Abstract
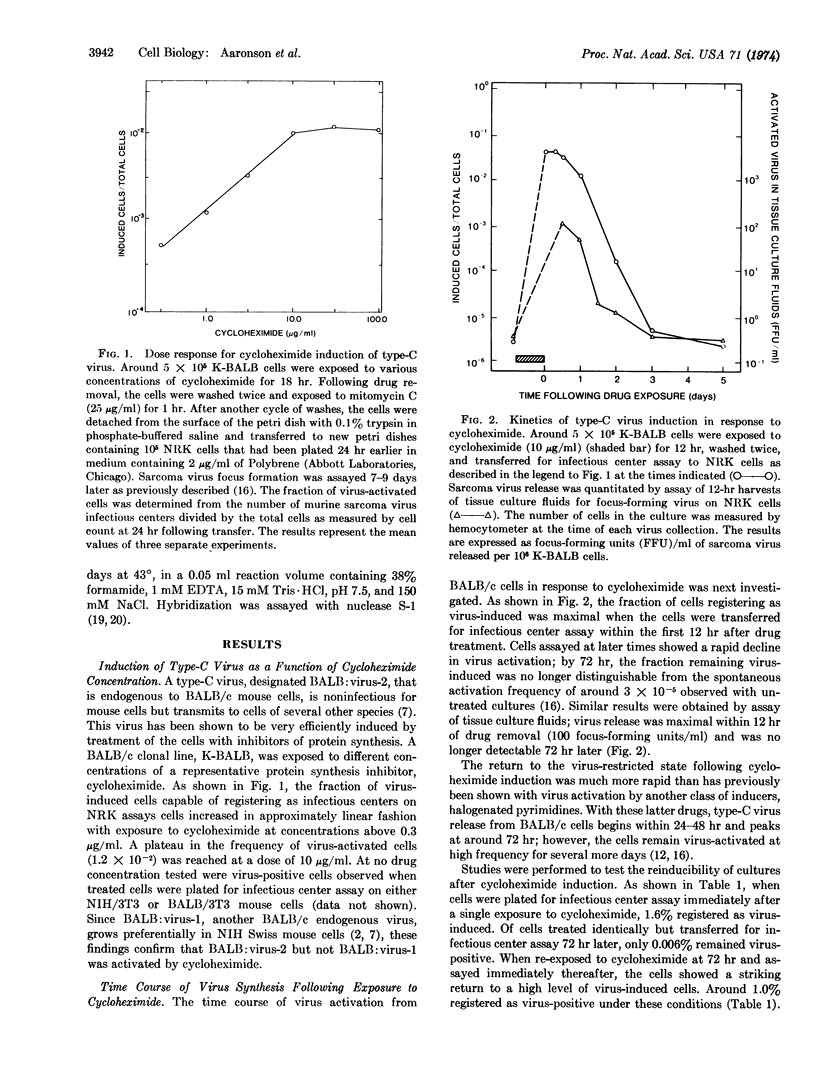
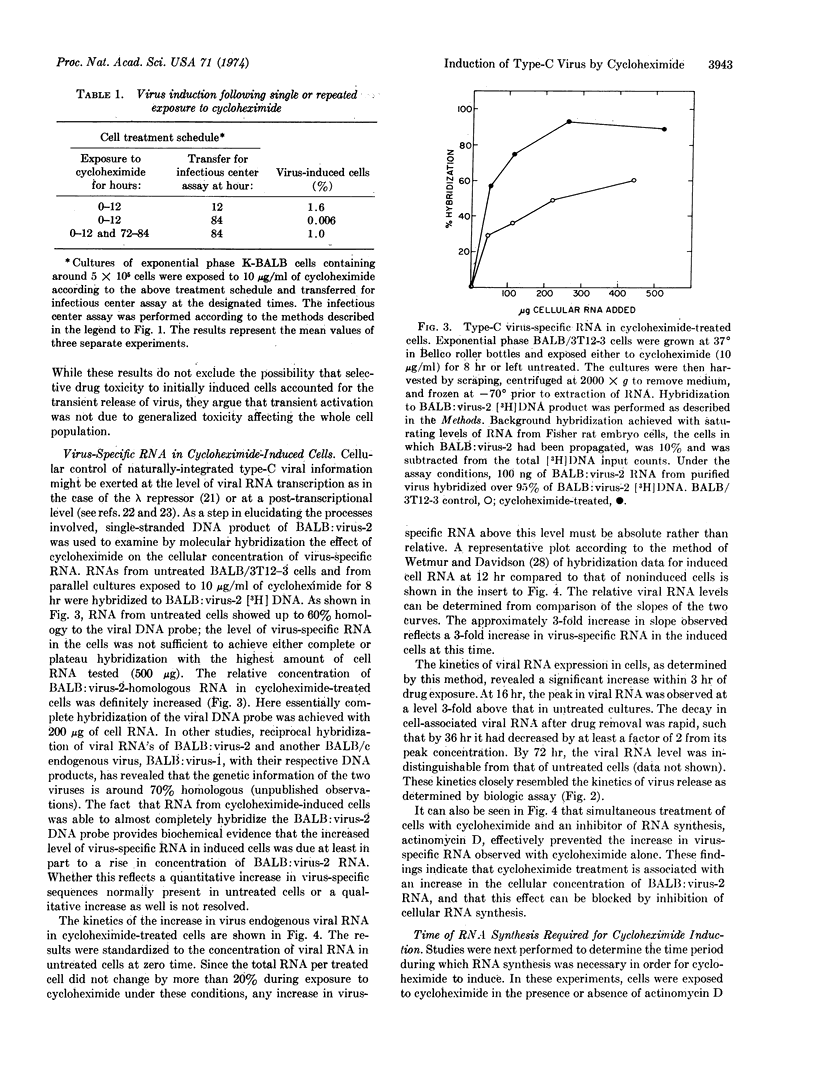
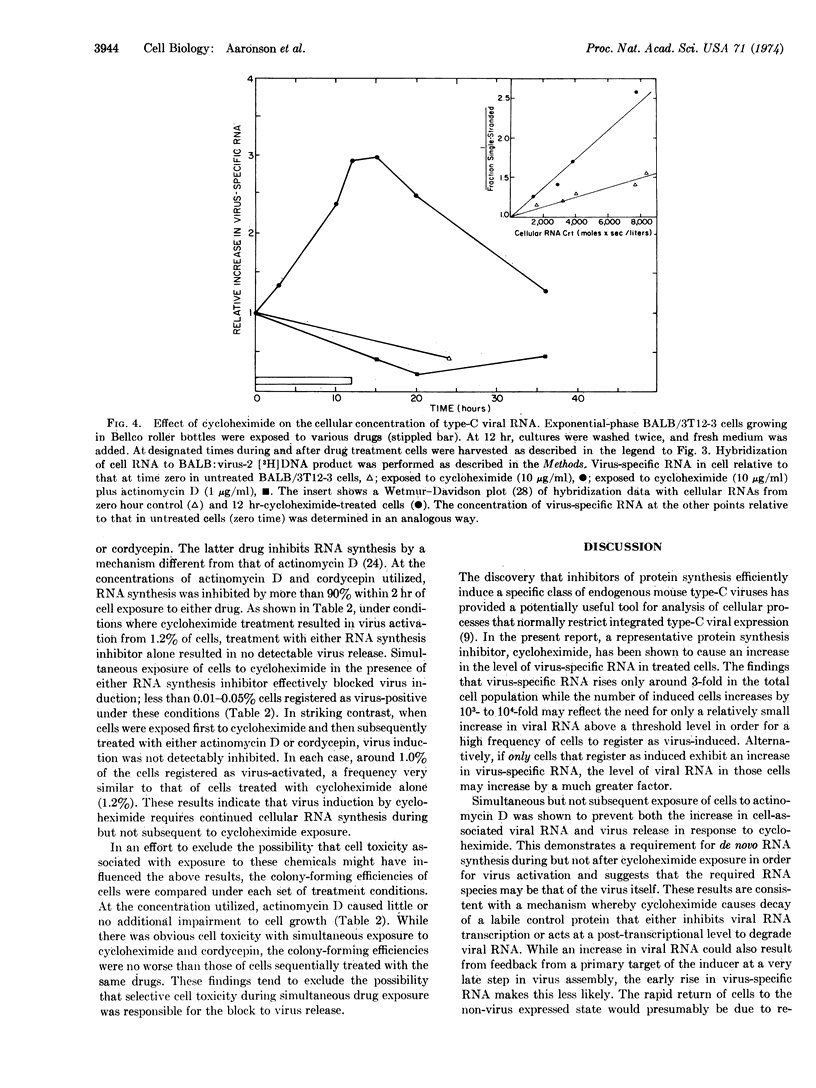
Mouse cells contain the genetic information for multiple endogenous type-C RNA viruses. The mechanisms by which the cell controls expression of these naturally integrated viruses are not yet known. Recently, chemicals that inhibit protein synthesis have been shown to induce a specific type-C virus at high frequency from BALB/c mouse embryo cells. In the present studies, virus activation in response to a representative translational inhibitor, cycloheximide, is demonstrated to be transient, with virus release primarily occurring within the first 12-24 hr following drug exposure. Analysis of virus-specific RNA in cells by molecular hybridization revealed an absolute increase in viral RNA concentration in cycloheximide-treated cells. This was blocked by simultaneous exposure of the cells to actinomycin D. Further, inhibition of RNA synthesis during but not subsequent to cycloheximide exposure prevented virus activation. These findings show that virus induction by cycloheximide requires de novo RNA synthesis during but not after drug exposure and suggest that the required RNA species may be that of the virus itself. The present results are consistent with the hypothesis that translational inhibitors prevent synthesis of a labile protein whose normal action is to inhibit viral RNA transcription or to cause degradation of viral RNA.
Keywords: viral RNA transcription, protein synthesis inhibition, tumor virus, cancer
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A. Chemical induction of focus-forming virus from nonproducer cells transformed by murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3069–3072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Dunn C. Y. Endogenous C-type viruses of BALB-c cells: frequencies of spontaneous and chemical induction. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):181–185. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.181-185.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Dunn C. Y. High-frequency C-type virus induction by inhibitors of protein synthesis. Science. 1974 Feb 1;183(4123):422–424. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4123.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Jainchill J. L., Todaro G. J. Murine sarcoma virus transformation of BALB-3T3 cells: lack of dependence on murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1236–1243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Stephenson J. R. Independent segregation of loci for activation of biologically distinguishable RNA C-type viruses in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2055–2058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Stephenson J. R. Widespread natural occurrence of high titers of neutralizing antibodies to a specific class of endogenous mouse type-C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1957–1961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Development of 3T3-like lines from Balb-c mouse embryo cultures: transformation susceptibility to SV40. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Oct;72(2):141–148. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Weaver C. A. Characterization of murine sarcoma virus (Kirsten) transformation of mouse and human cells. J Gen Virol. 1971 Nov;13(2):245–252. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-2-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Scolnick E. M. RNA in mammalian sarcoma virus transformed nonproducer cells homologous to murine leukemia virus RNA. Virology. 1973 Feb;51(2):370–382. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90436-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Teich N. M., Levine A. S., Rowe W. P. Evidence that the AKR murine-leukemia-virus genome is complete in DNA of the high-virus AKR mouse and incomplete in the DNA of the "virus-negative" NIH mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARREN L. D., HOWELL R. R., TOMKINS G. M., CROCCO R. M. A PARADOXICAL EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN D: THE MECHANISM OF REGULATION OF ENZYME SYNTHESIS BY HYDROCORTISONE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1121–1129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelb L. D., Milstien J. B., Martin M. A., Aaronson S. A. Characterization of murine leukaemia virus-specific DNA present in normal mouse cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 18;244(133):76–79. doi: 10.1038/newbio244076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huu Duc-Nguyen, Rosenblum E. N., Zeigel R. F. Persistent infection of a rat kidney cell line with Rauscher murine leukemia virus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1133-1140.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klement V., Nicolson M. O., Huebner R. J. Rescue of the genome of focus forming virus from rat non-productive lines by 5'-bromodeoxyruidine. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 3;234(44):12–14. doi: 10.1038/newbio234012a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. A., Garapin A. C., Jackson N., Fanshier L., Levinson W., Bishop J. M. Virus-specific ribonucleic acid in cells producing rous sarcoma virus: detection and characterization. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):891–902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.891-902.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Pincus T. Demonstration of biological activity of a murine leukemia virus of New Zealand black mice. Science. 1970 Oct 16;170(3955):326–327. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3955.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A. Xenotropic viruses: murine leukemia viruses associated with NIH Swiss, NZB, and other mouse strains. Science. 1973 Dec 14;182(4117):1151–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4117.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manly K. F., Smoler D. F., Bromfeld E., Baltimore D. Forms of deoxyribonucleic acid produced by virions of the ribonucleic acid tumor viruses. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):106–111. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.106-111.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A., Moscona M. H., Saenz N. Enzyme induction in embryonic retina: the role of transcription and translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):160–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Rosbash M., Penman M. Messenger and heterogeneous nuclear RNA in HeLa cells: differential inhibition by cordycepin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1878–1885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P. Studies of genetic transmission of murine leukemia virus by AKR mice. I. Crosses with Fv-1 n strains of mice. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1272–1285. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. A genetic locus for inducibility of C-type in BALB-c cells: the effect of a nonlinked regulatory gene on detection of virus after chemical activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2798–2801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. Murine sarcoma and leukemia viruses: genetic differences determined by RNA-DNA hybridization. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):480–484. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. Segregation of loci for C-type virus induction in strains of mice with high and low incidence of leukemia. Science. 1973 May 25;180(4088):865–866. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4088.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Greenberger J. S., Aaronson S. A. Oncogenicity of an endogenous C-type virus chemically activated from mouse cells in culture. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):237–240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.237-240.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. A., Meier H., Myers D. D. Host-gene control of C-type RNA tumor virus: inheritance of the group-specific antigen of murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3190–3194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



