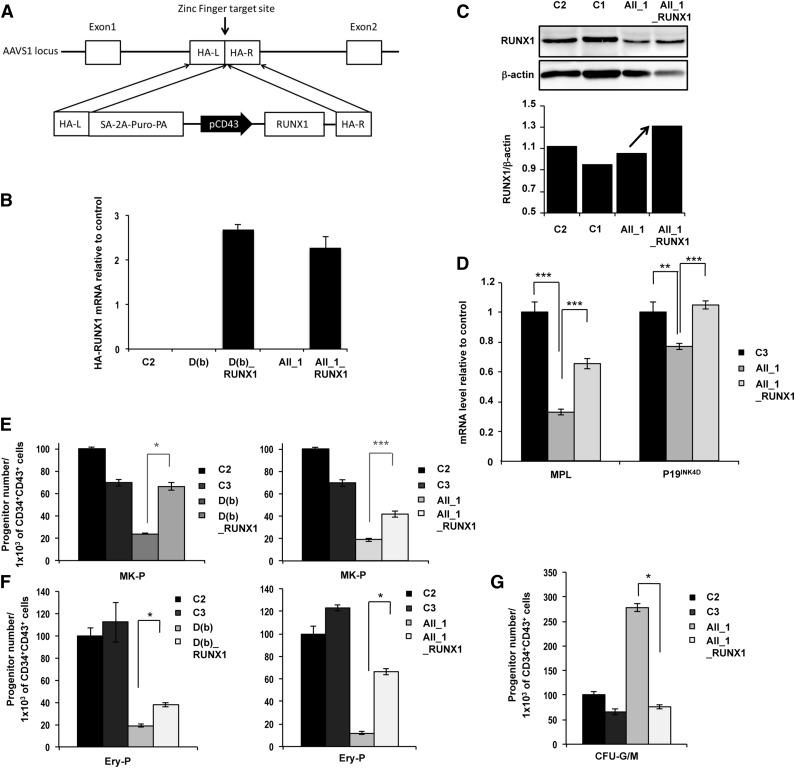
Figure 4.
Genetic rescue by RUNX1 WT overexpression in FPD/AML iPSC lines. AII_1 represents iPSC clones of 1 patient from pedigree A; D(b) represents 1 clone of 1 patient from pedigree D; AII_1_RUNX1 and D(b)_RUNX1 are the iPSC clones overexpressing WT RUNX1; and C1, C2, and C3 are control iPSCs. (A) Gene correction strategy. The constitutively active AAVS1 “safe harbor” locus is shown on the top line and the targeting construct is shown below. Complementary DNA (cDNA) expression cassette driving expression of WT RUNX1 cDNA under the leukosialin promoter (pCD43) was inserted by zinc finger-mediated homologous recombination into intron 1 of AAVS1. HA: homologous arms left (L) and right (R); SA-2A-Puro-PA: puromycin drug resistance cassette. (B) Overexpression of HA-RUNX1 measured by qRT-PCR using forward primer in HA epitope and reverse primer in RUNX1 cDNA. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals (CIs). (C) Western blot analysis of total (endogenous and overexpressed) RUNX1. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of MPL and P19INK4D expression level in MKs (CD41+CD42+) sorted at day 14. Data are normalized to PPIA transcript level, and expression is compared with control C3 (n = 3). (E-G) Cell numbers were normalized in all experiments to those produced by the C2 clone. (E-F) CD34+CD43+ cells were sorted at day 11 and tested for their colony-forming potential. (E) Assessment of MK progenitors in fibrin clot cultures (n = 3) (F) Assessment of erythroid progenitors in methylcellulose culture (n = 3) (G) CD34+CD43+ cells of pedigree A were sorted at day 14 and tested for their CFU-GM colony-forming potential in methylcellulose assay (n = 3). (D-G) Error bars represent ± SD of triplicate. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001; Student t test.