Abstract
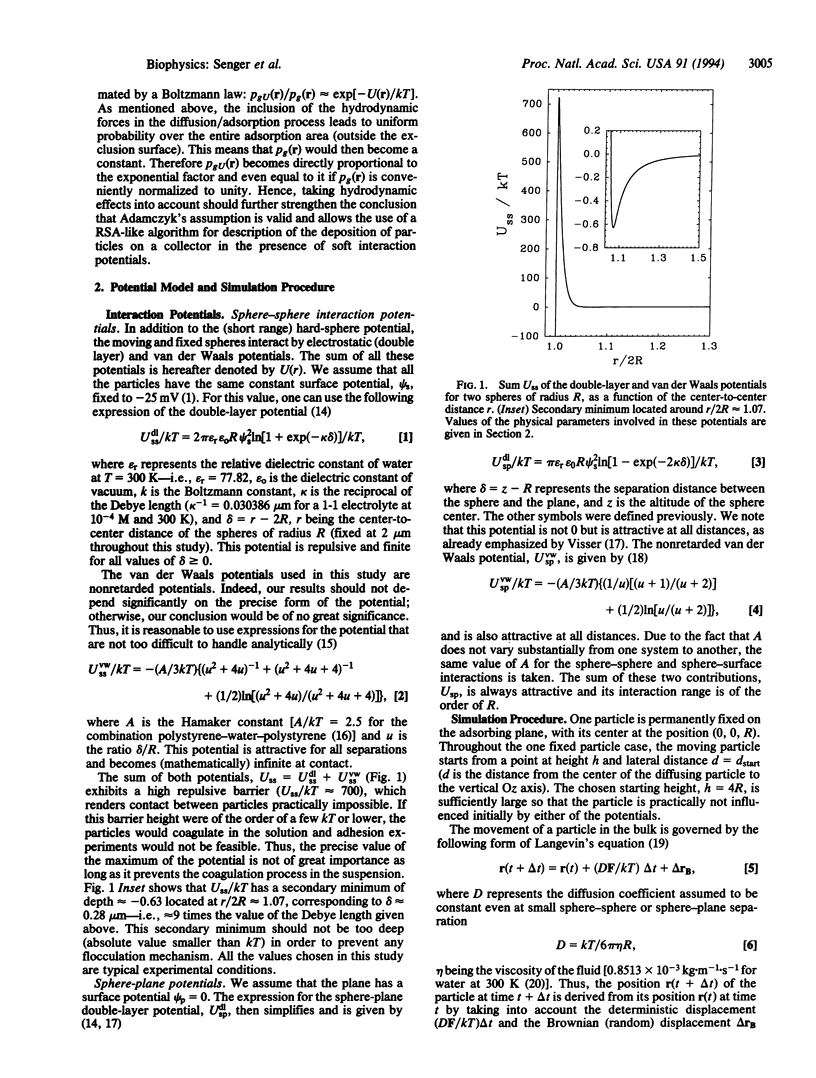
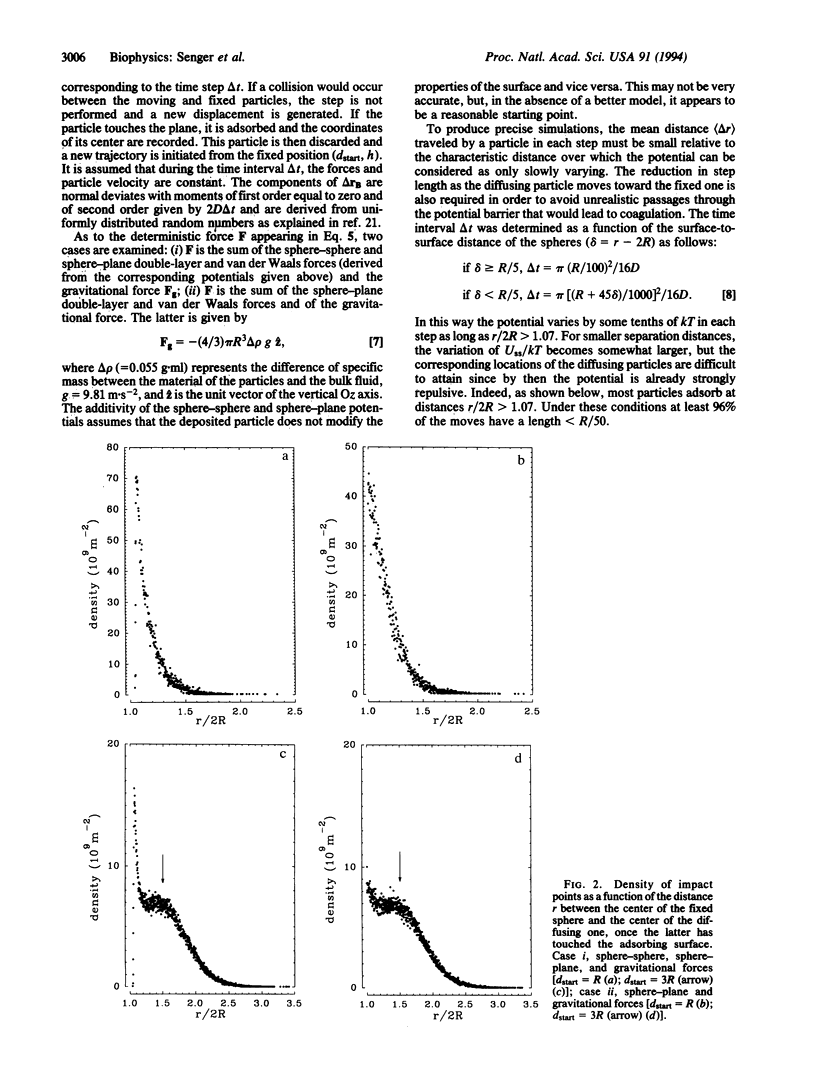
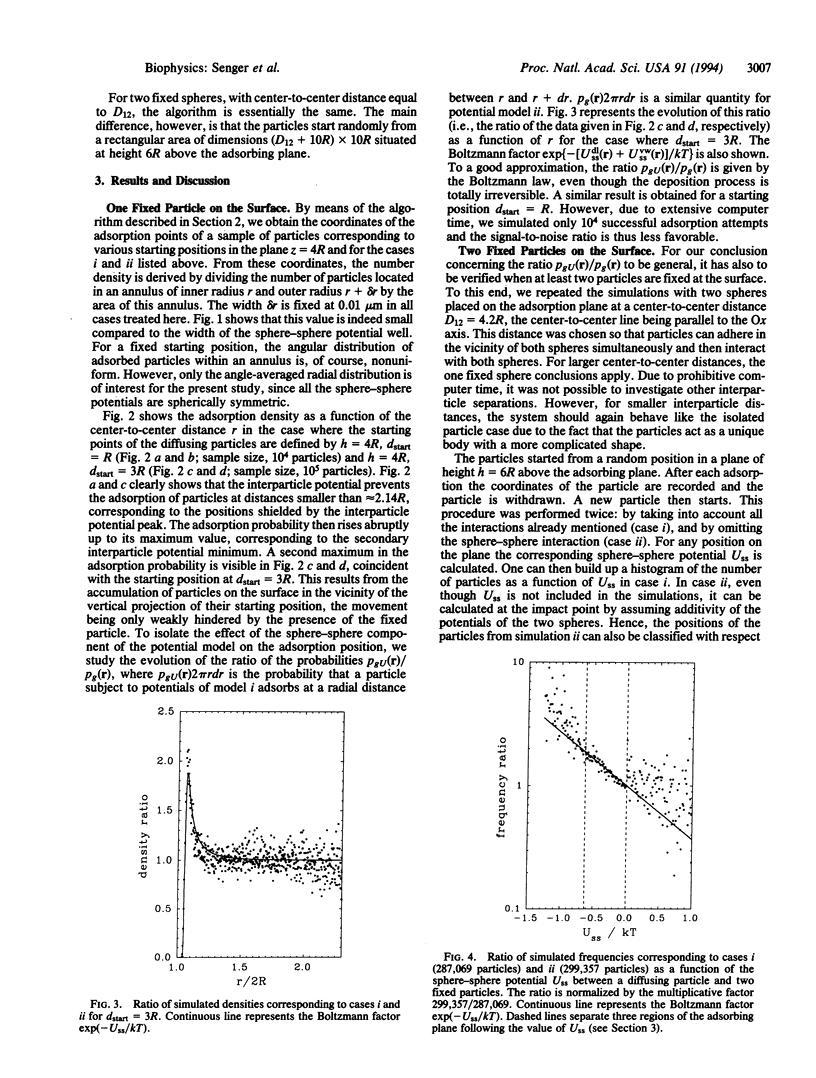
The deposition process of colloidal particles or microorganisms on flat surfaces is analyzed by means of computer simulations. Interparticle interactions (double layer and van der Waals) and weak gravitational forces are taken into account; hydrodynamic interactions, on the other hand, are neglected. In particular, the deposition probability as a function of the deposition location of a particle in the presence of one or two identical fixed particles is discussed. It is shown, in particular, that the ratio of the adhesion probabilities at a given location r, for particles subject to weak gravitation, in the presence and in the absence of the interparticle interaction U(r) follows approximately a Boltzmann law exp[-U(r)/kT], even though the adsorption process is fully irreversible. This result validates, as far as the distribution function of particles on a surface is concerned, Adamczyk's assumption [Adamczyk, Z., Zembala, M., Siwek, B. & Warszynski, P. (1990) J. Colloid Interface Sci. 140, 123-137] that the adhesion process of Brownian particles can be modeled by a random sequential adsorption model with an adsorption probability equal to exp[-U(r)/kT].
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bafaluy J, Senger B, Voegel J, Schaaf P. Effect of hydrodynamic interactions on the distribution of adhering Brownian particles. Phys Rev Lett. 1993 Feb 1;70(5):623–626. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.70.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busscher H. J., Cowan M. M., van der Mei H. C. On the relative importance of specific and non-specific approaches to oral microbial adhesion. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1992 Jun;8(3-4):199–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb04988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busscher H. J., Doornbusch G. I., Van der Mei H. C. Adhesion of mutants streptococci to glass with and without a salivary coating as studied in a parallel-plate flow chamber. J Dent Res. 1992 Mar;71(3):491–500. doi: 10.1177/00220345920710031301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozens-Roberts C., Quinn J. A., Lauffenberger D. A. Receptor-mediated adhesion phenomena. Model studies with the Radical-Flow Detachment Assay. Biophys J. 1990 Jul;58(1):107–125. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82357-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onoda GY, Liniger EG. Experimental determination of the random-parking limit in two dimensions. Phys Rev A Gen Phys. 1986 Jan;33(1):715–716. doi: 10.1103/physreva.33.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaaf P, Johner A, Talbot J. Asymptotic behavior of particle deposition. Phys Rev Lett. 1991 Mar 25;66(12):1603–1605. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.66.1603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kooten T. G., Schakenraad J. M., Van der Mei H. C., Busscher H. J. Development and use of a parallel-plate flow chamber for studying cellular adhesion to solid surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res. 1992 Jun;26(6):725–738. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820260604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Mei H. C., de Soet J. J., de Graaff J., Rouxhet P. G., Busscher H. J. Comparison of the physicochemical surface properties of Streptococcus rattus with those of other mutans streptococcal species. Caries Res. 1991;25(6):415–423. doi: 10.1159/000261404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


