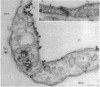
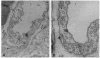
Abstract
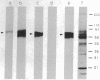
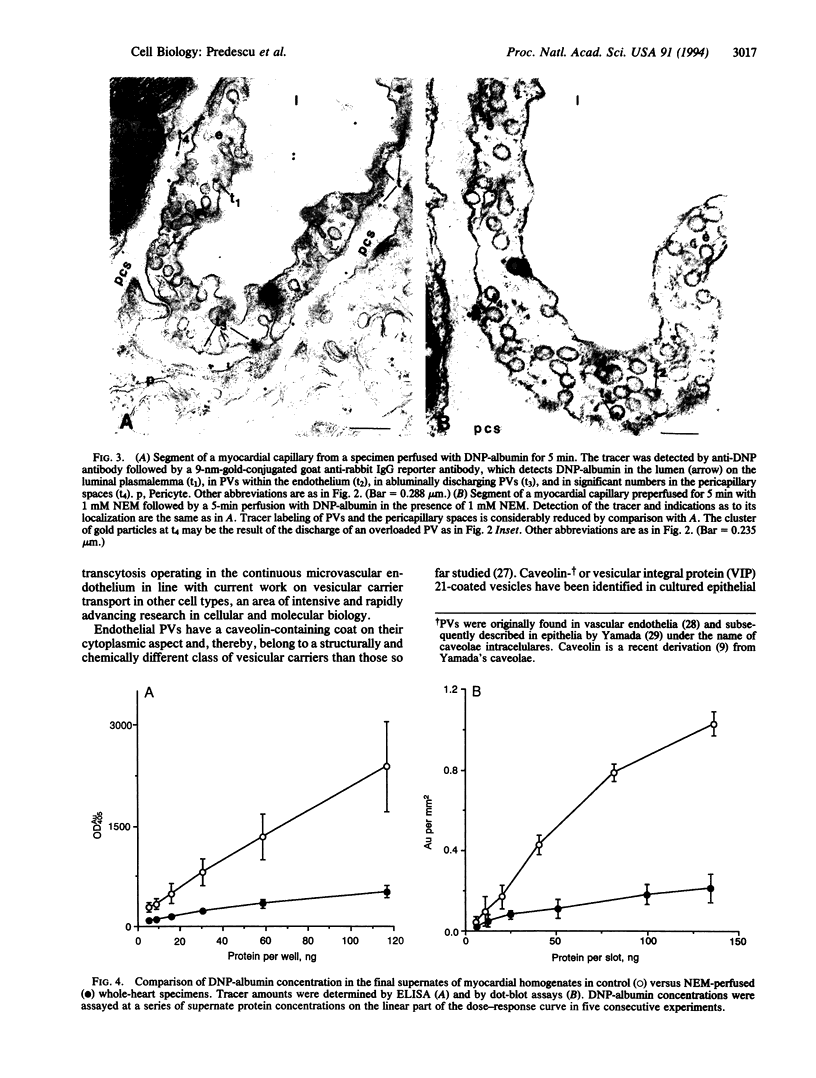
In a murine heart perfusion system, we were able to "turn off" the transport of derivatized albumin [dinitrophenylated albumin (DNP-albumin)] from the perfusate to the tissue, by preperfusing the system with 1 mM N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) for 5 min at 37 degrees C, followed by a 5-min perfusion of DNP-albumin in the presence of NEM. Using a postembedding immunocytochemical procedure, we showed that (i) a 30-sec to 1-min treatment of heart vasculature with 1 mM NEM reduces the transendothelial transport of DNP-albumin and nearly stops it after 5 min, and (ii) DNP-albumin is detected exclusively in plasmalemmal vesicles (PVs) while in transit across endothelial cells. Perfusion with 10 mM dithiothreitol for 1 min before NEM prevents the inhibition of vesicular transport. To quantitate the NEM effect on vesicular transport inhibition, we developed an ELISA and a dot-blot assay for measuring DNP-albumin in supernatants of perfused whole-heart homogenates. The results obtained indicate that the treatment of the heart vasculature with 1 mM NEM decreases the vesicular transport of DNP-albumin by 78-80%. Since NEM is known to inhibit the fusion of different types of vesicular carriers with their target membranes in other cell types and in in vitro reconstituted cellular systems, by alkylating a NEM-sensitive factor, we assume that the same mechanism applies in our in situ system. The decrease of vesicular transport can be explained by NEM preventing the fusion of recycling vesicles with their targets--i.e., the abluminal and luminal domains of the plasmalemma. The results open to question previous interpretations from other laboratories according to which plasmalemmal vesicles are sessile, immobile structures.
Full text
PDF

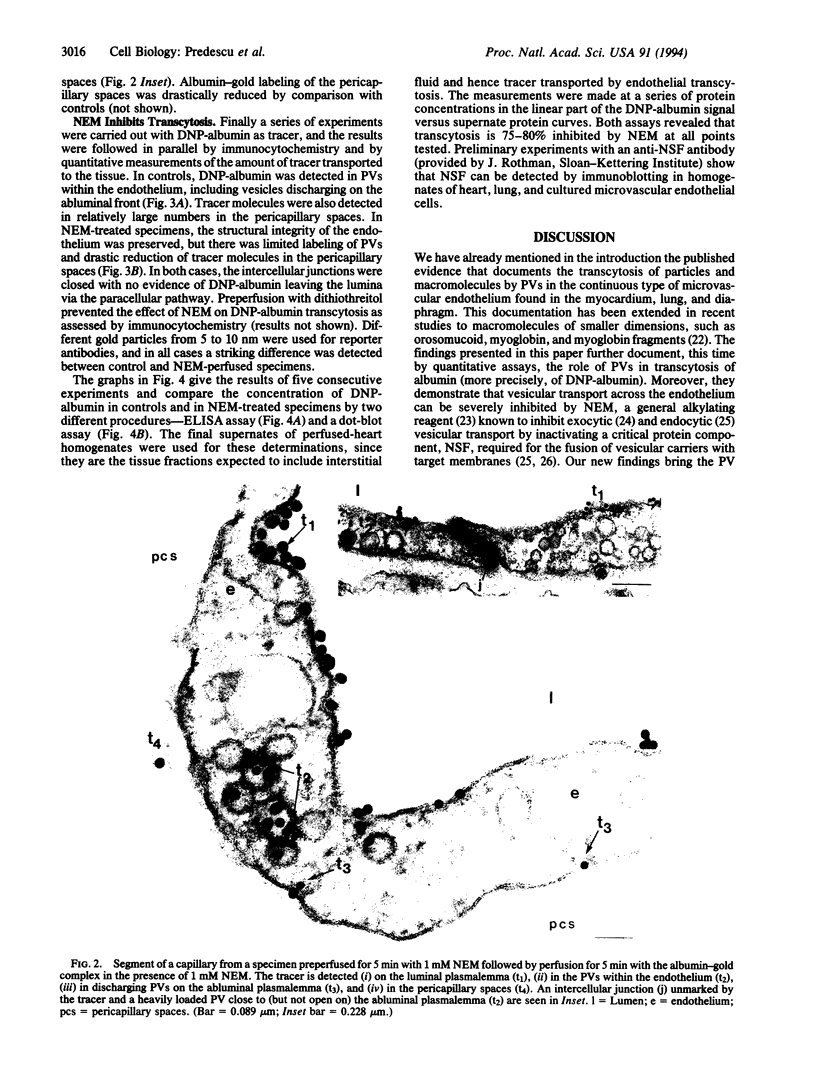

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Kamen B. A., Rothberg K. G., Lacey S. W. Potocytosis: sequestration and transport of small molecules by caveolae. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):410–411. doi: 10.1126/science.1310359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundgaard M., Hagman P., Crone C. The three-dimensional organization of plasmalemmal vesicular profiles in the endothelium of rat heart capillaries. Microvasc Res. 1983 May;25(3):358–368. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(83)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C. Modulation of solute permeability in microvascular endothelium. Fed Proc. 1986 Feb;45(2):77–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Mayorga L. S., Weidman P. J., Rothman J. E., Stahl P. D. Vesicle fusion following receptor-mediated endocytosis requires a protein active in Golgi transport. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):398–400. doi: 10.1038/339398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupree P., Parton R. G., Raposo G., Kurzchalia T. V., Simons K. Caveolae and sorting in the trans-Golgi network of epithelial cells. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1597–1605. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05804.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frøkjaer-Jensen J. The plasmalemmal vesicular system in striated muscle capillaries and in pericytes. Tissue Cell. 1984;16(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(84)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto T. Calcium pump of the plasma membrane is localized in caveolae. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1147–1157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto T., Nakade S., Miyawaki A., Mikoshiba K., Ogawa K. Localization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-like protein in plasmalemmal caveolae. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1507–1513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghitescu L., Bendayan M. Transendothelial transport of serum albumin: a quantitative immunocytochemical study. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(4):745–755. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley V. H., Curry F. E. Differential actions of albumin and plasma on capillary solute permeability. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 2):H1645–H1654. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.260.5.H1645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler K. F., Barth R. F., Wong K. P. Physicochemical studies of dinitrophenylated bovine serum albumin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1982 Jul;20(1):73–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1982.tb02655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzchalia T. V., Dupree P., Parton R. G., Kellner R., Virta H., Lehnert M., Simons K. VIP21, a 21-kD membrane protein is an integral component of trans-Golgi-network-derived transport vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1003–1014. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra V., Serafini T., Orci L., Shepherd J. C., Rothman J. E. Purification of a novel class of coated vesicles mediating biosynthetic protein transport through the Golgi stack. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90847-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milici A. J., Watrous N. E., Stukenbrok H., Palade G. E. Transcytosis of albumin in capillary endothelium. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2603–2612. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. E., Simionescu M., Simionescu N. Structural aspects of the permeability of the microvascular endothelium. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1979;463:11–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M., Robinson M. S. Clathrin, adaptors, and sorting. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:151–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Predescu D., Palade G. E. Plasmalemmal vesicles represent the large pore system of continuous microvascular endothelium. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 2):H725–H733. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.2.H725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quagliarello V. J., Ma A., Stukenbrok H., Palade G. E. Ultrastructural localization of albumin transport across the cerebral microvasculature during experimental meningitis in the rat. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):657–672. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg K. G., Heuser J. E., Donzell W. C., Ying Y. S., Glenney J. R., Anderson R. G. Caveolin, a protein component of caveolae membrane coats. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90143-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Molecular dissection of the secretory pathway. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):409–415. doi: 10.1038/355409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Movement of proteins through the Golgi stack: a molecular dissection of vesicular transport. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1460–1468. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2407590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargiacomo M., Sudol M., Tang Z., Lisanti M. P. Signal transducing molecules and glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-linked proteins form a caveolin-rich insoluble complex in MDCK cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):789–807. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu N. Cellular aspects of transcapillary exchange. Physiol Rev. 1983 Oct;63(4):1536–1579. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1983.63.4.1536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztul E., Colombo M., Stahl P., Samanta R. Control of protein traffic between distinct plasma membrane domains. Requirement for a novel 108,000 protein in the fusion of transcytotic vesicles with the apical plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1876–1885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztul E., Kaplin A., Saucan L., Palade G. Protein traffic between distinct plasma membrane domains: isolation and characterization of vesicular carriers involved in transcytosis. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90210-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Griff I. C., Rothman J. E. Proteins involved in vesicular transport and membrane fusion. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):615–620. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90031-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. W., Whiteheart S. W., Orci L., Rothman J. E. Intracellular membrane fusion. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Sep;16(9):334–337. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90138-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. W., Whiteheart S. W., Wiedmann M., Brunner M., Rothman J. E. A multisubunit particle implicated in membrane fusion. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):531–538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMADA E. The fine structure of the gall bladder epithelium of the mouse. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Sep 25;1(5):445–458. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.5.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]