Abstract
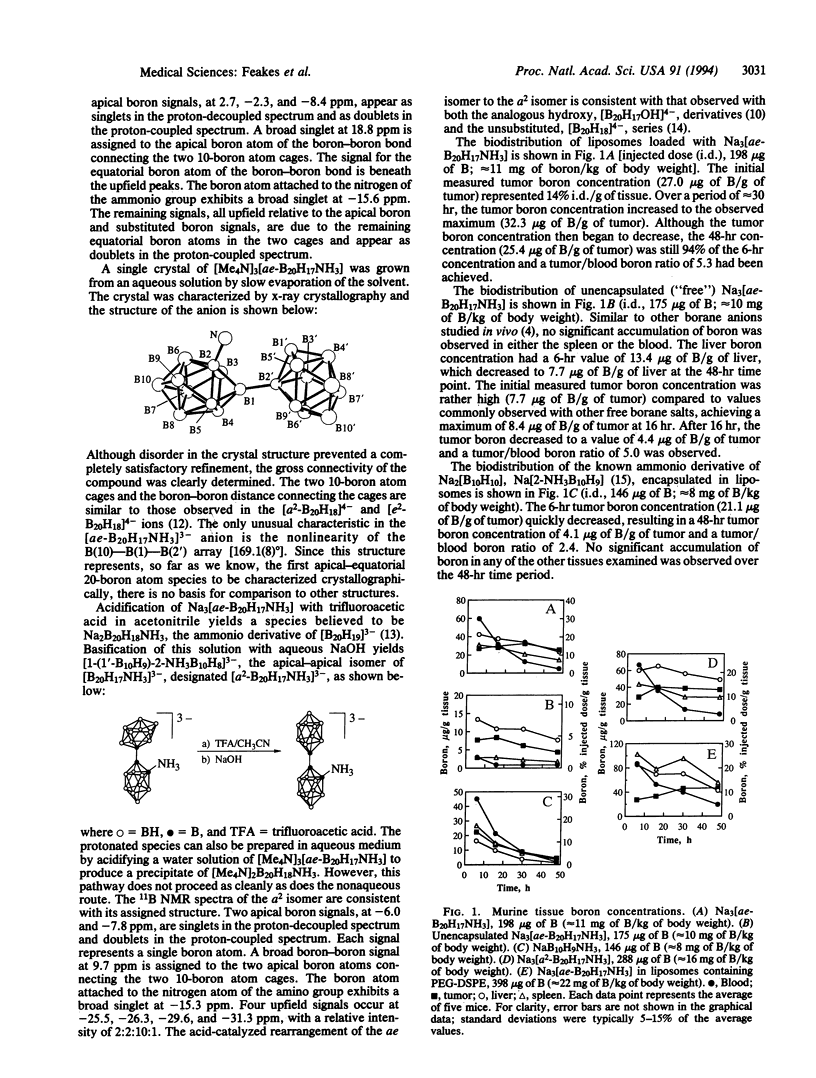
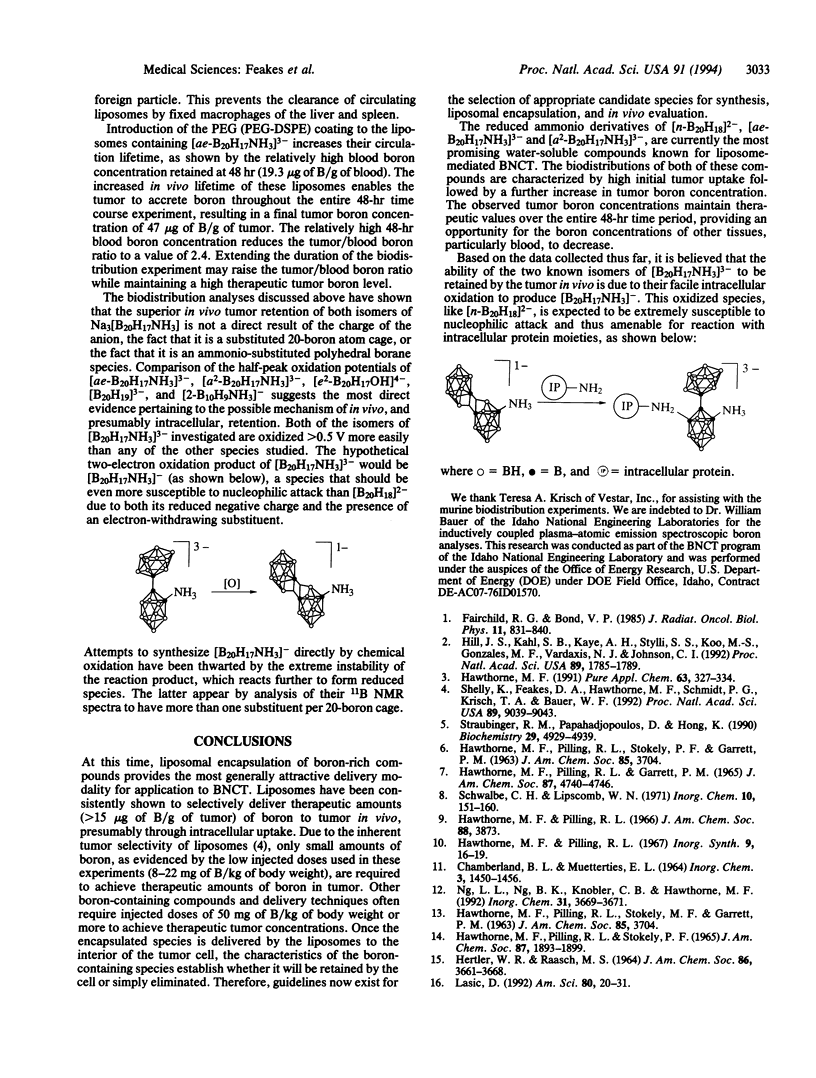
The polyhedral borane ion [n-B20H18]2- reacts with liquid ammonia in the presence of a suitable base to produce an apical-equatorial (ae) isomer of the [B20H17NH3]3- ion, [1-(2'-B10H9)-2-NH3B10H8]3-. The structure of this product has been confirmed by 11B NMR spectroscopy and x-ray crystallography. This species undergoes acid-catalyzed rearrangement to an apical-apical (a2) isomer, [1-(1'-B10H9)-2-NH3B10H8]3-, whose structure has been determined by 11B NMR spectroscopy. The sodium salts of both the ae and the a2 isomers of [B20H17NH3]3- have been encapsulated within small unilamellar liposomes, composed of distearoyl phosphatidylcholine/cholesterol (1:1), and investigated as boron-delivery agents for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) of cancer. The biodistribution of boron was determined after the injection of liposomal suspensions into BALB/c mice bearing EMT6 tumors. Both [B20H17NH3]3- isomers exhibited excellent tumor uptake and selectivity at very low injected doses, achieving peak tumor boron concentrations of 30-40 micrograms of B/g of tissue and tumor/blood boron ratios of approximately 5. The enhanced retention of the [B20H17NH3]3- isomers by EMT6 tumors may be attributed to their facile intracellular oxidation to an extremely reactive NH3-substituted [n-B20H18]2- ion, the electrophilic [B20H17NH3]- ion. Both isomers of [B20H17NH3]3- are at least 0.5 V more easily oxidized than other previously investigated species containing 20 boron atoms. In another experiment, [ae-B20H17NH3]3- was encapsulated in liposomes prepared with 5% PEG-2000-distearoyl phosphatidylethanolamine in the liposome membrane. As expected, these liposomes exhibited a longer circulation lifetime in the biodistribution experiment, resulting in the continued accumulation of boron in the tumor over the entire 48-hr experiment and reaching a maximum of 47 micrograms of B/g of tumor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fairchild R. G., Bond V. P. Current status of 10B-neutron capture therapy: enhancement of tumor dose via beam filtration and dose rate, and the effects of these parameters on minimum boron content: a theoretical evaluation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1985 Apr;11(4):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(85)90318-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne M. F., Berry T. E., Wegner P. A. The electronic properties of the 1,2- and 1,7-dicarbaclovododecaborane(12) groups bonded at carbon. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Nov 5;87(21):4746–4750. doi: 10.1021/ja00949a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. S., Kahl S. B., Kaye A. H., Stylli S. S., Koo M. S., Gonzales M. F., Vardaxis N. J., Johnson C. I. Selective tumor uptake of a boronated porphyrin in an animal model of cerebral glioma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1785–1789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelly K., Feakes D. A., Hawthorne M. F., Schmidt P. G., Krisch T. A., Bauer W. F. Model studies directed toward the boron neutron-capture therapy of cancer: boron delivery to murine tumors with liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9039–9043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straubinger R. M., Papahadjopoulos D., Hong K. L. Endocytosis and intracellular fate of liposomes using pyranine as a probe. Biochemistry. 1990 May 22;29(20):4929–4939. doi: 10.1021/bi00472a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



