Background: Ceramides play crucial roles in cell signaling and survival, yet regulation of their biosynthesis remains poorly understood.
Results: Phosphorylation of the catalytic subunits of ceramide synthase (CerS) by CK2 is essential for CerS activity and cell viability.
Conclusion: CK2 is an important regulator of ceramide biosynthesis.
Significance: Ceramides may provide a link between elevated CK2 activity and cancer.
Keywords: Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), Lipid, Membrane, Protein Kinase, Signaling, Yeast, Sphingolipids
Abstract
Complex sphingolipids are important components of eukaryotic cell membranes and, together with their biosynthetic precursors, including sphingoid long chain bases and ceramides, have important signaling functions crucial for cell growth and survival. Ceramides are produced at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane by a multicomponent enzyme complex termed ceramide synthase (CerS). In budding yeast, this complex is composed of two catalytic subunits, Lac1 and Lag1, as well as an essential regulatory subunit, Lip1. Proper formation of ceramides by CerS has been shown previously to require the Cka2 subunit of casein kinase 2 (CK2), a ubiquitous enzyme with multiple cellular functions, but the precise mechanism involved has remained unidentified. Here we present evidence that Lac1 and Lag1 are direct targets for CK2 and that phosphorylation at conserved positions within the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of each protein is required for optimal CerS activity. Our data suggest that phosphorylation of Lac1 and Lag1 is important for proper localization and distribution of CerS within the ER membrane and that phosphorylation of these sites is functionally linked to the COP I-dependent C-terminal dilysine ER retrieval pathway. Together, our data identify CK2 as an important regulator of sphingolipid metabolism, and additionally, because both ceramides and CK2 have been implicated in the regulation of cancer, our findings may lead to an enhanced understanding of their relationship in health and disease.
Introduction
Sphingolipids are important structural components of cellular membranes, in particular the plasma membrane, where they play important roles in signaling and intracellular trafficking (1). Recent evidence supports the importance of sphingolipids and their biosynthetic precursors as second messengers, with roles in the regulation of diverse processes, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, inflammation, angiogenesis, and differentiation (2–5). Because these processes play a central role in carcinogenesis, sphingolipids have generated much interest as attractive targets for novel cancer therapies (6). The early steps of sphingolipid biosynthesis involve a number of important metabolites that are conserved among eukaryotes, most notably (i) sphingoid long chain bases (LCBs),5 (ii) the phosphorylated forms of these LCBs (LCBPs), and (iii) ceramides (4, 7, 8). A prevailing view for these intermediates has been that LCBPs act within progrowth and survival signaling pathways in mammalian cells, whereas ceramides act in an antiproliferative manner (e.g. inhibiting growth and activating apoptosis-mediated cell death) (9). More recently, ceramides have also been associated with cancer progression, creating a complex relationship between these intermediates and cell survival and death (10, 11). Regulation of the balance of these intermediates is often referred to as the “ceramide/LCBP rheostat” (12) (Fig. 1A, dashed box).
FIGURE 1.
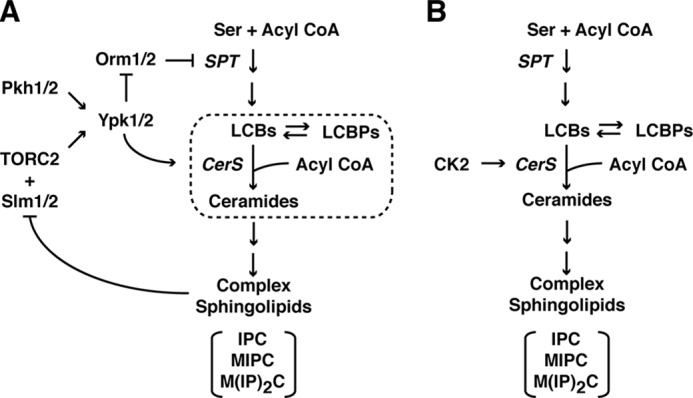
Simplified diagram of the sphingolipid biosynthesis pathway in S. cerevisiae, including regulation of distinct steps within the pathway proposed to be regulated by TORC1/Ypk1/2 signaling (A) and proposed direct regulation of CerS by CK2 (B). In A, the dotted box denotes reactions that compose the so-called ceramide-LCBP rheostat. The major complex sphingolipids in yeast are indicated: inositol phosphorylceramide (IPC), mannose inositol phosphoceramide (MIPC), and mannose-(inositol phosphate)2 ceramide (M(IP)2C). Other components are as described throughout the text.
Synthesis of ceramides represents one of the most evolutionarily conserved steps within the sphingolipid biosynthetic pathway, where close homologs of ceramide synthase (CerS) have been identified in both yeast and mammalian cells (13, 14). Specifically, in yeast, two functionally redundant isoforms exist, encoded by the genes LAC1 and LAG1, whereas at least six different isoforms exist in mammalian cells (CerS1 to -6) (15). In addition, yeast have an essential regulatory subunit encoded by LIP1 that is required for CerS activity both in vitro and in vivo (16). The early steps of the pathway, including formation of ceramides by CerS, take place within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane (17). Remarkably, very little is known about the mechanism(s) by which CerS is regulated; however, we have presented evidence that the function of this enzyme is controlled by the conserved TORC2 (target of rapamycin complex 2)/Ypk1/2 signaling pathway (18, 19) (Fig. 1A). Very recently, Thorner and co-workers (20) have extended these findings by demonstrating Lac1 and Lag1 are direct targets for Ypk1 phosphorylation. Interestingly, TORC2/Ypk1/2 signaling has also been proposed to regulate the first step carried out by the enzyme serine palmitoyltransferase by negatively regulating the ER-associated Orm1/2 proteins (21) (Fig. 1A). Independently, it has been reported that the Cka2 subunit of the casein kinase 2 (CK2) also regulates ceramide production (12), suggesting that both TORC2/Ypk1/2 and CK2 are required for CerS activity and may collaborate to control reactions within the early steps of the pathway (Fig. 1, A and B).
CK2 is a broadly expressed and highly conserved serine/threonine kinase, for which a large number of substrates have been identified that encompass a variety of progrowth cellular events (22). Indeed, because CK2 is a potent suppressor of apoptosis, it has received attention recently as a target for cancer therapy (23, 24). CK2 is a tetrameric enzyme, composed in yeast of two catalytic subunits, encoded by CKA1 and CKA2, and two regulatory subunits, encoded by CKB1 and CKB2. CK2 has been localized to multiple cellular compartments, including at the ER membrane, thus making it potentially available to interact directly with components of CerS (25). Here we present evidence that Lac1 and Lag1 are indeed direct targets for phosphorylation by CK2 and that this phosphorylation is required for efficient ceramide biosynthesis, in part because it maintains proper localization of CerS within the ER membrane. Because of the increasingly recognized role of ceramides in cancer cell growth, regulation of CerS by CK2 may contribute to our understanding of the oncogenic activity of this kinase.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Strains, Media, and Plasmids
Yeast strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. Culture medium used was synthetic complete dextrose (SCD) (0.8% yeast nitrogen base without amino acids, pH 5.5, 2% dextrose) supplemented with amino acids as described previously (26). All yeast transformations were conducted using a lithium acetate procedure (27). Construction of deletion strains by replacement of complete open reading frames (ORFs) with a selectable marker was performed as described previously (28). Construction of expression plasmids was performed by PCR amplification, with mutations introduced by PCR SOEing.
TABLE 1.
S. cerevisiae strains used in this study
| Strain | Genotype | Source |
|---|---|---|
| LHY291 | Mat (a) his3 trp1 lys2 ura3 leu2 bar1 | L. Hicke |
| LHY300 | Mat (α) his3 trp1 lys2 ura3 leu2 bar1 | L. Hicke |
| PLY697 | LHY300, except avo3-30-myc::TRP | This study |
| PLY979 | LHY291, except cka2::TRP | This study |
| PLY981 | LHY291, except cka2::HIS | This study |
| PLY865 | LHY291, except HA3-LAC1:His | This study |
| PLY890 | LHY291, except HA3-LAG1:His | This study |
| PLY1044 | LHY291, except cka2::TRP, HA3-LAC1:His | This study |
| PLY1045 | LHY291, except cka2::TRP, HA3-LAG1:His | This study |
| PLY1225 | LHY291, except lac1::HIS3 lag1::TRP1 + [pPL276] | This study |
| PLY1226 | LHY291, except lac1::HIS3 lag1::TRP1 + [pPL277] | This study |
| PLY1345 | LHY291, expect cka1::TRP | This study |
| PLY1500 | LHY291, except lac1::HIS lag1::TRP + [pPL546] | This study |
| PLY1501 | LHY291, except lac1::HIS lag1::TRP + [pPL547] | Ref. 18 |
TABLE 2.
Plasmids used in this study
| Parent vector | Plasmid | Insert/ORF | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| pRS315 | Ref. 43 | ||
| pPL419 | Ref. 29 | ||
| p416Met25 | Ref. 44 | ||
| pGEX 6-P-2 | GE Healthcare | ||
| pJK59 | SEC63-GFP | Ref. 45 | |
| pPL264 | pRS315 | CKA2 | This study |
| pPL267 | p416Met25 | N-terminal 3-HA | This study |
| pPL276 | pPL267 | LAC1 | This study |
| pPL277 | pPL267 | LAG1 | This study |
| pPL278 | pPL267 | LAC1S393A/S395A/S397A | This study |
| pPL279 | pPL267 | LAG1S393A/S395A/S397A | This study |
| pPL284 | pPL267 | LAC1S61A/S74A | This study |
| pPL285 | pPL267 | LAC1S61A/S74A/S393A/S395A/S397A | This study |
| pPL288 | pPL267 | LAG1S61A/S74A/S393A/S395A/S397A | This study |
| pPL298 | pPL267 | LAG1S61A/S74A | This study |
| pPL325 | pPL419 | LAC1 | This study |
| pPL326 | pPL419 | LAG1 | This study |
| pPL327 | pPL419 | LAC1S393A/S395A/S397A | This study |
| pPL328 | pPL419 | LAG1S393A/S395A/S397A | This study |
| pPL329 | pPL419 | LAC1S74A | This study |
| pPL330 | pPL419 | LAG1S61A/S74A | This study |
| pPL331 | pPL419 | LAC1S74A/S393A/S395A/S397A | This study |
| pPL332 | pPL419 | LAG1S61A/S74A/S393A/S395A/S397A | This study |
| pPL345 | pPL419 | LAC1S393D/S395D/S397D | This study |
| pPL346 | pPL419 | LAG1S393D/S395D/S397D | This study |
| pPL347 | pPL419 | LAC1S393E/S395E/S397E | This study |
| pPL348 | pPL419 | LAG1S393E/S395E/S397E | This study |
| pPL352 | pPL419 | LAG1 | This study |
| pPL353 | pPL419 | LAG1S393A/S395A/S397A | This study |
| pPL358 | pPL419 | LAC1S393A | This study |
| pPL359 | pPL419 | LAC1S395A | This study |
| pPL360 | pPL419 | LAC1S397A | This study |
| pPL362 | pPL419 | LAG1S393A | This study |
| pPL363 | pPL419 | LAG1S395A | This study |
| pPL364 | pPL419 | LAG1S397A | This study |
| pPL367 | pPL419 | LAC1S393A/S395A/S397A/K415Q/K416Q | This study |
| pPL368 | pPL419 | LAC1S393D/S395D/S397D/K415Q/K416Q | This study |
| pPL369 | pPL419 | LAC1S393E/S395E/S397E/K415Q/K416Q | This study |
| pPL373 | pPL419 | LAG1S393A/S395A/S397A/K407Q/K409Q | This study |
| pPL374 | pPL419 | LAG1S393D/S395D/S397D/K407Q/K409Q | This study |
| pPL375 | pPL419 | LAG1S393E/S395E/S397E/K407Q/K409Q | This study |
| pPL471 | pGEX 6-P-2 | LAC1 (376–419) | This study |
| pPL472 | pGEX 6-P-2 | LAC1 (376–419) S393A/S395A/S397A | This study |
| pPL536 | P416Met25 | GFP-LAC1 | This study |
| pPL537 | P416Met25 | GFP-LAC1S393A/S395A/S397A | This study |
| pPL540 | P416Met25 | GFP-LAG1 | This study |
| pPL541 | P416Met25 | GFP-LAG1S393A/S395A/S397A | This study |
| pPL546 | pRS315 | TetR-LAC1 | This study |
| pPL547 | pRS315 | TetR-LAG1 | Ref. 18 |
LC-MS/MS Analysis of LCBs, LCBPs, and Ceramides
Lipids were extracted and analyzed as described previously (19), using a Applied Biosystems Qtrap 4000 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer coupled to a Waters Acquity Ultra Performance LC system (University of California Davis Metabolomics Core).
In Vitro Ceramide Synthase Assay
Microsomal membranes were prepared from WT and cka2Δ cells as described (19). In vitro ceramide synthase assays were performed as described (19). Briefly, 10 μl of protein lysate was combined in a 100-μl reaction with 20 μm SPHc17 base and 2–150 μm C20-CoA. The reactions were incubated at 22 °C for 25 min and stopped by the addition of 500 μl of cold ethanol containing C17-ceramide as an internal standard. Lipids were extracted and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. The product of the reaction was quantified based on a calibration curve constructed using C17-SPH as a standard.
Purification of Bacterially Expressed Recombinant Lac1
Recombinant Lac1 expression plasmids were generated by inserting PCR-amplified Lac1 WT and Ser3 → A mutant C-terminal sequences corresponding to amino acids 376–419 into the expression vector pGEX 6-P-2 (GE Healthcare). Escerhichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells were transformed with the resulting constructs, and expression of Lac1 was induced by the addition of 42.5 μm isopropyl 1-thio-β-d-galactopyranoside to 1 liter of exponentially growing cells. Cells were harvested by centrifugation after 12 h at 25 °C. Lac1 was isolated from soluble lysates by GST purification using glutathione-Sepharose 4B beads according to the manufacturer's instructions (GE Healthcare).
CK2 in Vitro Kinase Assay
Reaction mixtures (25 μl) contained 20 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 50 mm KCl, and 10 mm MnCl2, 2 μl (∼1 μg) of purified recombinant human casein kinase II (New England Biolabs) and 1 μg of purified WT or Ser3 → Ala mutant GST-Lac1(376–419) or GST alone. Reactions were started by adding 4 μl of ATP mix (2 mm ATP, 5 μCi/μl [γ-32P]ATP, 3000 Ci/mmol; PerkinElmer Life Sciences). Samples were incubated at 30 °C for 1 h, and reactions were stopped by the addition of 6.3 μl of 5× SDS-PAGE sample buffer. Proteins were run on a 12.5% gel, which was dried and exposed to a PhosphorImager screen and then analyzed using a STORM 860 system and software provided by the manufacturer (GE Healthcare).
Western Blotting
Protein extracts from at least three separate experiments were prepared using the NaOH cell lysis method (28), loaded onto SDS-polyacrylamide gels, and transferred to nitrocellulose membrane. Membranes were probed with α-HA (12CA5, 1:5000; Covance), α-GFP (1:1000; Antibodies Inc.), and α-G6PDH (1:100,000; Sigma-Aldrich) primary antibodies and visualized using the appropriate secondary antibodies conjugated to IRDye (1:5000; LI-COR Biosciences) on the Odyssey Infrared Imaging System (LI-COR Biosciences). Images were quantified using ImageQuant software (GE Healthcare).
Fluorescence Microscopy
Imaging was performed using a Nikon E600 fluorescent microscope as described (29).
Phosphatase Treatment
Microsomal membranes from 250 A600 units of cells were isolated by centrifugal separation at 100,000 × g. HA3-tagged Lac1 and Lag1 were immunopurified from this fraction by α-HA antibody-bound Protein G beads. 25 μl of protein-bound beads were treated with 10 μl (100 units) of CIP (New England Biolabs) or without enzyme in CIP buffer (50 mm Tris, pH 8.5, 5 mm MgCl2) at 37 °C for 2 h.
Statistical Analysis
Averages are presented with means ± S.D. p values were calculated using Student's t test.
RESULTS
Cka2 Regulates Sphingolipid Biosynthesis at the Step of Ceramide Synthesis
The CK2 subunit Cka2 was identified previously in a genetic screen for regulators of sphingolipid biosynthesis, where cka2Δ cells possessed decreased levels of sphingolipids and a concomitant increase in LCBs (12). Moreover, ER-enriched microsomal membranes isolated from cka2Δ cells were observed to be deficient in de novo ceramide formation, suggesting that CK2 regulates sphingolipid biosynthesis at the level of CerS (Fig. 1B). Because of our interest in understanding the regulation of sphingolipid biosynthesis and signaling, we wanted to explore further the role of CK2 in CerS regulation and thus first confirmed these results by using LC-MS/MS to measure levels of the major species of ceramide in yeast, C26-PHS, where a significant decrease was observed in cka2Δ versus WT cells (Fig. 2A). In addition, we confirmed that microsomes isolated from cka2Δ cells have significantly reduced CerS activity, in vitro (Fig. 2B). We next examined levels of the direct precursors to ceramides, the LCBs dihydrosphingosine (DHS) and phytosphingosine (PHS), as well as their phosphorylated forms (DHS-P and PHS-P in Fig. 2), where we observed a significant increase in each of these species in cka2Δ versus WT cells (Fig. 2, C and D). Together, these results are consistent with cka2Δ cells being impaired in CerS function. We confirmed that the defect in C26-PHS production in cka2Δ cells was due specifically to loss of Cka2 activity, because expression of a plasmid-borne wild type copy of CKA2 restored C26-ceramide essentially to wild type levels in cka2Δ cells (Fig. 2E).
FIGURE 2.
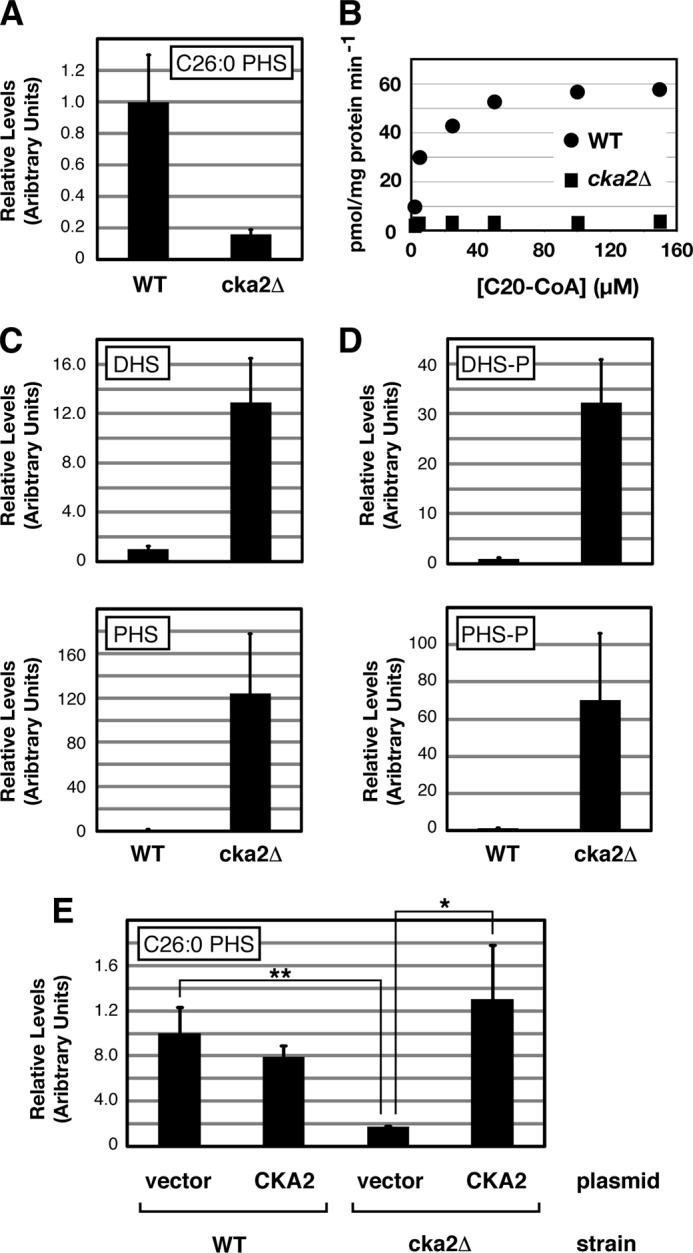
Cka2 regulates sphingolipid biosynthesis. A, levels of C26-phytoceramide were analyzed in extracts derived from WT (LHY291) and cka2Δ (PLY979) cells. B, ceramide synthase in vitro activity, using microsomal membranes isolated from WT and cka2Δ cells and increasing concentrations of C20-CoA. Levels of LCBs (DHS and PHS) (C) and phospho-LCBs (DHS-P and PHS-P) (D) were analyzed in extracts derived from WT and cka2Δ cells. E, empty vector (pRS315) and a plasmid expressing CKA2 (pPL264) were introduced into WT and cka2Δ cells as noted. Levels of C26-phytoceramide were analyzed from cell extracts. In A and C–E, the average is presented with means ± S.D. (error bars) (n = 3). p values were calculated using Student's t test. *, p between 0.05 and 0.01; **, p ≤ 0.01. The significance of differences in values between WT and cka2Δ in A, C, and D corresponds to p ≤ 0.01.
Evidence That Lac1 and Lag1 Are Direct Targets of Cka2
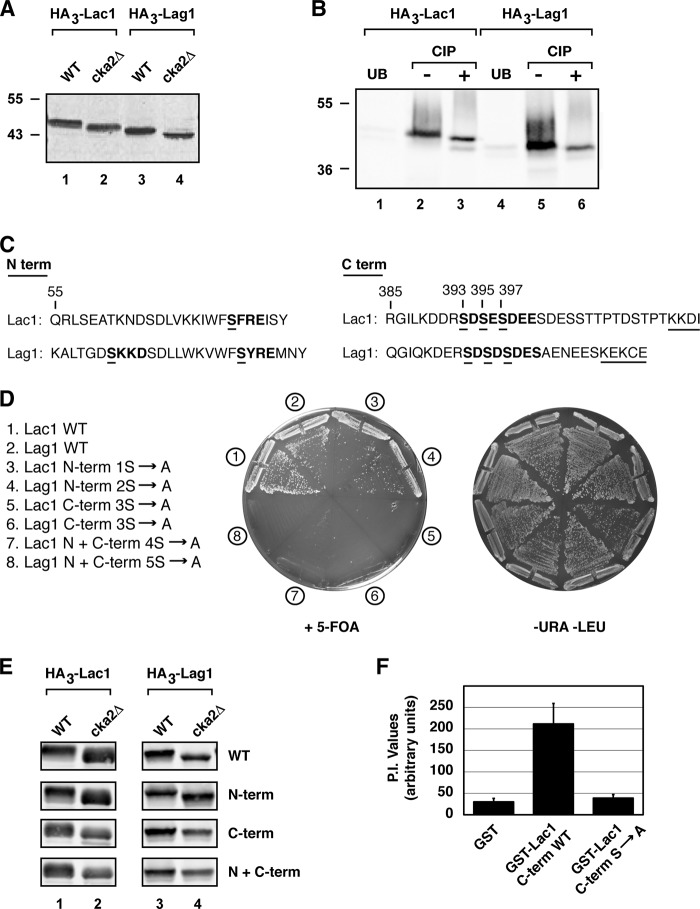
To explore the molecular basis for CK2-dependent regulation of CerS activity, we constructed functional, N-terminal epitope-tagged versions of Lac1, Lag1, and Lip1 and examined their electrophoretic mobility in whole cell extracts by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting. Here we observed subtle but reproducible shifts in mobility for both HA3-Lac1 and HA3-Lag1, in that they displayed faster mobilities in extracts prepared from cka2Δ versus WT cells (Fig. 3A). Immunoprecipitation of HA3-Lac1 and HA3-Lag1 from protein extracts prepared from WT cells, followed by treatment with calf intestinal phosphatase in vitro, resulted in similar mobility shifts for both proteins (Fig. 3B), indicating that Lac1 and Lag1 are phosphoproteins. By contrast, no mobility shift of HA3-Lip1 was observed under these conditions, suggesting that Lip1 is not a phosphoprotein, at least not one that can be detected under these conditions (data not shown).
FIGURE 3.
Lac1 and Lag1 are direct targets of Cka2. A, protein extracts from WT and cka2Δ cells expressing HA3-tagged versions of Lac1 (PLY865 and PLY1044) and Lag1 (PLY890 and PLY1045) were prepared and resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with α-HA antibody. B, immunopurified extracts from microsomal membrane fractions of WT cells expressing HA3-tagged versions of Lac1 (PLY865) and Lag1 (PLY890) were treated with calf intestinal phosphatase (CIP) where noted, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Samples bound and unbound (UB) to beads were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with α-HA antibody. C, N-terminal and C-terminal amino acid sequence of Lac1 and Lag1. The consensus CK2 sequence is in boldface type, with proposed phosphoserines underlined. The C-terminal dilysine ER retrieval motif is also noted with an underline. D, strain PLY1225 (lac1Δlag1Δ + pPL276 (WT Lac1)) was transformed with plasmids expressing WT Lag1 or various potential Lag1 CK2 phosphorylation site mutants, and strain PLY1226 (lac1Δlag1Δ + pPL277 (WT Lag1)) was transformed with plasmids expressing WT Lac1 or various potential Lac1 CK2 phosphorylation site mutants. The resulting transformants were streaked onto SCD minus uracil and leucine or onto 5-fluoroorotic acid (5-FOA) solid agar plates and grown at 30 °C for ∼2 days. E, protein extracts from WT and cka2Δ cells expressing HA3-tagged versions of WT Lac1, WT Lag1, or various potential Lac1 or Lag1 CK2 phosphorylation site mutants were prepared and resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with α-HA antibody. F, CK2 phosphorylation of recombinant GST-tagged C-terminal cytoplasmic portion of WT Lac1 and Lac1 serine to alanine (3S to A) mutant or GST alone. The [γ-32P]ATP-labeled proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and quantified following autoradiography (P.I.= PhosphorImager). Averages are presented as mean values ± S.D. (error bars) (n = 3).
CK2 targets serine and threonine residues within the consensus sequence (S/T)XX(E/D) (22, 30). Examination of the amino acid sequences of Lac1 and Lag1 revealed a number of potential CK2 phosphorylation sites within the N and C termini of both proteins (Fig. 3C). Previous structural analyses of the transmembrane topologies of Lac1 and Lag1 indicate that the N and C termini of both proteins are predicted to be located within the cytoplasm, where they would be accessible to CK2 (31). Accordingly, we examined the functional significance of these sites by introducing serine to alanine substitutions, using a plasmid shuffle assay to assess the ability of these mutations in Lac1 and Lag1 to support growth, taking advantage of the fact that in our strain, background loss of both LAC1 and LAG1 is lethal. We observed that although mutation of N-terminal serine residues had no effect on either protein, constructs harboring mutations of the three serine residues (Ser-393, Ser-395, Ser-397) at the C termini of both Lac1 and Lag1 were unable to support growth of a lac1Δ lag1Δ strain, demonstrating that these sites are essential for Lac1 and Lag1 function (Fig. 3D). Consistent with this conclusion, examination of the electrophoretic mobilities of WT and mutant forms of HA3-Lac1 and HA3-Lag1 revealed that phosphorylation of C-terminal serine residues was necessary and sufficient to account for the slower mobility of Lac1 and Lag1 in WT versus cka2Δ cells (Fig. 3E).
We next used an in vitro kinase assay to demonstrate that a recombinant protein consisting of the wild type sequence of the C terminus of Lac1, but not the Lac1 sequence possessing the Ser3 → Ala mutations, fused to GST, behaves as a substrate for CK2 (Fig. 3F). From these results, we conclude that Lac1 and, by extension, Lag1 are likely to be bona fide targets of CK2 and that CK2-dependent phosphorylation of these proteins is important for Lac1- and Lag1-dependent cell growth. We used the plasmid shuffle assay to test whether all three C-terminal CK2 sites are required for Lac1 and Lag1 function, where we observed that mutation of a single position, Ser-393, to alanine was sufficient to render Lac1 as well as Lag1 non-functional, whereas single site mutations at Ser-395 or Ser-397 conferred no deleterious phenotypes (data not shown). However, we observed that the S393A mutation on its own was insufficient to account for the phosphorylation-dependent mobility shift of either Lac1 or Lag1 in cka2Δ cells, suggesting that Ser-395 and/or Ser-397 sites are also likely to be phosphorylated by CK2 (data not shown).
Evidence That CerS Activity Is Regulated by CK2-dependent Phosphorylation
To examine whether phosphorylation of CK2-dependent sites within the C termini of Lac1 and Lag1 is required for efficient ceramide biosynthesis, we introduced phosphomimetic serine to glutatamate (Ser3 → Glu) or serine to aspartate (Ser3 → Asp) mutations at positions Ser-393, Ser-395, and Ser-397 into plasmid-borne versions for each gene. We then used the plasmid shuffle assay to test their functionality, where we observed that, in contrast to the Ser3 → Ala mutants, both phosphomimetic substitutions resulted in functional Lac1 as well as Lag1 proteins (Fig. 4A). We note, however, that growth was more robust for the Ser3 → Glu mutants compared with the Ser3 → Asp mutants, in particular for Lac1 (Fig. 4A). We next examined levels of C26-PHS ceramide as well as the LCBs PHS and DHS in cka2Δ cells transformed either with the Ser3 → Ala mutant or Ser3 → Glu phosphomimetic version of Lac1. As expected, expression of Ser3 → Ala Lac1 in cka2Δ cells resulted in reduced ceramides and an increase in the LCBs DHS and PHS (Fig. 4B). By contrast, expression of the Ser3 → Glu phosphomimetic version of Lac1 resulted in a significant increase in C26-ceramides and a concomitant reduction in both DHS and PHS in cka2Δ cells (Fig. 4B). Thus, we conclude that efficient CerS activity requires C-terminal phosphorylation of Lac1 and, by extension, Lag1 by CK2.
FIGURE 4.
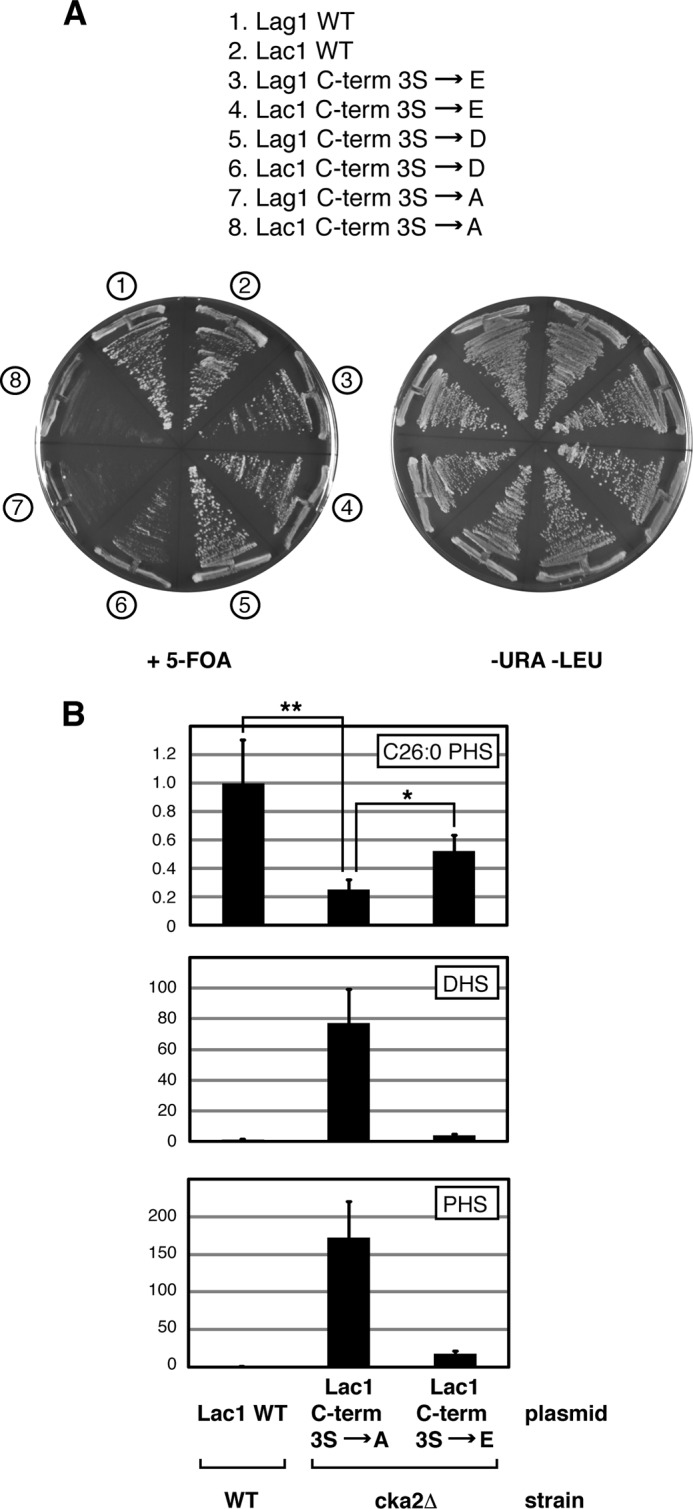
Sphingolipid synthesis is regulated by Lac1 and Lag1 phosphorylation. A, strain PLY1225 (lac1Δlag1Δ + pPL276 (WT Lac1)) was transformed with plasmids expressing WT Lag1 or various potential Lag1 CK2 phosphorylation site mutants, and strain PLY1226 (lac1Δlag1Δ + pPL277 (WT Lag1)) was transformed with the corresponding Lac1 plasmids. The resulting transformants were streaked onto SCD minus uracil and leucine or onto 5-fluoroorotic acid (5-FOA) solid agar plates and grown at 30 °C for ∼2 days. B, plasmid expressing various forms of Lac1 (WT, C-term S to A, and C-term S to E) were introduced into WT and cka2Δ cells as noted. Levels of C26-phytoceramide, DHS, and PHS were analyzed from cell extracts. The average presented with means ± S.D. (error bars) (n = 3). p values were calculated using Student's t test. *, p between 0.05 and 0.01; **, p ≤ 0.01. The significance of differences in values in DHS and PHS under the different conditions correspond to p ≤ 0.01.
Proper ER Localization of Lac1 and Lag1 Requires Phosphorylation at C-terminal CK2 Sites
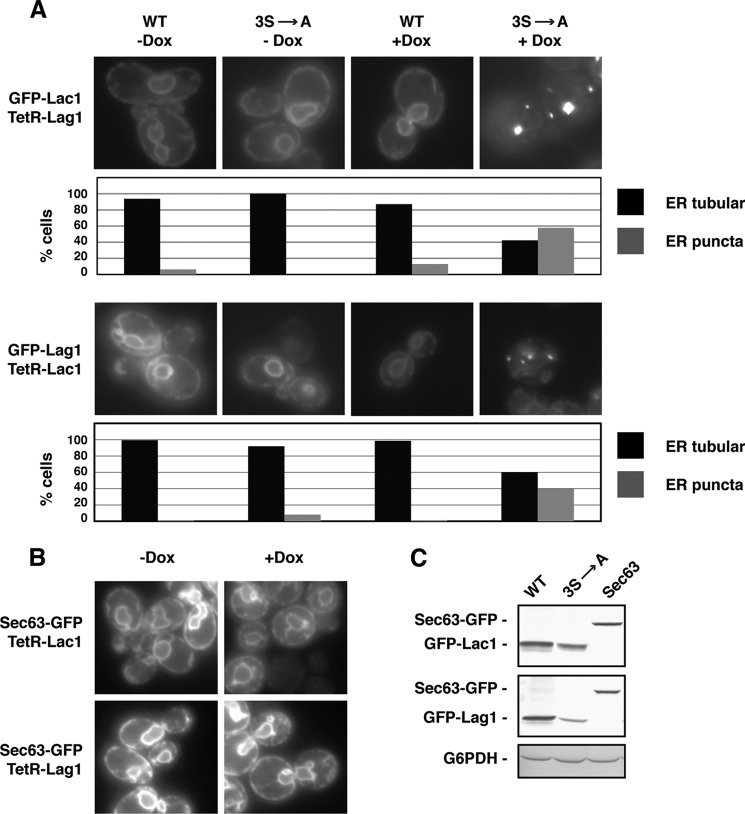
To understand further the role of phosphorylation of Lac1 and Lag1, we wanted to examine the intracellular localization of GFP-tagged versions of wild type and C-terminal Ser3 → Ala mutants under conditions where these were sole source of Lac1 or Lag1 within cells, in part to avoid issues related to the reported hetero-oligomerization of these subunits (16). However, because the alanine mutants are lethal in the context of a lac1Δ lag1Δ strain, we used a tetracycline-repressible (TetR) system (32), wherein a repressible version of WT Lac1 or Lag1 was paired with constitutively expressed, GFP-tagged versions of the other subunit. Accordingly, following treatment with doxycycline (Dox), we observed a significant change in the distribution of mutant Lac1-GFP and Lag1-GFP, where in a significant number (40–50%) of cells, both mutant proteins formed punctate structures within the ER membrane (Fig. 5A). By contrast, no such puncta were observed following Dox treatment of cells expressing WT Lac1-GFP or Lag1-GFP (Fig. 5A). We also examined the localization of a different ER-resident membrane protein, Sec63-GFP, in the presence of either Tet-Lac1 or Tet-Lag1, where no change in distribution was observed following Dox treatment (Fig. 5B). This latter finding indicates that the punctate distribution of the C-terminal Ser3 → Ala Lac1 and Lag1 mutants is not simply a consequence of the loss of functional CerS in Dox-treated cells that results in general mislocalization of ER membrane proteins. Accordingly, we conclude that phosphorylation of Lac1 and Lag1 plays an important role in establishing and/or maintaining the normal distribution of CerS within the ER membrane. We note that accumulation of Lag1 and, to a lesser extent, Lac1 into ER-associated puncta correlated with a reduction in steady state levels of protein in Dox-treated cells (Fig. 5C).
FIGURE 5.
Phosphorylation impacts Lac1 and Lag1 ER localization and protein stability. A, strain PLY1501 ((lac1Δlag1Δ + pPL547 (TetR-Lag1)) expressing GFP-tagged WT Lac1 or Lac1 Ser3 → Ala and strain PLY1500 (lac1Δlag1Δ + pPL546 (TetR-Lac1)) expressing GFP-tagged WT Lag1 or Lag1 Ser3 → Ala were grown for 3 days in SCD medium treated with water (−Dox) or 30 μg/ml doxycyclin (+Dox) (cultured diluted and retreated daily). All strains were imaged by fluorescence microscopy. Quantification represents the percentage of GFP-Lac1 or GFP-Lag1 localized to ER tubular or ER punctal structures in at least 100 cells. B, strains PLY1500 and PLY1501 both expressing GFP-Sec63 were grown and imaged as in A. C, strains PLY1500 and PLY1501 expressing GFP-tagged WT Lac1, Lac1 Ser3 → Ala, and Sec63 protein extracts were grown as in A and then prepared and resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with α-GFP and α-G6PDH antibodies.
Functional Interactions between CerS Phosphorylation and the ER Retrieval Pathway
The C-terminal CK2 phosphorylation sites in Lac1 and Lag1 are adjacent to consensus ER dilysine retrieval sequences, KKXX and KXKXX, respectively, that are predicted to interact with components of the COP I transport machinery to maintain steady state ER localization of resident membrane proteins (33, 34) (Fig. 6A). In the course of our studies, we made two observations that suggest that functional interactions exist between the ER retrieval pathway and casein kinase-dependent phosphorylation of Lac1 and Lag1. First, synthetic lethal interactions resulted when mutations in Lac1 and Lag1 (KK to QQ and KEK to QEQ, respectively), predicted to abolish efficient ER retrieval, were paired with the serine to aspartate (Ser3 → Asp) phosphomimetic substitutions, based on results using the plasmid shuffle assay (Fig. 6B). By contrast, no synthetic lethal phenotypes were observed when the glutamate (Ser3 → Glu) phosphomimetic substitutions and dilysine motif mutants were combined (Fig. 6B), consistent with our observations that glutamic acid acts as a stronger phosphomimetic substitution (Fig. 4A).
FIGURE 6.
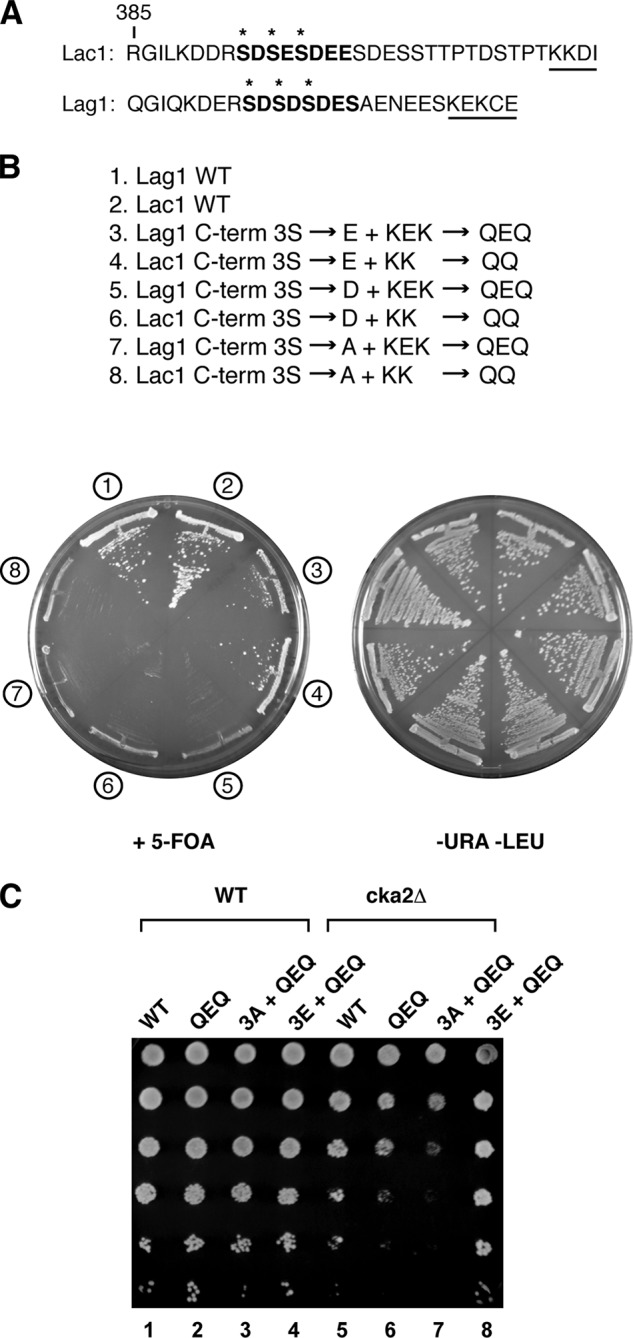
CK2 and dilysine ER retrieval motif collaborate for optimal CerS activity. A, C-terminal amino acid sequence of Lac1 and Lag1. Consensus CK2 sequence is in boldface type, with proposed phosphoserines starred. The C-terminal dilysine ER retrieval motif is noted with an underline. B, strain PLY1225 (lac1Δlag1Δ + pPL276 (WT Lac1)) was transformed with plasmids expressing WT Lag1 or various potential Lag1 CK2 phosphorylation site mutants, and strain PLY1226 (lac1Δlag1Δ + pPL277 (WT Lag1)) was transformed with the corresponding Lac1 plasmids. The resulting transformants were streaked onto SCD minus uracil and leucine or onto 5-fluoroorotic acid (5-FOA) solid agar plates and grown at 30 °C for ∼2 days. C, plasmids expressing WT Lag1 (pPL326) or dilysine mutants (QEQ) in the context of C-terminal serine (pPL365), alanine (pPL373), or glutamate (pPL375) residues were introduced into WT and cka2Δ cells. Equal numbers of cells were serially diluted and plated on SCD minus leucine and grown for ∼2 days.
Second, we observed that transformation of cka2Δ cells with plasmids that expressed versions of LAG1 that carried mutations in the dilysine motif alone (KEK to QEQ) or, more dramatically, in combination with the C-terminal Ser3 → Ala mutations conferred dominant negative phenotypes (Fig. 6C). Remarkably, the deleterious phenotype of the QEQ mutations was suppressed completely by introduction of the Ser3 → Glu phosphomimetic substitutions, confirming that the dominant negative phenotype of the dilysine motif mutations is related to defects in CK2-dependent phosphorylation of Lag1 in cka2Δ cells (Fig. 6C). Together, these findings support functional interactions between CK2-dependent phosphorylation of Lac1 and Lag1 and the ER retrieval pathway. Whether phosphorylation directly influences ER retrieval or, alternatively, whether ER retrieval becomes essential when phosphorylation is impaired remains to be determined.
DISCUSSION
Kobayashi and Nagiec (12) first reported that cka2Δ mutants are defective in CerS activity; however, the underlying mechanism for this observation was not determined. We have now extended these findings by providing evidence that Lac1 and Lag1, the catalytic subunits of CerS, are direct targets for phosphorylation by CK2. In particular, we find that phosphorylation of three C-terminal serine residues is important for optimal ceramide formation and contributes to proper ER localization and protein stability as well as interacting functionally with the Golgi to ER retrieval pathway for both proteins. Together these findings reveal a functionally important post-translational modification of CerS and identify an important step in the regulation of sphingolipid biosynthesis.
These observations contribute to our evolving understanding of how the early steps of sphingolipid biosynthesis, including ceramide formation, are regulated within cells. Previously, we have provided evidence that TORC2/Ypk1/Ypk2 signaling plays a role in the regulation of CerS (18, 19). Thorner and co-workers (20) have recently extended these findings by demonstrating that the N-terminal cytoplasmic domains of Lac1 and Lag1 are direct targets of Ypk1 and, moreover, that phosphorylation of these subunits contributes to the full activity of CerS. Unlike phosphorylation of the C-terminal sites by CK2, however, phosphorylation of Lac1 and Lag1 by Ypk1 is apparently not essential for cell viability (20).
We have also observed that inhibition of both TORC2 and Ypk1 activity results in a decrease in LCBs and a concomitant increase in LCBPs, suggesting that loss of TORC2/Ypk1 signaling results in the shuttling of LCBs to the formation of LCBPs (18, 19). Thus, in addition to directly affecting CerS activity, we believe that TORC2/Ypk1 signaling more broadly controls the flow of intermediates within the ceramide/LCBP rheostat (Fig. 1A). We argue that this regulation is also distinct from inhibition by Ypk1 of the Orm1/2 proteins, which negatively regulate serine palmitoyltransferase at the first step of sphingolipid biosynthesis (35) (Fig. 1A). An outstanding question raised by these findings is the extent to which TORC2/Ypk1/2 and CK2-dependent control of sphingolipid biosynthesis are co-regulated. In this regard, we have observed that a cka2Δ mutant is synthetically lethal with a temperature-sensitive mutation (termed avo3-30; (19)) in the essential TORC2 component Avo3 at 25 °C, a temperature that is normally permissive for this mutant, demonstrating that there are important functional interactions between these components (data not shown).
CK2 is believed to phosphorylate more than 300 substrates involved in diverse cellular processes, including cell proliferation, signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, translation, and metabolism (22). Interestingly, although both CK2 and many of the proteins that it targets are essential, mutations of predicted CK2 sites within these proteins often have limited effects on their function (36–38). By contrast, we found that phosphorylation of C-terminal CK2 sites on Lac1 and Lag1 is essential for cell viability, suggesting that CK2-dependent regulation of sphingolipid biosynthesis may be uniquely important among processes regulated by this kinase. Because cka2Δ cells are viable, we suggest that the redundant ortholog Cka1 is likely to phosphorylate Lac1 and Lag1, at least in the absence of Cka2 activity.
Because its activity is elevated in a number of tumors (23, 39, 40), CK2 has emerged as a therapeutic target for cancer biology; however, the specific functions of CK2 responsible for oncogenicity remain to be determined. Based on our findings presented here, it is relevant that ceramide levels are elevated in a number of cancers, indicating that regulation of sphingolipid biosynthesis is likely to play a critical role in the development of cancer (11, 41, 42). Examination of amino acid sequences of the mammalian CerS homologs (CerS1 to -6) reveals the presence of consensus CK2 phosphorylation sites at the C termini of all six of the CerS isoforms. Therefore, we predict that CK2 regulation of CerS is likely to be conserved and suggest that understanding the role of CK2 in ceramide formation in human cells will be important for a complete understanding of sphingolipid-mediated oncogenesis.
Acknowledgments
We thank the members of the Powers laboratory for helpful discussions.
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grant GM086387 (to T. P.).
- LCB
- long chain base
- LCBP
- phosphorylated LCB
- CerS
- ceramide synthase
- DHS
- dihydrosphingosine
- PHS
- phytosphingosine
- Dox
- doxycycline
- TetR
- tetracycline-repressible
- ER
- endoplasmic reticulum
- CK2
- casein kinase 2
- SCD
- synthetic complete dextrose.
REFERENCES
- 1. Hannich J. T., Umebayashi K., Riezman H. (2011) Distribution and functions of sterols and sphingolipids. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 10.1101/cshperspect.a004762 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Hannun Y. A., Luberto C., Argraves K. M. (2001) Enzymes of sphingolipid metabolism: from modular to integrative signaling. Biochemistry 40, 4893–4903 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Saba J. D., Hla T. (2004) Point-counterpoint of sphingosine 1-phosphate metabolism. Circ. Res. 94, 724–734 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Dickson R. C., Sumanasekera C., Lester R. L. (2006) Functions and metabolism of sphingolipids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Prog. Lipid Res. 45, 447–465 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Maceyka M., Spiegel S. (2014) Sphingolipid metabolites in inflammatory disease. Nature 510, 58–67 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Ogretmen B., Hannun Y. A. (2004) Biologically active sphingolipids in cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 4, 604–616 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Cowart L. A., Obeid L. M. (2007) Yeast sphingolipids: recent developments in understanding biosynthesis, regulation, and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1771, 421–431 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Sims K. J., Spassieva S. D., Voit E. O., Obeid L. M. (2004) Yeast sphingolipid metabolism: clues and connections. Biochem. Cell Biol. 82, 45–61 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Hannun Y. A., Obeid L. M. (2002) The Ceramide-centric universe of lipid-mediated cell regulation: stress encounters of the lipid kind. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 25847–25850 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Furuya H., Shimizu Y., Kawamori T. (2011) Sphingolipids in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 30, 567–576 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Schiffmann S., Sandner J., Birod K., Wobst I., Angioni C., Ruckhäberle E., Kaufmann M., Ackermann H., Lötsch J., Schmidt H., Geisslinger G., Grösch S. (2009) Ceramide synthases and ceramide levels are increased in breast cancer tissue. Carcinogenesis 30, 745–752 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Kobayashi S. D., Nagiec M. M. (2003) Ceramide/long-chain base phosphate rheostat in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: regulation of ceramide synthesis by Elo3p and Cka2p. Eukaryot. Cell 2, 284–294 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Schorling S., Vallée B., Barz W. P., Riezman H., Oesterhelt D. (2001) Lag1p and Lac1p are essential for the acyl-CoA-dependent ceramide synthase reaction in Saccharomyces cerevisae. Mol. Biol. Cell 12, 3417–3427 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Guillas I., Jiang J. C., Vionnet C., Roubaty C., Uldry D., Chuard R., Wang J., Jazwinski S. M., Conzelmann A. (2003) Human homologues of LAG1 reconstitute Acyl-CoA-dependent ceramide synthesis in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 37083–37091 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Levy M., Futerman A. H. (2010) Mammalian ceramide synthases. IUBMB Life 62, 347–356 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Vallée B., Riezman H. (2005) Lip1p: a novel subunit of acyl-CoA ceramide synthase. EMBO J. 24, 730–741 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Futerman A. H., Hannun Y. A. (2004) The complex life of simple sphingolipids. EMBO Rep. 5, 777–782 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Niles B. J., Joslin A. C., Fresques T., Powers T. (2014) TOR complex 2-Ypk1 signaling maintains sphingolipid homeostasis by sensing and regulating ROS accumulation. Cell Rep. 6, 541–552 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Aronova S., Wedaman K., Aronov P. A., Fontes K., Ramos K., Hammock B. D., Powers T. (2008) Regulation of ceramide biosynthesis by TOR complex 2. Cell Metab. 7, 148–158 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Muir A., Ramachandran S., Roelants F. M., Timmons G., Thorner J. (2014) TORC2-dependent protein kinase Ypk1 phosphorylates ceramide synthase to stimulate synthesis of complex sphingolipids. Elife 10.7554/eLife.03779 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Roelants F. M., Breslow D. K., Muir A., Weissman J. S., Thorner J. (2011) Protein kinase Ypk1 phosphorylates regulatory proteins Orm1 and Orm2 to control sphingolipid homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 19222–19227 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Meggio F., Pinna L. A. (2003) One-thousand-and-one substrates of protein kinase CK2? FASEB J. 17, 349–368 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Sarno S., Pinna L. A. (2008) Protein kinase CK2 as a druggable target. Mol. Biosyst. 4, 889–894 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Trembley J. H., Wang G., Unger G., Slaton J., Ahmed K. (2009) Protein kinase CK2 in health and disease: CK2: a key player in cancer biology. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 66, 1858–1867 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Faust M., Jung M., Günther J., Zimmermann R., Montenarh M. (2001) Localization of individual subunits of protein kinase CK2 to the endoplasmic reticulum and to the Golgi apparatus. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 227, 73–80 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Sherman F. (1991) Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 194, 3–21 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Geitz R. D., Woods R. A. (1998) Transformation of yeast by the lithium acetate/single-stranded carrier DNA/PEG method. Methods Microbiol. 26, 53–66 [Google Scholar]
- 28. Dilova I., Aronova S., Chen J. C., Powers T. (2004) Tor signaling and nutrient-based signals converge on Mks1p phosphorylation to regulate expression of Rtg1.Rtg3p-dependent target genes. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 46527–46535 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Niles B. J., Mogri H., Hill A., Vlahakis A., Powers T. (2012) Plasma membrane recruitment and activation of the AGC kinase Ypk1 is mediated by target of rapamycin complex 2 (TORC2) and its effector proteins Slm1 and Slm2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, 1536–1541 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Kuenzel E. A., Mulligan J. A., Sommercorn J., Krebs E. G. (1987) Substrate specificity determinants for casein kinase II as deduced from studies with synthetic peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 9136–9140 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Kageyama-Yahara N., Riezman H. (2006) Transmembrane topology of ceramide synthase in yeast. Biochem. J. 398, 585–593 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Marx C. J., Lidstrom M. E. (2002) Broad-host-range cre-lox system for antibiotic marker recycling in Gram-negative bacteria. BioTechniques 33, 1062–1067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Jackson M. R., Nilsson T., Peterson P. A. (1990) Identification of a consensus motif for retention of transmembrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J. 9, 3153–3162 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Popoff V., Adolf F., Brügger B., Wieland F. (2011) COPI budding within the Golgi stack. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 3, a005231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Breslow D. K., Collins S. R., Bodenmiller B., Aebersold R., Simons K., Shevchenko A., Ejsing C. S., Weissman J. S. (2010) Orm family proteins mediate sphingolipid homeostasis. Nature 463, 1048–1053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Leroy D., Alghisi G. C., Roberts E., Filhol-Cochet O., Gasser S. M. (1999) Mutations in the C-terminal domain of topoisomerase II affect meiotic function and interaction with the casein kinase 2 β subunit. Mol. Cell Biochem. 191, 85–95 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Maiti T., Bandyopadhyay A., Maitra U. (2003) Casein kinase II phosphorylates translation initiation factor 5 (eIF5) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 20, 97–108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Russo G. L., van den Bos C., Sutton A., Coccetti P., Baroni M. D., Alberghina L., Marshak D. R. (2000) Phosphorylation of Cdc28 and regulation of cell size by the protein kinase CKII in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem. J. 351, 143–150 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Homma M. K., Homma Y. (2008) Cell cycle and activation of CK2. Mol. Cell Biochem. 316, 49–55 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Münstermann U., Fritz G., Seitz G., Lu Y. P., Schneider H. R., Issinger O. G. (1990) Casein kinase II is elevated in solid human tumours and rapidly proliferating non-neoplastic tissue. Eur. J. Biochem. 189, 251–257 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Koybasi S., Senkal C. E., Sundararaj K., Spassieva S., Bielawski J., Osta W., Day T. A., Jiang J. C., Jazwinski S. M., Hannun Y. A., Obeid L. M., Ogretmen B. (2004) Defects in cell growth regulation by C18:0-ceramide and longevity assurance gene 1 in human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 44311–44319 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Koyanagi S., Kuga M., Soeda S., Hosoda Y., Yokomatsu T., Takechi H., Akiyama T., Shibuya S., Shimeno H. (2003) Elevation of de novo ceramide synthesis in tumor masses and the role of microsomal dihydroceramide synthase. Int. J. Cancer 105, 1–6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Sikorski R. S., Heiter P. (1989) A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 122, 19–27 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Mumberg D., Müller R., Funk M. (1994) Regulatable promoters of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: comparison of transcriptional activity and their use for heterologous expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 5767–5768 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Prinz W. A., Grzyb L., Veenhuis M., Kahana J. A., Silver P. A., Rapoport T. A. (2000) Mutants affecting the structure of the cortical endoplasmic reticulum in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Cell Biol. 150, 461–474 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]