Abstract
Postoperative prognosis is better for hormonal receptor-positive breast cancer than for other phenotypes; however, there are no definitive predictive factors for relapse or survival. This study aimed to evaluate the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) on 18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT) and clinicopathological characteristics as possible predictors of postoperative relapse-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) in hormonal receptor-positive breast cancer patients. We evaluated 262 patients with Stage I–III breast cancer diagnosed as luminal type (luminal A, 166; luminal B, 96 patients) who underwent preoperative FDG-PET/CT between January 2006 and December 2011 at two institutions. The relationships among SUVmax and clinicopathological factors (age, clinical T/N stage, nuclear grade, lymph node metastasis and vascular invasion) were evaluated. A phantom study was performed to correct differences in PET/CT analysis between two institutions. The patients were divided according to the SUVmax cutoff on receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis for OS (≤6.0 group vs. >6.0 group, AUC = 0.742). Clinical T-factor and nuclear grade were significantly correlated with SUVmax (p < 0.0001 and p = 0.0092, respectively). In the uni- and multivariate analyses using the Cox model for relapse, SUVmax was significant (p = 0.013 and p = 0.055, respectively) among characteristics. RFS curves showed that prognosis was significantly better for the SUVmax ≤ 6.0 group than for the SUVmax > 6.0 group (p = 0.004). Similarly, SUVmax was significant for OS (p = 0.007 and p = 0.008). OS was significantly different between the SUVmax ≤ 6.0 and >6.0 groups (p < 0.001). SUVmax was useful for predicting outcomes in patients with luminal-type breast cancer.
Keywords: FDG-PET/CT, Breast cancer, Luminal type
Introduction
A new modality for detection of cancer lesions in the body, 18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT), is useful for staging of primary cancer and detecting metastasis [1–5]. In addition, FDG-PET/CT is reportedly efficient for evaluating chemotherapeutic effects in many types of cancer, because it can assess functional activities of certain kinds of cancer [6–8]. Furthermore, several studies have shown correlations between the intensity of FDG uptake and some tumor characteristics of breast cancer such as tumor type, grade, hormonal receptor status, and human epidermal growth factor receptor type-2 (HER2) status [9–19]. As a new predictor for postoperative clinical outcome, the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) on FDG-PET/CT is useful for diagnosing high-grade malignancy and predicting the prognosis in lung and breast cancer patients [20–22]. Kadoya et al. [22] reported that SUVmax on PET/CT and the estrogen receptor (ER) status were useful for predicting malignancy grades and prognosis of patients with breast cancer.
Tumor subtypes of breast cancer patients have been reported to show different outcomes, including poor prognosis for the basal-like subtype and a significant difference in the outcome for the two ER-positive groups [23, 24]. According to the phenotype classification stratified by hormonal receptor and HER2 expressions, early breast cancer patients are now treated with chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and anti-HER2 therapy with high confidence for success. In patients with ER-positive breast cancer, the luminal type, including type A and B, have superior clinical responses to drug therapy and better survival than other types of breast cancer. However, clinical identification of early and late relapse of luminal-type breast cancer patients is a great concern for physicians, and efficient predictors of prognosis are required.
Therefore, we retrospectively evaluated the utility of SUVmax on FDG-PET/CT and clinicopathological characteristics for predicting relapse and survival in patients with early breast cancers, especially luminal type A and B.
Patients & methods
Patients
A total of 344 clinical Stage I–III breast cancer patients received FDG-PET/CT before initial therapy between January 2006 and December 2011 at the Shikoku Cancer Center and Hiroshima University Hospital. The patients were classified into five subtypes according to the hormonal receptors status, HER2 expression, and nuclear grade (NG): luminal A was characterized by ER (+) or progesterone receptor (PgR)(+), HER2(−), and NG 1–2; luminal B was characterized by ER(+) or PgR (+), HER2(−), and NG3; luminal HER2 was characterized by ER(+) or PgR(+) and HER2(+); HER2 enriched was characterized by ER(−),PgR(−), and HER2(+); and triple negative was characterized by ER(−),PgR(−), and HER2(−). The records of a total of 262 luminal-type patients (luminal A, 166; luminal B, 96) were evaluated. There were not enough Ki-67 data in the case series because the assay for Ki-67 labeling has not been established. Therefore, Ki-67 labeling was not used for distinguishing luminal A from luminal B tumors in this study. Two relapse cases were found for luminal A and four cases for luminal B. The relationships among clinicopathological characteristics such as age, clinical T and N stage, nuclear grade, lymph node metastasis, vascular invasion, and SUVmax were assessed. The Chi square test and log-rank test were used, and p values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
FDG-PET/CT imaging
Patients fasted for >4 h before being intravenously injected with 3.0–3.7 MBq/kg body weight of FDG, and then relaxed for 1–1.5 h before FDG-PET/CT scanning. The serum glucose level was measured before tracer injection to confirm the value of <150 mg/dL. Patients with serum glucose values ≥150 mg/dL during PET/CT image acquisition were excluded. PET/CT imaging was performed on a Discovery ST (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK) or Aquiduo (Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation, Otawara, Japan) integrated PET/CT scanner. Low-dose unenhanced CT images of a 2- to 4-mm section thickness for attenuation correction and localization of lesions identified by PET were obtained from the head to the pelvic floor of each patient by following a standard protocol. Immediately after CT, PET covered the identical axial field of view (FOV) for 2–4 min per table position, depending on the condition of the patient and scanner performance. All PET images with a 50-cm FOV were reconstructed using an iterative algorithm with CT-derived attenuation correction.
SUVmax was calculated by drawing regions of interest (ROI) around the primary tumor on attenuation-corrected FDG-PET images and calculated using the integrated CT scanner software according to the formula below:
where C is defined as the maximal activity at a pixel within the tissue identified by the ROI. ID is defined as the injected dose/kg of body weight (W), as reported in a study performed by Kadoya [22].
Histological examination
The tumor nuclear grade was determined according to General Rules for Clinical and Pathological Recording of Breast Cancer, 16th edition [25]. Positive ER and PgR were assessed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and scored according to the Allred system. HER-2 positivity was defined as 3+ by IHC or 2+ by gene amplification using fluorescent in situ hybridization >2.2.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as numbers (%) or mean ± standard deviation unless otherwise stated. Frequencies were compared using the Chi square test for categorical variables in all patients. Continuous variables were assessed using the t test. Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t test and the log-rank test, and p values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
SUVmax values were assessed as grouping thresholds for predictive value for overall survival (OS) using Student t test and the log-rank test, and p values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
A Cox proportional hazard regression model (forced-entry method) was used for uni- and multivariate analysis for recurrence and survival. Relapse-free survival (RFS) was defined as the time from the date of surgery until the first event (relapse or death from any cause) or last follow-up. OS was defined as the time from the date of surgery until death from any cause or last follow-up. The durations of RFS and OS were analyzed by the Kaplan–Meier method, and their differences were assessed using the log-rank test. Data were analyzed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (v 10.5; SPSS Inc., Chicago, Ill, USA).
Results
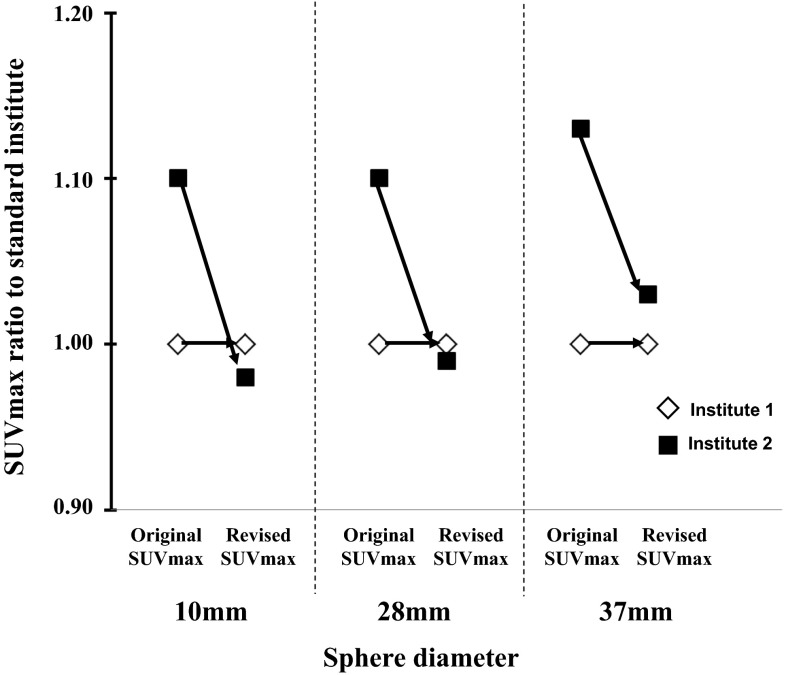
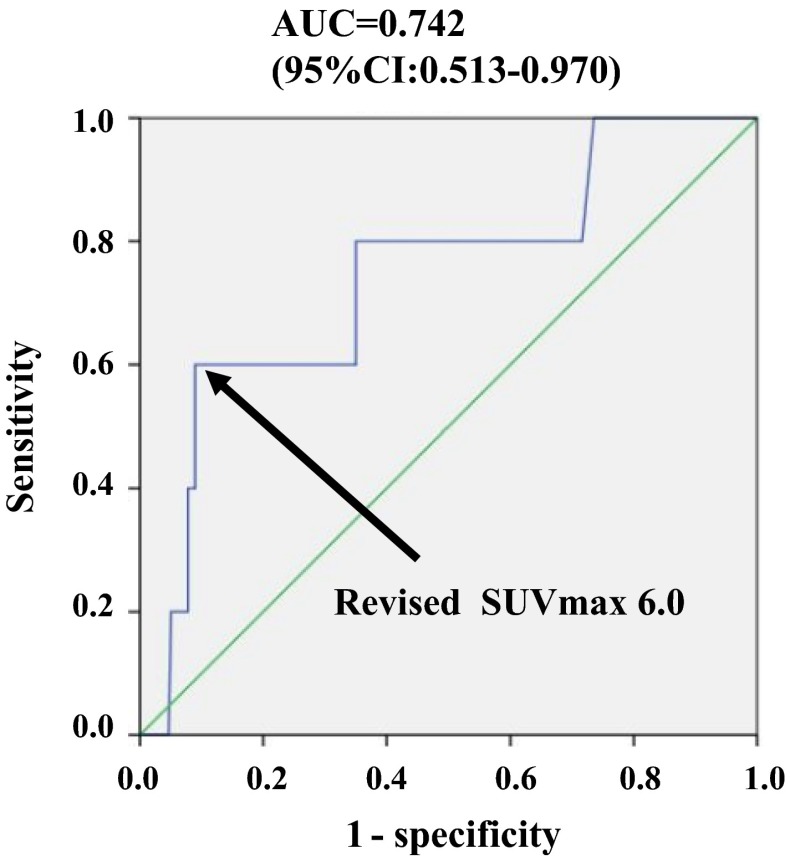
Because of the heterogeneity of PET techniques and performance, we corrected inter-institutional errors in SUVmax using an international electrotechnical commission body phantom set corresponding to the NU 2-2001 standard published by the National Electrical Manufactures Association (NEMA). Variations in SUV between two institutions were minimized using an anthropomorphic body and six spheres (inner diameter, 10, 13, 17, 22, 28, and 37 mm). From the phantom study, a calibration factor was calculated by dividing the actual SUV by the measured mean SUV in the phantom background to reduce inter-institutional SUV variability. The final SUV is referred to as the revised SUVmax [22, 26]. After revision, the SUVmax ratio of the two institutions was very close to 1.00 (Fig. 1). The revised SUVmax for OS was used to create a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (area under the curve = 0.742, 95 % CI 0.513–0.970), and the SUVmax cutoff value was set to 6.0 (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1.
Maximum standardized uptake (SUVmax) adjusted by analyzing an experimental phantom (revised SUVmax) at two institutions. After revision, the SUVmax ratio of the two institutions was close to 1.00
Fig. 2.
Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves of revised maximum standardized uptake (SUVmax) for overall survival in luminal-type breast cancer (n = 262). The SUVmax cutoff value for overall survival was set to 6.0 after evaluating the ROC area under the curve (0.742 with 95 % CI 0.513–0.970)
The characteristics of the 262 patients are presented in Table 1. The proportion of the patients in clinical Stages I and II was almost 96.2 %. Revised SUVmax values were added to each patient’s dataset.
Table 1.
Patient characteristics
| n | Rate | Revised SUVmax | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||
| 58.2 ± 12.7(21–91) | 262 | 3.24 ± 2.64 | |
| Procedure | |||
| Breast conserving surgery | 175 | 66.8 % | 2.76 ± 2.10 |
| Mastectomy | 87 | 33.2 % | 4.22 ± 3.28 |
| Clinical T stage | |||
| T1 | 187 | 71.4 % | 2.49 ± 1.86 |
| T2 | 74 | 28.2 % | 5.10 ± 3.32 |
| T3 | 1 | 0.4 % | 6.17 |
| Clinical N stage | |||
| N0 | 203 | 77.5 % | 3.11 ± 2.62 |
| N1 | 49 | 18.7 % | 3.59 ± 2.61 |
| N2 | 7 | 2.7 % | 4.61 ± 3.45 |
| N3 | 3 | 1.1 % | 3.72 ± 2.34 |
| Clinical stage | |||
| I | 153 | 58.4 % | 2.35 ± 1.61 |
| II | 99 | 37.8 % | 4.51 ± 3.27 |
| III | 10 | 3.8 % | 4.34 ± 3.06 |
| Pathology | |||
| Papillotubular carcinoma | 42 | 16.0 % | 2.72 ± 2.15 |
| Solid-tubular carcinoma | 46 | 17.6 % | 4.66 ± 3.85 |
| Scirrhous carcinoma | 138 | 52.7 % | 3.14 ± 2.38 |
| Other ductal carcinoma | 21 | 8.0 % | 2.21 ± 1.02 |
| Lobular carcinoma | 10 | 3.8 % | 2.09 ± 0.90 |
| Others | 5 | 1.9 % | 4.07 ± 1.76 |
| Nuclear grade | |||
| Grade I | 67 | 25.6 % | 2.90 ± 1.89 |
| Grade II | 99 | 37.8 % | 2.82 ± 2.48 |
| Grade III | 96 | 36.6 % | 3.92 ± 3.10 |
| Lymph node metastasis | |||
| Negative | 180 | 68.7 % | 3.03 ± 2.60 |
| Positive | 82 | 31.3 % | 3.71 ± 2.66 |
| Vascular invasion | |||
| Negative | 194 | 74.0 % | 3.08 ± 2.55 |
| Positive | 68 | 26.0 % | 3.72 ± 2.84 |
Two hundred and sixty-two luminal-type patients (luminal A and B) were evaluated in this study
Clinicopathological parameters and revised SUVmax values are presented in Table 2. The patients were divided into two groups according to SUVmax (SUVmax ≤ 6.0 group, n = 233; SUVmax > 6.0 group, n = 29). Prognostic factor candidates such as age, clinical T and N stage, nuclear grade, lymph node metastasis, and vascular invasion were evaluated for each SUVmax group. T stage and nuclear grade were significantly associated with SUVmax (p < 0.0001 and p = 0.0092, respectively). In addition, adjuvant therapies such as hormonal therapy, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy were evaluated for each SUVmax group (SUVmax ≤ 6.0 group, n = 228; SUVmax > 6.0 group, n = 29). Only radiation therapy was significantly associated with SUVmax (p = 0.0399).
Table 2.
Comparison of clinicopathological parameters and types of adjuvant therapy
| Variables | Revised SUVmax ≤ 6.0 (n = 233) |
Revised SUVmax > 6.0 (n = 29) |
Odds ratio (95 % CI) |
p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 58.6 ± 12.8 | 54.9 ± 11.8 | 0.1347 | |
| Clinical T stage | ||||
| T1 | 180 | 7 | 10.67 (4.32–26.36) | <0.0001 |
| T2, T3 | 53 | 22 | ||
| Clinical N stage | ||||
| N0 | 184 | 19 | 1.98 (0.86–4.52) | 0.1616 |
| N1, N2, N3 | 49 | 10 | ||
| Nuclear grade | ||||
| I, II | 154 | 12 | 2.76 (1.26–6.09) | 0.0092 |
| III | 79 | 17 | ||
| Lymph node metastasis | ||||
| Negative | 164 | 16 | 1.93 (0.88–4.23) | 0.0957 |
| Positive | 69 | 13 | ||
| Vascular invasion | ||||
| Negative | 176 | 18 | 1.89 (0.84–4.23) | 0.1187 |
| Positive | 57 | 11 | ||
| Variables | Revised SUVmax ≤ 6.0 (n = 228) |
Revised SUVmax > 6.0 (n = 29) |
Odds ratio (95 % CI) |
p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjuvant therapy | ||||
| Hormonal therapy | ||||
| Yes | 212 | 28 | 0.47 (0.06–3.71) | 0.7400 |
| No | 16 | 1 | ||
| Chemotherapy | ||||
| Yes | 81 | 15 | 0.51 (0.24–1.12) | 0.0894 |
| No | 147 | 14 | ||
| Radiation therapy | ||||
| Yes | 154 | 14 | 2.23 (1.02–4.86) | 0.0399 |
| No | 74 | 15 | ||
The clinicopathological parameters and types of adjuvant therapy of the revised SUVmax ≤ 6.0 and SUVmax > 6.0 groups were compared by assessing the odds ratios and statistical significance. T stage and nuclear grade were significantly associated with SUVmax (p < 0.0001 and p = 0.0092, respectively, Table 2). Radiation therapy was significantly associated with SUVmax (p = 0.0399, Table 2)
Age, clinical T and N stage, nuclear grade, and revised SUVmax were included in the uni- and multivariate analyses for relapse. Revised SUVmax was identified as the only significant factor (p = 0.013 and p = 0.055 in Table 3). The types of adjuvant therapy were also evaluated in the uni- and multivariate analyses for relapse, but they were not significant factors (data not shown).
Table 3.
Uni- and multivariate analyses using clinical factors for relapse-free survival
| Factors | Favorable | Unfavorable | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard ratio (95 % CI) |
p value | Hazard ratio (95 % CI) |
p value | |||
| Age | <58 | ≥58 | 0.981 (0.198–4.867) | 0.981 | 1.189 (0.233–6.075) | 0.835 |
| Clinical T factor | T1 | T2, T3 | 2.283 (0.459–11.346) | 0.313 | 0.911 (0.135–6.144) | 0.924 |
| Clinical N factor | N0 | N1, N2, N3 | 1.655 (0.303–9.041) | 0.561 | 1.097 (0.193–6.229) | 0.917 |
| Nuclear grade | I,II | III | 3.531 (0.646–19.294) | 0.145 | 2.553 (0.433–15.050) | 0.301 |
| Revised SUVmax | ≤6.0 | >6.0 | 7.596 (1.527–37.785) | 0.013 | 6.436 (0.963–42.991) | 0.055 |
SUVmax was identified as a significant predictor of relapse-free survival (p = 0.013 and p = 0.055, respectively)
The RFS curves for the prognostic factors, including revised SUVmax and nuclear grade, are shown in Fig. 3. In the log-rank test, RFS was significantly better for the revised SUVmax ≤ 6.0 group than for the SUVmax > 6.0 group (p = 0.004) (Fig. 3). In the log-rank test, there was no significant difference in RFS between nuclear grades I/II versus grade III (p = 0.120).
Fig. 3.
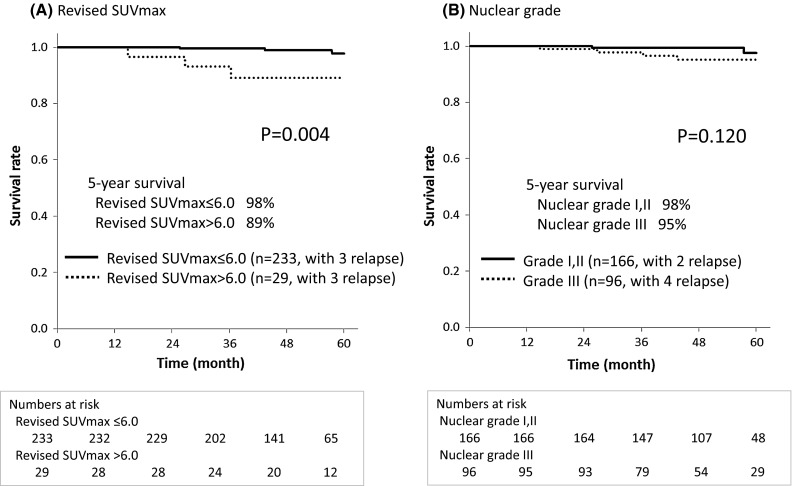
Relapse-free survival (RFS) curves for prognostic factors, considering the revised maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) and nuclear grade. The RFS of the revised SUVmax ≤ 6.0 group was significantly better than that of the revised SUVmax > 6.0 group in the log-rank test (p = 0.004). There was no significant difference in RFS between the nuclear grades (nuclear grades I/and II versus grade III) in the log-rank test (p = 0.120)
In the uni- and multivariate analyses for OS, revised SUVmax was identified as the only significant factor (p = 0.007 and p = 0.008, respectively, Table 4). The types of adjuvant therapy were also evaluated, but they were not significant factors (data not shown). Similar to the findings for RFS, OS was significantly better for the revised SUVmax ≤ 6.0 group (n = 233) than for the SUVmax > 6.0 group (n = 29) in the log-rank test (p < 0.001) (Fig. 4). There were no significant differences in OS among the nuclear grades (p = 0.254).
Table 4.
Uni-and multivariate analyses using clinical factors for overall survival
| Factors | Favorable | Unfavorable | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard ratio (95 % CI) |
p value | Hazard ratio (95 % CI) |
p value | |||
| Age | <58 | ≥58 | 1.388 (0.232–8.309) | 0.719 | 1.537 (0.239–9.891) | 0.651 |
| Clinical T factor | T1 | T2, T3 | 1.558 (0.260–9.334) | 0.627 | 0.454 (0.500–4.100) | 0.482 |
| Clinical N factor | N0 | N1, N2, N3 | 0.033 (0.000–220.589) | 0.447 | 0.000 (0.000–) | 0.981 |
| Nuclear grade | I,II | III | 2.714 (0.453–16.250) | 0.274 | 2.212 (0.334–14.628) | 0.410 |
| Revised SUVmax | ≤6.0 | >6.0 | 11.770 (1.966–70.459) | 0.007 | 17.294 (2.118–141.237) | 0.008 |
SUVmax was identified as a significant predictor of overall survival (p = 0.007 and p = 0.008, respectively)
Fig. 4.
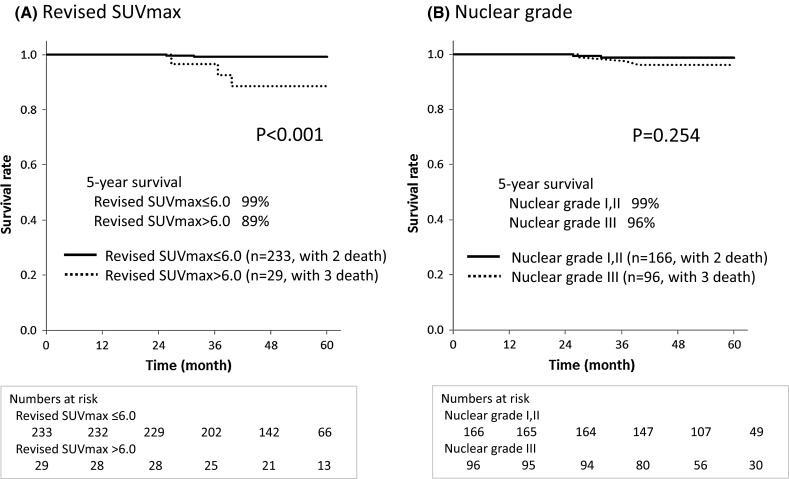
Overall survival (OS) curves for revised maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) and nuclear grade. The OS of the revised SUVmax ≤ 6.0 group was significantly better than that of the revised SUVmax > 6.0 group in the log-rank test (p < 0.001). There were no significant differences in OS among the nuclear grades in the log-rank test (p = 0.254)
Discussion
Breast cancer patients were classified into five phenotypes according to hormonal receptor and HER2 expressions: luminal A, luminal B, luminal HER2, HER2, and triple-negative subtypes. Luminal-type breast cancer has been reported to have better prognosis than the HER2 and triple-negative types. In the statement of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013, Goldhirsch et al. [27] reported that luminal A disease generally requires only endocrine therapy as an adjuvant therapy and chemotherapy is considered for most patients with luminal B, HER2-positive, and triple-negative disease, with the addition of trastuzumab especially in HER2-positive disease. This statement reveals that individual adjuvant therapies should be considered for improving patient outcomes. A new classification was required for predicting the clinical outcome. According to the new classification, the strategy of adjuvant therapy is selected according to the molecular information obtained for individual breast cancer patients [28]. Cheang et al. [28] reported that the expressions of ER, PgR, and HER2 and the Ki-67 index appear to distinguish luminal A from luminal B breast cancer subtypes. Furthermore, late relapse in ER-positive breast cancer has been a big concern for physicians and patients [29, 30]. Saphner et al. [31] reported better long-term survival for ER-positive breast cancer patients than for receptor-negative breast cancer patients, but late relapse occurred in ER-positive breast cancer patients from 5 to 10 years postoperatively. In a retrospective study that evaluated 595 ER-positive breast cancer patients, Ahn et al. [32] reported that tumor biology might have a more important role than tumor load for late relapse. Till date, however, there is no definitive parameter for predicting outcomes of luminal breast cancer types.
Imaging techniques should play an important role in the easy prediction of luminal breast cancer type outcomes. FDG-PET/CT has been reported to be one of such imaging techniques because it can be used not only for diagnosis but also for functional assessments of cancer. SUVmax has been reported to be a useful predictor of prognosis in lung cancer [20, 21] and hematological cancer [4]. In breast cancer, Basu et al. [33] reported that triple-negative breast tumors were associated with FDG uptake (SUVmax) because of their more aggressive biology compared with those of ER+/PgR+/HER2− breast cancers. Furthermore, Kadoya et al. [22] reported that SUVmax on FDG-PET/CT in patients with operable breast cancer had a predictive value for high-grade malignancy and prognosis in all types of operable breast cancer, and SUVmax values and the ER status were reported to be predictive factors in a multivariate analysis using a Cox proportional hazard regression model (p = 0.033 and p = 0.004, respectively). For triple-negative breast cancer, there have been some reports on the utility of FDG-PET/CT for predicting the effects of neoadjuvant chemotherapy or surgical outcome [6–8, 34].
In this retrospective study, we showed that SUVmax on FDG-PET/CT was useful for predicting prognosis (OS, RFS) in 262 cases of luminal-type breast cancer. Luminal-type breast cancer tends to have a better clinical outcome than those of HER2 or triple-negative type with respect to metastasis, progression, and survival. Furthermore, luminal-type breast cancer shows good response to hormonal therapy. However, luminal-type breast cancer occasionally has a poor prognosis, which indicates that, although occasionally, resistance to hormonal therapy and chemotherapy does occur. Early identification of luminal-type breast cancer patients who are likely to have a poor prognosis would enable a more intensive treatment from the beginning, improving their outcomes. The results of this study show that SUVmax on FDG-PET/CT could be useful for identifying patients who are likely to have a poor prognosis, especially those with luminal-type breast cancer.
In the RFS and OS analyses, the SUVmax threshold was initially set to 6.0 on the basis of ROC analysis for OS to establish two groups of patients in order to analyze potential prognostic factors, including age, clinical T and N stage, nuclear grade, lymph node metastasis, and vascular invasion. However, SUVmax was the only significant factor identified in uni- and multivariate analyses for RFS and OS.
A limitation of this retrospective study was its small size. Therefore, large-scale prospective studies are warranted to confirm the utility of SUVmax for predicting clinical outcomes at the diagnosis of breast cancer, which indicate the need of adjuvant chemotherapy adding to endocrine therapy. There may be a risk for underestimate the SUVmax of tumor less than 20 mm in diameter due to the partial volume effects. There is no definite way to make a precise adjustment of the SUVmax according to the tumor diameter to diminish the partial volume effects in the clinical use. Therefore, no adjustment was performed in this study.
Conclusion
FDG-PET/CT can be an alternative adjunct imaging modality for the screening and diagnosis of high-risk patients [35]. In this study, FDG-PET/CT SUVmax was useful for predicting OS and RFS in patients with luminal-type breast cancer. If the SUVmax on FDG-PET/CT is shown to be a prognostic factor for surgical, chemotherapeutic, and radiation treatments for breast cancer, physicians would be able to select the optimum treatment strategy for patients with luminal-type breast cancer in the future.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all members of the Department of Breast Oncology and Miss Kyoko Hamada at the Shikoku Cancer Center for providing and preparing patient data for the analysis. The authors would like to thank Enago (www.enago.jp) for the English language review.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Abbreviation
- AUC
Area under the curve,
- CT
Computed tomography,
- RFS
Relapse-free survival,
- FDG
18F-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose,
- PET
Positron emission tomography,
- ROC
Receiver operating characteristic,
- SUVmax
Maximum standardized uptake value,
- ER
Estrogen receptor,
- PgR
Progesterone receptor,
- HER2
Human epidermal growth factor receptor type-2
References
- 1.Vansteenkiste JF, Stroobants SG, Dupont PJ, De Leyn PR, Verbeken EK, Deneffe GJ, et al. Prognostic importance of the standardized uptake value on (18)F-fluoro-2-deoxy-glucose-positron emission tomography scan in non-small-cell lung cancer: an analysis of 125 cases. Leuven Lung Cancer Group. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:3201–3206. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1999.17.10.3201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Okazumi S, Isono K, Enomoto K, Kikuchi T, Ozaki M, Yamamoto H, et al. Evaluation of liver tumors using fluorine—18-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose PET. J Nucl Med. 1992;33:339–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fuster D, Duch J, Paredes P, Velasco M, Muñoz M, Santamaría G, et al. Preoperative staging of large primary breast cancer with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography compared with conventional imaging procedures. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4746–4751. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.1496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Groheux D, Hindié E, Delord M, Giacchetti S, Hamy AS, de Bazelaire C, et al. Prognostic impact of (18)FDG-PET-CT findings in clinical stage III and IIB breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104:1879–1887. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Okada J, Yoshikawa K, Itami M, Imaseki K, Uno K, Itami J, et al. Positron emission tomography using fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose in malignant lymphoma: a comparison with proliferative activity. J Nucl Med. 1992;33:325–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Groheux D, Hindié E, Giacchetti S, Hamy AS, Berger F, Merlet P, et al. Early assessment with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography can help predict the outcome of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple negative breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:1864–1871. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.04.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Berriolo-Riedinger A, Touzery C, Riedinger JM, Toubeau M, Coudert B, Arnould L, et al. [18F]FDG-PET predicts complete pathological response of breast cancer to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007;34:1915–1924. doi: 10.1007/s00259-007-0459-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Humbert O, Berriolo-Riedinger A, Riedinger JM, Coudert B, Arnould L, Cochet A, et al. Changes in 18F-FDG tumor metabolism after a first course of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: influence of tumor subtypes. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:2572–2577. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mds071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Buck A, Schirrmeister H, Kuhn T, Shen C, Kalker T, Kotzerke J, et al. FDG uptake in breast cancer: correlation with biological and clinical prognostic parameters. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002;29:1317–1323. doi: 10.1007/s00259-002-0880-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Smith TA, Sharma RI, Thompson AM, Paulin FE. Tumor 18F-FDG incorporation is enhanced by attenuation of P53 function in breast cancer cells in vitro. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:1525–1530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dehdashti F, Mortimer JE, Siegel BA, Griffeth LK, Bonasera TJ, Fusselman MJ, et al. Positron tomographic assessment of estrogen receptors in breast cancer: comparison with FDG-PET and in vitro receptor assays. J Nucl Med. 1995;36:1766–1774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Crippa F, Seregni E, Agresti R, Chiesa C, Pascali C, Bogni A, et al. Association between [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake and postoperative histopathology, hormone receptor status, thymidine labelling index and p53 in primary breast cancer: a preliminary observation. Eur J Nucl Med. 1998;25:1429–1434. doi: 10.1007/s002590050319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Avril N, Menzel M, Dose J, Schelling M, Weber W, Jänicke F, et al. Glucose metabolism of breast cancer assessed by 18F-FDG PET: histologic and immunohistochemical tissue analysis. J Nucl Med. 2001;42:9–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bos R, van Der Hoeven JJ, van Der Wall E, van Der Groep P, van Diest PJ, Comans EF, et al. Biologic correlates of (18)fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in human breast cancer measured by positron emission tomography. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:379–387. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.2.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kumar R, Chauhan A, Zhuang H, Chandra P, Schnall M, Alavi A. Clinicopathologic factors associated with false negative FDG-PET in primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;98:267–274. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9159-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Groheux D, Giacchetti S, Moretti JL, Porcher R, Espié M, Lehmann-Che J, et al. Correlation of high 18F-FDG uptake to clinical, pathological and biological prognostic factors in breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38:426–435. doi: 10.1007/s00259-010-1640-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fasanella S, Leonardi E, Cantaloni C, Eccher C, Bazzanella I, Aldovini D, et al. Proliferative activity in human breast cancer: Ki-67 automated evaluation and the influence of different Ki-67 equivalent antibodies. Diagn Pathol. 2011;6:S7. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-6-S1-S7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tchou J, Sonnad SS, Bergey MR, Basu S, Tomaszewski J, Alavi A, et al. Degree of tumor FDG uptake correlates with proliferation index in triple negative breast cancer. Mol Imaging Biol. 2010;12:657–662. doi: 10.1007/s11307-009-0294-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Oshida M, Uno K, Suzuki M, Nagashima T, Hashimoto H, Yagata H, et al. Predicting the prognoses of breast carcinoma patients with positron emission tomography using 2-deoxy-2-fluoro[18F]-D-glucose. Cancer. 1998;82:2227–2234. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19980601)82:11<2227::AID-CNCR18>3.0.CO;2-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Na F, Wang J, Li C, Deng L, Xue J, Lu Y. Primary tumor standardized uptake value measured on F18-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography is of prediction value for survival and local control in non-small-cell lung cancer receiving radiotherapy: meta-analysis. J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9:834–842. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Berghmans T, Dusart M, Paesmans M, Hossein-Foucher C, Buvat I, Castaigne C, et al. Primary tumor standardized uptake value (SUVmax) measured on fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) is of prognostic value for survival in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a systematic review and meta-analysis (MA) by the European Lung Cancer Working Party for the IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3:6–12. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31815e6d6b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kadoya T, Aogi K, Kiyoto S, Masumoto N, Sugawara Y, Okada M. Role of maximum standardized uptake value in fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography predicts malignancy grade and prognosis of operable breast cancer: a multi-institute study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;141:269–275. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2687-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406:747–752. doi: 10.1038/35021093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:10869–10874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191367098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.The Japanese Breast Cancer Society . General rules for clinical and pathological recording of breast cancer. 16. Tokyo: Kanehara; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nakayama H, Okumura S, Daisaki H, Kato Y, Uehara H, Adachi S, et al. Value of integrated positron emission tomography revised using a phantom study to evaluate malignancy grade of lung adenocarcinoma: a multicenter study. Cancer. 2010;116:3170–3177. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thürlimann B, Senn HJ, et al. Strategies for subtypes–dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:1736–1747. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D, Gao D, Leung S, Snider J, et al. Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;101:736–750. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djp082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Courdi A, Largillier R, Ferrero JM, Lallement M, Raoust I, Ettore F, et al. Early versus late local recurrences after conservative treatment of breast carcinoma: differences in primary tumor characteristics and patient outcome. Oncology. 2006;71:361–368. doi: 10.1159/000107771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sestak I, Dowsett M, Zabaglo L, Lopez-Knowles E, Ferree S, Cowens JW, et al. Factors predicting late recurrence for estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105(19):1504–1511. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djt244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Saphner T, Tormey DC, Gray R. Annual hazard rates of recurrence for breast cancer after primary therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14(10):2738–2746. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1996.14.10.2738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ahn SG, Lee HM, Cho SH, Bae SJ, Lee SA, Hwang SH, et al. The difference in prognostic factors between early recurrence and late recurrence in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: nodal stage differently impacts early and late recurrence. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e63510. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Basu S, Chen W, Tchou J, Mavi A, Cermik T, Czerniecki B, et al. Comparison of triple-negative and estrogen receptor-positive/progesterone receptor-positive/HER2-negative breast carcinoma using quantitative fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose/positron emission tomography imaging parameters: a potentially useful method for disease characterization. Cancer. 2008;112(5):995–1000. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ohara M, Shigematsu M, Tsutani Y, Emi A, Masumoto N, Ozaki S, et al. Role of FDG-PET/CT in evaluating surgical outcomes of operable breast cancer–usefulness for malignant grade of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast. 2013;22(5):958–963. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2013.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cintolo JA, Tchou J, Pryma DA. Diagnostic and prognostic application of positron emission tomography in breast imaging: emerging uses and the role of PET in monitoring treatment response. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;138(2):331–346. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2451-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]