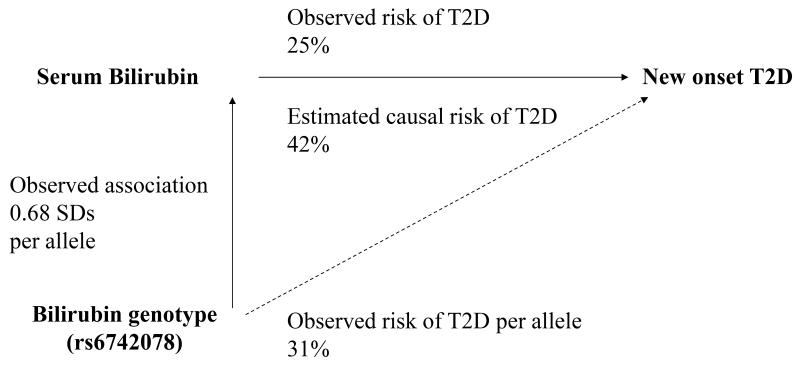
Figure 4. Mendelian randomization analysis for the association of levels of serum total bilirubin and the incidence of type 2 diabetes.
The observed effect of genotype on bilirubin levels (βgenotype-bilirubin) and risk of type 2 diabetes (βgenotype-T2D) was estimated per each copy of the T allele of rs6742078. The observed effect of bilirubin on type 2 diabetes was estimated per 1-SD increase in log-transformed bilirubin levels. The estimated causal risk of type 2 diabetes was calculated by the Wald-type method which is a ratio of βgenotype-T2D to βgenotype-bilirubin, where risk= (1-exp(β))×100.