Abstract
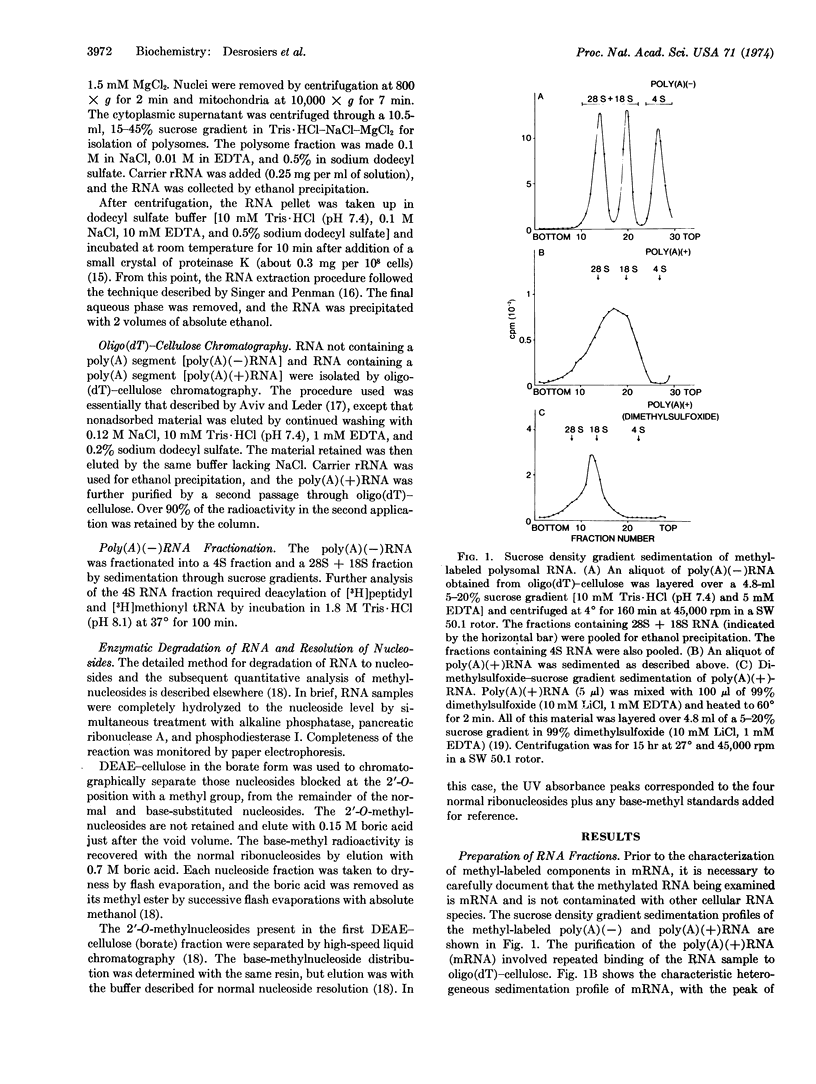
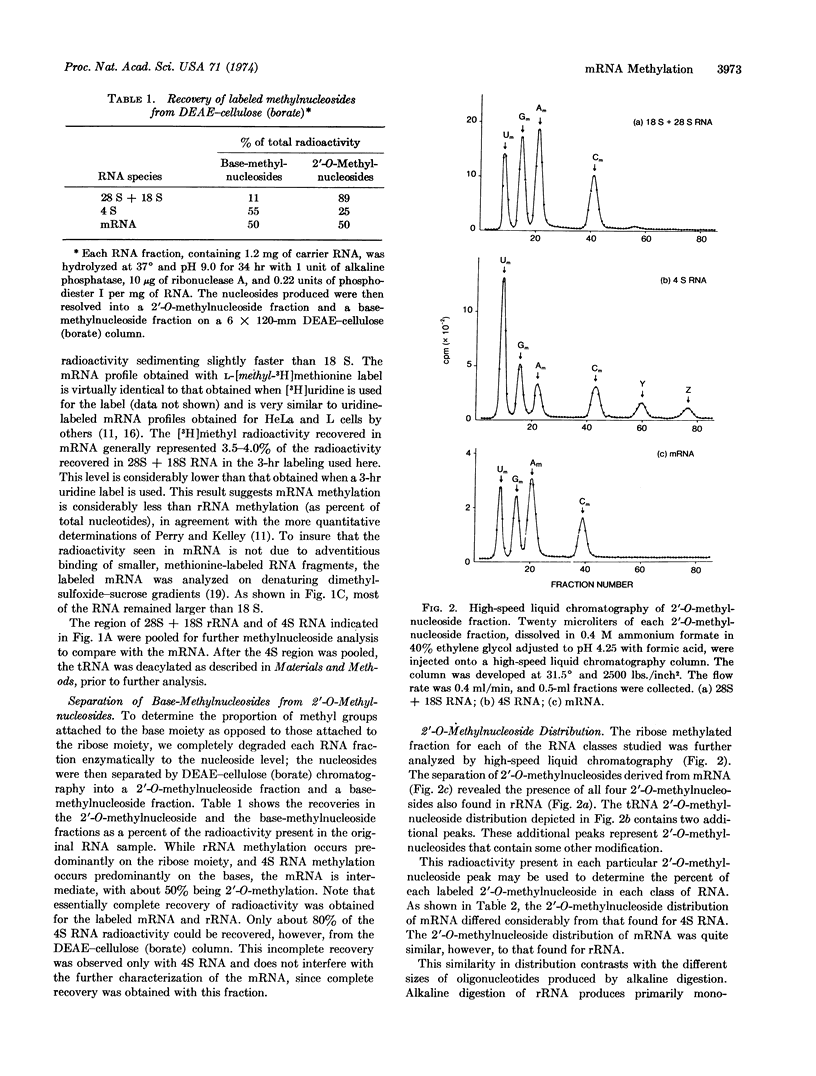
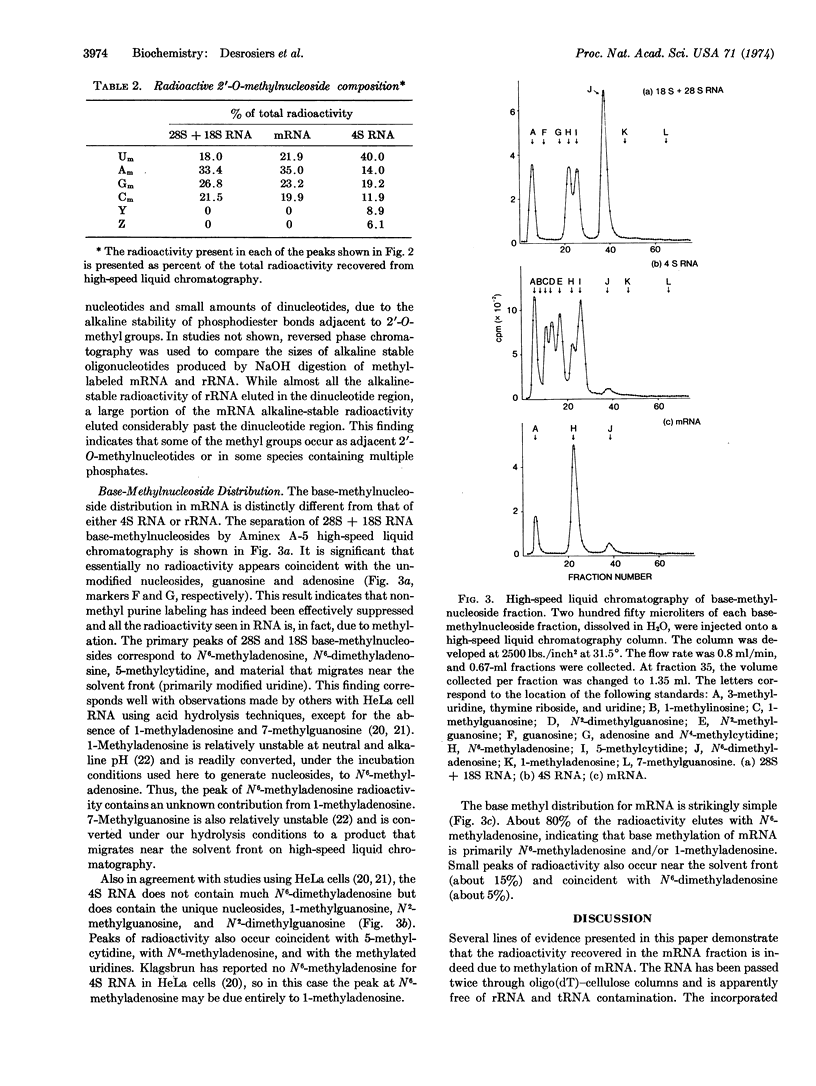
The poly(A) tract found in eukaryotic mRNA was used to study methylation in mRNA obtained from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Methyl labeling of RNA was achieved with L-[methyl-3H]methionine under conditions that suppress radioactive incorporation into the purine ring. RNA that contains a poly(A) segment was obtained from polysomal RNA by chromatography on oligo(dT)-cellulose. Sucrose density gradient centrifugation of this RNA revealed a pattern expected for mRNA. The composition of the methyl-labeled nucleosides in the RNA was analyzed after complete enzymatic degradation to nucleosides. By use of DEAE-cellulose (borate) chromatography, which separates 2′-O-methylnucleosides from normal and base-methylated nucleosides, about 50% of the radioactivity was recovered in the 2′-O-methylnucleoside fraction and 50% in the base-methylnucleoside fraction. High-speed liquid chromatography (Aminex A-5) of the 2′-O-methylnucleoside fraction produced four peaks coincident with the four 2′-O-methylnucleoside standards. Analysis of the base-methylnucleoside fraction revealed a unique pattern. While ribosomal RNA and tRNA possessed complex base-methylnucleoside patterns, the distribution in mRNA was quite simple, consisting predominantly of N6-methyladenosine. These results demonstrate a unique distribution of methylated nucleosides in mRNA. By analogy to ribosomal RNA synthesis, the presence of methylnucleosides in mRNA may reflect a cellular mechanism for the selective processing of certain mRNA sequences.
Keywords: RNA methylation, RNA processing, methylnucleoside composition
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbate J., Rottman F. Gas chromatographic method for determination of 2'-O-methylation in RNA. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jun;47(2):378–388. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskin F., Dekker C. A. A rapid and specific assay for sugar methylation in ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5447–5449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. M., Attardi G. Methylation of nucleic acids in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jul 26;20(3):298–302. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90363-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R., Perry R. P. Relative occurrence of polyadenylic acid sequences in messenger and heterogeneous nuclear RNA of L cells as determined by poly (U)-hydroxylapatite chromatography. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 14;72(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanami Y., Brown G. M. Methylated bases of ribosomal ribonucleic acid from HeLa cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):8–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90553-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W., Adesnik M., Salditt M., Sheiness D., Wall R., Molloy G., Philipson L., Darnell J. E. Further evidence on the nuclear origin and transfer to the cytoplasm of polyadenylic acid sequences in mammalian cell RNA. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 15;75(3):515–532. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90458-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M. An evolutionary study of the methylation of transfer and ribosomal ribonucleic acid in prokaryote and eukaryote organisms. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2612–2620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane B. G., Tamaoki T. Methylated bases and sugars in 16-S and 28-S RNA from L cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 22;179(2):332–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg U., Persson T. Isolation of mRNA from KB-cells by affinity chromatography on polyuridylic acid covalently linked to Sepharose. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 4;31(2):246–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE P. A., Jr, POTTER V. R. PYRIMIDINE METABOLISM IN TISSUE CULTURE CELLS DERIVED FROM RAT HEPATOMAS. I. SUSPENSION CELL CULTURES DERIVED FROM THE NOVIKOFF HEPATOMA. Cancer Res. 1965 May;25:499–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B. Methylation of messenger RNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):38–47. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Fujisawa T. Methylation of ribosomal RNA precursor and tRNA in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May 21;157(3):476–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazato H., Edmonds M., Kopp D. W. Differential metabolism of large and small poly(A) sequences in the heterogeneous nuclear RNA of HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):200–204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Cheng T. Y., Freed J. J., Greenberg J. R., Kelley D. E., Tartof K. D. Evolution of the transcription unit of ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):609–616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E., LaTorre J. Synthesis and turnover of nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylic acid in mouse L cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 25;82(3):315–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottman F., Friderici K., Comstock P., Khan M. K. Influence of 2'-O-alkylation on the structure of single-stranded polynucleotides and the stability of 2'-O-alkylated polynucleotide complexes. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 18;13(13):2762–2771. doi: 10.1021/bi00710a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salim M., Maden B. E. Early and late methylations in HeLa cell ribosome maturation. Nature. 1973 Aug 10;244(5415):334–336. doi: 10.1038/244334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer R. W., Smuckler E. A. Altered regulation of the transport of RNA from nucleus to cytoplasm in rat hepatoma cells. Cancer Res. 1972 Feb;32(2):339–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer R. H., Penman S. Stability of HeLa cell mRNA in actinomycin. Nature. 1972 Nov 10;240(5376):100–102. doi: 10.1038/240100a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart S. E., Rottman F. M. Synthetic polynucleotides as model substrates for ribosomal RNA processing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):1001–1008. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan M. H., Jr, Soeiro R., Warner J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr The effects of methionine deprivation on ribosome synthesis in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1527–1534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegers U., Hilz H. Rapid isolation of undegraded polysomal RNA without phenol. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 1;23(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80289-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



