Abstract
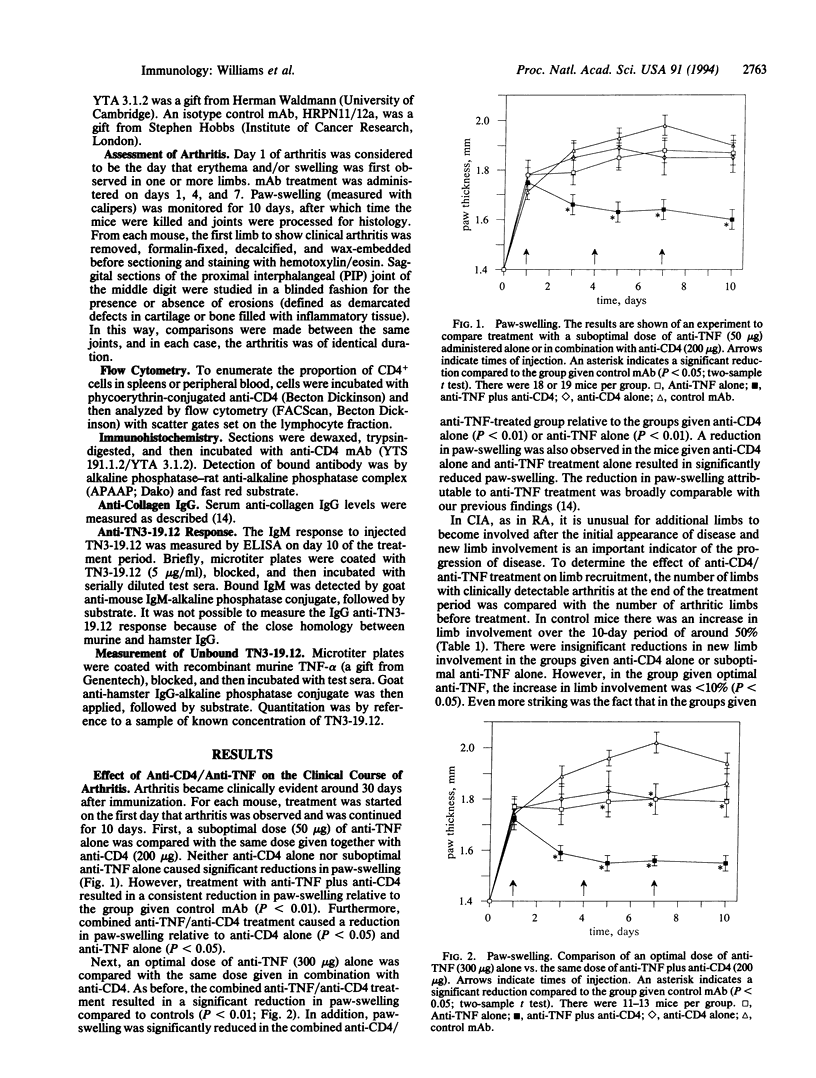
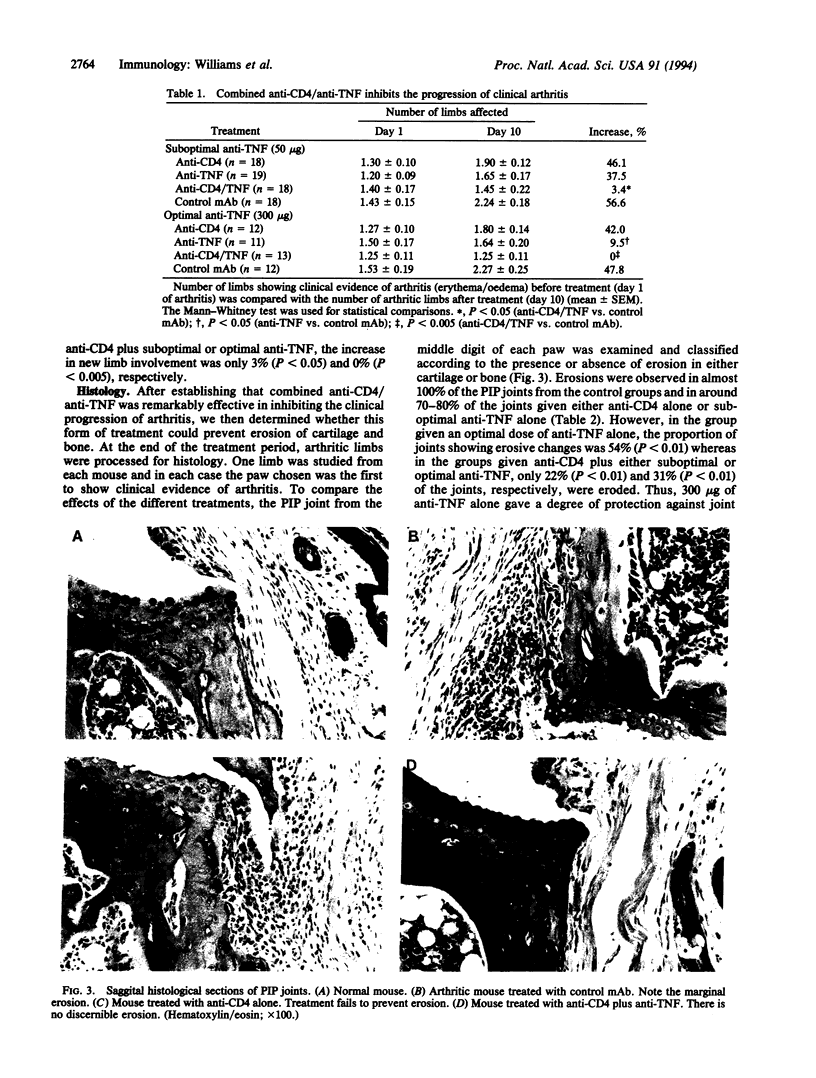
Anti-CD4 treatment is reported to prevent collagen-induced arthritis if administered before the onset of clinical disease but has relatively little effect on established arthritis. In contrast, we have recently shown that anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha/beta (TNF) treatment reduces the severity of established arthritis. We now study the effect of combined administration of anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody (YTS 191.1.2/YTA 3.1.2) and anti-TNF monoclonal antibody (TN3-19.12) in established arthritis. Anti-CD4 treatment caused some reduction in paw-swelling but did not significantly prevent joint erosion. A suboptimal dose of anti-TNF alone had no significant effect on arthritis. In contrast, anti-CD4 plus suboptimal anti-TNF significantly reduced paw-swelling, limb involvement, and joint erosion. As previously reported, an optimal dose of anti-TNF alone inhibited paw-swelling, limb involvement, and joint erosion. However, optimal anti-TNF combined with anti-CD4 caused significantly greater reductions in paw-swelling and joint erosion than those achieved by optimal anti-TNF alone. Coadministration of anti-CD4 was also effective in preventing an antibody response to the hamster anti-TNF antibody, which may have implications for long-term therapy in human disease. Thus anti-CD4 acts synergistically with anti-TNF in ameliorating established collagen-induced arthritis and this combined therapeutic approach may provide effective long-term control of rheumatoid arthritis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bancroft G. J., Sheehan K. C., Schreiber R. D., Unanue E. R. Tumor necrosis factor is involved in the T cell-independent pathway of macrophage activation in scid mice. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):127–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin R. J., Waldmann H. Induction of tolerance by monoclonal antibody therapy. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):449–451. doi: 10.1038/320449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini D. R., Nedwin G. E., Bringman T. S., Smith D. D., Mundy G. R. Stimulation of bone resorption and inhibition of bone formation in vitro by human tumour necrosis factors. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):516–518. doi: 10.1038/319516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahn E., Peacock D. J., Banquerigo M. L., Liu D. Y. Effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) on collagen arthritis. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1992 Oct;11(5):253–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan F. M., Chantry D., Jackson A., Maini R., Feldmann M. Inhibitory effect of TNF alpha antibodies on synovial cell interleukin-1 production in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1989 Jul 29;2(8657):244–247. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan F. M., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. TNF alpha--a pivotal role in rheumatoid arthritis? Br J Rheumatol. 1992 May;31(5):293–298. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.5.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester G. R., Horneff G., Emmrich F. Management of early inflammatory arthritis. Intervention with immunomodulatory agents: monoclonal antibody therapy. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1992 Jun;6(2):415–434. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3579(05)80183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavender D., Saegusa Y., Ziff M. Stimulation of endothelial cell binding of lymphocytes by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1855–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy E. H., Chikanza I. C., Kingsley G. H., Corrigall V., Panayi G. S. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with single dose or weekly pulses of chimaeric anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Aug;36(2):291–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb03102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. Q., Field M., Allard S., Abney E., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Detection of cytokines at the cartilage/pannus junction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: implications for the role of cytokines in cartilage destruction and repair. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Oct;31(10):653–661. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.10.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. Q., Field M., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Localization of tumor necrosis factor alpha in synovial tissues and at the cartilage-pannus junction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Sep;34(9):1125–1132. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold S. P., Jayasuriya A., Nash A., Prospero T. D., Waldmann H. Therapy with monoclonal antibodies by elimination of T-cell subsets in vivo. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):548–551. doi: 10.1038/312548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper W. O., Fava R. A., Gates C. A., Cremer M. A., Townes A. S. Acceleration of onset of collagen-induced arthritis by intra-articular injection of tumour necrosis factor or transforming growth factor-beta. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Aug;89(2):244–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06939.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2163–2168. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. J., Maini R. N., Feldmann M., Long-Fox A., Charles P., Katsikis P., Brennan F. M., Walker J., Bijl H., Ghrayeb J. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with chimeric monoclonal antibodies to tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Dec;36(12):1681–1690. doi: 10.1002/art.1780361206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C., Wright B. Rat x rat hybrid myelomas and a monoclonal anti-Fd portion of mouse IgG. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):131–133. doi: 10.1038/277131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. R., Harlan J. M., Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A. Stimulation of the adherence of neutrophils to umbilical vein endothelium by human recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8667–8671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt T. J., Andersson M., Malmström V., Holmdahl R. Activated type II collagen reactive T cells are not eliminated by in vivo anti-CD4 treatment. Implications for therapeutic approaches on autoimmune arthritis. Immunobiology. 1992 Apr;184(4-5):359–371. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt T. J., Holmdahl R. Anti-T cell receptor antibody treatment of rats with established autologous collagen-induced arthritis: suppression of arthritis without reduction of anti-type II collagen autoantibody levels. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1327–1330. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth C., Brennan F. M., Chantry D., Turner M., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Expression of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in rheumatoid arthritis: regulation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2575–2579. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog C., Walker C., Pichler W. J. New therapeutic approaches in rheumatoid arthritis. Concepts Immunopathol. 1989;7:79–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Jonsson R., Larsson P., Klareskog L. Early appearance of activated CD4+ T lymphocytes and class II antigen-expressing cells in joints of DBA/1 mice immunized with type II collagen. Lab Invest. 1988 Jan;58(1):53–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Mo J., Nordling C., Larsson P., Jansson L., Goldschmidt T., Andersson M., Klareskog L. Collagen induced arthritis: an experimental model for rheumatoid arthritis with involvement of both DTH and immune complex mediated mechanisms. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1989 Sep-Oct;7 (Suppl 3):S51–S55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom J. T., Bendele A. M., Carlson D. G. In vivo administration with IL-1 accelerates the development of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):834–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom J. T., Butler L. D., Riedl P. E., Bendele A. M. The progression of the inflammation in established collagen-induced arthritis can be altered by treatments with immunological or pharmacological agents which inhibit T cell activities. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):881–888. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keffer J., Probert L., Cazlaris H., Georgopoulos S., Kaslaris E., Kioussis D., Kollias G. Transgenic mice expressing human tumour necrosis factor: a predictive genetic model of arthritis. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4025–4031. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04978.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Structural studies on cartilage collagen employing limited cleavage and solubilization with pepsin. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4903–4909. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayi G. S., Lanchbury J. S., Kingsley G. H. The importance of the T cell in initiating and maintaining the chronic synovitis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jul;35(7):729–735. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Grau G. E., Vesin C., Loetscher H., Gentz R., Lesslauer W. Evolution of collagen arthritis in mice is arrested by treatment with anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF) antibody or a recombinant soluble TNF receptor. Immunology. 1992 Dec;77(4):510–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin S., Cobbold S., Tighe H., Benjamin R., Waldmann H. CD4 monoclonal antibody pairs for immunosuppression and tolerance induction. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Aug;17(8):1159–1165. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Sriram S., Cooper S. M. Prevention of type II collagen-induced arthritis by in vivo treatment with anti-L3T4. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1105–1110. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J. Tumour necrosis factor alpha stimulates resorption and inhibits synthesis of proteoglycan in cartilage. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):547–549. doi: 10.1038/322547a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan K. C., Ruddle N. H., Schreiber R. D. Generation and characterization of hamster monoclonal antibodies that neutralize murine tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3884–3893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorbecke G. J., Shah R., Leu C. H., Kuruvilla A. P., Hardison A. M., Palladino M. A. Involvement of endogenous tumor necrosis factor alpha and transforming growth factor beta during induction of collagen type II arthritis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7375–7379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. O., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Anti-tumor necrosis factor ameliorates joint disease in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9784–9788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




