Abstract
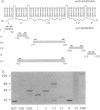
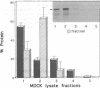
Ankyrin has emerged as a ubiquitous protein linking integral membrane transport proteins such as Na,K-ATPase to an underlying spectrin cytoskeleton. This interaction is mediated by the alpha subunit of Na,K-ATPase; however, the nature of the ankyrin binding site in Na,K-ATPase is unknown. As a step to determine the mechanism of this interaction, the ankyrin binding region of human erythrocyte spectrin and each of five putative cytoplasmic domains of the Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit have been prepared as recombinant fusion proteins in bacteria and analyzed for their interaction with erythrocyte and kidney ankyrin (Ank1 and Ank3, respectively) in vitro. Spectrin binds both Ank1 and Ank3 avidly, as expected. Two of the Na,K-ATPase domains, immobilized on a bioaffinity column, also interact specifically with both of these ankyrins. These ATPase domains are encoded by codons 140-290 (domain II) and 345-784 (domain III), with domain II displaying the greatest apparent affinity. Sequences in domain II are highly conserved between species and isoforms of Na,K-ATPase and are homologous to a cytoplasmic domain in H,K-ATPase and to a limited region of sequence in Ca-ATPase. Conversely, domain II shares no significant homology with other ankyrin binding proteins such as band 3 and Na(+)-channel proteins. These results identify a clear function for a conserved but previously not understood region of the alpha subunit of Na,K-ATPase and suggest that the interaction of ankyrin with membrane transport proteins may involve complex tertiary structural determinants not easily deduced from the primary sequence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett V. Ankyrins. Adaptors between diverse plasma membrane proteins and the cytoplasm. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8703–8706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. Spectrin-based membrane skeleton: a multipotential adaptor between plasma membrane and cytoplasm. Physiol Rev. 1990 Oct;70(4):1029–1065. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.4.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. Q., Bennett V. The anion exchanger and Na+K(+)-ATPase interact with distinct sites on ankyrin in in vitro assays. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17252–17256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. Q., McLaughlin T., Bennett V. Ankyrin-binding proteins related to nervous system cell adhesion molecules: candidates to provide transmembrane and intercellular connections in adult brain. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):121–133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. H., Bennett V. Mapping the binding sites of human erythrocyte ankyrin for the anion exchanger and spectrin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10589–10596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. H., Otto E., Bennett V. Specific 33-residue repeat(s) of erythrocyte ankyrin associate with the anion exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11163–11169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey E. G., Wan K. M., Penman S. Epithelial cytoskeletal framework and nuclear matrix-intermediate filament scaffold: three-dimensional organization and protein composition. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):1973–1984. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. P., Warren S. L., Forget B. G., Morrow J. S. Ankyrin binds to the 15th repetitive unit of erythroid and nonerythroid beta-spectrin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):267–277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert S., Yu H., Prchal J. T., Lawler J., Ruff P., Speicher D., Cheung M. C., Kan Y. W., Palek J. cDNA sequence for human erythrocyte ankyrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1730–1734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. P., Burke E. P., Frank J. S., Bennett V., Philipson K. D. The cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger binds to the cytoskeletal protein ankyrin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11489–11491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingrel J. B., Orlowski J., Shull M. M., Price E. M. Molecular genetics of Na,K-ATPase. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1990;38:37–89. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60708-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luna E. J., Hitt A. L. Cytoskeleton--plasma membrane interactions. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):955–964. doi: 10.1126/science.1439807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Bennett V. Analysis of cDNA for human erythrocyte ankyrin indicates a repeated structure with homology to tissue-differentiation and cell-cycle control proteins. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):36–42. doi: 10.1038/344036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchiodi-Albedi F., Ceccarini M., Winkelmann J. C., Morrow J. S., Petrucci T. C. The 270 kDa splice variant of erythrocyte beta-spectrin (beta I sigma 2) segregates in vivo and in vitro to specific domains of cerebellar neurons. J Cell Sci. 1993 Sep;106(Pt 1):67–78. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mische S. M., Mooseker M. S., Morrow J. S. Erythrocyte adducin: a calmodulin-regulated actin-bundling protein that stimulates spectrin-actin binding. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2837–2845. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. S., Cianci C. D., Ardito T., Mann A. S., Kashgarian M. Ankyrin links fodrin to the alpha subunit of Na,K-ATPase in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells and in intact renal tubule cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):455–465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Hammerton R. W. A membrane-cytoskeletal complex containing Na+,K+-ATPase, ankyrin, and fodrin in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells: implications for the biogenesis of epithelial cell polarity. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):893–902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Shore E. M., Wang A. Z., Hammerton R. W. Identification of a membrane-cytoskeletal complex containing the cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin (E-cadherin), ankyrin, and fodrin in Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):349–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Veshnock P. J. Ankyrin binding to (Na+ + K+)ATPase and implications for the organization of membrane domains in polarized cells. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):533–536. doi: 10.1038/328533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. Determination of total protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:95–119. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Nelson W. J. Morphogenesis of the polarized epithelial cell phenotype. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2672330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W., Mercer R. W., Caplan M., Emanuel J. R., Sweadner K. J., Benz E. J., Jr, Levenson R. Molecular cloning of rat brain Na,K-ATPase alpha-subunit cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6357–6361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J., Lingrel J. B. Molecular cloning of three distinct forms of the Na+,K+-ATPase alpha-subunit from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8125–8132. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J. Molecular cloning of two isoforms of the plasma membrane Ca2+-transporting ATPase from rat brain. Structural and functional domains exhibit similarity to Na+,K+- and other cation transport ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8646–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Lingrel J. B. Molecular cloning of the rat stomach (H+ + K+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16788–16791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. R., Bradford A. L., Joe E. H., Angelides K. J., Benos D. J., Saccomani G. Gastric parietal cell H(+)-K(+)-ATPase microsomes are associated with isoforms of ankyrin and spectrin. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 1):C63–C70. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.1.C63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. R., Saccomani G., Joe E. H., Angelides K. J., Benos D. J. Amiloride-sensitive sodium channel is linked to the cytoskeleton in renal epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6971–6975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan Y., Elmer L., Davis J., Bennett V., Angelides K. Ankyrin and spectrin associate with voltage-dependent sodium channels in brain. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):177–180. doi: 10.1038/333177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. On the crawling of animal cells. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1086–1094. doi: 10.1126/science.8493552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willardson B. M., Thevenin B. J., Harrison M. L., Kuster W. M., Benson M. D., Low P. S. Localization of the ankyrin-binding site on erythrocyte membrane protein, band 3. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15893–15899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelmann J. C., Forget B. G. Erythroid and nonerythroid spectrins. Blood. 1993 Jun 15;81(12):3173–3185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]