Full text
PDF
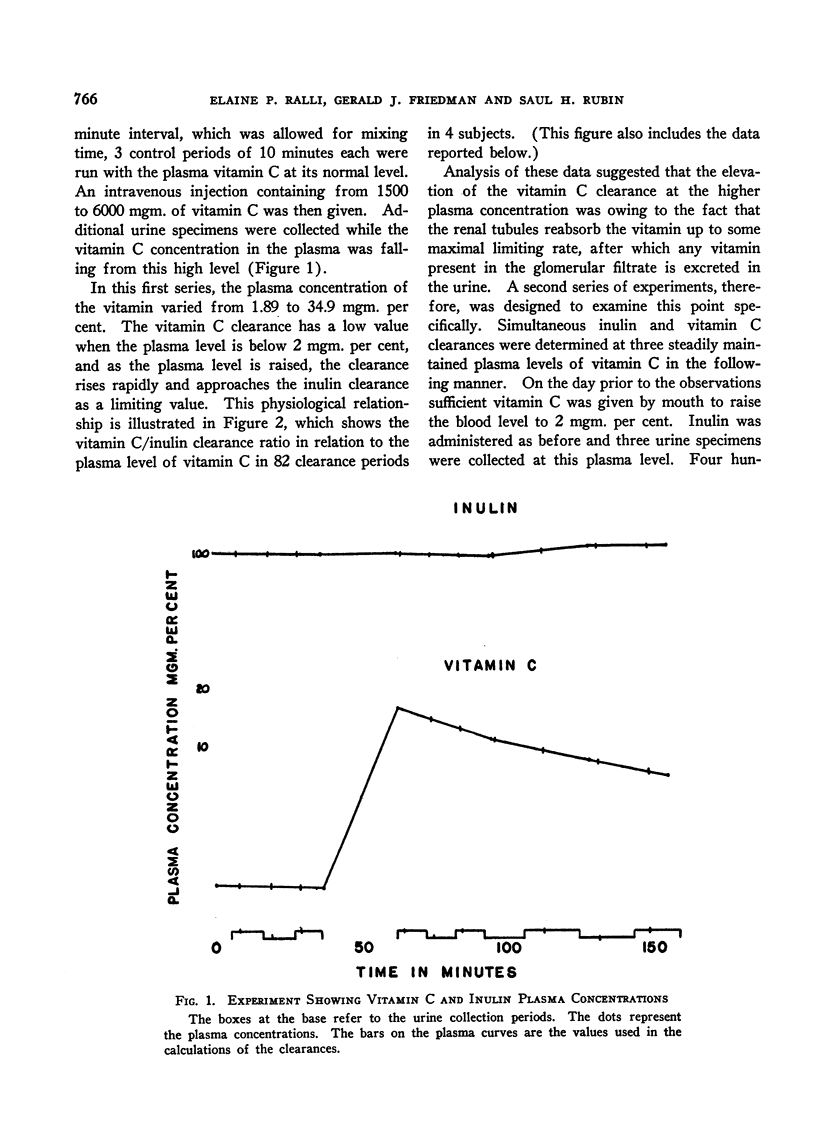
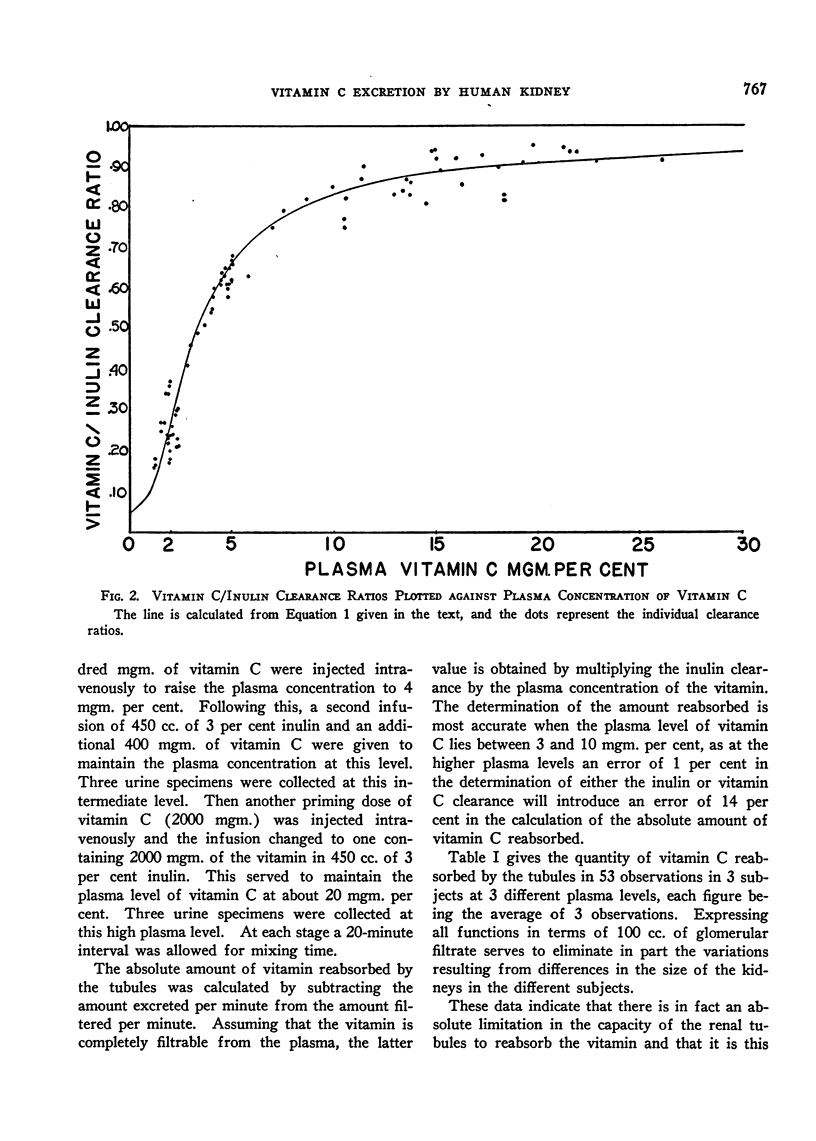
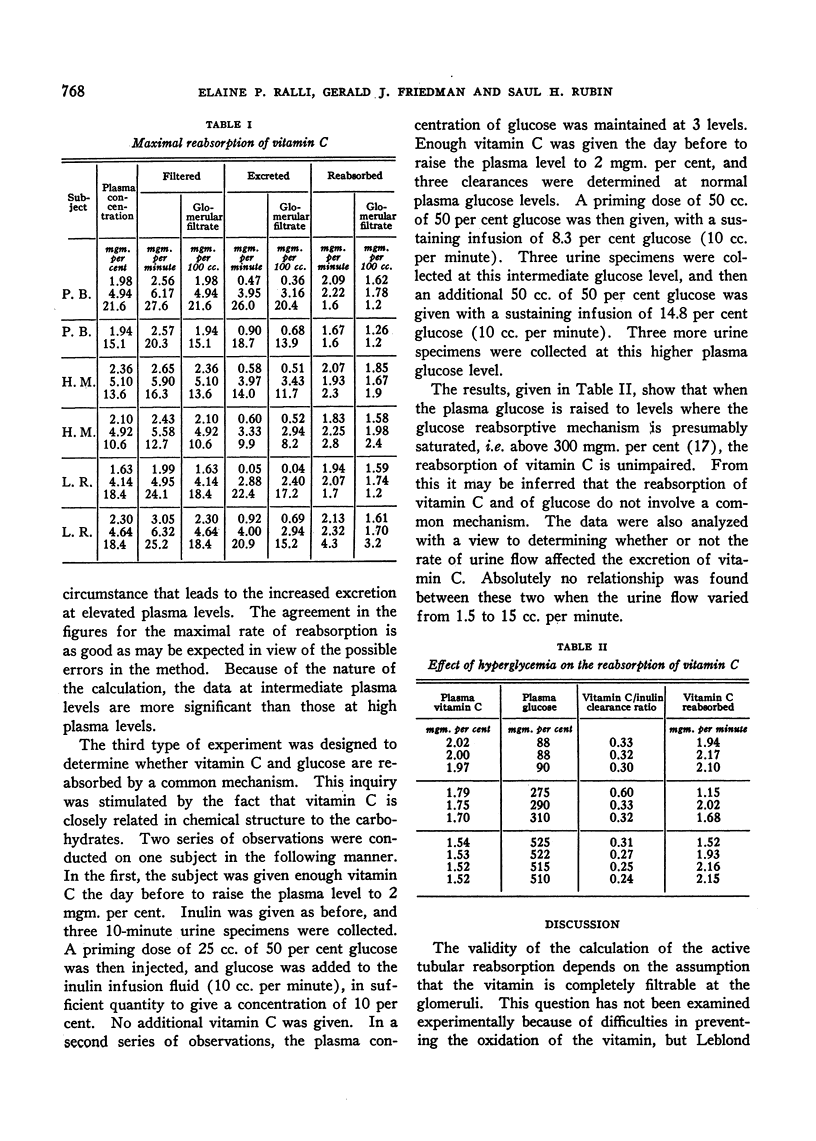


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birch T. W., Harris L. J., Ray S. N. A micro-chemical method for determining the hexuronic acid (vitamin C) content of foodstuffs, etc. Biochem J. 1933;27(2):590–594. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerie A., Van Eekelen M. The chemical determination of vitamin C with removal of interfering reducing and coloured substances. Biochem J. 1934;28(4):1153–1154. doi: 10.1042/bj0281153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner J. M., Taylor F. H. OBSERVATIONS ON THE RENAL THRESHOLD FOR ASCORBIC ACID IN MAN. J Clin Invest. 1938 Jan;17(1):69–75. doi: 10.1172/JCI100929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L. J., Ray S. N., Ward A. The excretion of vitamin C in human urine and its dependence on the dietary intake. Biochem J. 1933;27(6):2011–2015. doi: 10.1042/bj0272011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Goldring W., Chasis H. THE MEASUREMENT OF THE TUBULAR EXCRETORY MASS, EFFECTIVE BLOOD FLOW AND FILTRATION RATE IN THE NORMAL HUMAN KIDNEY. J Clin Invest. 1938 May;17(3):263–278. doi: 10.1172/JCI100950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eekelen M., Heinemann M. CRITICAL REMARKS ON THE DETERMINATION OF URINARY EXCRETION OF ASCORBIC ACID. J Clin Invest. 1938 May;17(3):293–299. doi: 10.1172/JCI100953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



