Abstract
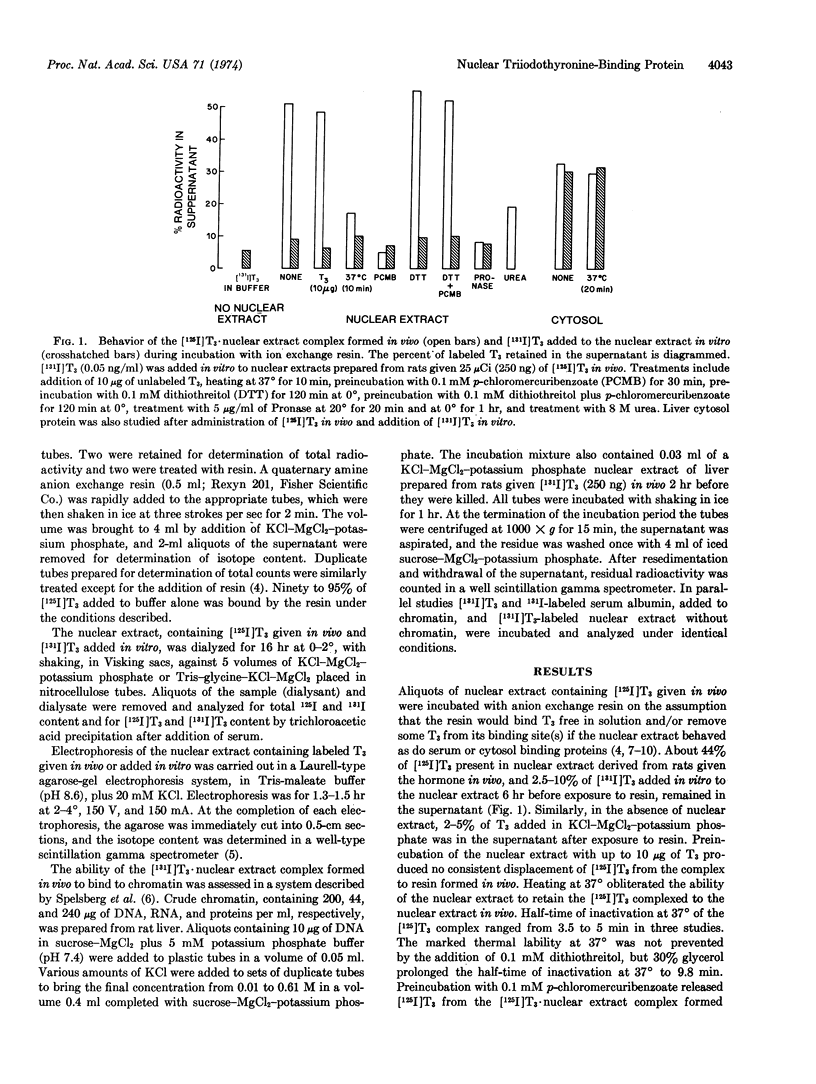
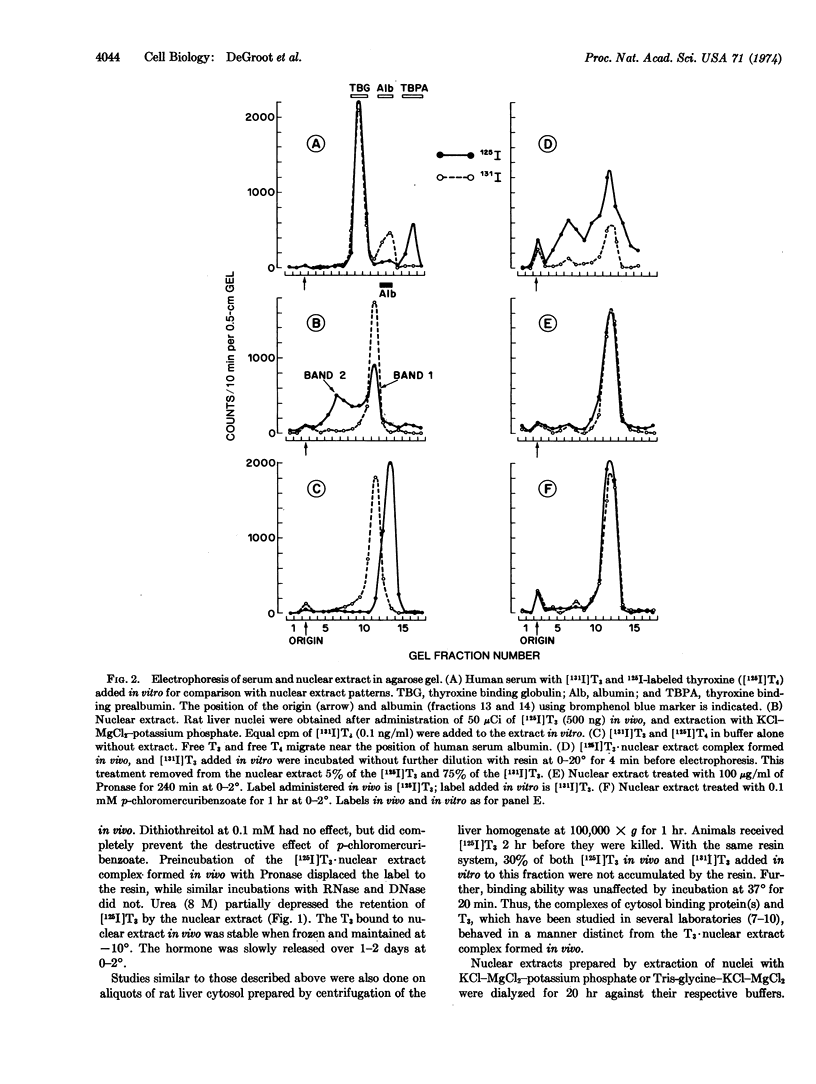
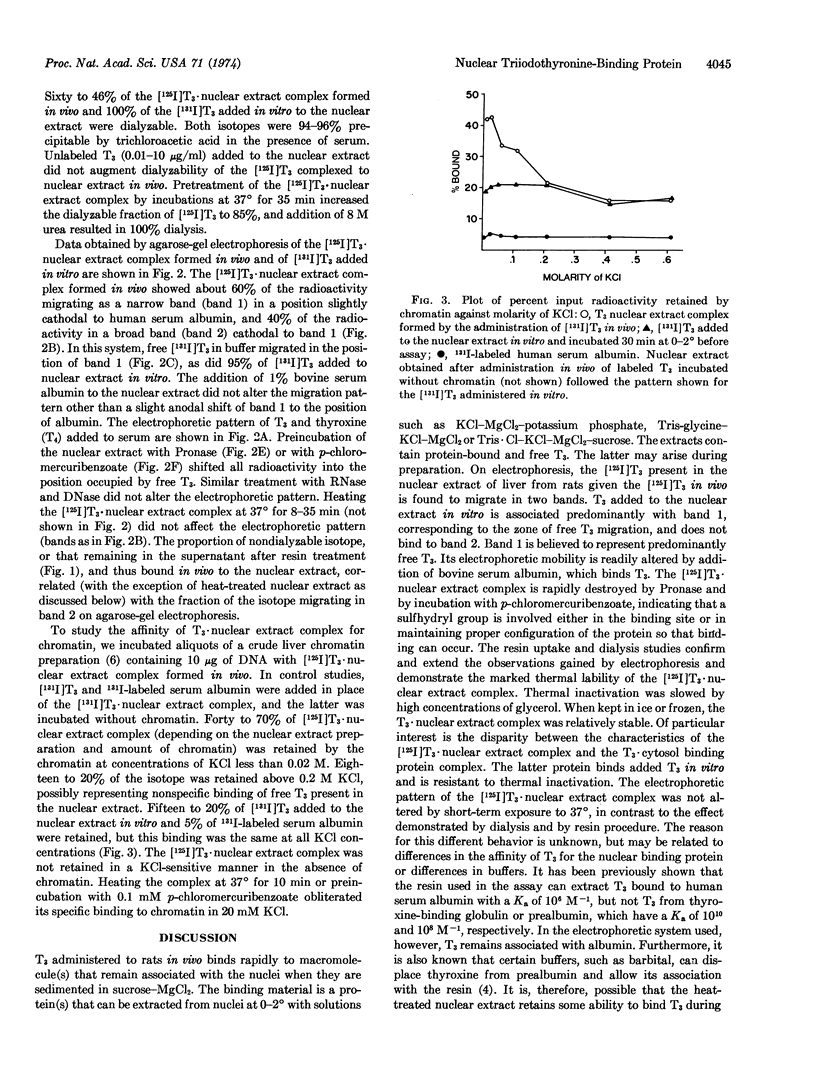
Nuclei were prepared by sucrose sedimentation of liver homogenates from rats given 125I-labeled triiodothyronine in vivo. The nuclear extract obtained by treatment of the nuclear pellet with 0.4 M KCl contains the [125I]triiodothyronine that had been injected in vivo bound to protein(s). The triiodothyronine bound to nuclear protein(s) in vivo does not readily exchange with triiodothyronine added to the extract in vitro. This triiodothyronine·nuclear extract complex retains triiodothyronine during dialysis or exposure to anion exchange resin and migrates as a broad band on agarose-gel electrophoresis. It is rapidly destroyed by Pronase, by 8 M urea, and by p-chloromercuribenzoic acid, but not by RNase or by DNase. It is also susceptible to thermal inactivation at 37°, possibly through changes in the affinity of triiodothyronine to the nuclear binding protein(s), since the bound triiodothyronine becomes more readily dialyzable, is absorbed by an anion exchange resin, but retains its characteristic mobility on electrophoresis. The triiodothyronine·nuclear extract complex formed in vivo binds to crude liver chromatin in vitro at low salt concentration, but can be completely extracted again at KCl concentrations greater than 0.2 M.
Keywords: thermal inactivation, electrophoresis, sulfhydryl groups, salt extraction, hormone action
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DeGroot L. J., Strausser J. L. Binding of T3 in rat liver nuclei. Endocrinology. 1974 Jul;95(1):74–83. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-1-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Numata M., Brecher P. I., Desombre E. R. Hormone-receptor interaction as a guide to biochemical mechanism. Biochem Soc Symp. 1971;32:133–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang T., Liao S. Interaction of estradiol- and progesterone-receptors with nucleoprotein: heat-labile acceptor factors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 14;277(3):590–594. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTE-BOUSCAYROL S., CARTOUZOU G., DEPIEDS R., LISSITZKY S. Electrophoretic characterization of cellular thyroxine-binding proteins: skeletal muscle and brain of rabbit. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1962 Apr;2:193–203. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(62)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire W. L., Huff K., Chamness G. C. Temperature-dependent binding of estrogen receptor to chromatin. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4562–4565. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Koerner D., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Specific nuclear triiodothyronine binding sites in rat liver and kidney. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Aug;35(2):330–333. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-2-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., Hagen S. R., Selenkow H. A. Estimation of the T 4 binding capacity of serum TBG and TBPA by a single T 4 load ion exchange resin method. J Nucl Med. 1972 Jan;13(1):2–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., Matalon R., Bigazzi M. Metabolism of L-thyroxine (T4) and L-triiodothyronine (T3) by human fibroblasts in tissue culture: evidence for cellular binding proteins and conversion of T4 to T3. Endocrinology. 1972 Oct;91(4):934–947. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-4-934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., Robin N. I., Fang V. S. Parameters of thyroid function in serum of 16 selected vertebrate species: a study of PBI, serum T4, free T4, and the pattern of T4 and T3 binding to serum proteins. Endocrinology. 1970 Apr;86(4):793–805. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-4-793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Tsai J. S. Thyroid hormone action in cell culture: domonstration of nuclear receptors in intact cells and isolated nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3488–3492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schadlow A. R., Surks M. I., Schwartz H. L., Oppenheimer J. H. Specific triiodothyronine binding sites in the anterior pituitary of the rat. Science. 1972 Jun 16;176(4040):1252–1254. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4040.1252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel E., Tobias C. A. Actions of thyroid hormones on cultured human cells. Nature. 1966 Dec 17;212(5068):1318–1321. doi: 10.1038/2121318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaulding S. W., Davis P. J. Thyroxine binding to soluble proteins in rat liver and its sex dependence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 19;229(1):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelsberg T. C., Steggles A. W., O'Malley B. W. Progesterone-binding components of chick oviduct. 3. Chromatin acceptor sites. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4188–4197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Koerner D., Dillman W., Oppenheimer J. H. Limited capacity binding sites for L-triiodothyronine in rat liver nuclei. Localization to the chromatin and partial characterization of the L-triiodothyronine-chromatin complex. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7066–7072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TATA J. R., ERNSTER L., SURANYI E. M. Interaction between thyroid hormones and cellular constituent. II. Intracellular distribution and the cell-sap effect. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 16;60:480–491. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90867-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. In vivo synthesis of nuclear protein during growth of the liver induced by hormones. Nature. 1966 Dec 17;212(5068):1312–1314. doi: 10.1038/2121312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


