Abstract
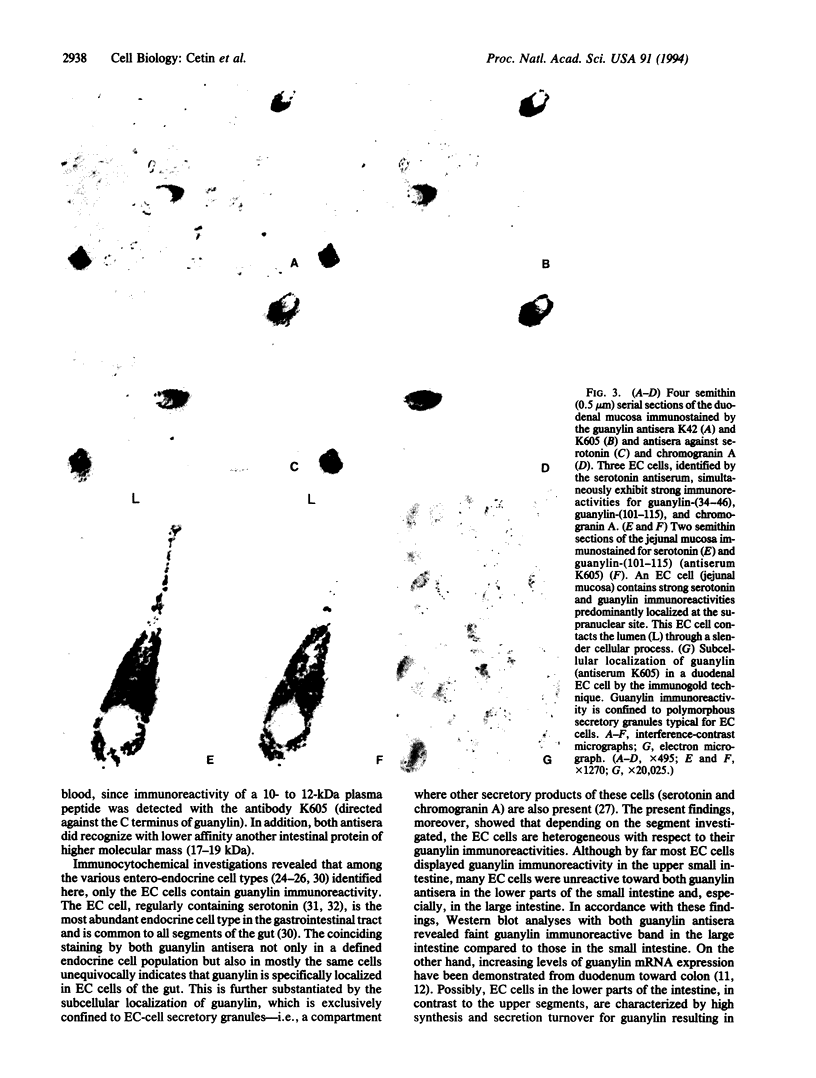
Guanylin, a bioactive peptide, has recently been isolated from the intestine; this peptide activates intestinal guanylate cyclase (i.e., guanylate cyclase C) and thus is potentially involved in the regulation of water/electrolyte transport in the gastrointestinal mucosa. As yet, the cells involved in synthesis, storage, or secretion of guanylin have not been identified by immunocytochemistry. We raised antisera against guanylin and investigated the entire gastrointestinal tract of guinea pigs by light and electron microscopical immunocytochemistry. Extracts of various intestinal segments and plasma analyzed on a Western blot revealed a peptide band corresponding to the molecular mass of guanylin. Localization studies in the entire digestive tract showed that guanylin is exclusively confined to enterochromaffin (EC) cells. Remarkably, most EC cells contacted the gut lumen by cell processes that were highly immunoreactive for guanylin. In addition to the well known secretion in an endocrine fashion, EC cells by circumstantial evidence may release guanylin into the gut lumen to activate guanylate cyclase C that is immediately located on the brush border of adjacent enterocytes. The unique localization of guanylin in EC cells may indicate that these cells are involved in the regulation of fluid secretion in the gastrointestinal mucous membrane.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlman H., DeMagistris L., Zinner M., Jaffe B. M. Release of immunoreactive serotonin into the lumen of the feline gut in response to vagal nerve stimulation. Science. 1981 Sep 11;213(4513):1254–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.6168020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTER R., PEARSE A. G. Detection of 5-hydroxytryptamine in mammalian enterochromaffin cells. Nature. 1953 Oct 31;172(4383):810–810. doi: 10.1038/172810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cetin Y. A novel endocrine cell type in the guinea-pig gastric mucosa: cellular source of pro-enkephalin-derived peptides. A histochemical, immunohistochemical, and electron microscopical characterization. Histochemistry. 1990;94(1):31–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00266787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cetin Y., Aunis D., Bader M. F., Galindo E., Jörns A., Bargsten G., Grube D. Chromostatin, a chromogranin A-derived bioactive peptide, is present in human pancreatic insulin (beta) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2360–2364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cetin Y., Bargsten G., Grube D. Mutual relationships between chromogranins A and B and gastrin in individual gastrin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2912–2916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cetin Y., Grube D. Immunoreactivities for chromogranin A and B, and secretogranin II in the guinea pig entero-endocrine system: cellular distributions and intercellular heterogeneities. Cell Tissue Res. 1991 May;264(2):231–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00313960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cetin Y., Grube D. Topology of chromogranins in secretory granules of endocrine cells. Histochemistry. 1991;96(4):301–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00271350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. K., Giannella R. A. Amino acid sequence of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Escherichia coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7744–7746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. S., Lowe D. G., Lewis M., Hellmiss R., Chen E., Goeddel D. V. Differential activation by atrial and brain natriuretic peptides of two different receptor guanylate cyclases. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):68–72. doi: 10.1038/341068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie M. G., Fok K. F., Kato J., Moore R. J., Hamra F. K., Duffin K. L., Smith C. E. Guanylin: an endogenous activator of intestinal guanylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):947–951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERSPAMER V., ASERO B. Identification of enteramine, the specific hormone of the enterochromaffin cell system, as 5-hydroxytryptamine. Nature. 1952 May 10;169(4306):800–801. doi: 10.1038/169800b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz J. C., Jaso-Friedman L., Robertson D. C. Binding of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin to rat intestinal cells and brush border membranes. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):622–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.622-630.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Osaka M., Yanatori Y. Granule release of enterochromaffin (EC) cells by cholera enterotoxin in the rabbit. Arch Histol Jpn. 1974 May;36(5):367–378. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.36.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett K. L., Grounds M. D., Beilharz M. W. Nonspecific binding of nucleic acid probes to Paneth cells in the gastrointestinal tract with in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Oct;40(10):1613–1618. doi: 10.1177/40.10.1527380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Luttrell M., Thompson M. Binding of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin to receptors on rat intestinal cells. Am J Physiol. 1983 Oct;245(4):G492–G498. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.4.G492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grube D., Forssmann W. G. Morphology and function of the entero-endocrine cells. Horm Metab Res. 1979 Nov;11(11):589–606. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1092785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grube D. The endocrine cells of the digestive system: amines, peptides, and modes of action. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1986;175(2):151–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00389591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grønstad K. O., DeMagistris L., Dahlström A., Nilsson O., Price B., Zinner M. J., Jaffe B. M., Ahlman H. The effects of vagal nerve stimulation on endoluminal release of serotonin and substance P into the feline small intestine. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 Mar;20(2):163–169. doi: 10.3109/00365528509089650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Raida M., Adermann K., Schulz-Knappe P., Gerzer R., Heim J. M., Forssmann W. G. The circulating bioactive form of human guanylin is a high molecular weight peptide (10.3 kDa). FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 1;318(2):205–209. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80022-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathan M., Hughes J., Whitehead R. The morphogenesis of the human Paneth cell. An immunocytochemical ultrastructural study. Histochemistry. 1987;87(1):91–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00518730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osaka M., Fujita T., Yanatori Y. On the possible role of intestinal hormones as the diarrhoeagenic messenger in cholera. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1975 Sep 11;18(4):287–296. doi: 10.1007/BF02889255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G., Polak J. M., Adams C., Kendall P. A. Diethylpyrocarbonate, a vapour-phase fixative for immunofluorescence studies on polypeptide hormones. Histochem J. 1974 May;6(3):347–352. doi: 10.1007/BF01312253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson G., Ahlman H., Bhargava H. N., Dahlström A., Kewenter J., Larsson I., Siepler J. K. The effect of propranolol on the serotonin concentration in the portal plasma after vagal nerve stimulation in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Dec;107(4):327–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb06483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz S., Green C. K., Yuen P. S., Garbers D. L. Guanylyl cyclase is a heat-stable enterotoxin receptor. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):941–948. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90497-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam J. P. Synthetic peptide vaccine design: synthesis and properties of a high-density multiple antigenic peptide system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5409–5413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaandrager A. B., Schulz S., De Jonge H. R., Garbers D. L. Guanylyl cyclase C is an N-linked glycoprotein receptor that accounts for multiple heat-stable enterotoxin-binding proteins in the intestine. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2174–2179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand R. C., Kato J., Currie M. G. Rat guanylin cDNA: characterization of the precursor of an endogenous activator of intestinal guanylate cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):812–817. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91699-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand R. C., Kato J., Huang M. D., Fok K. F., Kachur J. F., Currie M. G. Human guanylin: cDNA isolation, structure, and activity. FEBS Lett. 1992 Oct 19;311(2):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81387-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Fischer-Colbrie R. The chromogranins A and B: the first 25 years and future perspectives. Neuroscience. 1992 Aug;49(3):497–528. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90222-N. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. S., Garbers D. L. Guanylyl cyclase-linked receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1992;15:193–225. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.15.030192.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Sauvage F. J., Keshav S., Kuang W. J., Gillett N., Henzel W., Goeddel D. V. Precursor structure, expression, and tissue distribution of human guanylin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9089–9093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]