Abstract
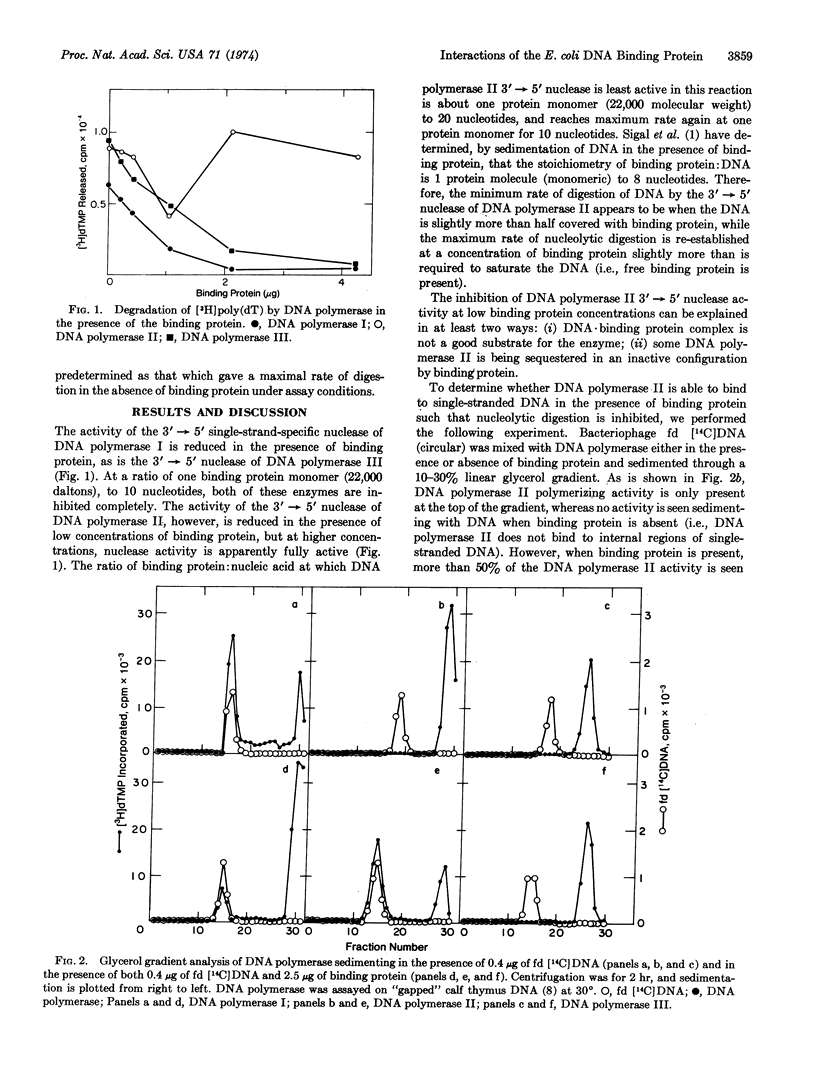
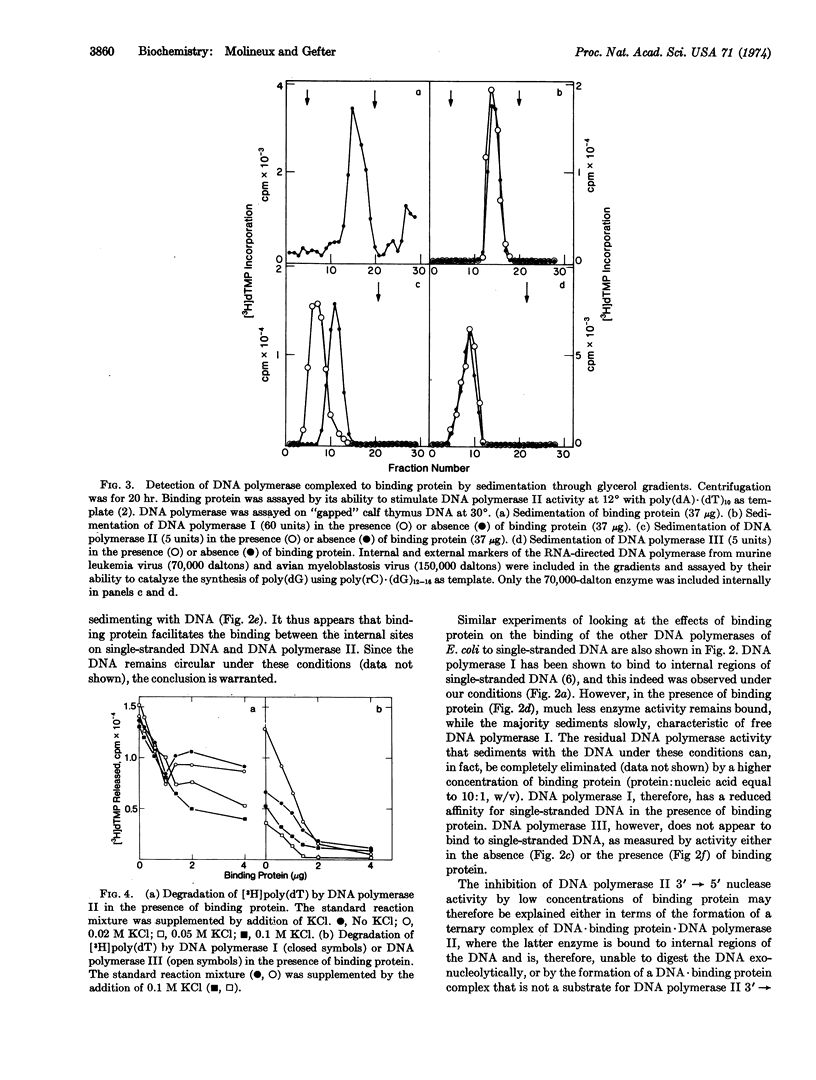
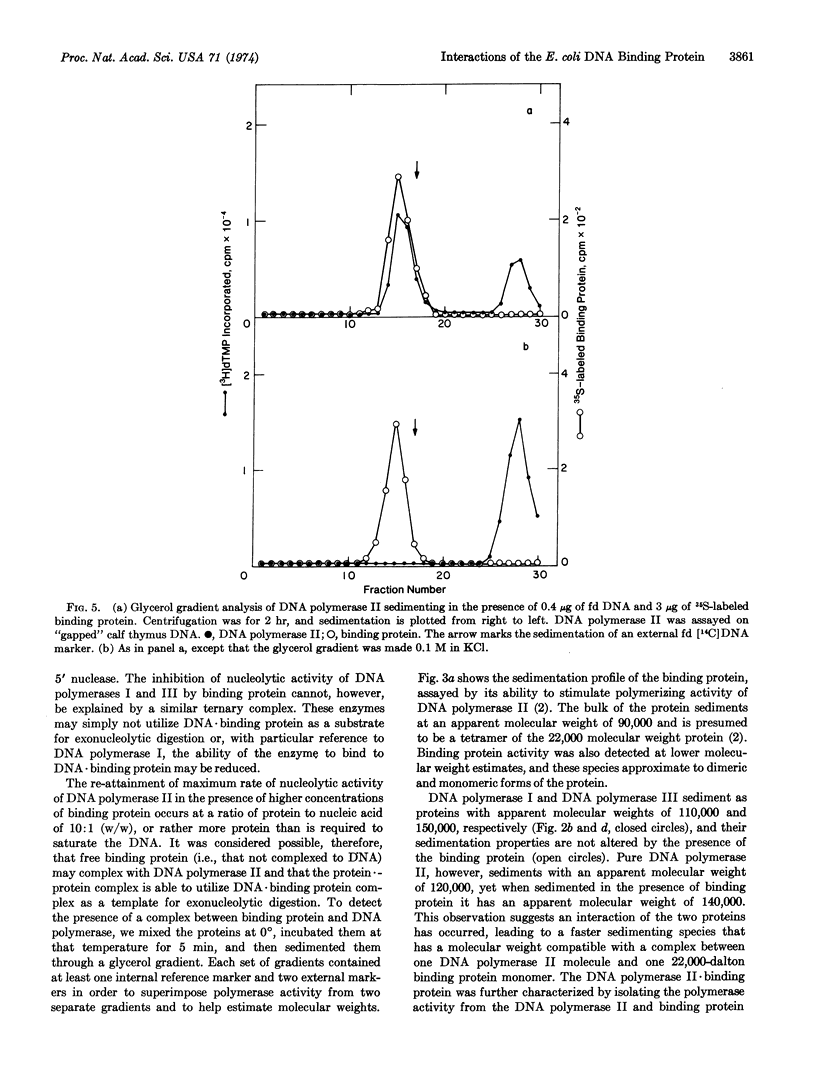
The E. coli DNA binding protein reduces the activity of the single-strand-specific nucleases associated with all three DNA polymerases known in E. coli. A slight excess of binding protein over that required to saturate the DNA template leads to total inhibition of activity of the 3′ → 5′ nucleases associated with DNA polymerases I and III, but restores maximum activity of the DNA polymerase II-associated nuclease. The binding protein forms a specific complex with DNA polymerase II in the absence of DNA, and it is this complex that degrades a DNA·binding protein complex. Binding protein also facilitates the binding of DNA polymerase II to single-stranded DNA, whereas the binding to DNA of DNA polymerase I is inhibited. These data may explain the specificity with which the binding protein enhances the synthetic ability of DNA polymerase II.
Keywords: single-strand-specific nuclease, protein·protein and DNA·protein interactions
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gefter M. L., Molineux I. J., Kornberg T., Khorana H. G. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in cell-free extracts. 3. Catalytic properties of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3321–3326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W. M., Lehman I. R. On the exonuclease activity of phage T4 deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3139–3146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Kornberg A., Alberts B. M. Stimulation of T4 bacteriophage DNA polymerase by the protein product of T4 gene 32. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 28;62(1):39–52. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., Englund P. T., Bertsch L. L. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXVI. Physical and chemical studies of a homogeneous deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 10;244(11):2996–3008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg A. Active center of DNA polymerase. Science. 1969 Mar 28;163(3874):1410–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3874.1410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg T., Gefter M. L. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in cell-free extracts. IV. Purification and catalytic properties of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5369–5375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg T., Gefter M. L. Purification and DNA synthesis in cell-free extracts: properties of DNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):761–764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben R. C., Gefter M. L. A DNA-binding protein induced by bacteriophage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1846–1850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal N., Delius H., Kornberg T., Gefter M. L., Alberts B. A DNA-unwinding protein isolated from Escherichia coli: its interaction with DNA and with DNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3537–3541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



