Abstract
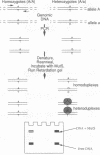
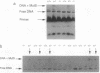
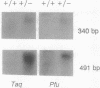
An experimental strategy for detecting heterozygosity in genomic DNA has been developed based on preferential binding of Escherichia coli MutS protein to DNA molecules containing mismatched bases. The binding was detected by a gel mobility-shift assay. This approach was tested by using as a model the most commonly occurring mutations within the cystic fibrosis (CFTR) gene. Genomic DNA samples were amplified with 5'-end-labeled primers that bracket the site of the delta F508 3-bp deletion in exon 10 of the CFTR gene. The renatured PCR products from homozygotes produced homoduplexes; the PCR products from heterozygotes produced heteroduplexes and homoduplexes (1:1). MutS protein bound more strongly to heteroduplexes that correspond to heterozygous carriers of delta F508 and contain a CTT or a GAA loop in one of the strands than to homoduplexes corresponding to homozygotes. The ability of MutS protein to detect heteroduplexes in PCR-amplified DNA extended to fragments approximately 500 bp long. The method was also able to detect carriers of the point mutations in exon 11 of the CFTR gene by a preferential binding of MutS to single-base mismatches in PCR-amplified DNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Au K. G., Welsh K., Modrich P. Initiation of methyl-directed mismatch repair. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12142–12148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chehab F. F., Wall J. Detection of multiple cystic fibrosis mutations by reverse dot blot hybridization: a technology for carrier screening. Hum Genet. 1992 May;89(2):163–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00217117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R. G. Current methods of mutation detection. Mutat Res. 1993 Jan;285(1):125–144. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(93)90060-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilley M., Holmes J., Yashar B., Modrich P. Mechanisms of DNA-mismatch correction. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):253–267. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90009-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiricny J., Su S. S., Wood S. G., Modrich P. Mismatch-containing oligonucleotide duplexes bound by the E. coli mutS-encoded protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):7843–7853. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.7843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. L., Hsu I. C. Detection of single DNA base mutations with mismatch repair enzymes. Genomics. 1992 Oct;14(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80213-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg K. S., Shoemaker D. D., Adams M. W., Short J. M., Sorge J. A., Mathur E. J. High-fidelity amplification using a thermostable DNA polymerase isolated from Pyrococcus furiosus. Gene. 1991 Dec 1;108(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90480-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S. F., McCusker J. H., Sander M. A., Kee Y., Modrich P., Brown P. O. Genomic mismatch scanning: a new approach to genetic linkage mapping. Nat Genet. 1993 May;4(1):11–18. doi: 10.1038/ng0593-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss J., Krawczak M., Schloesser M., Wagner M., Cooper D. N. The effect of replication errors on the mismatch analysis of PCR-amplified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):973–978. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J., Kerem B. S., Greer W., Chang P., Tsui L. C., Ray P. Rapid nonradioactive detection of the major cystic fibrosis mutation. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Feb;46(2):395–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossiter B. J., Caskey C. T. Molecular scanning methods of mutation detection. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12753–12756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. H., Barker P., Griffith J. Visualization of diagnostic heteroduplex DNAs from cystic fibrosis deletion heterozygotes provides an estimate of the kinking of DNA by bulged bases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4911–4915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielenski J., Rozmahel R., Bozon D., Kerem B., Grzelczak Z., Riordan J. R., Rommens J., Tsui L. C. Genomic DNA sequence of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):214–228. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90503-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]