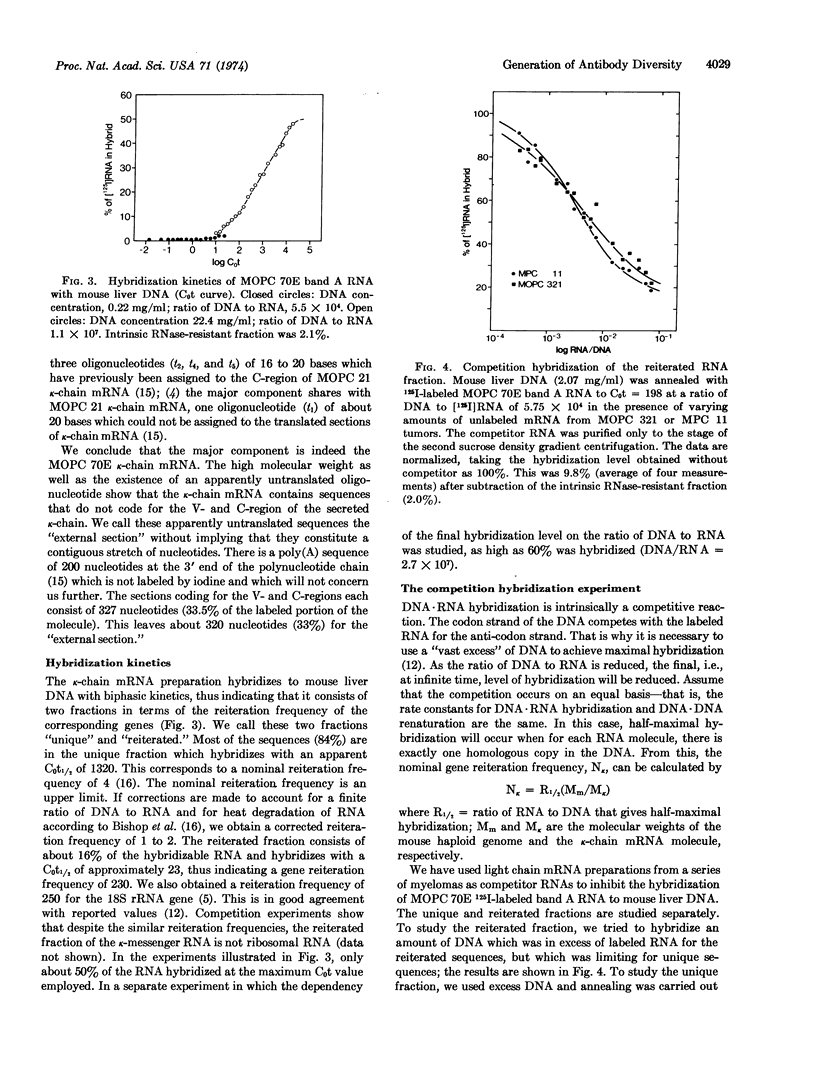
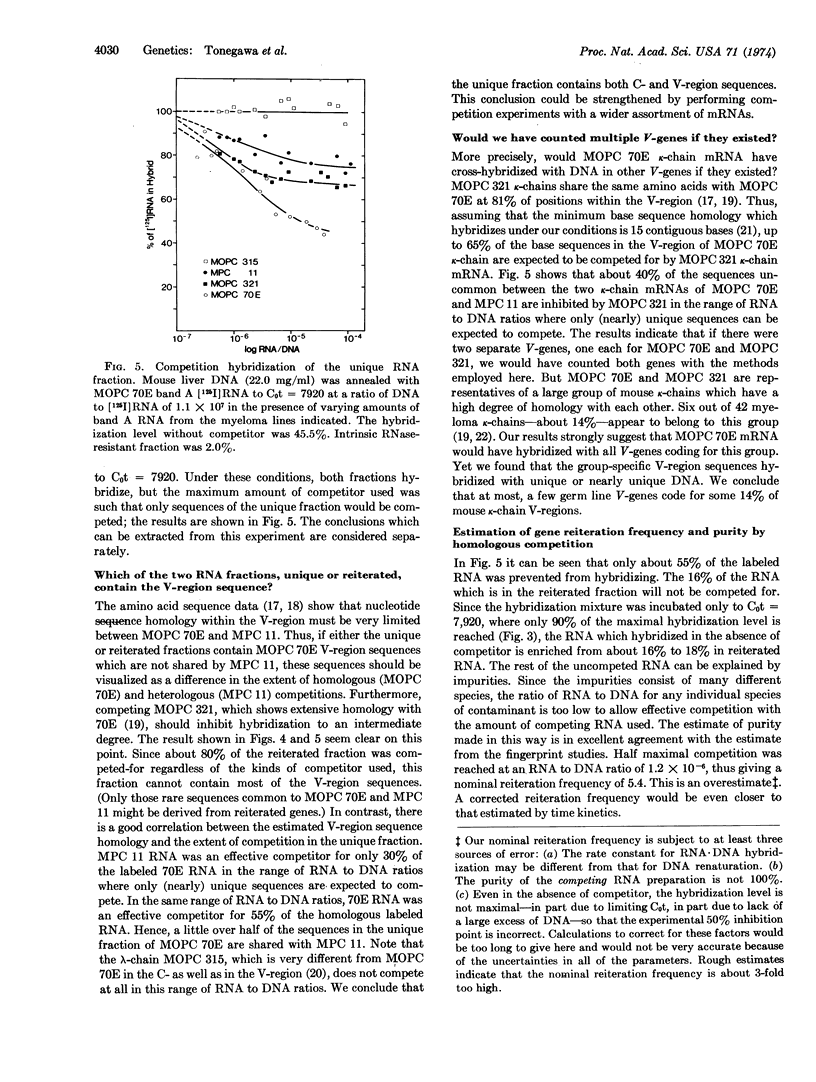
Abstract
RNA preparations containing 70-80% mouse κ-chain mRNA have been prepared. The remainder consists of many RNA species, each of which represents a small fraction of the total RNA. The κ-chain mRNA preparation hybridizes with mouse liver DNA with bi-phasic kinetics, indicating that it consists of two fractions —“unique” and “reiterated.” Competition hybridization experiments show that the homology among the unique fractions from different mRNAs is the same as the homology among the amino acid sequences of the corresponding κ-chains. Hence, in addition to the C-region (constant-region) sequences, (most of) the V-region (variable-region) sequences are also derived from unique germ line genes. The reiterated fractions from different κ-chain mRNAs show essentially complete homology with each other. This fraction seems to consist mostly of sequences which do not code for amino-acid sequences of the secreted polypeptide chain, i.e., the “external” section of the mRNA molecule. It is concluded that the number of germ line genes is too small to account for the observed diversity of antibody molecules.
Keywords: RNA·DNA hybridization, κ-chain mRNA
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernardini A., Tonegawa S. Hybridization studies with an antibody heavy chain mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1974 Apr 15;41(1):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80957-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O. Molecular hybridization of ribonucleic acid with a large excess of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1972 Jan;126(1):171–185. doi: 10.1042/bj1260171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Pemberton R., Baglioni C. Reiteration frequency of haemoglobin genes in the duck. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 23;235(60):231–234. doi: 10.1038/newbio235231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Cartwright E. M., Cowan N. J., Jarvis J. M., Milstein C. Purification and sequence of messenger RNA for immunoglobulin light chains. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 22;244(138):236–240. doi: 10.1038/newbio244236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B., Milstein C. Translation of messenger RNA for immunoglobulin light chains in a cell-free system from Krebs II ascites cells. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 15;23(2):244–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80352-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Sanger F., Barrell B. G. The sequence of 5 s ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):379–412. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Editorial: Antibody diversity: is it all coded for by the germ line genes? Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(1):1–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delovitch T., Baglioni C. Immunoglobulin genes: a test of somatic vs. germ line hypothesis by RNA-DNA hybridization. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:739–751. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dina D., Crippa M., Beccari E. Hybridization properties and sequence arrangement in a population of mRNAs. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 28;242(117):101–105. doi: 10.1038/newbio242101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube S. K. Use of 125I in fingerprinting RNA. Nature. 1973 Dec 21;246(5434):483–483. doi: 10.1038/246483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugan E. S., Bradshaw R. A., Simms E. S., Eisen H. N. Amino acid sequence of the light chain of a mouse myeloma protein (MOPC-315). Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 18;12(26):5400–5416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould H. J., Hamlyn P. H. The molecular weight of rabbit globin messenger RNA's. FEBS Lett. 1973 Mar 15;30(3):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80674-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. R., Dreyer W. J., Hood L. Mechanism of antibody synthesis: size differences between mouse kappa chains. Science. 1967 Jan 27;155(3761):465–467. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3761.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., McKean D., Farnsworth V., Potter M. Mouse immunoglobulin chains. A survey of the amino-terminal sequences of kappa chains. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):741–749. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. Molecular weights of ribosomal RNA in relation to evolution. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach B., Faust C., Vassalli P. Purification of 14S messenger RNA of immunoglobulin light chain that codes for a possible light-chain precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):451–455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean D., Potter M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin chains. Pattern of sequence variation among kappa chains with limited sequence differences. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):760–771. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melli M., Whitfield C., Rao K. V., Richardson M., Bishop J. O. DNA-RNA hybridization in vast DNA excess. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 5;231(18):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niyogi S. K., Thomas C. A., Jr The specific association of ribooligonucleotides of known chain length with denatured DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Jan 10;26(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90251-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pink J. R., Askonas B. A. Diversity of antibodies to cross-reacting nitrophenyl haptens in inbred mice. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Jun;4(6):426–430. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premkumar E., Shoyab M., Williamson A. R. Germ line basis for antibody diversity: immunoglobulin VH-and CH-gene frequencies measured by DNA-RNA hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):99–103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Bishop J. O., Milstein C., Brownlee G. G. Comparative hybridization studies iwth an immunoglobulin light chain mRNA fraction and non-immunoglobulin mRNA of mouse. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80917-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Biologically and chemically pure mRNA coding for a mouse immunoglobulin L-chain prepared with the aid of antibodies and immobilized oligothymidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2256–2260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherberg N. H., Refetoff S. Hybridization of RNA labelled with 125 I to high specific activity. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 4;242(118):142–145. doi: 10.1038/newbio242142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Mouse immunoglobulin kappa chain MPC 11: extra amino-terminal residues. Science. 1973 Sep 7;181(4103):941–943. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4103.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan D., Aviv H., Leder P. Purification and properties of biologically active messenger RNA for a myeloma light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1967–1971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Baldi I. Electrophoretically homogeneous myeloma light chain mRNA and its translation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Mar 5;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90510-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Bernardini A., Weimann B. J., Steinberg C. Reiteration frequency of antibody genes. Studies with k-chain mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):92–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80901-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigzell H. Editorial: Antibody diversity: is it all coded for by the germ line genes? Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(3):199–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]