Abstract
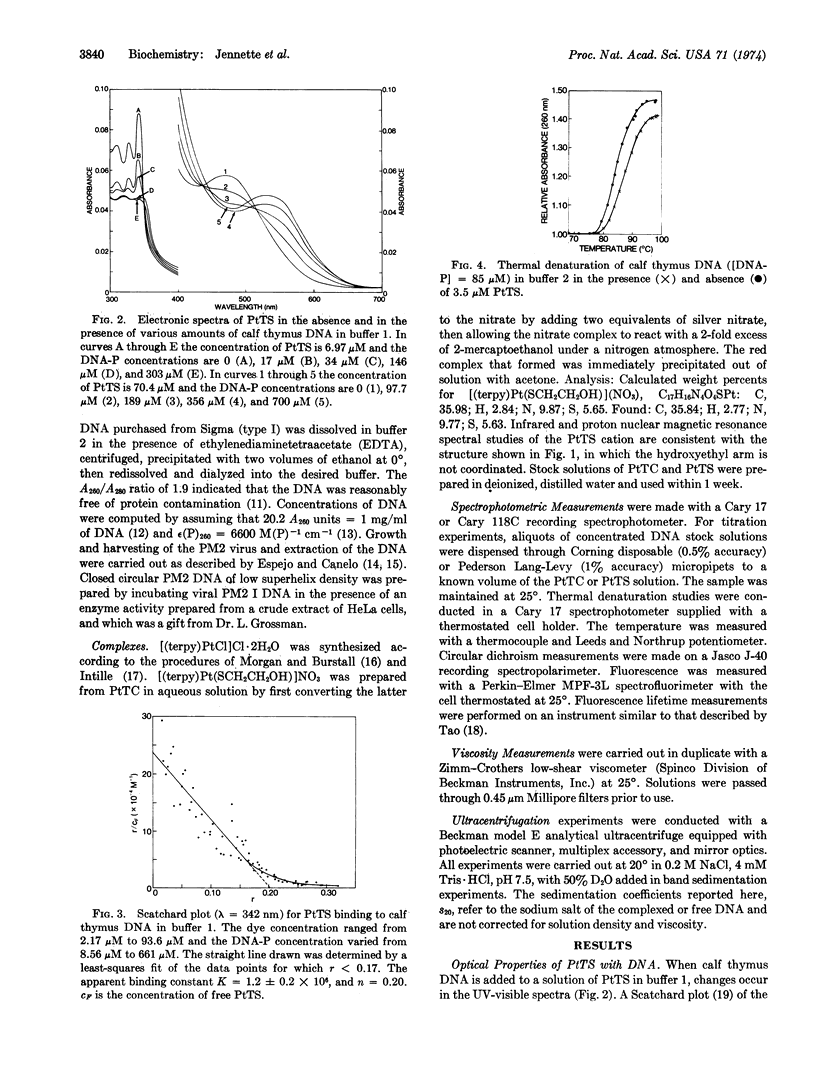
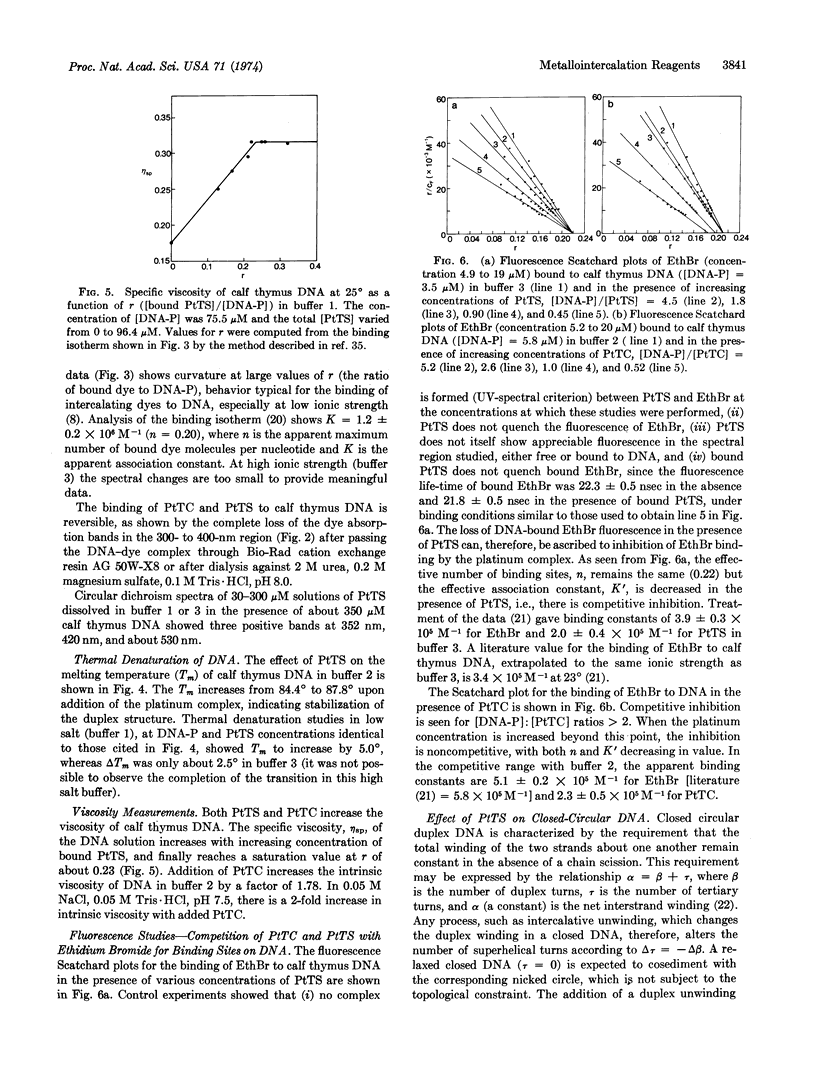
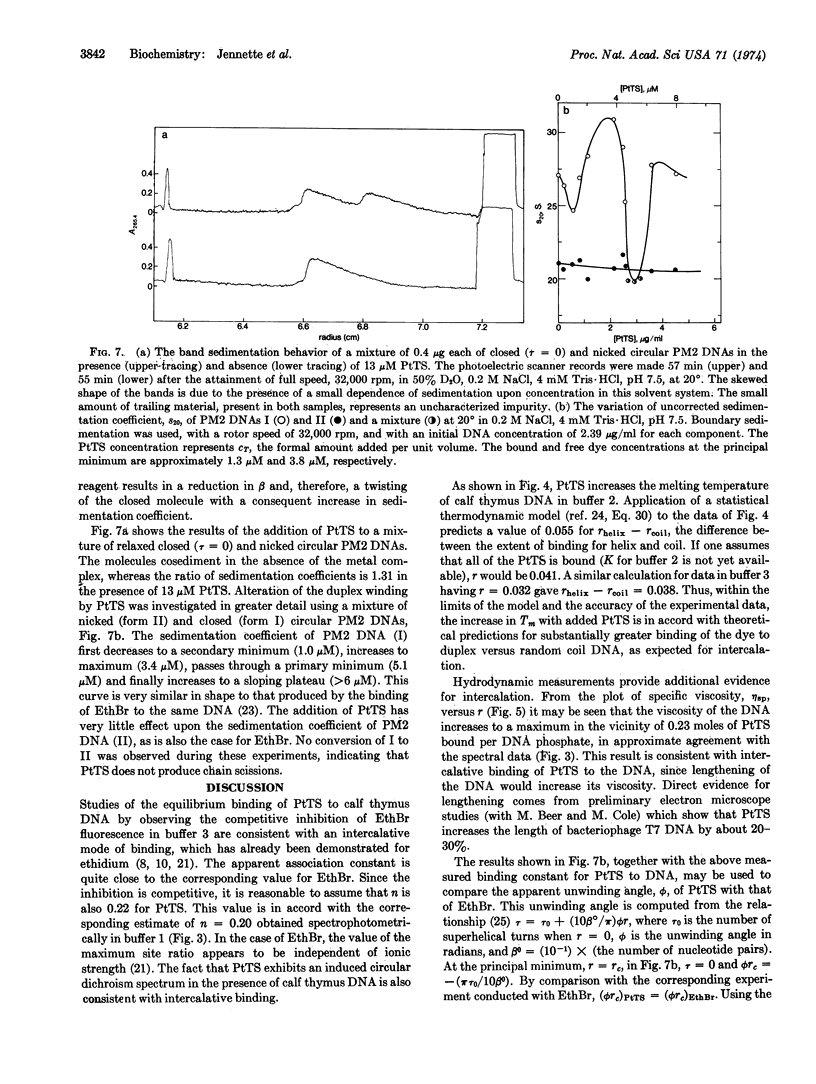
The red, cationic complex 2-hydroxy-ethanethiolato(2,2′,2″-terpyridine)platinum(II), [(terpy)-Pt(SCH2CH2OH)]+, binds strongly to DNA by a mechanism involving intercalation. By means of fluorescence spectroscopy, the platinum complex was shown to inhibit competitively the binding of the intercalating dye ethidium bromide to calf thymus DNA. This platinum complex increases the viscosity of calf thymus DNA, raises the melting temperature by up to 5°, and exhibits induced circular dichroism when bound to the DNA. The closed circular viral DNA from bacteriophage PM2 is unwound by the complex in a manner that is similar to that of ethidium bromide and with an unwinding angle that appears to be slightly less than that of ethidium. Studies of the related complex [(terpy)PtCl]+, which has a substitutionally more labile chloride ligand, suggest that it also intercalates, especially at [DNA-P]:[Pt] ratios greater than 2. The potential utility of these new metallointercalation reagents as heavy atom probes in fiber diffraction or electron microscopic studies of the interaction process is discussed.
Keywords: metal binding, supercoiled DNA, viscosity, thermal denaturation, fluorescence
Full text
PDF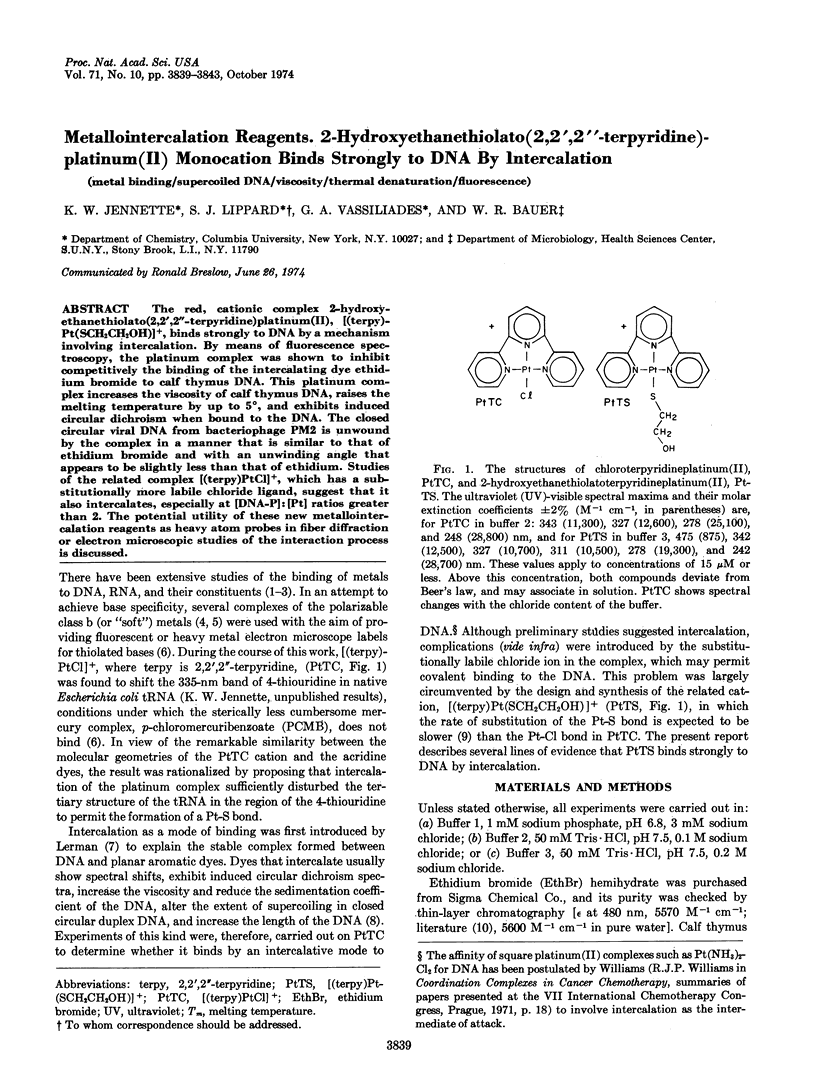

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aten J. B., Cohen J. A. Sedimentation-viscosity studies of high molecular weight DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):537–548. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80311-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEER M., ZOBEL C. R. Electron stains. II: Electron microscopic studies on the visibility of stained DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1961 Dec;3:717–726. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer W., Vinograd J. The interaction of closed circular DNA with intercalative dyes. I. The superhelix density of SV40 DNA in the presence and absence of dye. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):141–171. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake A., Peacocke A. R. The interaction of aminocridines with nucleic acids. Biopolymers. 1968;6(9):1225–1253. doi: 10.1002/bip.1968.360060902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crewe A. V., Wall J., Langmore J. Visibility of single atoms. Science. 1970 Jun 12;168(3937):1338–1340. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3937.1338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M. Calculation of binding isotherms for heterogenous polymers. Biopolymers. 1968 Apr;6(4):575–584. doi: 10.1002/bip.1968.360060411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M. Statistical thermodynamics of nucleic acid melting transitions with coupled binding equilibria. Biopolymers. 1971 Nov;10(11):2147–2160. doi: 10.1002/bip.360101110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond D. S., Pritchard N. J., Simpson-Gildemeister V. F., Peacocke A. R. Interaction of aminoacridines with deoxyribonucleic acid: viscosity of the complexes. Biopolymers. 1966 Oct-Nov;4(9):971–987. doi: 10.1002/bip.1966.360040903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Canelo E. S. Properties and characterization of the host bacterium of bacteriophage PM2. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1887–1891. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1887-1891.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Canelo E. S. Properties of bacteriophage PM2: a lipid-containing bacterial virus. Virology. 1968 Apr;34(4):738–747. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray H. B., Jr, Upholt W. B., Vinograd J. A buoyant method for the determination of the superhelix density of closed circular DNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 28;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitner H. I., Lippard S. J., Sunshine H. R. Metal binding by thionucleosides. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Dec 13;94(25):8936–8937. doi: 10.1021/ja00780a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izatt R. M., Christensen J. J., Rytting J. H. Sites and thermodynamic quantities associated with proton and metal ion interaction with ribonucleic acid, deoxyribonucleic acid, and their constituent bases, nucleosides, and nucleotides. Chem Rev. 1971 Oct;71(5):439–481. doi: 10.1021/cr60273a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERMAN L. S. Structural considerations in the interaction of DNA and acridines. J Mol Biol. 1961 Feb;3:18–30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePecq J. B., Paoletti C. A fluorescent complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. Physical-chemical characterization. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):87–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottensmeyer F. P., Schmidt E. E., Olbrecht A. J. Image of a sulfur atom. Science. 1973 Jan 12;179(4069):175–176. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4069.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. G. Acids and bases. Science. 1966 Jan 14;151(3707):172–177. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3707.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upholt W. B., Gray H. B., Jr, Vinograd J. Sedimentation velocity behavior of closed circular SV40 DNA as a function of superhelix density, ionic strength, counterion and temperature. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 28;62(1):21–38. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinograd J., Lebowitz J. Physical and topological properties of circular DNA. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jul;49(6):103–125. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.6.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. Complex formation between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):269–282. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


