Abstract
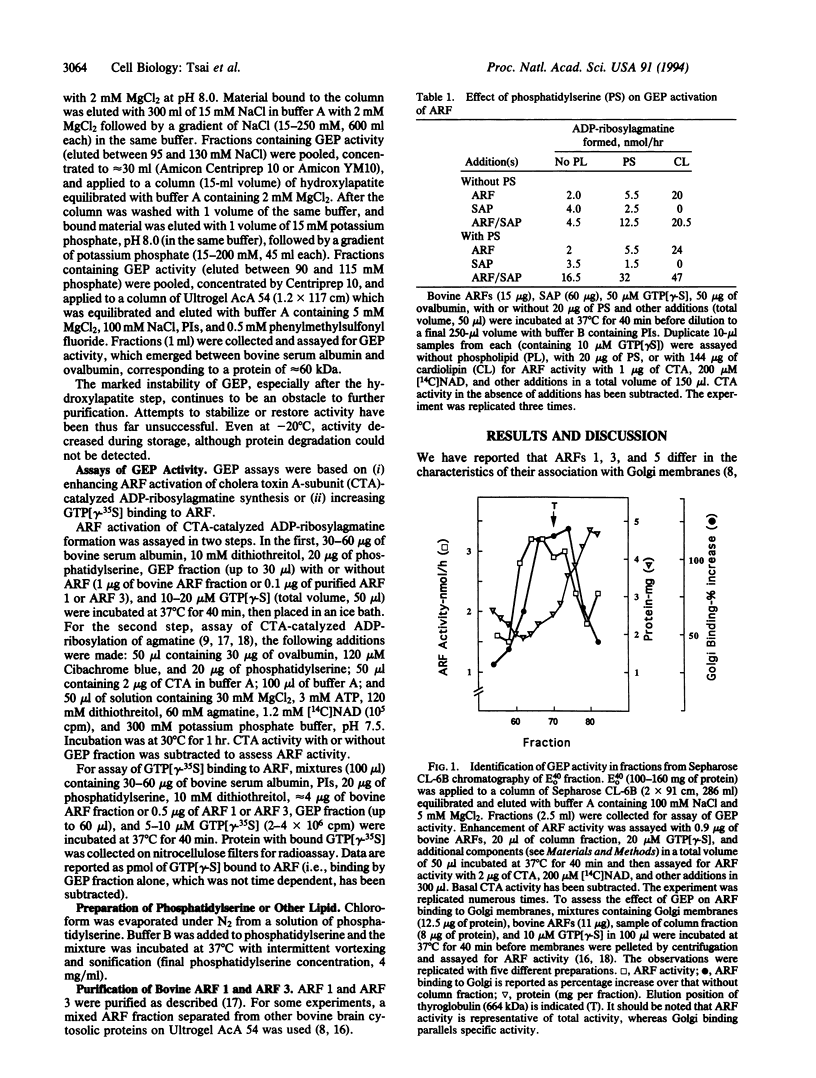
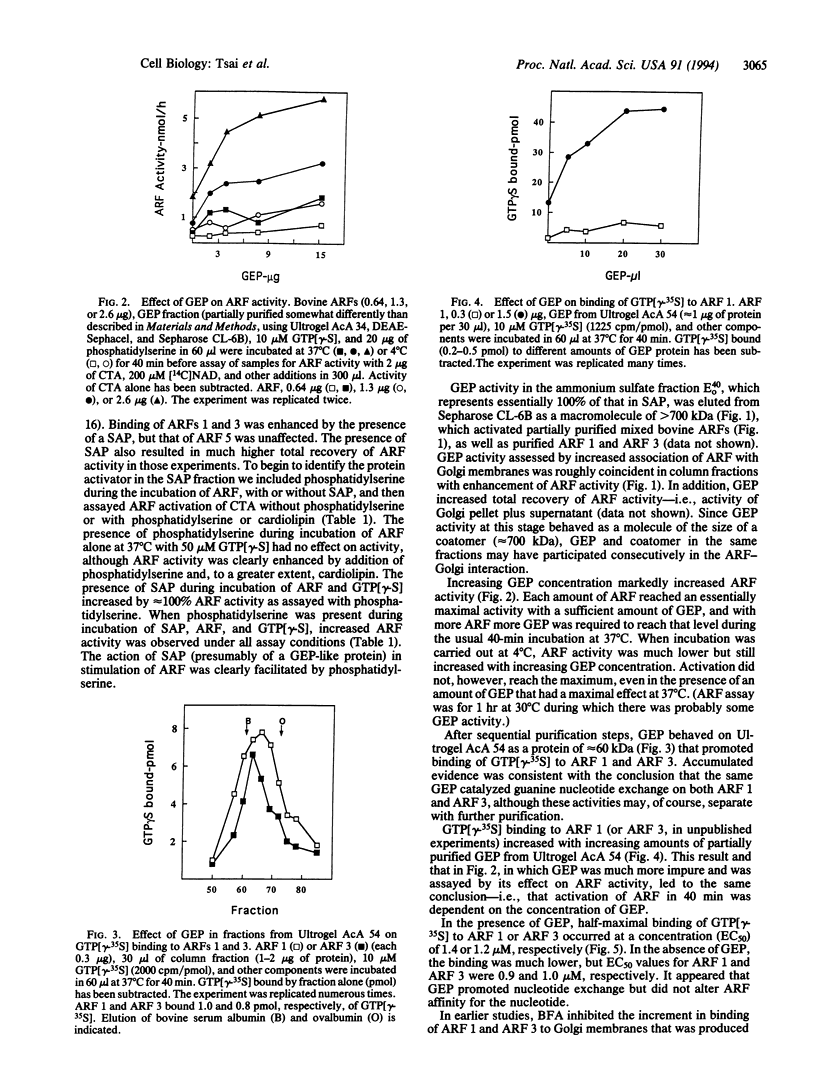
ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs) are approximately 20-kDa guanine nucleotide-binding proteins that participate in vesicular transport in the Golgi and other intracellular compartments and stimulate cholera toxin ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. ARFs are active in the GTP-bound form; hydrolysis of bound GTP to GDP, possibly with the assistance of a GTP hydrolysis (GTPase)-activating protein results in inactivation. Exchange of GDP for GTP and reactivation were shown by other workers to be enhanced by Golgi membranes in a brefeldin A-sensitive reaction, leading to the proposal that the guanine nucleotide-exchange protein (GEP) was a target of brefeldin A. In the studies reported here, a soluble GEP was partially purified from bovine brain. Exchange of nucleotide on ARFs 1 and 3, based on increased ARF activity in a toxin assay and stimulation of binding of guanosine 5'-[gamma-[35S]thio]triphosphate, was dependent on phospholipids, with phosphatidylserine being more effective than cardiolipin. GEP appeared to increase the rate of nucleotide exchange but did not affect the affinity of ARF for GTP. Whereas the crude GEP had a size of approximately 700 kDa, the partially purified GEP behaved on Ultrogel AcA 54 as a protein of 60 kDa. With purification, the GEP activity became insensitive to brefeldin A, consistent with the conclusion that, in contrast to earlier inferences, the exchange protein is not itself the target of brefeldin A.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Kahn R. A., Schwaninger R. ADP-ribosylation factor is required for vesicular trafficking between the endoplasmic reticulum and the cis-Golgi compartment. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13053–13061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlowe C., Schekman R. SEC12 encodes a guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor essential for transport vesicle budding from the ER. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):347–349. doi: 10.1038/365347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman A. L., Taylor T. C., Melançon P., Wilson K. L. A role for ADP-ribosylation factor in nuclear vesicle dynamics. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):512–514. doi: 10.1038/358512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Cassel D., Kahn R. A., Klausner R. D. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-binding protein, is required for binding of the coatomer protein beta-COP to Golgi membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6408–6412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Finazzi D., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A inhibits Golgi membrane-catalysed exchange of guanine nucleotide onto ARF protein. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):350–352. doi: 10.1038/360350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Kahn R. A., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Klausner R. D. Binding of ARF and beta-COP to Golgi membranes: possible regulation by a trimeric G protein. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1197–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.1957170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haun R. S., Tsai S. C., Adamik R., Moss J., Vaughan M. Effect of myristoylation on GTP-dependent binding of ADP-ribosylation factor to Golgi. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7064–7068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms J. B., Rothman J. E. Inhibition by brefeldin A of a Golgi membrane enzyme that catalyses exchange of guanine nucleotide bound to ARF. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):352–354. doi: 10.1038/360352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard J. M., Kahn R. A., Stahl P. D. Evidence for ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) as a regulator of in vitro endosome-endosome fusion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13047–13052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Multiple targets for brefeldin A. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):449–451. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90517-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randazzo P. A., Yang Y. C., Rulka C., Kahn R. A. Activation of ADP-ribosylation factor by Golgi membranes. Evidence for a brefeldin A- and protease-sensitive activating factor on Golgi membranes. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9555–9563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Movement of proteins through the Golgi stack: a molecular dissection of vesicular transport. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1460–1468. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2407590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serventi I. M., Moss J., Vaughan M. Enhancement of cholera toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation by guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;175:43–67. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76966-5_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns T., Willingham M. C., Botstein D., Kahn R. A. ADP-ribosylation factor is functionally and physically associated with the Golgi complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1238–1242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. C., Adamik R., Haun R. S., Moss J., Vaughan M. Differential interaction of ADP-ribosylation factors 1, 3, and 5 with rat brain Golgi membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9272–9276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. C., Adamik R., Haun R. S., Moss J., Vaughan M. Effects of brefeldin A and accessory proteins on association of ADP-ribosylation factors 1, 3, and 5 with Golgi. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10820–10825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. C., Noda M., Adamik R., Chang P. P., Chen H. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. Stimulation of choleragen enzymatic activities by GTP and two soluble proteins purified from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1768–1772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. W., Bobak D. A., Tsai S. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. GTP but not GDP analogues promote association of ADP-ribosylation factors, 20-kDa protein activators of cholera toxin, with phospholipids and PC-12 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3230–3235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeuzem S., Feick P., Zimmermann P., Haase W., Kahn R. A., Schulz I. Intravesicular acidification correlates with binding of ADP-ribosylation factor to microsomal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6619–6623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



