Abstract
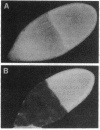
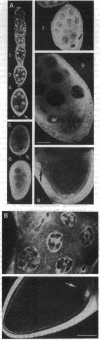
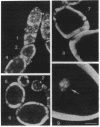
The Drosophila melanogaster hrp40 proteins are abundant nuclear pre-mRNA-binding proteins that are similar to the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) A/B proteins of vertebrates. Recently, hrp40 has been shown to be encoded by the squid gene, which is required for dorsoventral axis formation during oogenesis. Eggs and embryos from homozygous squid mothers are severely dorsalized, and complete deletion of the squid gene results in lethality. Here we have examined the expression and localization of hrp40 in wild-type and squid mutant ovaries. Using a monoclonal antibody specific for hrp40, the same isoforms of hrp40 are detected in both wild-type and squid ovaries, but the amount of hrp40 is reduced in squid ovaries. Furthermore, immunolocalization of hrp40 in wild-type egg chambers shows that hrp40 is present in the nurse cells, oocyte, and follicle cells. In contrast, in squid mutant egg chambers, hrp40 is absent from the germ-line-derived nurse cells and oocyte, but it is detected in the somatic follicle cells. The absence of hrp40 from the germ-line-derived cells of developing egg chambers is likely to lead to the striking dorsalized phenotype of squid eggs. In addition, dramatic stage-specific changes in the cellular localization of hrp40 are seen; the protein found in the nurse cell nuclei during early stages of oogenesis migrates to the cytoplasm at later stages. These findings reveal dynamic patterns of expression and localization of hnRNP proteins during development and provide evidence for an essential role for hnRNP proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein H., Gorman M., Nöthiger R. The sex-determining gene tra-2 of Drosophila encodes a putative RNA binding protein. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1025–1035. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L. R., Maine E. M., Schedl P., Cline T. W. Sex-lethal, a Drosophila sex determination switch gene, exhibits sex-specific RNA splicing and sequence similarity to RNA binding proteins. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1037–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90248-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellen H. J., Kooyer S., D'Evelyn D., Pearlman J. The Drosophila couch potato protein is expressed in nuclei of peripheral neuronal precursors and shows homology to RNA-binding proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2125–2136. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Adam S. A., Choi Y. D. Physical change in cytoplasmic messenger ribonucleoproteins in cells treated with inhibitors of mRNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):415–423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Matunis M. J., Piñol-Roma S., Burd C. G. hnRNP proteins and the biogenesis of mRNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:289–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govind S., Steward R. Dorsoventral pattern formation in Drosophila: signal transduction and nuclear targeting. Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90456-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. R., Rubin G. M. Molecular analysis of no-on-transient A, a gene required for normal vision in Drosophila. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):711–723. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90197-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsch-Mizrachi I., Haynes S. R. The Rb97D gene encodes a potential RNA-binding protein required for spermatogenesis in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 11;21(9):2229–2235. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.9.2229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. L. Initial organization of the Drosophila dorsoventral axis depends on an RNA-binding protein encoded by the squid gene. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):948–960. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matunis E. L., Matunis M. J., Dreyfuss G. Characterization of the major hnRNP proteins from Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):257–269. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matunis M. J., Matunis E. L., Dreyfuss G. Isolation of hnRNP complexes from Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):245–255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Helfman D. M., Krainer A. R. Modulation of exon skipping and inclusion by heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 and pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2/ASF. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2993–3001. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Krainer A. R. Regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing by hnRNP A1 and splicing factor SF2. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90477-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuman-Silberberg F. S., Schüpbach T. The Drosophila dorsoventral patterning gene gurken produces a dorsally localized RNA and encodes a TGF alpha-like protein. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):165–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri G., Haynes S. R., Beyer A. L. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes and proteins in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):847–855. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinow S., Campos A. R., Yao K. M., White K. The elav gene product of Drosophila, required in neurons, has three RNP consensus motifs. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1570–1572. doi: 10.1126/science.3144044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siomi H., Siomi M. C., Nussbaum R. L., Dreyfuss G. The protein product of the fragile X gene, FMR1, has characteristics of an RNA-binding protein. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90420-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue F., Cooley L. kelch encodes a component of intercellular bridges in Drosophila egg chambers. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):681–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Besser H., Schnabel P., Wieland C., Fritz E., Stanewsky R., Saumweber H. The puff-specific Drosophila protein Bj6, encoded by the gene no-on transient A, shows homology to RNA-binding proteins. Chromosoma. 1990 Dec;100(1):37–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00337601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]