNA synthesis
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burger M. M., Bombik B. M., Breckenridge B. M., Sheppard J. R. Growth control and cyclic alterations of cyclic AMP in the cell cycle. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 11;239(93):161–163. doi: 10.1038/newbio239161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulbecco R., Elkington J. Conditions limiting multiplication of fibroblastic and epithelial cells in dense cultures. Nature. 1973 Nov 23;246(5430):197–199. doi: 10.1038/246197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank W. Cyclic 3':5' AMP and cell proliferation in cultures of embryonic rat cells. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Mar;71(1):238–241. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Goldberg B. Synthesis of collagen by mammalian cell lines of fibroblastic and nonfibroblastic origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1360–1365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadden J. W., Hadden E. M., Haddox M. K., Goldberg N. D. Guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate: a possible intracellular mediator of mitogenic influences in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):3024–3027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.3024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Mamont P., Shields R., Tomkins G. M. "Pleiotypic response". Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug;232(33):206–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley R. W., Kiernan J. A. "Contact inhibition" of cell division in 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):300–304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley R. W., Kiernan J. A. Control of the initiation of DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells: low-molecular weight nutrients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2942–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kram R., Tomkins G. M. Pleiotypic control by cyclic AMP: interaction with cyclic GMP and possible role of microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1659–1663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE E. M., BECKER Y., BOONE C. W., EAGLE H. CONTACT INHIBITION, MACROMOLECULAR SYNTHESIS, AND POLYRIBOSOMES IN CULTURED HUMAN DIPLOID FIBROBLASTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:350–356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisler A. I. Studies on contact inhibition of growth in the mouse fibroblast, 3T3. II. Effects of amino acid deprivation and serum on growth rate. J Cell Sci. 1973 May;12(3):861–873. doi: 10.1242/jcs.12.3.861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee A. S., Washburn L. L., Banerjee M. R. Role of insulin as a "permissive" hormone in mammary gland development. Nature. 1973 Nov 16;246(5429):159–160. doi: 10.1038/246159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten J., Johnson G. S., Pastan I. Regulation of cell growth by cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Effect of cell density and agents which alter cell growth on cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7082–7087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1286–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D., Henahan M., Walter S. Changes in growth control and growth requirements associated with neoplastic transformation in vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Nov;53(5):1499–1503. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.5.1499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D. Quiescent SV40 virus transformed 3T3 cells in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):745–753. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudland P. S. Control of translation in cultured cells: continued synthesis and accumulation of messenger RNA in nondividing cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):750–754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudland P. S., Gospodarowicz D., Seifert W. Activation of guanyl cyclase and intracellular cyclic GMP by fibroblast growth factor. Nature. 1974 Aug 30;250(5469):741-2, 773-4. doi: 10.1038/250741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudland P. S., Seeley M., Seifert W. Cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP levels in normal and transformed fibroblasts. Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):417–419. doi: 10.1038/251417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudland P. S., Seifert W., Gospodarowicz D. Growth control in cultured mouse fibroblasts: induction of the pleiotypic and mitogenic responses by a purified growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2600–2604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher C. D., Stathakos D., Antoniades H. N. Dissociation of cell division stimulating capacity for Balb-c-3T3 from the insulin-like activity in human serum. Nature. 1974 Feb 1;247(5439):279–281. doi: 10.1038/247279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert W. E., Rudland P. S. Possible involvement of cyclic GMP in growth control of cultured mouse cells. Nature. 1974 Mar 8;248(5444):138–140. doi: 10.1038/248138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert W., Paul D. Levels of cyclic AMP in sparse and dense cultures of growing and quiescent 3T3 cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 27;240(104):281–283. doi: 10.1038/newbio240281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard J. R. Difference in the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels in normal and transformed cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 1;236(61):14–16. doi: 10.1038/newbio236014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J., Brown R. F., Husakova A., Gilbertson J. R., Zemel R., Lieberman I. Induction of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in the liver of the intact animal. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1757–1766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Parker C. W., Kipnis D. M. Radioimmunoassay for cyclic nucleotides. I. Preparation of antibodies and iodinated cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1106–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Lazar G. K., Green H. The initiation of cell division in a contact-inhibited mammalian cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Dec;66(3):325–333. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030660310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dilla M. A., Trujillo T. T., Mullaney P. F., Coulter J. R. Cell microfluorometry: a method for rapid fluorescence measurement. Science. 1969 Mar 14;163(3872):1213–1214. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3872.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


