Abstract
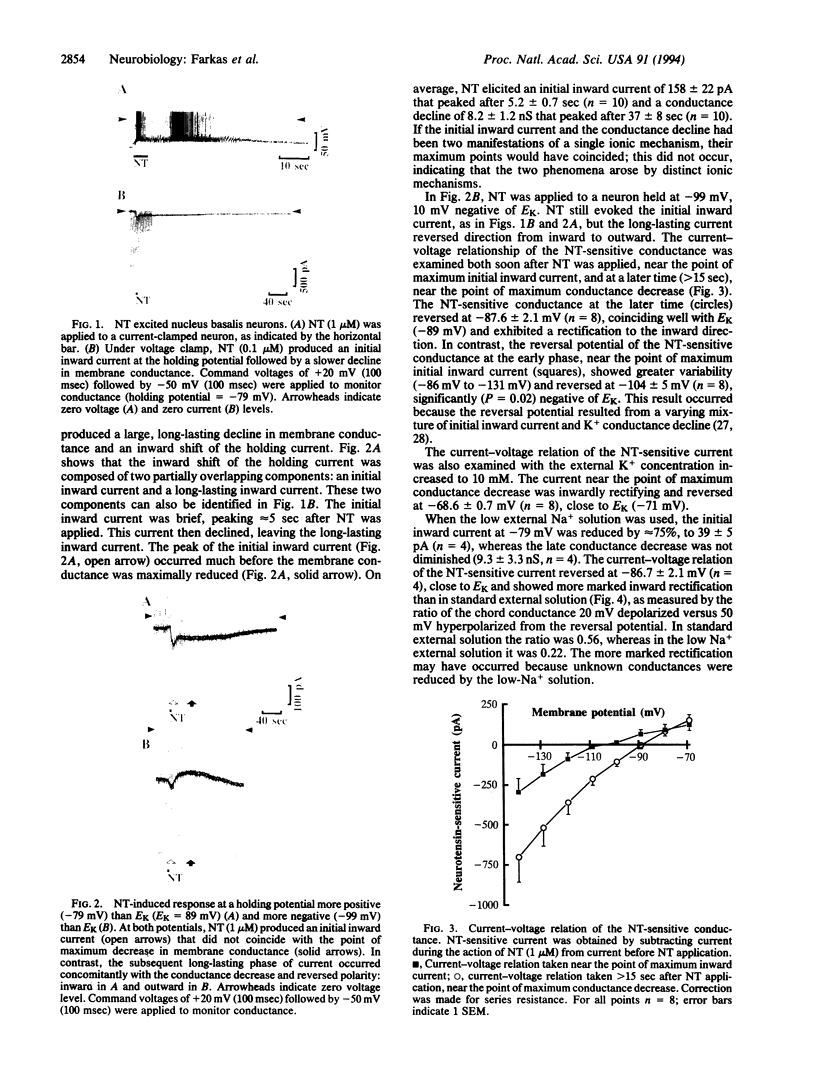
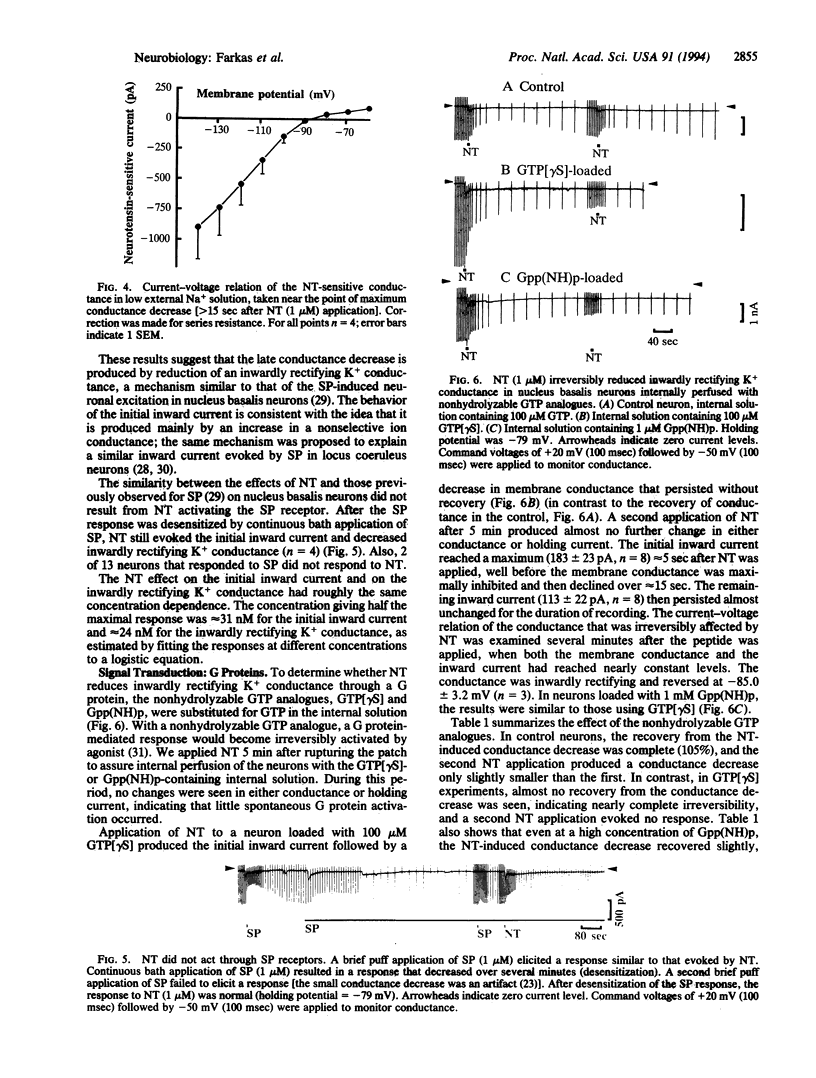
The whole-cell patch-clamp technique was used to investigate the effect of neurotensin on cholinergic neurons cultured from the rat nucleus basalis of Meynert. Neurotensin excited the neurons by inducing an initial inward current carried, at least in part, by Na+ and by reducing inwardly rectifying K+ conductance. Reduction of the inwardly rectifying K+ conductance was mediated by a pertussis toxin-insensitive G protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Audinat E., Hermel J. M., Crépel F. Neurotensin-induced excitation of neurons of the rat's frontal cortex studied intracellularly in vitro. Exp Brain Res. 1989;78(2):358–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00228907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson D. M., Blitzer R. D., Landau E. M. An analysis of the depolarization produced in guinea-pig hippocampus by cholinergic receptor stimulation. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:479–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Katada T., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3560–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A. G-proteins and potassium currents in neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:215–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6854–6861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Activation of turkey erythrocyte adenylate cyclase and blocking of the catecholamine-stimulated GTPase by guanosine 5'-(gamma-thio) triphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):868–873. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Price D. L., DeLong M. R. Alzheimer's disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1184–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.6338589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas R. H., Nakajima S., Nakajima Y. Cultured neurons infected with an HSV-1-derived vector remain electrically excitable and responsive to neurotransmitter. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Jan 3;165(1-2):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90732-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Pinnock R. D., Downes C. P., Mantyh P. W., Emson P. C. Neurotensin stimulates inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat brain slices. Brain Res. 1984 Dec 3;323(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry J. L. Electrophysiological studies on the neuroactive properties of neurotensin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;400:216–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb31571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennes L., Stumpf W. E., Kalivas P. W. Neurotensin: topographical distribution in rat brain by immunohistochemistry. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Sep 20;210(3):211–224. doi: 10.1002/cne.902100302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J., ROOTS L. A "DIRECT-COLORING" THIOCHOLINE METHOD FOR CHOLINESTERASES. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Mar;12:219–221. doi: 10.1177/12.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyano K., Velimirovic B. M., Grigg J. J., Nakajima S., Nakajima Y. Two signal transduction mechanisms of substance P-induced depolarization in locus coeruleus neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1993 Sep 1;5(9):1189–1197. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey A. I., Wainer B. H., Mufson E. J., Mesulam M. M. Co-localization of acetylcholinesterase and choline acetyltransferase in the rat cerebrum. Neuroscience. 1983 May;9(1):9–22. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mau S. E., Saermark T. Substance P stimulation of polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat anterior pituitary membranes involves a GTP-dependent mechanism. J Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;130(1):63–70. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1300063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam M. M., Mufson E. J., Wainer B. H., Levey A. I. Central cholinergic pathways in the rat: an overview based on an alternative nomenclature (Ch1-Ch6). Neuroscience. 1983 Dec;10(4):1185–1201. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metherate R., Cox C. L., Ashe J. H. Cellular bases of neocortical activation: modulation of neural oscillations by the nucleus basalis and endogenous acetylcholine. J Neurosci. 1992 Dec;12(12):4701–4711. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-12-04701.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletić V., Randić M. Neurotensin excites cat spinal neurones located in laminae I-III. Brain Res. 1979 Jun 29;169(3):600–604. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murase K., Ryu P. D., Randić M. Tachykinins modulate multiple ionic conductances in voltage-clamped rat spinal dorsal horn neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Apr;61(4):854–865. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.4.854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima Y., Nakajima S., Inoue M. Pertussis toxin-insensitive G protein mediates substance P-induced inhibition of potassium channels in brain neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3643–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima Y., Nakajima S., Obata K., Carlson C. G., Yamaguchi K. Dissociated cell culture of cholinergic neurons from nucleus basalis of Meynert and other basal forebrain nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6325–6329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Leibowitz M. D., Subers E. M., Nathanson N. M., Almers W., Hille B. Agonists that suppress M-current elicit phosphoinositide turnover and Ca2+ transients, but these events do not explain M-current suppression. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. Muscarine and t-LHRH suppress M-current by activating an IAP-insensitive G-protein. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3343–3353. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03343.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnock R. D. Neurotensin depolarizes substantia nigra dopamine neurones. Brain Res. 1985 Jul 8;338(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen K. Z., North R. A. Substance P opens cation channels and closes potassium channels in rat locus coeruleus neurons. Neuroscience. 1992 Sep;50(2):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90428-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R., Nakajima Y., Yamaguchi K. Substance P raises neuronal membrane excitability by reducing inward rectification. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):498–501. doi: 10.1038/315498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanzione P., Zieglgänsberger W. Action of neurotensin on spinal cord neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 1983 May 23;268(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90395-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szigethy E., Wenk G. L., Beaudet A. Anatomical substrate for neurotensin-acetylcholine interactions in the rat basal forebrain. Peptides. 1988 Nov-Dec;9(6):1227–1234. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Masu M., Nakanishi S. Structure and functional expression of the cloned rat neurotensin receptor. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R. D., Katzman R. Senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Ann Neurol. 1983 Nov;14(5):497–506. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Snyder S. H. Regional and subcellular distributions of brain neurotensin. Life Sci. 1976 Dec 15;19(12):1827–1832. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volterra A., Siegelbaum S. A. Role of two different guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in the antagonistic modulation of the S-type K+ channel by cAMP and arachidonic acid metabolites in Aplysia sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7810–7814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenk H., Bigl V., Meyer U. Cholinergic projections from magnocellular nuclei of the basal forebrain to cortical areas in rats. Brain Res. 1980 Dec;2(3):295–316. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(80)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Nakajima Y., Nakajima S., Stanfield P. R. Modulation of inwardly rectifying channels by substance P in cholinergic neurones from rat brain in culture. J Physiol. 1990 Jul;426:499–520. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota Y., Sasai Y., Tanaka K., Fujiwara T., Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Kakizuka A., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA for rat substance P receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17649–17652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahm D. S. Neurotensin-immunoreactive neurons in the ventral striatum of the adult rat: ventromedial caudate-putamen, nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Oct 16;81(1-2):41–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90337-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]