Background: Some nanoparticles are known to induce endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and lead to cell death.
Results: Silver nanoparticles induce ATF-6 degradation, leading to activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome and pyroptosis.
Conclusion: ATF-6 is an important target to silver nanoparticles.
Significance: Our results provide a new link between ER stress and activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome.
Keywords: Caspase, Caspase 1 (CASP1), Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress (ER Stress), Inflammasome, Nanotechnology, Caspase 4, Silver Nanoparticles, NLRP-3 Inflammasome, Pyroptosis
Abstract
In the past decade, the increasing amount of nanoparticles (NP) and nanomaterials used in multiple applications led the scientific community to investigate the potential toxicity of NP. Many studies highlighted the cytotoxic effects of various NP, including titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, and silver nanoparticles (AgNP). In a few studies, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress was found to be associated with NP cytotoxicity leading to apoptosis in different cell types. In this study, we report for the first time that silver nanoparticles of 15 nm (AgNP15), depending on the concentration, induced different signature ER stress markers in human THP-1 monocytes leading to a rapid ER stress response with degradation of the ATF-6 sensor. Also, AgNP15 induced pyroptosis and activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome as demonstrated by the processing and increased activity of caspase-1 and secretion of IL-1β and ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD domain) pyroptosome formation. Transfection of THP-1 cells with siRNA targeting NLRP-3 decreased the AgNP15-induced IL-1β production. The absence of caspase-4 expression resulted in a significant reduction of pro-IL-1β. However, caspase-1 activity was significantly higher in caspase-4-deficient cells when compared with WT cells. Inhibition of AgNP15-induced ATF-6 degradation with Site-2 protease inhibitors completely blocked the effect of AgNP15 on pyroptosis and secretion of IL-1β, indicating that ATF-6 is crucial for the induction of this type of cell death. We conclude that AgNP15 induce degradation of the ER stress sensor ATF-6, leading to activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome regulated by caspase-4 in human monocytes.
Introduction
Nanoparticles (NP)3 are used in many applications and in a variety of sectors, including textile, aerospace, electronics, and medical healthcare. Silver nanoparticles (AgNP) are among the most commonly used NP in nanomedicine, mainly because of their potent antimicrobial properties, increasing the interest to use them for drug delivery (1). Indeed, silver ions and nanosilver were shown to be highly toxic for various types of microorganisms, including Pseudomonas spp. and Escherichia spp. (2, 3). Even if potential exposure of humans to AgNP is already high, it will certainly increase in the becoming years. Because the toxicity of AgNP in humans is not fully understood, it is highly relevant to investigate their mode of action at the cellular and molecular level in humans.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress leads to unfolded protein response, a major hallmark of cytotoxicity. To date, three ER stress sensors have been documented: protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE-1), and activating transcription factor 6 (ATF-6). IRE-1 and PERK both contain cytoplasmic kinase domains known to be activated by homodimerization and autophosphorylation in the presence of ER stressors (4–6). In the case of ATF-6, accumulation of unfolded proteins induces ATF-6 transition to the Golgi, where it is cleaved by two transmembrane proteins, Site-1 and Site-2 proteases (7). ATF-6 cleavage yields a cytoplasmic protein acting as an active transcription factor. Although short-term ER stress events lead to pro-survival transcriptional activities, prolonged ER stress activates the major apoptotic pathways (8, 9). Moreover, ER stress-related events were recently proposed as an early biomarker for nanotoxicological evaluation (10). A few studies have reported ER stress-related events induced by NP in human cell lines and in zebrafish (10–12).
Pyroptosis, a type of programmed cell death sharing common features with apoptosis and necrosis, leads to the assembly of the inflammasomes and the formation of large structures called pyroptosomes characterized by aggregation of apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD domain (ASC) (13). Formation of pyroptosomes allows recruitment and processing of caspase-1 into two active fragments, p10 and p20 (14). Caspase-1 controls processing and secretion of IL-1β, one of the most potent endogenous pyrogenic molecules. IL-1β is responsible for inflammatory cell infiltration and is known to induce cyclooxygenase and increase expression of adhesion molecules, production of reactive oxygen species, and other inflammatory soluble mediators (15). Secretion of high concentrations of IL-1β is also associated with chronic inflammatory conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel diseases (16). Interestingly, treatment of some auto-immune diseases with anti-IL-1β antibodies results in significant reduction of disease severity and symptoms. Pyroptosis also leads to the release of cytosolic content via formation of pore in the cellular membrane, thereby increasing the inflammatory process (17). Some NP were shown to induce pyroptosis in human cells, namely carbon nanotubes, carbon black NP, and AgNP (18–20). Therefore, studying the impact of several distinct NP in the regulation of the inflammasome has become highly relevant for investigating their toxicity.
In this study, we show that low concentrations of silver nanoparticles of 15 nm (AgNP15) induced ER stress response but did not led to cell death, whereas higher concentrations resulted in atypical ER stress response associated with ATF-6 degradation and pyroptotic cell death through NLRP-3 inflammasome activation. Our data suggest a link between these two processes.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Reagents
AgNP15 were obtained from US Research Nanomaterials (Houston, TX). Staurosporine and ATP were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Caspase-1, caspase-3, caspase-7, and phospho-eIF2α antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling (Danvers, MA). GAPDH (full-length), ASC, caspase-4, phospho-PERK, ATF-6α (full-length), GRP-78, and pro-IL-1β (H-153) specific antibodies were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). NLRP-3/NALP-3 antibody was purchased from Enzo Life Sciences (Farmingdale, NY). RPMI 1640, HEPES, penicillin and streptomycin, heat-inactivated FBS, Opti-MEM medium, and Hanks' balanced salt solution were purchased from Life Technologies. All secondary antibodies were purchased from Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories (West Grove, PA). Ultrapure LPS from Salmonella spp. was purchased from InvivoGen (San Diego, CA). Phospho-IRE-1, total IRE-1, and ATF-6 (cleaved form) were purchased from Pierce. HSP-70 and HSP-90 antibodies were purchased from StressGen Biotechnologies (San Diego, CA). Anti-sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 (SREBP-1) was purchased from EMD Millipore (Temecula, CA).
Characterization of AgNP15
The AgNP15 suspension obtained from the manufacturer was examined by transmission electronic microscopy using a Hitachi H-7100 transmission electron microscope (21). The size distribution and electric charge (ζ potential) of AgNP15 were determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS) using a Malvern Zetasizer Nano-ZS (model ZEN3600; Malvern Instruments Inc., Westborough, MA). Measurements were performed at 1, 5, 10, and 25 μg/ml AgNP15 in RPMI 1640 with HEPES and 100 units/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin (further referred to as RPMI) + 10% heat-inactivated FBS, at 37 °C.
Cell Culture
WT human monocytic THP-1 cells were purchased from ATCC. Stable caspase-4-deficient (clone TB) THP-1 cells and the corresponding cell line containing a scrambled sequence (vector control) were kindly given by Dr. Alan G. Porter (22). These cells line were cultured in RPMI. Cell density never exceeded 1 × 106 cells/ml, and viability was evaluated before each experiment and was always above 95%. For primary culture of monocytes and macrophages, PBMCs were first isolated from healthy blood donors after centrifugation over Ficoll-Hypaque gradient, as previously published (23). For monocyte isolation, 25 × 106 PBMCs were incubated at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere for 2 h in RPMI containing 10% autologous heat-inactivated serum in a Petri dish. Monocytes obtained by removing the non-adherent PBMCs were further incubated in RPMI + 10% heat-inactivated FBS for another 12 h. The monocytes were washed twice with Hanks' balanced salt solution without Ca2+ and Mg2+ with 2 mm EDTA and harvested with a cell scraper. Human monocyte-derived macrophages were generated by incubating 2 × 106 PBMCs at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere for 2 h in RPMI with 10% heat-inactivated autologous serum in 48-well plates. Cells were then washed twice with warm Hanks' balanced salt solution and further incubated in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 2 ng/ml GM-CSF for 7 days, with medium renewal every 3 days, to obtain macrophages.
Transfection of siRNA
THP-1 cells were transfected with Silencer Select Pre-designed siRNA from Ambion (Austin, TX) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Briefly, 5 × 105 cells were suspended in 1 ml of Opti-MEM reduced serum medium containing 2 μl of Lipofectamine RNAiMAX reagent (Life Technologies) and 10 μm siRNA targeting NLRP-3 (sense, GGAGAGACCUUUAUGAGAATT; antisense, UUCUCAUAAGGUCUCUCCTG) or control non-silencing siRNA (sense, UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT; antisense, ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGGAGAATT). After 24–48 h, cells were washed and treated with the indicated agents.
Cell Death Assessment
For assessment of cell death, THP-1 cells were treated for 1 or 24 h with the indicated agents. After different periods of time, cells were harvested and washed twice in PBS and then stained with FITC-annexin-V and propidium iodine, according to the manufacturer's protocol (Life Technologies). Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry using a BD FACScan.
Western Blot Analysis
Cells were stimulated at 1 × 106 cells/ml with the indicated agonists for various periods of time, as specified. At the end of the incubation periods, cells were lysed in Laemmli sample buffer (0.25 m Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 8% SDS, 40% glycerol, and 20% 2-mercaptoethanol), and aliquots corresponding to 5 × 105 cells were loaded onto 10% SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes for the detection of specific proteins. Membranes were blocked for 1 h at room temperature in 5% nonfat dry milk. After washing, the primary antibodies were added at a final dilution of 1:1000 in TBS-Tween 0.15%. The membranes were kept overnight at 4 °C, and then washed with TBS-Tween and incubated for 1 h at room temperature with the appropriate secondary HRP antibody 1:25,000 in TBS-Tween followed by several washes. Protein expression was revealed using Luminata Forte Western HRP substrate (Millipore). Membranes were stripped with ReBlot Plus Strong (Millipore) and reprobed to confirm equal loading of proteins. Chemiluminescence was revealed with a chemiDocTM MP imaging system from Bio-Rad.
Assembly of Pyroptosome by Confocal Microscopy
THP-1 cells were incubated on poly-l-lysine coverslips for 30 min at 37 °C and then incubated with the indicated agonist for 30 min. In some experiments, cells were primed with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 4 h. Coverslips were then washed three times with PBS and fixed in 3.7% paraformaldehyde. After three washes in PBS, cells were permeabilized in PBS containing 0.1% saponin and 0.05% Tween 20. Cells were blocked with a blocking solution containing 5% goat serum, 1% BSA, and 1% dry fat milk and stained with mouse anti-ASC (2 μg/ml) primary antibody. After three washes with PBS, cells were incubated with Alexa Fluor®-488 goat anti-mouse IgG (1:500) secondary antibody. Cells were washed three times with PBS, and coverslips were mounted using ProLong Gold® antifade reagent containing DAPI. Cells were then visualized with a Zeiss LSM780 on Axio Observer Z1 confocal microscope using a Plan-Apochromat 63 × 1.4 NA oil differential interference contrast objective. Five fields with at least 50 cells/field were evaluated for the presence of pyroptosome.
Caspase-1 Assay
Caspase-1 activity was measured with the caspase-1 colorimetric assay kit (R&D Systems) as described previously (24). Briefly, 4 × 106 cells were stimulated with agonists for the indicated periods of time and lysed with ice-cold lysis buffer after incubation for 10 min on ice. Cells were centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 1 min, and supernatants were used for enzymatic reaction. Caspase-1 colorimetric substrate (WEHD-pNA) was added to each reaction mixture with the corresponding volume of cell lysate, reaction buffer, and DTT. The plate was incubated for 2 h at 37 °C. After incubation, results were read with a microplate reader using a wavelength of 405 nm. Results are expressed as -fold increase of caspase-1 activity.
Caspase-3 and Caspase-4 Activity Assays
Caspase-3 and caspase-4 activity assays were performed as previously published with a few modifications (25). Briefly, THP-1 cells (1 × 106 cells/ml) were stimulated as indicated in figure legends. Cells were washed twice in PBS and disrupted using a lysis buffer containing 25 mm Hepes, pH 7.5, 5 mm EDTA, 5 mm MgCl2, 10 mm DTT, 0.5% Triton X-100, and protease inhibitor mixture (Pierce, Thermo Fisher). Protein concentration was determined using the Bradford assay. An amount of 10 μg of proteins was mixed in 200 μl of reaction buffer containing 50 mm Hepes, 10% sucrose, 0.1% CHAPS, 10 mm DTT with 100 μm of the caspase-3 (DEVD-pNA) or caspase-4 (LEVD-pNA) substrate for 2 h at 37 °C. Cleavage of the caspase substrate was monitored using a spectrophotometer at 405 nm.
Transmission Electronic Microscopy
Cells were treated with 25 μg/ml AgNP15 or buffer for 1 h and then fixed with glutaraldehyde (2.5%) and examined by transmission electron microscopy, as above.
IL-1β Production
The measurement of IL-1β was determined with a commercially available ELISA kit (Life Technologies). THP-1 cells, primary monocytes, or macrophages were incubated with the indicated agonists for 1 h in a 24-well plate in RPMI-10% FBS or autologous serum. In some experiments, cells were pre-incubated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 4 h. Supernatants were harvested after centrifugation and stored at −80 °C before determining the concentration of IL-1β.
Statistical Analysis
Experimental data are expressed as means ± S.E. One-way analysis of variance (Dunnett's multiple-comparison test) and two-way analysis of variance (Bonferroni's post test) were performed using GraphPad Prism (version 5.01).
RESULTS
Characterization of AgNP15
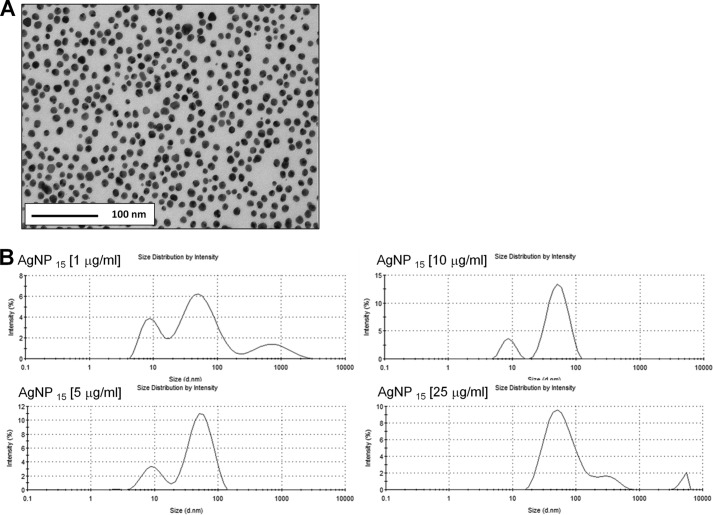
We first characterized AgNP15 from the manufacturer stock solution by transmission electron microscopy, confirming a diameter close to 15 nm, but also indicating that the suspension contains NP with different ratios between smaller and larger diameters (Fig. 1A). Because RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FBS was the medium used for all experiments throughout this study, the size distribution and ζ potential of AgNP15 were determined by DLS for all tested concentrations in this medium at 37 °C, the temperature at which cells were incubated. As shown in Fig. 1B and Table 1, the DLS analysis revealed a tri-modal size distribution for a concentration of 1, 5, and 25 μg/ml and a bi-modal size distribution at 10 μg/ml with a polydispersion index of 0.4 ± 0.3, 0.4 ± 0.3, 0.2 ± 0.1, and 0.3 ± 0.1 (n = 6) for 1, 5, 10, and 25 μg/ml, respectively. The ζ potential was stable, ranging from −8.4 ± 0.4 to −9.5 ± 1.0 mV.
FIGURE 1.
Transmission electronic microscopy image of the primary stock solution of AgNP15 and behavior of the nanoparticle under different concentrations in culture medium evaluated by DLS analysis. A, a sample of the solution stock from the manufacturer was used for characterization by transmission electronic microscopy illustrating that the suspension was relatively homogeneous with the majority of AgNP with a diameter close to 15 nm, but also that other particles had different ratios between smaller and larger diameters. B, representative data obtained by DLS analysis performed at 37 °C with a concentration of 1, 5, 10, or 25 μg/ml AgNP15 in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FBS, the experimental conditions used in this study. Data are from one representative experiment out of three.
TABLE 1.
Characterization of AgNP15 by dynamic light scattering
Results are means from 3–6 different lectures ±S.D. PdI, polydispersity index.
| Concentration (μg/ml) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 10 | 25 | |
| Size (nm)a | 66.8 ± 37.5 (69.8% ± 4.4) | 86.6 ± 38.8 (79.7% ± 2.0) | 54.0 ± 3.2 (85.7% ± 0.7) | 64.4 ± 7.3 (93.6% ± 4.0) |
| 10.0 ± 0.5 (26.7% ± 3.2) | 10.5 ± 2.2 (18.0% ± 2.9) | 9.1 ± 0.5 (14.3% ± 0.7) | 641.8 ± 1782.0 (5.5% ± 2.8) | |
| 1629.0 ± 2236.0 (3.5% ± 5.3) | 2108.0 ± 2372.0 (2.4% ± 2.7) | 1121.0 ± 2225.0 (0.9% ± 1.7) | ||
| ζ potential (mV) | −8.4 ± 0.3 | −9.5 ± 1.0 | −8.7 ± 1.2 | −9.0 ± 0.7 |
| PdI | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
a Values in parentheses indicate intensity.
AgNP15 Induce Morphological Changes in Human THP-1 Monocyte Cells
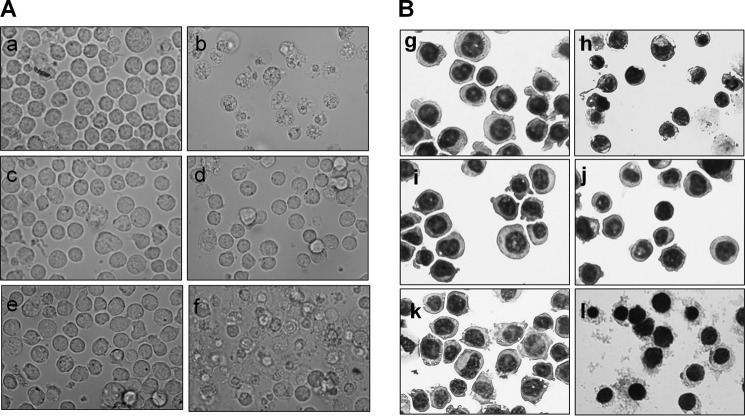
Fig. 2 illustrates that, after 24 h of treatment, the cell morphology remained unchanged at a concentration of 1 or 5 μg/ml AgNP15. However, morphological changes became apparent at 10 μg/ml AgNP15 where numerous vacuoles were observed in the cytosol (panel e). Cell morphology was markedly altered at 25 μg/ml AgNP15 (panel f), an effect that is clearly different from that of the apoptosis-inducing agent staurosporine, suggesting a different type of cell death.
FIGURE 2.
AgNP15 alter the morphology of human monocyte THP-1 cells. Cells were treated for 24 h with buffer (panels a and g); 1 μm staurosporine (panels b and h); or 1 (panels c and i), 5 (panels d and j), 10 (panels e and k), or 25 (panels f and l) μg/ml AgNP15. Live cells in plates (A, panels a–f) or Cytospin preparations of cells colored with Hema 3-stained solution (B, panels g–l) were then visualized by optical light microscopy at a magnification of 200× (panels a–f) or 400× (panels g–l). Data are from one representative experiment out of three.
AgNP15 Are Internalized in THP-1 Cells
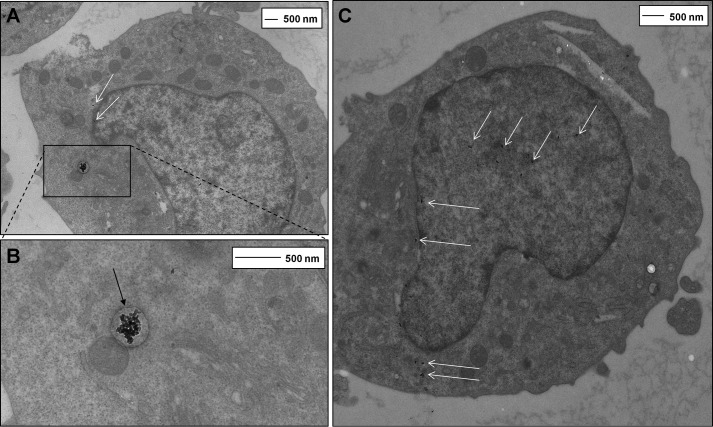
We next investigated potential internalization of AgNP15 because we previously reported that silver nanoparticles of 20 nm (AgNP20) could be found inside human neutrophils, another cell type of myeloid origin (21). As illustrated in Fig. 3, incubation of AgNP15 with THP-1 cells leads to internalization of nanoparticles in the cytosol and nucleus as determined by transmission electron microscopy (Fig. 3). Larger aggregates of AgNP15 were visibly taken up by a mechanism requiring the formation of phagosomes/vacuoles, whereas well dispersed or small aggregates were mainly found inside the nucleus. Well dispersed nanoparticles were also found in the cytosol but were not internalized inside vacuoles.
FIGURE 3.
Internalization of AgNP15 in human monocyte THP-1 cells. A–C, cells were incubated for 1 h with 25 μg/ml AgNP15, the highest tested concentration, and were visualized by transmission electronic microscopy, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Panel B is an enlarged section of A. The presence of AgNP15 large aggregates inside a cytosolic vacuole (black arrows) and small AgNP15 aggregates in the cytosol and nucleus (white arrows) is shown. Data are from one representative experiment out of three.
AgNP15 Induce ER Stress-related Events
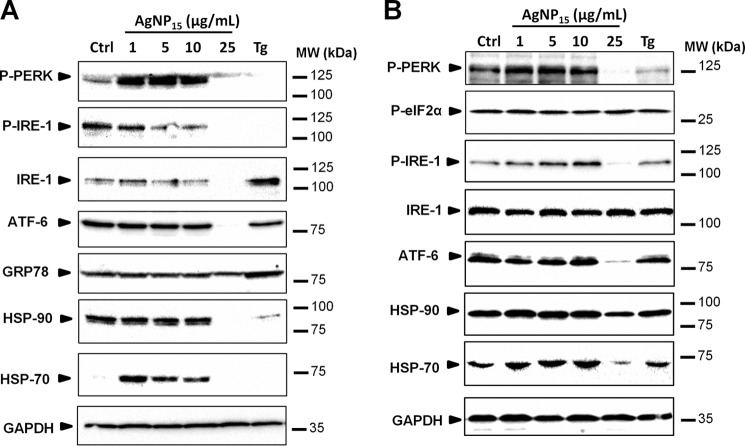
A 24-h treatment of cells with AgNP15 resulted in a dose-dependent dephosphorylation of IRE-1, suggesting that this pathway was not activated (Fig. 4A). Although the PERK pathway was strongly activated with 1–10 μg/ml AgNP15, it remained similar to basal level with a treatment with 25 μg/ml. In addition, low concentrations of AgNP15 induced synthesis of HSP-70, whereas the higher concentration induced degradation of HSP-90. GRP-78 expression levels remained unchanged in all tested conditions except thapsigargin, the positive control. Although the expression level of ATF-6 remained similar in cells treated with 0–10 μg/ml AgNP15, this protein was degraded at 25 μg/ml, despite the fact that an equivalent of proteins was loaded (see GAPDH lane). Interestingly, degradation of ATF-6 occurred rapidly after 1 h (Fig. 4B). Degradation of other components such as HSP-70 was also observed, whereas the expression level of total IRE-1 and HSP-90 remained relatively stable after 1 h of stimulation. These results suggest that AgNP15 induce ER stress-related events in human THP-1 cells.
FIGURE 4.
AgNP15 induce ER stress events in human monocyte THP-1 cells. ER stress markers were followed by Western blot, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Cells were treated for 24 h (A) or 1 h (B) with 1–25 μg/ml AgNP15, 10 μg/ml thapsigargin (Tg), or the equivalent volume of buffer (Ctrl). Data are from one representative experiment out of three. One example of loading control systematically performed with GAPDH is shown at the bottom of each panel. MW, molecular weight markers; P-PERK, phospho-PERK; P-IRE-1, phospho-IRE-1; P-eIF2α, phospho-eIF2α.
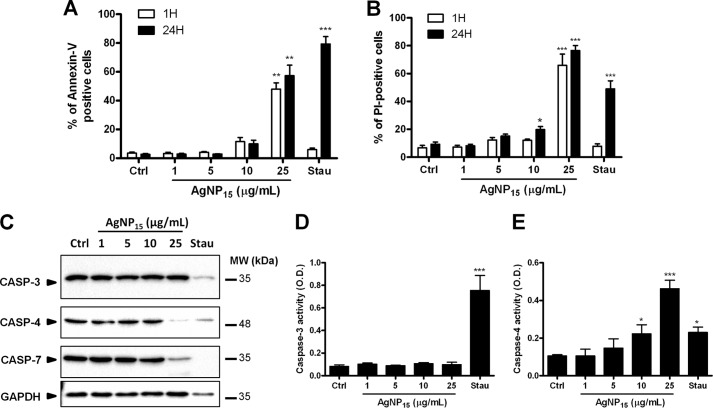
AgNP15 Induce a Rapid Cell Death Distinct from Apoptosis
As prolonged ER stress response is usually associated with apoptosis, we next investigated the role of AgNP15 in THP-1 cell death. After only 1 h, cells treated with 25 μg/ml AgNP15 were annexin-V- and PI-positive, whereas cells treated with the proapoptotic agent staurosporine were negative for both markers (Fig. 5, A and B). However, after 24 h, cells were annexin-V- and PI-positive whether they were treated with AgNP15 or staurosporine. This suggests that AgNP15, at 25 μg/ml, induce a cell death that is different from staurosporine-induced apoptosis. To confirm this hypothesis, we next monitored the processing of several important caspases, including the executioner caspase-3 and caspase-7, and the inflammatory caspase-4, known to be associated with ER stress-induced apoptosis (27). As illustrated in Fig. 5C, staurosporine induced processing of caspase-3, caspase-4, and caspase-7, but not AgNP15 at 1, 5, or 10 μg/ml. At 25 μg/ml, AgNP15 were found to induce the processing of caspase-4 and caspase-7 but not caspase-3. We also observed a variation in the expression of level of GAPDH in staurosporine-treated cells, a phenomenon previously observed at the mRNA level in neutrophils (28). However, membrane coloration revealed an equivalent amount of proteins (data not shown). The activity of caspase-3 and caspase-4 was also monitored using a caspase assay. Only the positive control staurosporine induced activation of caspase-3, whereas AgNP15 strongly activated caspase-4 at 25 μg/ml (Fig. 5, D and E). These results indicate that AgNP-induced cell death is distinct from apoptosis.
FIGURE 5.
AgNP15 induce cell death in human monocyte THP-1 cells. A and B, cell viability was assessed by flow cytometry using annexin-V-PI staining. C, caspase (Casp) processing was determined by Western blot, and caspase activity was quantified using a caspase assay, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Cells were stimulated for 1 h (A and B) or 24 h (A–C) with buffer (Ctrl), 1–25 μg/ml AgNP15 or 1 μm staurosporine (Stau). MW, molecular weight markers. D and E, quantifications of caspase-3 and caspase-4 activity. O.D., optical density. Data are means ± S.E. of three (A and B; D and E) or are from one representative experiment out of three (C). Differences were considered statistically significant as follows: *, p ≤ 0.05, **, p ≤ 0.01, and ***, p ≤ 0.005 versus control or appropriate diluent.
AgNP15 Induce Pyroptosis and Activation of the Inflammasome
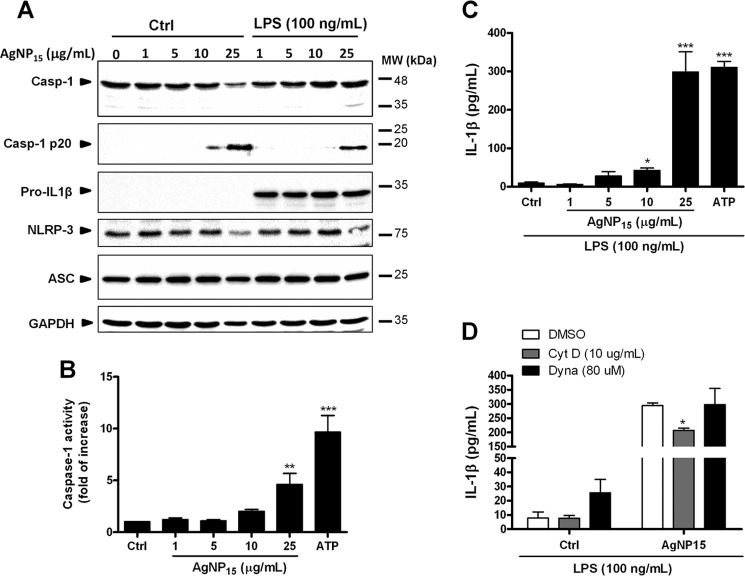
Knowing that activation of caspase-4 and caspase-7 is associated with activation of the inflammasome (13, 29, 30), in addition to the loss of membrane integrity observed after PI staining (this study), we next investigated the role of AgNP15 in the activation of inflammasomes. Because pyroptosis, another type of cell death, is dependent on caspase-1, we also followed its processing as well as its activation and other components of the NLRP-3 inflammasome. AgNP15 treatment at 25 μg/ml resulted in the presence of the p20 caspase-1 fragment. (Fig. 6A). Such caspase-1 processing was also observed at 25 μg/ml AgNP15 when cells were pre-treated with LPS, suggesting that the effect is due to AgNP alone independently of the LPS pre-treatment. Of note, in the absence of LPS, pro-IL-1β was undetectable, but when cells were pretreated with LPS, a strong expression of pro-IL-1β was observed. ASC expression remained relatively constant whether or not cells were pre-treated with LPS. Because AgNP15 induced processing of caspase-1, suggesting that it induces its activity, we next verified whether AgNP15 could activate caspase-1, using a specific activity assay. As shown in Fig. 6B, the caspase-1 assay revealed that 25 μg/ml AgNP15 significantly increased caspase-1 activity. Also, the activity of caspase-1 was found to correlate with the secretion of IL-1β in the extracellular milieu where 25 μg/ml AgNP15 significantly increased the IL-β secretion from 9.5 ± 2.8 pg/ml to 298.2 ± 52.7 pg/ml (Fig. 6C). Of note, secretion of mature IL-1β required priming with LPS because unstimulated cells failed to secrete this cytokine (see Fig. 11B). We next investigated the importance of AgNP15 internalization for its effect on IL-1β secretion. Therefore, cells were pre-treated or not with the endocytosis dynamin inhibitor (Dynasore) or with the actin depolarizing agent (cytochalasin D) before incubation with AgNP15. Cytochalasin D reduced slightly the secretion of IL-1β induced by AgNP15, whereas dynasore has no effect on its secretion (Fig. 6D). These results suggested that internalization of AgNP15 might be dispensable for their effect on secretion of IL-1β.
FIGURE 6.
AgNP15 induce activation of the inflammasome in human monocyte THP-1 cells. Cells were treated or not with 100 ng/ml LPS for 4 h and then were incubated for 1 h with the indicated concentrations of AgNP15, 2 mm ATP, or buffer (Ctrl). A and B, after treatment, the pellets were lysed in Laemmli buffer for Western blot experiments (A) or caspase-1 (Casp-1) lysis buffer for caspase-1 assay (B), as described under “Experimental Procedures.” MW, molecular weight markers. C and D, for IL-1β quantification, cells were primed 4 h with 100 ng/ml LPS. Cells were then incubated with cytochalasin D (10 μg/ml), Dynasore (80 μm), or the equivalent volume of diluent (dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)) for 30 min before the addition of the indicated agonists for 1 h (D). Supernatants were harvested to quantify IL-1β by ELISA. Results are from one representative experiment out of three (A) are expressed as means ± S.E. of three independent experiments (B–D). Differences were considered statistically significant as follows: *, p ≤ 0.05, **, p ≤ 0.01, and ***, p ≤ 0.005 versus control or appropriate diluent.
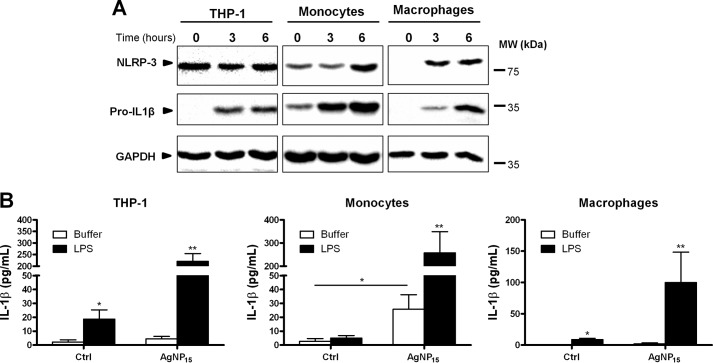
FIGURE 11.
AgNP15 induce secretion of IL-1β in human primary monocytes and macrophages. A, cells were primed with LPS (100 ng/ml) for different periods of time. Protein expression of pro-IL-1β and NLRP-3 was determined by Western blot, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” MW, molecular weight markers. B, for IL-1β quantification, cells were primed or not with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 4 h and then stimulated for 1 h with 25 μg/ml AgNP15 or buffer (Ctrl). Supernatants were harvested to quantify IL-1β by ELISA. Data are from one representative experiment out of four (A) or are expressed as means ± S.E. of five independent experiments (B). Differences were considered statistically significant as follows: *, p ≤ 0.05 and **, p ≤ 0.01 versus control or appropriate diluent.
Formation of pyroptosome is a well documented feature of pyroptotic cell death, characterized by aggregation of ASC proteins into normally one aggregate as observed in murine macrophages or in human monocyte THP-1 cells (13, 14). Therefore, we have followed the formation of this structure by confocal microscopy using an ASC specific antibody. As illustrated in Fig. 7A, AgNP15 induced formation of a pyroptosome structure (Fig. 7A, arrows) similar to that of ATP (positive control) (31), whereas the localization of ASC protein remained diffuse in control cells. The number of cells expressing pyroptosome structures was also quantified in response to 25 μg/ml AgNP15 where close to 20% of cells showed the presence of ASC pyroptosome in the experimental conditions tested (Fig. 7B).
FIGURE 7.
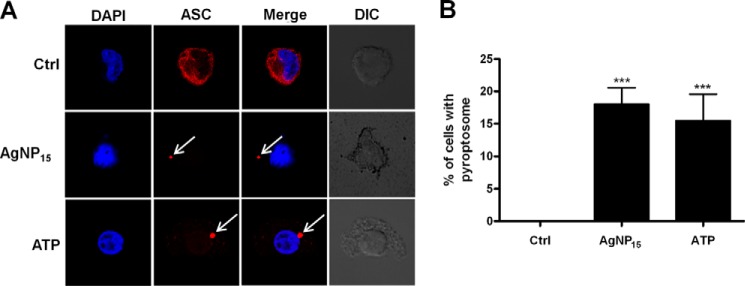
AgNP15 induce pyroptosome assembly in human monocyte THP-1 cells. Cells were stimulated with 25 μg/ml AgNP15, 2 mm ATP, or buffer (Ctrl) for 1 h. A, cells were then fixed, and formation of pyroptosome was followed by confocal microscopy, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” DIC, differential interference contrast. B, quantification of percentage of cells with pyroptosome assembly. Data are from one representative experiment out of three (A) or are expressed as means ± S.E. of three independent experiments (B). Differences were considered statistically significant as follows: ***, p ≤ 0.005 versus control or appropriate diluent.
AgNP15 Induce Activation of the NRLP-3 Inflammasome
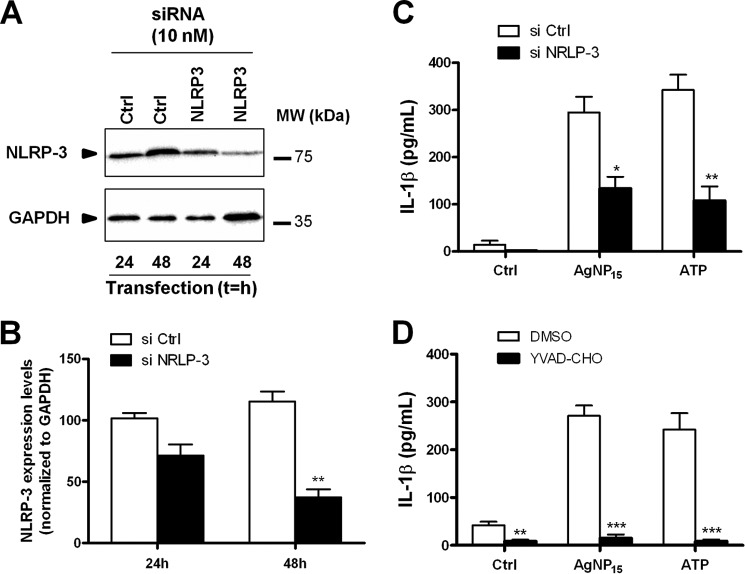
Several inflammasomes are found in monocytes including NLRP-3, the most common and best characterized inflammasome (32). To determine whether AgNP15 induce specific activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome, siRNA targeting NLRP-3 were transfected in THP-1 cells. NLRP-3 expression levels were then followed by Western blot to determine the efficiency of transfection. A marked decreased of NLRP-3 protein expression was observed after a transfection period of 48 h, but not 24 h (Fig. 8, A and B). Therefore, we next selected this 48-h time point for further experiments. As illustrated in Fig. 8C, a significant decrease in IL-1β secretion was observed in cells transfected with silencing NLRP-3 siRNA, confirming that AgNP15 activate the NLRP-3 inflammasome. Activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome is dependent on caspase-1 (33). We have therefore evaluated the importance of caspase-1 in the activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome by AgNP15. Caspase-1 was found to be crucial for activation of this inflammasome because its inhibition with YVAD-CHO completely abolished the secretion of IL-1β, thereby confirming the importance of caspase-1 in this process (Fig. 8D).
FIGURE 8.
NLRP-3 inflammasome activation by AgNP15 is dependent on caspase-1 in human monocyte THP-1 cells. A–C, cells were transfected with siRNA targeting NLRP-3 or nonspecific sequence (Ctrl) for 24 or 48 h. A and B, protein expression of NLRP-3 was followed by Western blot, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” C, quantification of IL-1β secretion. si Ctrl, siRNA targeting nonspecific sequence; si NRLP-3, siRNA targeting NLRP-3. D, cells were primed with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 4 h, treated or not with 10 μm YVAD-CHO, and then stimulated for 1 h with 25 μg/ml AgNP15, 2 mm ATP, or buffer (Ctrl). Supernatants were harvested to quantify IL-1β by ELISA. Data are from one representative experiment out of three (A) and are expressed as means ± S.E. of three independent experiments (B–D). Differences were considered statistically significant as follows: *, p ≤ 0.05, **, p ≤ 0.01, and ***, p ≤ 0.005 versus control or appropriate diluent.
Caspase-4 Regulates the Activation of the NRLP-3 Inflammasome
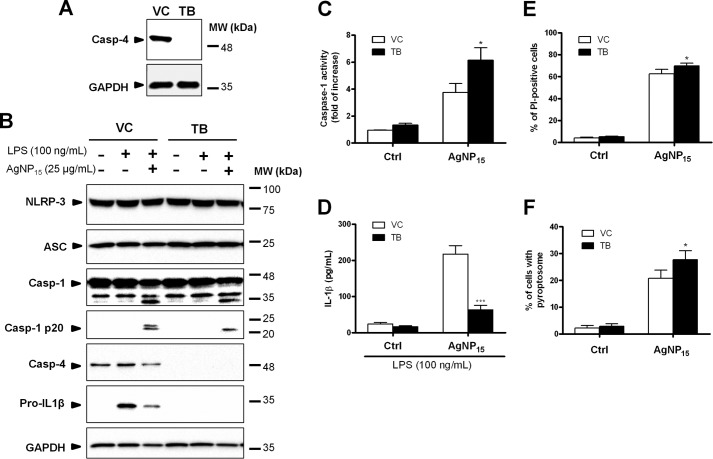
Caspase-4 is known to be required for the activation of the inflammasome through interaction with caspase-1 (30). Because AgNP15 induced activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome and also processing of caspase-4, we tested whether caspase-4 was involved in this process. To do so, we used caspase-4-deficient THP-1 cells (22, 34) to characterize the role of this caspase in AgNP15-induced pyroptosis. The absence of caspase-4 protein expression was confirmed in the caspase-4-deficient THP-1 cell clone TB in contrast to the clone vector control where caspase-4 was strongly expressed (Fig. 9A). Western blot experiments indicate that NLRP-3 and ASC protein levels were relatively stable in all tested conditions (Fig. 9B). However, the protein expression of pro-IL-1β was undetectable in caspase-4-deficient cells even if primed with LPS, a known NLRP-3 inflammasome primer (35). AgNP15 were found to induce cleavage of caspase-1 and appearance of the p20 caspase-1 fragment in both control and caspase-4-deficient cells primed with LPS. Despite the fact that AgNP15 induced an increase caspase-1 activity in caspase-4-deficient cells (Fig. 9C), the IL-1β secretion was decreased in caspase-4-deficient cells versus the corresponding control (Fig. 9D). In addition, a significantly higher proportion of PI-positive cells was observed in caspase-4-deficient cells (Fig. 9E), classically used to identify pyroptotic cells (reviewed in Ref. 33). Finally, caspase-4-deficient cells had an increased amount of pyroptosome when compared with control cells (Fig. 9F). These results suggested that caspase-4 is essential for priming of the NLRP-3 inflammasome component pro-IL-1β, but would negatively regulate its activation by AgNP15.
FIGURE 9.
Role of caspase-4 in the activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome induced by AgNP15 in human monocytes THP-1 cells. Caspase-4-(Casp-4) deficient (TB) or wild type THP-1 cells containing an empty vector (VC) were incubated with buffer or 100 ng/ml LPS for 4 h and were then stimulated for 1 h with buffer (Ctrl) or 25 μg/ml AgNP15). A–C, cell pellets were prepared and lysed in Laemmli buffer (A and B) for Western blot experiments or lysed in caspase-1 lysis buffer for caspase-1 assay (C). For IL-1β quantification, cells were primed 4 h with 100 ng/ml LPS before incubation with the indicated agonists. MW, molecular weight markers. D, supernatants were harvested to quantify IL-1β by ELISA. E and F, cells were stained with PI for flow cytometry analyses (E) or with ASC specific antibody for pyroptosome formation (F). Data are from one representative experiment out of three (A and B) or are expressed as means ± S.E. of three independent experiments (C–F). Differences were considered statistically significant as follows: *, p ≤ 0.05 and ***, p ≤ 0.005 versus control or appropriate diluent.
ATF-6 Degradation Leads to Inflammasome Activation and Pyroptotic Cell Death
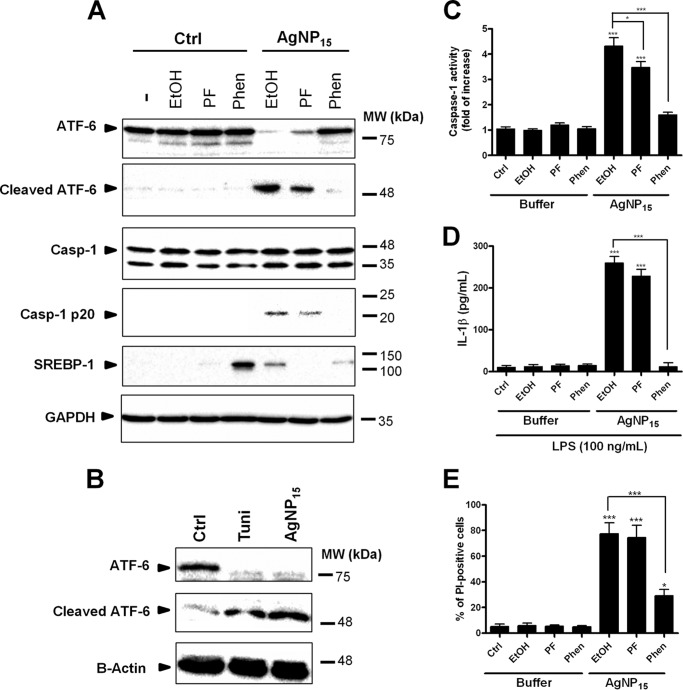
Because AgNP15 induce ER stress events accompanied by a rapid degradation of the ATF-6 sensor, we next determined whether or not this pathway could regulate the activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome. To do so, we used specific inhibitors of S1P and S2P, two proteases involved in ATF-6 cleavage (7). We first evaluated the efficiency of the two inhibitors of PF-429242 (S1P inhibitor) and 1,10-phenanthroline (S2P inhibitor) on processing of one of their main substrates, SREBP-1. 1,10-Phenanthroline strongly inhibited the processing of SREBP-1, whereas PF-429242 did not appear to block its degradation. Of note, AgNP15 alone reduced its processing. Pre-treatment of the cells with PF-429242 reduced moderately AgNP15-induced ATF-6 processing into its active fragment, but the use of 1,10-phenanthroline was found to drastically prevent its processing and appearance of its cleaved fragment(Fig. 10A). The effect of AgNP15 was similar to the ER stressor tunicamycin, which alone induced processing of ATF-6, but after 6 h of stimulation (Fig. 10B). In addition, ATF-6 processing correlated with increased caspase-1 processing and activity (Fig. 10C) as well as with IL-1β secretion (Fig. 10D) and the percentage of PI-positive cells (Fig. 10E), suggesting an important role for ATF-6 in the control of pyroptosis. Importantly, treatment with the S2P inhibitor led to a reduction in caspase-1 activity, IL-1β secretion, and the percentage of PI-positive cells. These results suggest a possible link between ATF-6 degradation and induction of pyroptotic cell death.
FIGURE 10.
Role of ATF-6 in the activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome induced by AgNP15 in human monocytes. A, cells were pre-incubated with 20 μm PF-429242 (PF), 500 μm 1,10-phenanthroline (Phen), or diluent (EtOH) for 30 min and then stimulated for 1 h with 25 μg/ml AgNP15 or buffer (Ctrl). MW, molecular weight markers. B, tunicamycin (Tuni, 5 μg/ml) treatment for 6 h was used as positive control. A–C and E, cells were lysed in Laemmli buffer (A and B) for Western blot experiments, lysed in caspase-1 (Casp-1) lysis buffer for caspase-1 assay (C), or stained with PI for flow cytometry analyses (E). For IL-1β quantification, cells were primed for 4 h with 100 ng/ml LPS before incubation with inhibitors and stimulation with the indicated agonists. D, supernatants were harvested to perform IL-1β ELISA. Data are from one representative experiment out of three (A and B) or are expressed as means ± S.E. of three independent experiments(C–E). Differences were considered statistically significant as follows: *, p ≤ 0.05 and ***, p ≤ 0.005 versus control or appropriate diluent.
AgNP15 Induce Activation of the Inflammasome in Primary Human Monocytes and Macrophages
We then wanted to compare the effect of AgNP15 on activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome in primary human monocytes and macrophage cells. Expression of pro-IL-1β and NLRP-3 was clearly different in primary monocytes and macrophages when compared with THP-1 cells. Indeed, expression of pro-IL-1β was undetectable in THP-1 cells and macrophages, whereas we observed a basal level in monocytes. Moreover, NLRP-3 expression in THP-1 cells remained similar even after 6 h of priming, whereas its expression in monocytes and macrophages increased over time after 3–6 h of stimulation with LPS (Fig. 11A). Secretion of mature IL-1β was also quantified in these three cell types in response to AgNP15. Priming with LPS alone was sufficient to induce the secretion of IL-1β in THP-1 and macrophages (Fig. 11B). Conversely, treatment with AgNP15 alone, without LPS priming, led to a significant production of IL-1β in primary monocytes, suggesting that these cells respond differently than THP-1 and macrophages. However in these three cell types, priming with LPS followed by stimulation with AgNP15 induced the strongest response.
DISCUSSION
AgNP are gaining increasing attention as the utilization of these NP is becoming more and more important in a plethora of medical products (36) and, therefore, increasing potential human exposure, raising important toxicological considerations. In this study, we provide new evidences for a potential cytotoxic role of AgNP15, as demonstrated by activation of ER stress events accompanied by the activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome and pyroptosis. Different types of nanoparticles were shown to induce ER stress response, including zinc oxide (10). However, only a few studies reported that AgNP can induce ER stress events in zebrafish and in human Chang liver cells (11, 12).
Accumulation of unfolded proteins in the ER leads to transition of ATF-6, where it is processed by S1P and S2P (7). The results of the present study indicate that 25 μg/ml AgNP15 induce rapid processing of ATF-6 (within 1 h) in human monocytes, an effect not observed at lower concentrations. Interestingly, activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome was also induced only in response to stimulation with 25 μg/ml AgNP15, suggesting that ATF-6 could act as a molecular switch to induce the activation of this inflammasome. Indeed, inhibition of S2P (and S1P, to a lesser extent) blocked not only ATF-6 processing, but also activation of the inflammasome. Our results are in agreement with others reporting that inhibition of S2P was more efficient than S1P to block processing of ATF-6 (38, 39). Interestingly, a recent study demonstrated that the classical ER stressor, tunicamycin, is sufficient for the induction of IL-1β, suggesting a possible link between ER stress and the inflammasome (40). Moreover, tunicamycin was previously shown to induce ATF-6 degradation (7). Another study also demonstrates that inhibition of ER stress by sodium 4-phenylbutyrate results in a significant reduction in IL-1β levels, supporting the role of ER stress in IL-1β production (41). However, to the best of our knowledge, the role of ATF-6 in the activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome had never been investigated before.
The inflammasomes are multiprotein complexes activated upon cytosolic perturbations such as cellular infection (17, 32). This complex mediates the activation of the inflammatory caspase-1, which is critical for the secretion of mature IL-1β and formation of pores at the cell membrane (42). Multiple inflammasomes have been characterized including NLRC-4, AIM-2, and NLRP-3. Among them, NLRP-3 is the one that has been more studied and is known to be activated upon various types of stimuli, including asbestos, silica, uric acid, and ATP (43–45). Conversely to the NLRC-4 or the AIM-2, the NLRP-3 inflammasome is controlled by a priming step that requires de novo protein translation (35). Although carbon nanotubes and carbon black have also been reported to activate this inflammasome in THP-1 and murine bone marrow-derived cells (20, 46), the effect of AgNP on the inflammasome has never been reported. Herein, we show a cytotoxic and inflammatory role of AgNP15 as evidenced by induction of pyroptotic cell death and IL-1β secretion. Indeed, AgNP15-treated cells harbored the characteristics of pyroptotic cell death: increased processing and activity of caspase-1, pyroptosome formation, loss of membrane integrity, and secretion of IL-1β. The experiments on THP-1, primary monocytes, and macrophages also provide new mechanisms of action of the regulation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome. For instance, the basal expression level of the different components of this pathway were found to be slightly different in THP-1, primary monocytes, and macrophages. This resulted in a significant variation in the amount of mature IL-1β secreted within the extracellular space. Indeed, AgNP15-treated primary monocytes secreted significant amount of IL-1β without the priming of LPS. Of note, we could detect a significant expression level of NLRP-3 and pro-IL-1β in resting monocytes, possibly explaining the secretion of IL-1β in AgNP15-treated cells.
Secretion of IL-1β is associated with acute inflammation and pathogenesis of multiple chronic inflammatory diseases (16), fitting well with previous studies indicating that nanosilver particles possess some toxic and proinflammatory effects (47–50). However, in a subacute murine inhalation model, some authors reported that AgNP induce minimal lung toxicity or inflammation (51). These observations explain why some authors are interested in trying to answer whether AgNP are allies or adversaries (52). Therefore, the results of the present study are in line with the need to further study the mechanisms of the action of AgNP on mammalian cells at the molecular level, to assure a safe application of AgNP.
Although we provide new evidences in the toxicity of AgNP, the exact mechanisms underlying the effects of AgNP15 still remain to be clarified. Even if we clearly observed AgNP15 inside cells, particularly close to or in the nucleus, we cannot definitely conclude that AgNP have to penetrate cells to exert biological effects. Based on the internalization inhibition experiments, we may speculate that internalization of AgNP15 might be dispensable for its effects on IL-1β secretion. Moreover, the effect of AgNP15 was clearly dependent on caspase-1 as inhibition of this protein resulted in abolition of IL-1β secretion. Furthermore, although we observed ATF-6 degradation in response to AgNP15, it cannot be ruled out that silver ions are somewhat involved. However, it is important to specify that we have used a commercial source of AgNP, and we have used them as is, as they are probably used in different applications. Our results also indicate that the processing of ATF-6 and the appearance of the cleaved fragment correlate with the increased expression of caspase-1 p20, caspase-1 activity, IL-1β secretion, and the percentage of PI-positive cells, supporting inflammasome activation. Through inhibition of ATF-6 processing, we clearly see a reduction in caspase-1 activity, IL-1β secretion, and the percentage of PI-positive cells, suggesting that ATF-6 degradation is an event related to activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome and pyroptotic cell death. It is noteworthy that this effect was clearly different from apoptosis cell death.
Caspase-4 belongs to the human inflammatory caspase family along with caspase-1, caspase-5, and caspase-12 (53). The involvement of caspase-4 in ER stress has been previously established (25, 27) but has also been recently challenged (34, 54). Nevertheless, to date, only a few studies reported the potential involvement of caspase-4 in the activation of the inflammasomes (30, 55). Our results indicate that caspase-4 is indeed required for the priming of the inflammasome, as the absence of this caspase resulted in a severe impairment of pro-IL-1β synthesis. However, the absence of caspase-4 also resulted in a significant increase in the activity of active caspase-1 and the proportion of PI-positive and pyroptosome-positive cells. These results suggest that caspase-4 would therefore regulate negatively the NLRP-3 inflammasome activation but would play an important role in its priming step. It is noteworthy that, in caspase-4-deficient THP-1 cells, the NF-κB pathway is markedly affected because caspase-4 was previously found to interact with TRAF-6, agreeing with the lack of pro-IL-1β in these cells (22). In another study, IL-1β production was found to be dependent on NF-κB in THP-1 cells (37). Together with the fact that priming of the inflammasomes is dependent of NF-κB activation and that caspase-4-deficient cells have reduced NF-κB transduction, this information is in agreement with our observation on the impairment of pro-IL-1β in caspase-4-deficient cells. Because we made our observations at a concentration of 25 μg/ml AgNP15, and not at 1–10 μg/ml, it would be of interest in the future to establish whether the same would be true for AgNP with a different starting diameter because this variable is highly important in the induction of different biological effects previously reported for cell toxicity of AgNP in bacteria, yeast, algae, crustaceans, and mammalian cells in vitro (26). Because of the great potential and interest that AgNP represent for developing future therapies based on drug delivery, further studies need to be conducted to limit undesired potential effects of AgNP.
Footnotes
- NP
- nanoparticle(s)
- AgNP
- silver nanoparticle(s)
- AgNP15
- silver nanoparticle(s) of 15 nm
- ER
- endoplasmic reticulum
- PERK
- protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase
- IRE-1
- inositol-requiring enzyme 1
- ATF-6
- activating transcription factor 6
- SREBP-1
- sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1
- DLS
- dynamic light scattering
- PBMC
- peripheral blood mononuclear cell
- pNA
- p-nitroanilide
- PI
- propidium iodine
- S1P
- Site-1 protease
- S2P
- Site-2 protease.
REFERENCES
- 1. Kim J. S., Kuk E., Yu K. N., Kim J. H., Park S. J., Lee H. J., Kim S. H., Park Y. K., Park Y. H., Hwang C.-Y., Kim Y. K., Lee Y. S., Jeong D. H., Cho M. H. (2007) Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 3, 95–101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Slawson R., Trevors J., Lee H. (1992) Silver accumulation and resistance in Pseudomonas stutzeri. Arch. Microbiol. 158, 398–404 [Google Scholar]
- 3. Sondi I., Salopek-Sondi B. (2004) Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 275, 177–182 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Bertolotti A., Zhang Y., Hendershot L. M., Harding H. P., Ron D. (2000) Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2, 326–332 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Liu C. Y., Schröder M., Kaufman R. J. (2000) Ligand-independent dimerization activates the stress response kinases IRE1 and PERK in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 24881–24885 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Harding H. P., Zhang Y., Ron D. (1999) Protein translation and folding are coupled by an endoplasmic-reticulum-resident kinase. Nature 397, 271–274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Ye J., Rawson R. B., Komuro R., Chen X., Davé U. P., Prywes R., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. (2000) ER stress induces cleavage of membrane-bound ATF6 by the same proteases that process SREBPs. Mol. Cell 6, 1355–1364 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Yoshida H., Matsui T., Yamamoto A., Okada T., Mori K. (2001) XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 107, 881–891 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Lin J. H., Li H., Yasumura D., Cohen H. R., Zhang C., Panning B., Shokat K. M., Lavail M. M., Walter P. (2007) IRE1 signaling affects cell fate during the unfolded protein response. Science 318, 944–949 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Chen R., Huo L., Shi X., Bai R., Zhang Z., Zhao Y., Chang Y., Chen C. (2014) Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by zinc oxide nanoparticles is an earlier biomarker for nanotoxicological evaluation. ACS Nano 8, 2562–2574 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Zhang R., Piao M. J., Kim K. C., Kim A. D., Choi J. Y., Choi J., Hyun J. W. (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling is involved in silver nanoparticles-induced apoptosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 44, 224–232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Christen V., Capelle M., Fent K. (2013) Silver nanoparticles induce endoplasmatic reticulum stress response in zebrafish. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 272, 519–528 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Labbé K., Saleh M. (2011) Pyroptosis: A Caspase-1-dependent programmed cell death and a barrier to infection. in The Inflammasomes (Couillin I., Pétrilli V., Martinon F., eds), pp. 17–36, Springer; Basel [Google Scholar]
- 14. Fernandes-Alnemri T., Wu J., Yu J. W., Datta P., Miller B., Jankowski W., Rosenberg S., Zhang J., Alnemri E. S. (2007) The pyroptosome: a supramolecular assembly of ASC dimers mediating inflammatory cell death via caspase-1 activation. Cell Death Differ 14, 1590–1604 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Dinarello C. A. (2009) Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 27, 519–550 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Dinarello C. A. (2011) Interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Blood 117, 3720–3732 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Franchi L., Eigenbrod T., Muñoz-Planillo R., Nuñez G. (2009) The inflammasome: a caspase-1-activation platform that regulates immune responses and disease pathogenesis. Nat. Immunol. 10, 241–247 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Meunier E., Coste A., Olagnier D., Authier H., Lefèvre L., Dardenne C., Bernad J., Béraud M., Flahaut E., Pipy B. (2012) Double-walled carbon nanotubes trigger IL-1β release in human monocytes through Nlrp3 inflammasome activation. Nanomedicine 8, 987–995 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Yang E. J., Kim S., Kim J. S., Choi I. H. (2012) Inflammasome formation and IL-1β release by human blood monocytes in response to silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 33, 6858–6867 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Reisetter A. C., Stebounova L. V., Baltrusaitis J., Powers L., Gupta A., Grassian V. H., Monick M. M. (2011) Induction of inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis by carbon black nanoparticles. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 21844–21852 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Poirier M., Simard J. C., Antoine F., Girard D. (2014) Interaction between silver nanoparticles of 20 nm (AgNP20) and human neutrophils: induction of apoptosis and inhibition of de novo protein synthesis by AgNP20 aggregates. J. Appl. Toxicol. 34, 404–412 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Lakshmanan U., Porter A. G. (2007) Caspase-4 interacts with TNF receptor-associated factor 6 and mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-κB-dependent production of IL-8 and CC chemokine ligand 4 (macrophage-inflammatory protein-1). J. Immunol. 179, 8480–8490 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Vallières F., Girard D. (2013) IL-21 enhances phagocytosis in mononuclear phagocyte cells: identification of spleen tyrosine kinase as a novel molecular target of IL-21. J. Immunol. 190, 2904–2912 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Simard J. C., Cesaro A., Chapeton-Montes J., Tardif M., Antoine F., Girard D., Tessier P. A. (2013) S100A8 and S100A9 induce cytokine expression and regulate the NLRP3 inflammasome via ROS-dependent activation of NF-κB. PLoS One 8, e72138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Binet F., Chiasson S., Girard D. (2010) Evidence that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and caspase-4 activation occur in human neutrophils. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 391, 18–23 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Ivask A., Kurvet I., Kasemets K., Blinova I., Aruoja V., Suppi S., Vija H., Käkinen A., Titma T., Heinlaan M., Visnapuu M., Koller D., Kisand V., Kahru A. (2014) Size-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles to bacteria, yeast, algae, crustaceans and Mammalian cells in vitro. PLoS One 9, e102108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Hitomi J., Katayama T., Eguchi Y., Kudo T., Taniguchi M., Koyama Y., Manabe T., Yamagishi S., Bando Y., Imaizumi K., Tsujimoto Y., Tohyama M. (2004) Involvement of caspase-4 in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and Aβ-induced cell death. J. Cell Biol. 165, 347–356 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Edamatsu T., Xiao Y. Q., Tanabe J., Mue S., Ohuchi K. (1997) Induction of neutrophil chemotactic factor production by staurosporine in rat peritoneal neutrophils. Br. J. Pharmacol. 121, 1651–1658 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Labbé K., Saleh M. (2008) Cell death in the host response to infection. Cell Death Differ. 15, 1339–1349 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Sollberger G., Strittmatter G. E., Kistowska M., French L. E., Beer H. D. (2012) Caspase-4 is required for activation of inflammasomes. J. Immunol. 188, 1992–2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Akhtar M. J., Ahamed M., Alhadlaq H. A., Alrokayan S. A., Kumar S. (2014) Targeted anticancer therapy: overexpressed receptors and nanotechnology. Clin. Chim. Acta 436, 78–92 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Schroder K., Tschopp J. (2010) The inflammasomes. Cell 140, 821–832 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Miao E. A., Rajan J. V., Aderem A. (2011) Caspase-1-induced pyroptotic cell death. Immunol. Rev. 243, 206–214 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Binet F., Chiasson S., Girard D. (2010) Arsenic trioxide induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-related events in neutrophils. Int. Immunopharmacol. 10, 508–512 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Bauernfeind F. G., Horvath G., Stutz A., Alnemri E. S., MacDonald K., Speert D., Fernandes-Alnemri T., Wu J., Monks B. G., Fitzgerald K. A., Hornung V., Latz E. (2009) Cutting edge: NF-κB activating pattern recognition and cytokine receptors license NLRP3 inflammasome activation by regulating NLRP3 expression. J. Immunol. 183, 787–791 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Nowack B., Krug H. F., Height M. (2011) 120 years of nanosilver history: implications for policy makers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 1177–11783 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Yallapu M. M., Gupta B. K., Jaggi M., Chauhan S. C. (2010) Fabrication of curcumin encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles for improved therapeutic effects in metastatic cancer cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 351, 19–29 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Guan M., Fousek K., Chow W. A. (2012) Nelfinavir inhibits regulated intramembrane proteolysis of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 and activating transcription factor 6 in castration-resistant prostate cancer. FEBS J. 279, 2399–2411 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Guan M., Fousek K., Jiang C., Guo S., Synold T., Xi B., Shih C. C., Chow W. A. (2011) Nelfinavir induces liposarcoma apoptosis through inhibition of regulated intramembrane proteolysis of SREBP-1 and ATF6. Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 1796–1806 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Kim S., Joe Y., Jeong S. O., Zheng M., Back S. H., Park S. W., Ryter S. W., Chung H. T. (2014) Endoplasmic reticulum stress is sufficient for the induction of IL-1β production via activation of the NF-κB and inflammasome pathways. Innate Immun. 20, 799–815 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Kim H. J., Jeong J. S., Kim S. R., Park S. Y., Chae H. J., Lee Y. C. (2013) Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung inflammation through modulation of NF-κB/HIF-1α signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 3, 1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Fink S. L., Cookson B. T. (2006) Caspase-1-dependent pore formation during pyroptosis leads to osmotic lysis of infected host macrophages. Cell Microbiol. 8, 1812–1825 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Martinon F., Pétrilli V., Mayor A., Tardivel A., Tschopp J. (2006) Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature 440, 237–241 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Dostert C., Pétrilli V., Van Bruggen R., Steele C., Mossman B. T., Tschopp J. (2008) Innate immune activation through Nalp3 inflammasome sensing of asbestos and silica. Science 320, 674–677 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Kahlenberg J. M., Lundberg K. C., Kertesy S. B., Qu Y., Dubyak G. R. (2005) Potentiation of caspase-1 activation by the P2X7 receptor is dependent on TLR signals and requires NF-κB-driven protein synthesis. J. Immunol. 175, 7611–7622 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Yang M., Flavin K., Kopf I., Radics G., Hearnden C. H., McManus G. J., Moran B., Villalta-Cerdas A., Echegoyen L. A., Giordani S., Lavelle E. C. (2013) Functionalization of carbon nanoparticles modulates inflammatory cell recruitment and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Small 9, 4194–4206 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Kanapathipillai M., Brock A., Ingber D. E. (2014) Nanoparticle targeting of anti-cancer drugs that alter intracellular signaling or influence the tumor microenvironment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 10.1016/j.addr.2014.05.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Lohcharoenkal W., Wang L., Chen Y. C., Rojanasakul Y. (2014) Protein nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers for cancer therapy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 180549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Chen X., Schluesener H. J. (2008) Nanosilver: a nanoproduct in medical application. Toxicol Lett. 176, 1–12 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Kulthong K., Srisung S., Boonpavanitchakul K., Kangwansupamonkon W., Maniratanachote R. (2010) Determination of silver nanoparticle release from antibacterial fabrics into artificial sweat. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 7, 8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Stebounova L. V., Adamcakova-Dodd A., Kim J. S., Park H., O'Shaughnessy P. T., Grassian V. H., Thorne P. S. (2011) Nanosilver induces minimal lung toxicity or inflammation in a subacute murine inhalation model. Part Fibre Toxicol. 8, 5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Bartłomiejczyk T., Lankoff A., Kruszewski M., Szumiel I. (2013) Silver nanoparticles: allies or adversaries? Ann Agric. Environ. Med. 20, 48–54 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. McIlwain D. R., Berger T., Mak T. W. (2013) Caspase functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 5, a008656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Obeng E. A., Boise L. H. (2005) Caspase-12 and caspase-4 are not required for caspase-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 29578–29587 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Kajiwara Y., Schiff T., Voloudakis G., Gama Sosa M. A., Elder G., Bozdagi O., Buxbaum J. D. (2014) A critical role for human caspase-4 in endotoxin sensitivity. J. Immunol. 193, 335–343 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]