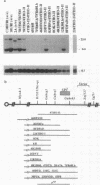
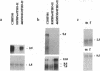
Abstract
Three genes (Gabrg3, Gabra5, and Gabrb3) encoding the gamma 3, alpha 5, and beta 3 subunits of the type A gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor, respectively, are known to map near the pink-eyed dilution (p) locus in mouse chromosome 7. This region shares homology with a segment of human chromosome 15 that is implicated in Angelman syndrome, an inherited neurobehavioral disorder. By mapping Gabrg3 on a panel of p-locus deletions, we have determined that the order of genes within this cluster is centromere-p(D15S12h)-Gabrg3-Gabra5-Gabrb3-telom ere. Like Gabrb3, neither the Gabra5 nor Gabrg3 gene is functionally imprinted in adult mouse brain. Mice deleted for all three subunits die at birth with a cleft palate, although there are rare survivors (approximately 5%) that do not have a cleft palate but do exhibit a neurological abnormality characterized by tremor, jerky gait, and runtiness. We have previously suggested that deficiency of the beta 3 subunit may be responsible for the clefting defect. Most notably, however, in this report we describe mice carrying two overlapping, complementing p deletions that fail to express the gamma 3 transcript, as well as mice from another line that express neither the gamma 3 nor alpha 5 transcripts. Surprisingly, mice from both of these lines are phenotypically normal and do not exhibit any of the neurological symptoms characteristic of the rare survivors that are deleted for all three (gamma 3, alpha 5, and beta 3) subunits. These mice therefore provide a whole-organism type A gamma-aminobutyric-acid receptor background that is devoid of any receptor subtypes that normally contain the gamma 3 and/or alpha 5 subunits. The absence of an overt neurological phenotype in mice lacking the gamma 3 and/or alpha 5 subunits also suggests that mutations in these genes are unlikely to provide useful animal models for Angelman syndrome in humans.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brilliant M. H. The mouse pink-eyed dilution locus: a model for aspects of Prader-Willi syndrome, Angelman syndrome, and a form of hypomelanosis of Ito. Mamm Genome. 1992;3(4):187–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00355717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckwalter M. S., Lossie A. C., Scarlett L. M., Camper S. A. Localization of the human chromosome 5q genes Gabra-1, Gabrg-2, Il-4, Il-5, and Irf-1 on mouse chromosome 11. Mamm Genome. 1992;3(10):604–607. doi: 10.1007/BF00350629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt D. R., Kamatchi G. L. GABAA receptor subtypes: from pharmacology to molecular biology. FASEB J. 1991 Nov;5(14):2916–2923. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.14.1661244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattanach B. M., Barr J. A., Evans E. P., Burtenshaw M., Beechey C. V., Leff S. E., Brannan C. I., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Jones J. A candidate mouse model for Prader-Willi syndrome which shows an absence of Snrpn expression. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):270–274. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubini E., Gaiarsa J. L., Ben-Ari Y. GABA: an excitatory transmitter in early postnatal life. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Dec;14(12):515–519. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90003-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton-Smith J., Pembrey M. E. Angelman syndrome. J Med Genet. 1992 Jun;29(6):412–415. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.6.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culiat C. T., Stubbs L., Nicholls R. D., Montgomery C. S., Russell L. B., Johnson D. K., Rinchik E. M. Concordance between isolated cleft palate in mice and alterations within a region including the gene encoding the beta 3 subunit of the type A gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5105–5109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting G. R., Curristin S., Zoghbi H., O'Hara B., Seldin M. F., Uhl G. R. Identification of a putative gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor subunit rho2 cDNA and colocalization of the genes encoding rho2 (GABRR2) and rho1 (GABRR1) to human chromosome 6q14-q21 and mouse chromosome 4. Genomics. 1992 Apr;12(4):801–806. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90312-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChiara T. M., Robertson E. J., Efstratiadis A. Parental imprinting of the mouse insulin-like growth factor II gene. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90513-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritschy J. M., Benke D., Mertens S., Oertel W. H., Bachi T., Möhler H. Five subtypes of type A gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors identified in neurons by double and triple immunofluorescence staining with subunit-specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6726–6730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greger V., Woolf E., Lalande M. Cloning of the breakpoints of a submicroscopic deletion in an Angelman syndrome patient. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):921–924. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalscheuer V. M., Mariman E. C., Schepens M. T., Rehder H., Ropers H. H. The insulin-like growth factor type-2 receptor gene is imprinted in the mouse but not in humans. Nat Genet. 1993 Sep;5(1):74–78. doi: 10.1038/ng0993-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J. H., Sinnett D., Wagstaff J., Glatt K., Wilcox A. S., Whiting P. M., Wingrove P., Sikela J. M., Lalande M. FISH ordering of reference markers and of the gene for the alpha 5 subunit of the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor (GABRA5) within the Angelman and Prader-Willi syndrome chromosomal regions. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Feb;2(2):183–189. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korpi E. R., Kleingoor C., Kettenmann H., Seeburg P. H. Benzodiazepine-induced motor impairment linked to point mutation in cerebellar GABAA receptor. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):356–359. doi: 10.1038/361356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano A., Mutirangura A., Dittrich B., Buiting K., Horsthemke B., Saitoh S., Niikawa N., Ledbetter S. A., Greenberg F., Chinault A. C. Molecular dissection of the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome region (15q11-13) by YAC cloning and FISH analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Sep;1(6):417–425. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.6.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. J., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. The distribution of thirteen GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. III. Embryonic and postnatal development. J Neurosci. 1992 Nov;12(11):4151–4172. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-11-04151.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., King T. R., Gondo Y., Gardner J. M., Nakatsu Y., Eicher E. M., Brilliant M. H. Genetic and molecular analysis of recessive alleles at the pink-eyed dilution (p) locus of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6968–6972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan A. J., Brecha N., Khrestchatisky M., Sternini C., Tillakaratne N. J., Chiang M. Y., Anderson K., Lai M., Tobin A. J. Independent cellular and ontogenetic expression of mRNAs encoding three alpha polypeptides of the rat GABAA receptor. Neuroscience. 1991;43(2-3):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. A., Seperack P. K., Strobel M. C., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Novel myosin heavy chain encoded by murine dilute coat colour locus. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):709–713. doi: 10.1038/349709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsu Y., Tyndale R. F., DeLorey T. M., Durham-Pierre D., Gardner J. M., McDanel H. J., Nguyen Q., Wagstaff J., Lalande M., Sikela J. M. A cluster of three GABAA receptor subunit genes is deleted in a neurological mutant of the mouse p locus. Nature. 1993 Jul 29;364(6436):448–450. doi: 10.1038/364448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D. Genomic imprinting and candidate genes in the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Jun;3(3):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90119-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Gottlieb W., Russell L. B., Davda M., Horsthemke B., Rinchik E. M. Evaluation of potential models for imprinted and nonimprinted components of human chromosome 15q11-q13 syndromes by fine-structure homology mapping in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):2050–2054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Tobin A. J. Molecular biology of GABAA receptors. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1469–1480. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2155149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis A., Kunze J., Ladanyi L., Enders H., Klein-Vogler U., Niemann G. Exclusion of the GABAA-receptor beta 3 subunit gene as the Angelman's syndrome gene. Lancet. 1993 Jan 9;341(8837):122–123. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92606-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinchik E. M., Bultman S. J., Horsthemke B., Lee S. T., Strunk K. M., Spritz R. A., Avidano K. M., Jong M. T., Nicholls R. D. A gene for the mouse pink-eyed dilution locus and for human type II oculocutaneous albinism. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):72–76. doi: 10.1038/361072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh S., Kubota T., Ohta T., Jinno Y., Niikawa N., Sugimoto T., Wagstaff J., Lalande M. Familial Angelman syndrome caused by imprinted submicroscopic deletion encompassing GABAA receptor beta 3-subunit gene. Lancet. 1992 Feb 8;339(8789):366–367. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91686-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Darlison M. G., Fujita N., Burt D. R., Stephenson F. A., Rodriguez H., Rhee L. M., Ramachandran J., Reale V., Glencorse T. A. Sequence and functional expression of the GABA A receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):221–227. doi: 10.1038/328221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin N. Neurotransmitter action: opening of ligand-gated ion channels. Cell. 1993 Jan;72 (Suppl):31–41. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagstaff J., Chaillet J. R., Lalande M. The GABAA receptor beta 3 subunit gene: characterization of a human cDNA from chromosome 15q11q13 and mapping to a region of conserved synteny on mouse chromosome 7. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):1071–1078. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90034-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagstaff J., Knoll J. H., Fleming J., Kirkness E. F., Martin-Gallardo A., Greenberg F., Graham J. M., Jr, Menninger J., Ward D., Venter J. C. Localization of the gene encoding the GABAA receptor beta 3 subunit to the Angelman/Prader-Willi region of human chromosome 15. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;49(2):330–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wee E. L., Zimmerman E. F. Involvement of GABA in palate morphogenesis and its relation to diazepam teratogenesis in two mouse strains. Teratology. 1983 Aug;28(1):15–22. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420280104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox A. S., Warrington J. A., Gardiner K., Berger R., Whiting P., Altherr M. R., Wasmuth J. J., Patterson D., Sikela J. M. Human chromosomal localization of genes encoding the gamma 1 and gamma 2 subunits of the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor indicates that members of this gene family are often clustered in the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5857–5861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson-Shaw D., Robinson M., Gambarana C., Siegel R. E., Sikela J. M. A novel gamma subunit of the GABAA receptor identified using the polymerase chain reaction. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 24;284(2):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80687-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ymer S., Schofield P. R., Draguhn A., Werner P., Köhler M., Seeburg P. H. GABAA receptor beta subunit heterogeneity: functional expression of cloned cDNAs. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1665–1670. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman E. F., Wee E. L. Role of neurotransmitters in palate development. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1984;19:37–63. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60394-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]