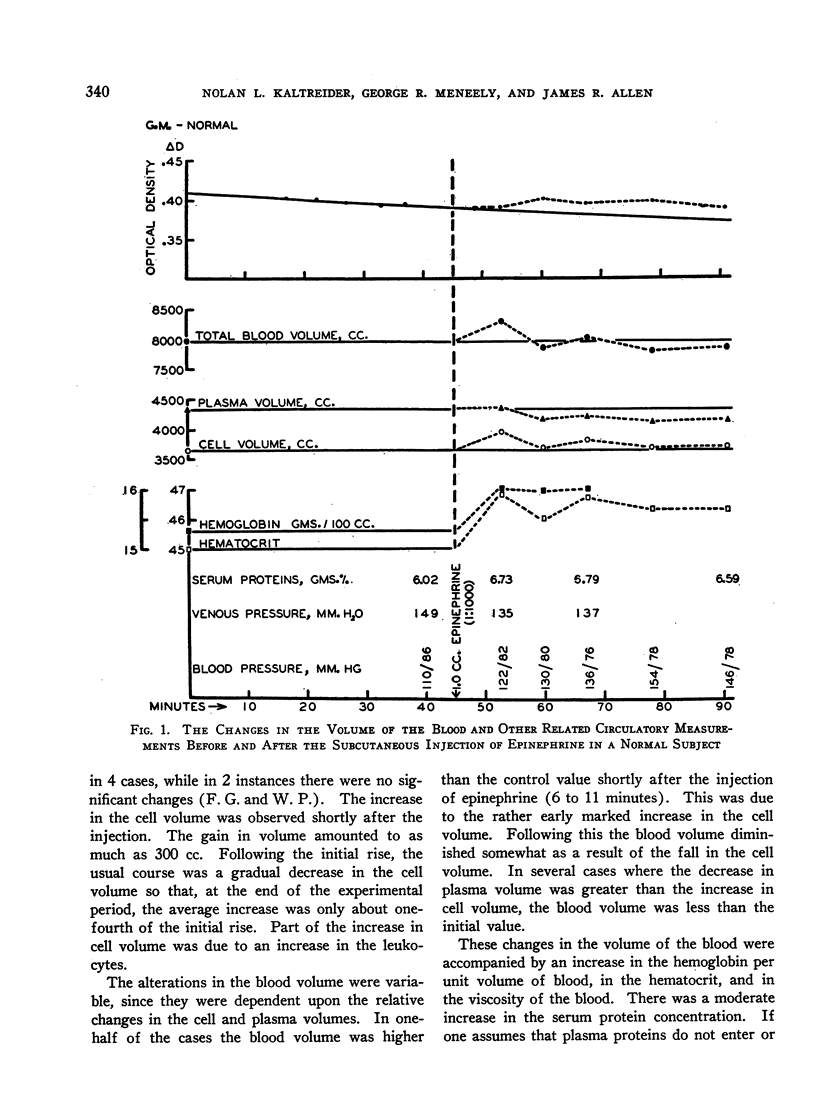
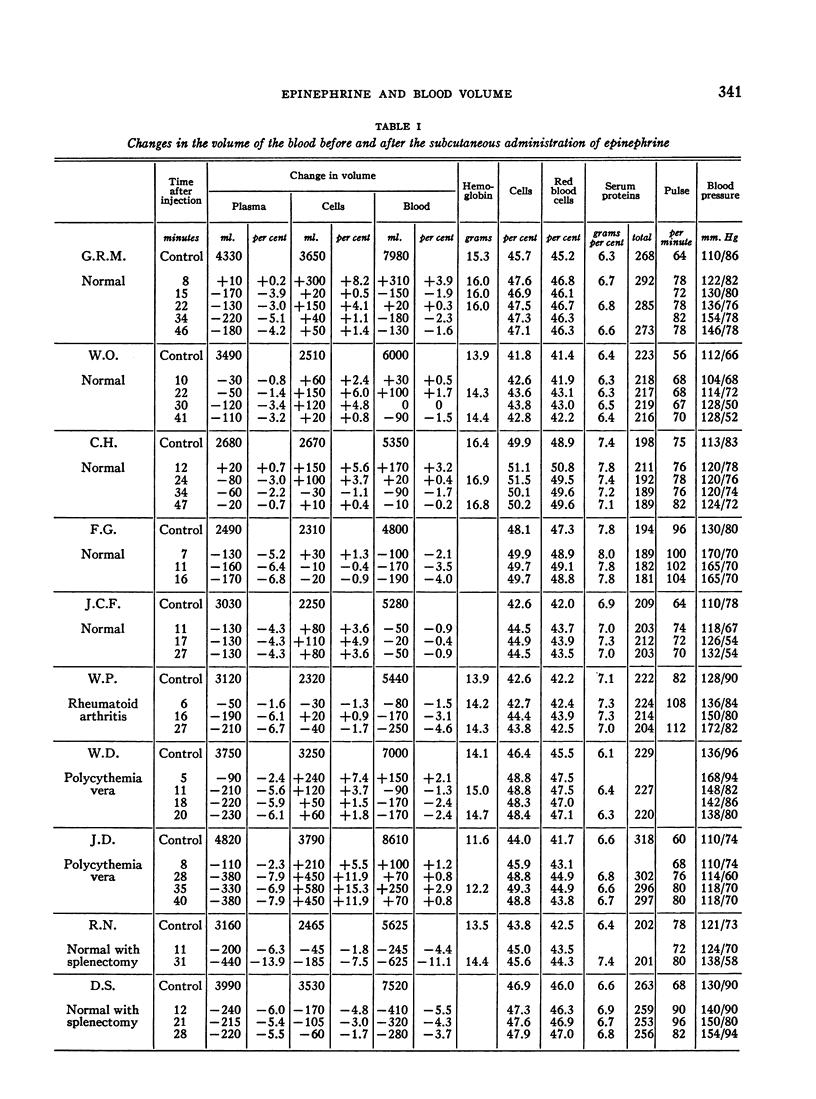
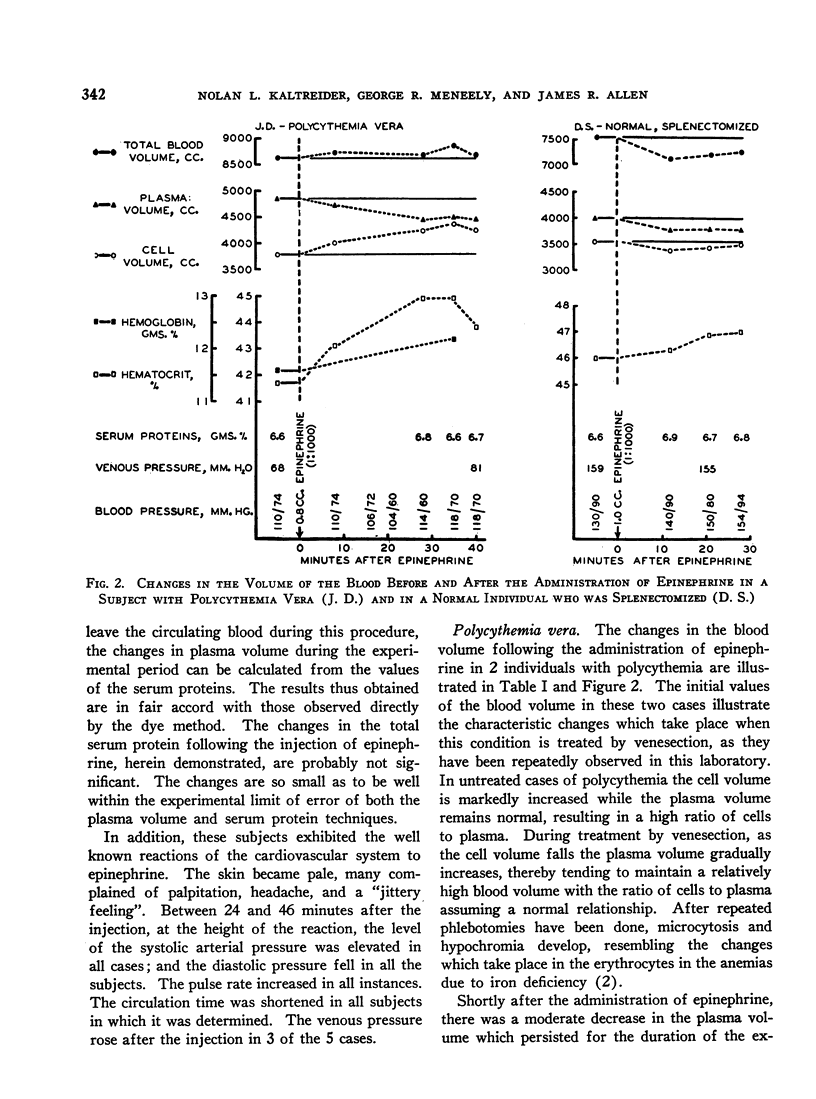
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dill D. B., Talbott J. H., Edwards H. T. Studies in muscular activity: VI. Response of several individuals to a fixed task. J Physiol. 1930 May 31;69(3):267–305. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1930.sp002649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert R. V., Stead E. A. DEMONSTRATION THAT THE CELL PLASMA RATIO OF BLOOD CONTAINED IN MINUTE VESSELS IS LOWER THAN THAT OF VENOUS BLOOD. J Clin Invest. 1941 May;20(3):317–321. doi: 10.1172/JCI101225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. G., Evans W. A. CLINICAL STUDIES OF THE BLOOD VOLUME. I. CLINICAL APPLICATION OF A METHOD EMPLOYING THE AZO DYE "EVANS BLUE" AND THE SPECTROPHOTOMETER. J Clin Invest. 1937 May;16(3):301–316. doi: 10.1172/JCI100859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltreider N. L., Meneely G. R. THE EFFECT OF EXERCISE ON THE VOLUME OF THE BLOOD. J Clin Invest. 1940 Jul;19(4):627–634. doi: 10.1172/JCI101165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


