Abstract
The complete amino acid sequence of the heavy chain variable regions of two different molecules of immunoglobulin M anti-gamma globulin has been determined. These proteins, from different human patients, had independently been shown to share idiotypic specificity. Only eight sequence differences were discernible for the entire length of their heavy chain variable regions. Five of the differences occurred outside hypervariable regions, while three were placeable within such regions. A comparison of these molecules of anti-gamma globulin with the seven human VHIII variable region sequences presently available for immunoglobulins without known antibody activity showed that the great majority of sequence differences between the two idiotypically similar antibodies and these seven proteins were confined to hypervariable regions.
This study illustrates in precise terms a convergence of the distinct immunological properties of idiotypy, hypervariable region structure, and combining site specificity as they relate to the variable region of the immunoglobulin molecule. To a great degree these properties now appear to be a reflection of the same structural attributes of the variable region.
Keywords: amino-acid sequence, cross-idiotypic specificity, antibody combining site
Full text
PDF
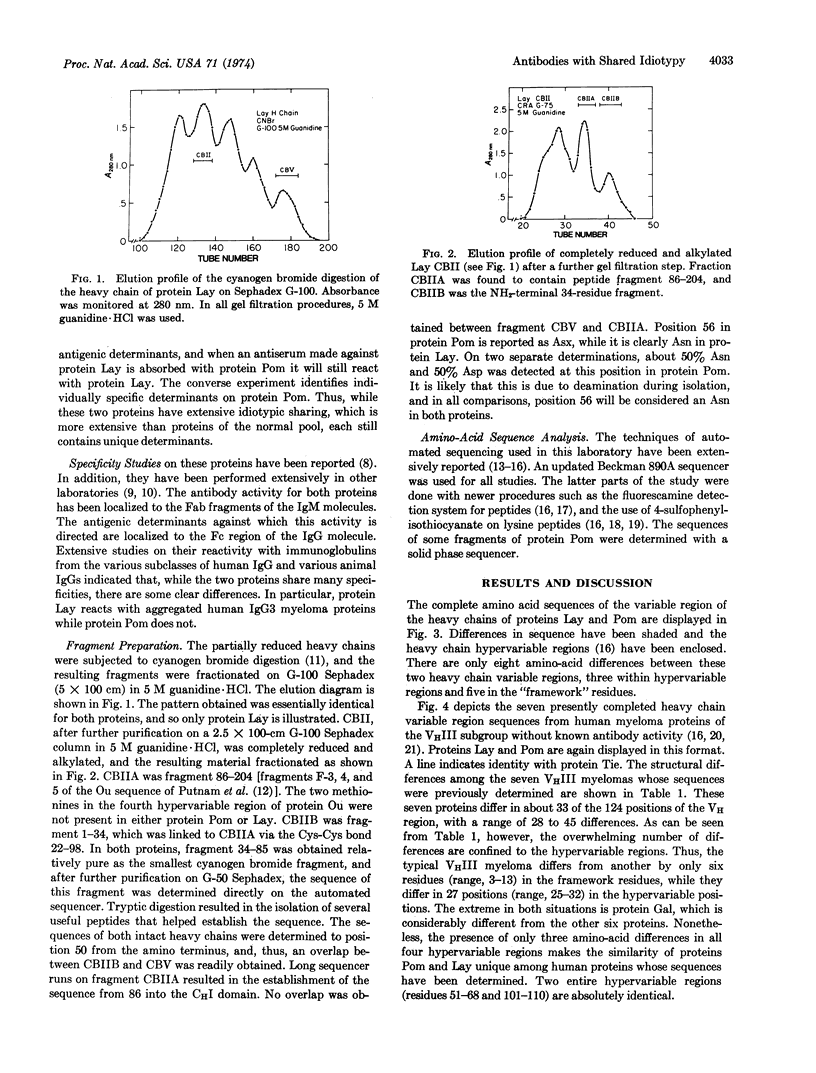
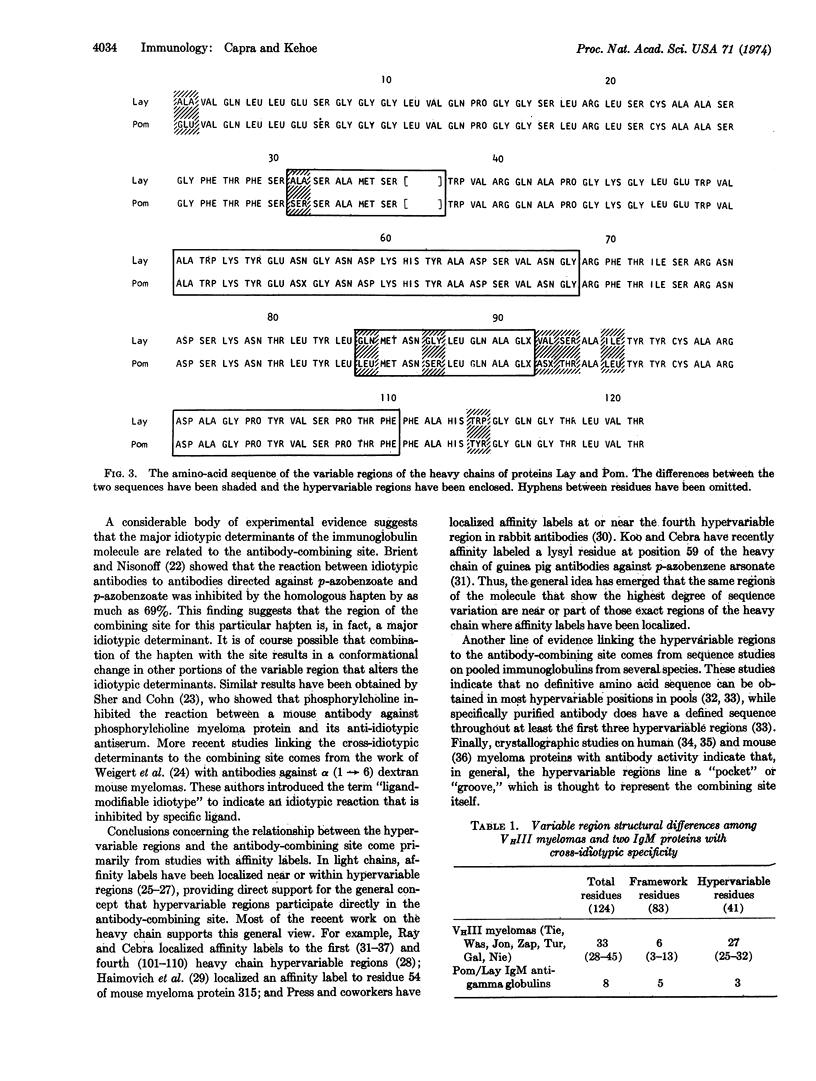


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amzel L. M., Poljak R. J., Saul F., Varga J. M., Richards F. F. The three dimensional structure of a combining region-ligand complex of immunoglobulin NEW at 3.5-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1427–1430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brient B. W., Nisonoff A. Quantitative investigations of idiotypic antibodies. IV. Inhibition by specific haptens of the reaction of anti-hapten antibody with its anti-idiotypic antibody. J Exp Med. 1970 Nov;132(5):951–962. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.5.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D. Hypervariable region of human immunoglobulin heavy chains. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 10;230(10):61–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio230061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Editorial: Antibody diversity: is it all coded for by the germ line genes? Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(1):1–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Variable region sequences of five human immunoglobulin heavy chains of the VH3 subgroup: definitive identification of four heavy chain hypervariable regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):845–848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M., Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. Structure-function relationships among anti-gamma globulin antibodies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 31;190:371–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Wasserman R. L., Kehoe J. M. Phylogenetically associated residues within the VH3 subgroup of several mammalian species. Evidence for a "pauci-gene" basis for antibody diversity. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):410–427. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebra J. J., Givol D., Porter R. R. Common peptides from the N-terminal half of heavy chain of immunoglobulin G from normal rabbit serum and a specific antibody. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(1):69–77. doi: 10.1042/bj1070069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Metzger H. Affinity labeling of a phosphorylcholine binding mouse myeloma protein. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):766–771. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn M. The take-home lesson--1971. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 31;190:529–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Berek C. Mendelian segregation of a mouse antibody idiotype. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Sep;3(9):599–601. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Kindt T. J. The inheritance of individual antigenic specificities of rabbit antibodies to streptococcal carbohydrates. J Exp Med. 1971 Aug 1;134(2):532–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.2.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEISCHMAN J. B., PORTER R. R., PRESS E. M. THE ARRANGEMENT OF THE PEPTIDE CHAINS IN GAMMA-GLOBULIN. Biochem J. 1963 Aug;88:220–228. doi: 10.1042/bj0880220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. A., Bruenger E., Gray W. R., Sandberg L. B. Isolation and amino acid sequences of tropoelastin peptides. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2876–2879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franek F. Affinity labeling by m-nitrobenzenediazonium fluoroborate of porcine ANTI-dinitrophenyl antibodies. Position of labeled tyrosine in the lambda-chains. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 11;19(2):176–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS E., WITKOP B. Nonenzymatic cleavage of peptide bonds: the methionine residues in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1856–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Metzger H. Affinity labeling of a mouse myeloma protein which binds nitrophenyl ligands. Kinetics of labeling and isolation of a labeled peptide. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 3;9(5):1267–1278. doi: 10.1021/bi00807a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimovich J., Eisen H. N., Hurwitz E., Givol D. Localization of affinity-labeled residues on the heavy and light chain of two myeloma proteins with anti-hapten activity. Biochemistry. 1972 Jun 20;11(13):2389–2398. doi: 10.1021/bi00763a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman J. K., Hannon J. E., Appella E. Demonstration of a simple method for reducing losses of tryptic peptides during automated sequencing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 24;46(6):2075–2081. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90761-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe J. M., Capra J. D. Localization of two additional hypervariable regions in immunoglobulin heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2019–2021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo P. H., Cebra J. J. Affinity labeling of a distinctive lysyl residue within the second hypervariable region of gamma 2 chain of guinea pig anti-p-azobenzenearsonate antibody. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 1;13(1):184–195. doi: 10.1021/bi00698a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Agnello V., Joslin F. G., Winchester R. J., Capra J. D. Cross-idiotypic specificity among monoclonal IgM proteins with anti- -globulin activity. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):331–342. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Mannik M., Williams R. C. Individual Antigenic Specificity of Isolated Antibodies. Science. 1963 Jun 14;140(3572):1218–1219. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3572.1218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudin J. The genetic control of immunoglobulin synthesis. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Nov 22;166(1003):207–221. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padlan E. A., Segal D. M., Spande T. F., Davies D. R., Rudikoff S., Potter M. Structure at 4.5 A resolution of a phosphorylcholine-binding fab. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 10;245(145):165–167. doi: 10.1038/newbio245165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak L. L., Mushinski E. B., Nisonoff A., Potter M. Evidence for the linkage of the IGC H locus to a gene controlling the idiotypic specificity of anti-p-azophenylarsonate antibodies in strain A mice. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):22–31. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poljak R. J., Amzel L. M., Avey H. P., Chen B. L., Phizackerley R. P., Saul F. Three-dimensional structure of the Fab' fragment of a human immunoglobulin at 2,8-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3305–3310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponstingl H., Schwarz J., Reichel W., Hilschmann N. Die Primärstruktur eines monoklonalen gamma-1-Immunoglobulins (Myelomprotein NIE). I. Aminosäuresequenz des variablen Teils der H-Kette, Subgruppen variabler Teile. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Dec;351(12):1591–1594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam F. W., Florent G., Paul C., Shinoda T., Shimizu A. Complete amino acid sequence of the Mu heavy chain of a human IgM immunoglobulin. Science. 1973 Oct 19;182(4109):287–291. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4109.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Cebra J. J. Localization of affinity-labeled residues in the primary structure of anti-dinitrophenyl antibody raised in strain 13 guinea pigs. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3647–3657. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLATER R. J., WARD S. M., KUNKEL H. G. Immunological relationships among the myeloma proteins. J Exp Med. 1955 Jan 1;101(1):85–108. doi: 10.1084/jem.101.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrohenloher R. E., Mestecky J. Recombination of the polypeptide chains of a Waldenström's IgM that binds IgG. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1699–1711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A., Cohn M. Inheritance of an idiotype associated with the immune response of inbred mice to phosphorylcholine. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Aug;2(4):319–326. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. V., Houk J. C., Atluri R. L., Mugnaini E. Synaptic transmission at single glomeruli in the turtle cerebellum. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):881–883. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Barnikol H. U., Horn J., Bertram J., Hilschmann N. Die Primärstruktur eines monoklonalen IgM-Immunoglobulins (Makroglobulin Gal.), II. Die Aminosäuresequenz der H-Kette (mu-Typ,Subgruppe HIII), Struktur des gesamten IgM-Moleküls. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Oct-Nov;354(10-11):1505–1509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M., Raschke W. C., Carson D., Cohn M. Immunochemical analysis of the idiotypes of mouse myeloma proteins with specificity for levan or dextran. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):137–147. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willims R. C., Jr, Kunkel H. G., Capra J. D. Antigenic specificities related to the cold agglutinin activity of gamma M globulins. Science. 1968 Jul 26;161(3839):379–381. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3839.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


