Abstract
Cross-species studies enable rapid translational discovery and produce the broadest impact when both mechanism and phenotype are consistent across organisms. We developed a knock-in mouse that biologically recapitulates a common human mutation in the gene for fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) (C385A; rs324420), the primary catabolic enzyme for the endocannabinoid anandamide. This common polymorphism impacts the expression and activity of FAAH, thereby increasing anandamide levels. Here, we show that the genetic knock-in mouse and human variant allele carriers exhibit parallel alterations in biochemisty, neurocircuitry, and behavior. Specifically, there is reduced FAAH expression associated with the variant allele that selectively enhances fronto-amygdala connectivity and fear extinction learning, and decreases anxiety-like behaviors. These results suggest a gain-of-function in fear regulation and may indicate for whom and for what anxiety symptoms FAAH inhibitors or exposure-based therapies will be most efficacious, bridging an important translational gap between the mouse and human.
Introduction
Translational research holds the promise to leverage basic scientific findings into advances for human health. Studies in animal models play an important role in this process, enabling the precise delineation of the mechanisms underlying behavior in humans, in whom such fine-scale resolution is difficult to achieve. A critical requirement for the success of this translational approach is that the phenotypes of interest are consistent across species. In the present study, we show that a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) gene of the endocannabinoid system has parallel molecular, neural, and behavioral effects in both humans and mice engineered to express the variant human allele, filling an important translational gap.
The endocannabinoid system has been implicated in human anxiety1, 2, 3. Anandamide (AEA), an endogenous cannabinoid (eCB) agonist at the CB1 receptor, is proposed to play a central role in this effect2, 4. FAAH is a catabolic enzyme and primary regulator of AEA signaling in the brain5. In humans, differential expression of FAAH protein is associated with a common SNP (C385A; rs324420) of which ~38% of individuals of European descent are carriers (AC, AA genotypes)6. This polymorphism leads to the substitution of an evolutionarily conserved proline at amino acid position 129 with a threonine residue, which in turn renders the FAAH protein more vulnerable to proteolytic degradation. Accordingly, the FAAH C385A SNP enhances eCB signaling by reducing steady state levels of FAAH protein, which leads to elevated AEA levels7, 8, 9. Pharmacologic manipulations and genetic knockout of FAAH have been implicated in anxiolytic behaviors including enhanced fear extinction learning2, 10, 11. However, the ability to characterize the effects of the FAAH variant in the brain has been limited, since the variant is only present in humans. Here, we describe the development of a knock-in mouse that expresses the variant A (threonine) allele of the FAAH polymorphism in place of the conserved ancestral C (proline) allele, enabling the demonstration of parallel molecular, circuit-level, and behavioral phenotypes in humans and in the knock-in mice carrying this variant.
Results
Generation and validation of FAAH C385A knock-in mice
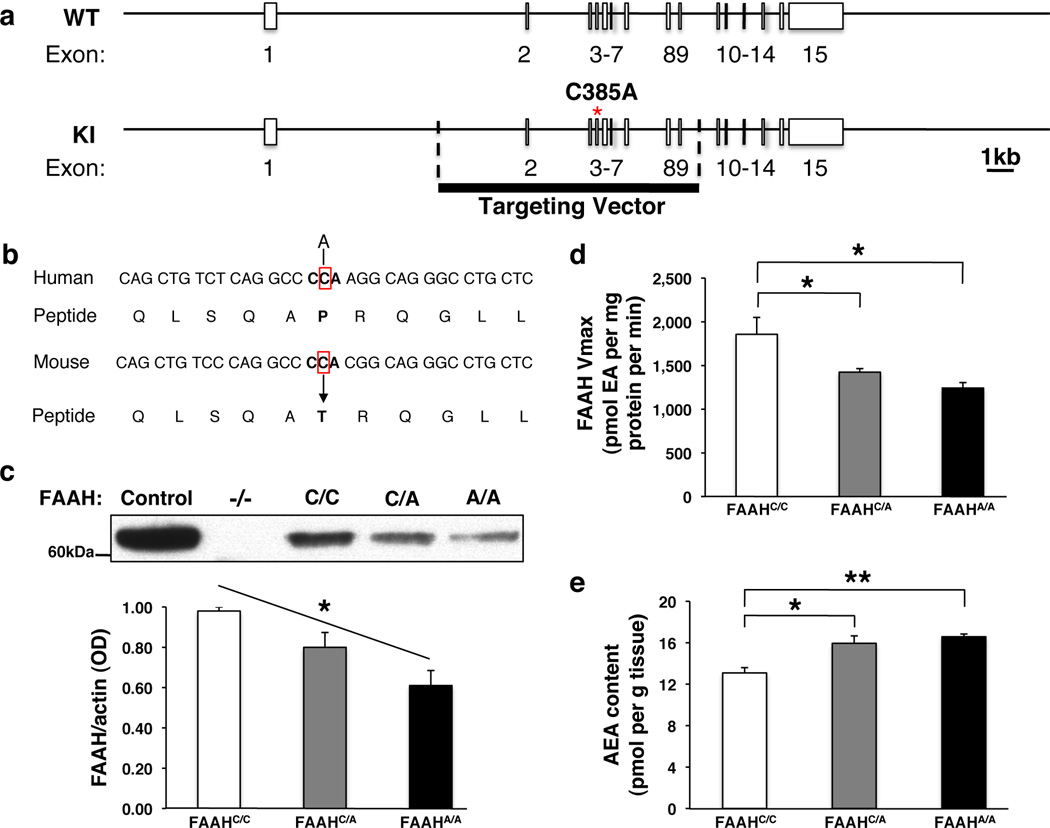
We examined molecular and biochemical effects in the FAAH knock-in mouse to determine if they paralleled effects of the human SNP (Fig. 1a, b). Specifically, human carriers of the A allele have been shown to have reduced FAAH protein levels in their lymphocytes due to protein folding abnormalities and increased proteolytic breakdown, leading to elevated plasma levels of AEA7, 8, 9. A fundamental question has been whether these alterations observed in peripheral tissues reflect parallel modulation of the eCB system by this SNP in the brain. In the FAAH knock-in mouse, analysis of relative protein expression levels in the forebrain showed a main effect of genotype on FAAH protein levels (ANOVA with post-hoc Dunnett’s test [F(2,6)=8.96, P < 0.02]) with an allele dose-dependent decrease in FAAH levels among knock-in mutants (Fig. 1c; Supplementary Fig. 1). There was also a main effect of genotype on FAAH hydrolytic activity (ANOVA with post-hoc Dunnett’s test [F(2,12)=7.89 P < 0.01]) (Fig. 1d) and AEA levels (ANOVA with post-hoc Dunnett’s test [F(2,11)=7.25, P < 0.02]) (Fig. 1e), but not for the levels of the endocannabinoid, 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), which is not a FAAH substrate (Supplementary Fig. 2). There was also no genotypic effect on the maximal binding site density for the CB1 receptor (Supplementary Fig. 3). This mouse model provides the first demonstration of biochemical changes within the brain due to the FAAH C385A SNP and mirrors its reported effects in human lymphocytes. These findings validate that the FAAH C385A knock-in mouse recapitulates the known molecular and biochemical phenotypes of the human FAAH C385A polymorphism supporting its use as a model of higher-level neural and behavioral phenotypes.
Figure 1. Generation and validation of FAAH C385A knock-in mice.
(a) A portion of coding region in the FAAH gene is replaced with C385A SNP. (b) The region encompassing the SNP has high homology between human and mouse FAAH genes. (c) FAAH protein levels in knock-in mice (FAAHC/A; FAAHA/A) and wild-type (FAAHC/C) littermates from 3 independent western blot analyses. Brain homogenates from FAAH−/− mice, and lysates from heterologous 293 cells overexpressing FAAH, were used as controls. (d) FAAH hydrolytic activity, and (e) anandamide (AEA) content in FAAH knock-in mouse forebrain homogenates (n = 4 per group). (EA; ethanolamine) Means ± SEM presented. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01
Enhanced fronto-amygdala connectivity in humans and mice
We tested for cross-species translation in genotypic effects of FAAH on fronto-amygdala circuitry and function in mice and humans with the variant A allele. In humans, FAAH C385A has been associated with variation in reactivity to threat1. However, it is unclear how the FAAH C385A polymorphism might alter the circuitry implicated in this behavioral domain. Fear conditioning studies in animal models suggest that dynamic interaction between the amygdala and two subregions of the prefrontal cortex (PFC) can drive opposing behavioral responses to threat12, 13, 14, 15. Whereas the prelimbic region (PL) promotes fear expression, the infralimbic region (IL) constrains the regulation of threat responses. Neuroimaging studies examining correlates of these opposing behaviors in humans suggest that a dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) region exhibits functional parallels to rodent PL and a subgenual region of ventromedial PFC (vmPFC) exhibits functional parallels to rodent IL16, 17, 18, 19.
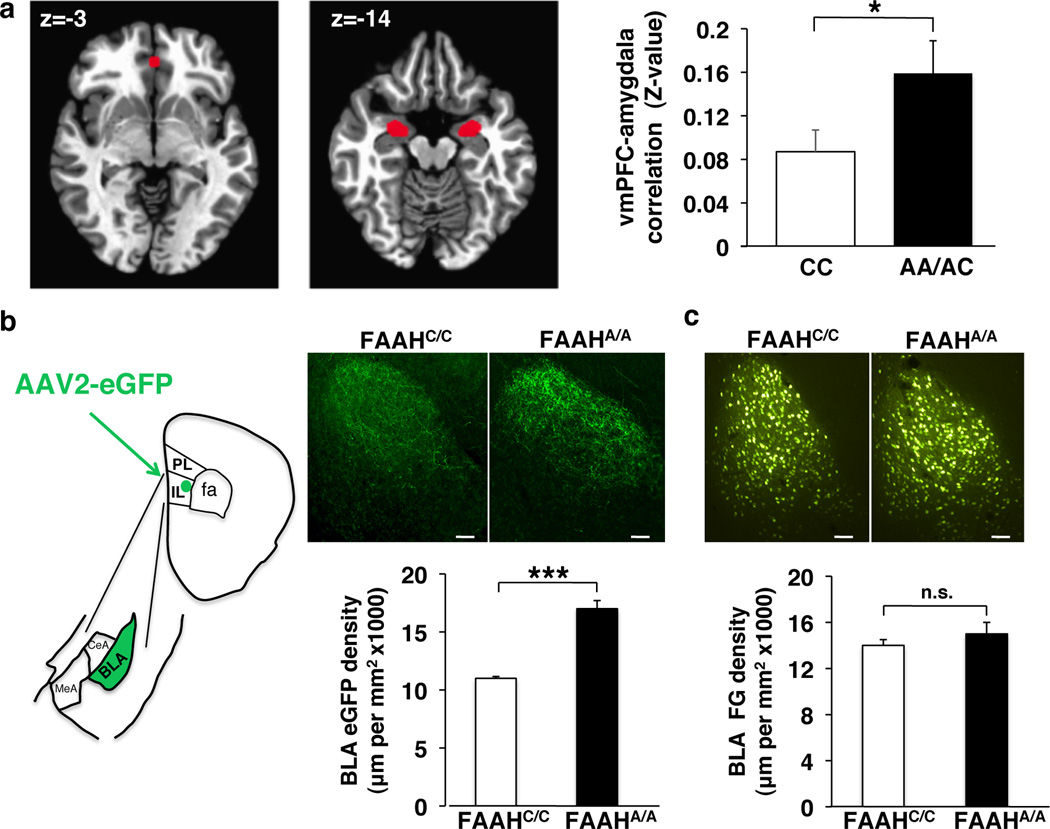
We performed species-specific connectivity analyses focusing on key regions within the fronto-amygdala circuitry that regulate fear responses and fear extinction learning. First, we examined resting state connectivity between the subgenual vmPFC and amygdala and the dorsal ACC and amygdala in humans by genotype. A-allele carriers (Supplementary Table 1) showed increased correlations between the blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) signals in the vmPFC and the bilateral amygdala [t(34)=2.71, P = 0.037] (Fig. 2a; Supplementary Fig. 4a; Bayesian statistical analysis in Supplementary Fig. 5a). This pattern was selective to subgenual vmPFC–amygdala connectivity with no genotypic difference in dorsal ACC-amygdala connectivity (Supplementary Fig. 6a). A substantial literature suggests that stronger inverse functional connectivity between the vmPFC and the amygdala during emotion-related tasks is associated with decreased anxiety or negative emotion20, 21, 22. In contrast, positive resting state functional connectivity between these regions has been associated with lower anxiety23,24, 25. Our present finding is consistent with this broader literature suggesting that greater positive corticoamygdala connectivity at rest predicts more effective emotional control26,23.
Figure 2. Functional and structural connectivity between ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) and amygdala in humans and mice with FAAH C385A.
(a) fMRI functional connectivity compared between subgenual vmPFC (x, y, z = 0, 40, −3) and bilateral amygdala in A-allele carriers (n = 17) relative to C homozygotes (n = 18). (b) Anterograde tracer (AAV2-eGFP; eGFP), targeted to IL, labeled afferents in BLA in FAAHA/A mice (n = 4) and controls (FAAHC/C; n = 4). Drawing illustrates anatomical boundaries. (c) Retrograde tracer (fluorogold; FG), targeted to IL, labeled BLA cell bodies in FAAHA/A mice (n = 4) and controls (FAAHC/C; n = 4). (Scale bars: 100µm) Means ± SEM presented. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001
To delineate the precise location and directionality of genotypic differences in fronto-amygdala circuitry we used anterograde (adeno-associated virus expressing enhanced green fluorescent protein; AAV2-eGFP) and retrograde (fluorogold) tracers in our FAAH knock-in mouse. These tract-tracing experiments revealed increased projections from IL to basolateral amygdala (BLA) in mice [FAAHA/A>FAAHC/C; two-tailed Student’s t-test, P < 0.001], but no genotypic differences in ascending projections from BLA to IL [FAAHA/A>FAAHC/C; two-tailed Student’s t-test, P > 0.56] (Fig. 2b, c). Mirroring the human imaging findings, we found no genotypic differences in descending or ascending projections between the PL and BLA in the mouse (Supplementary Fig. 6a, b, c). Selective increases in descending IL-amygdala projections offer a structural neuroanatomical basis for the increased functional connectivity in fronto-amygdala circuitry in human A-allele carriers and may help explain reported genotypic differences in emotion regulation1.
Enhanced cued fear extinction in humans and mice
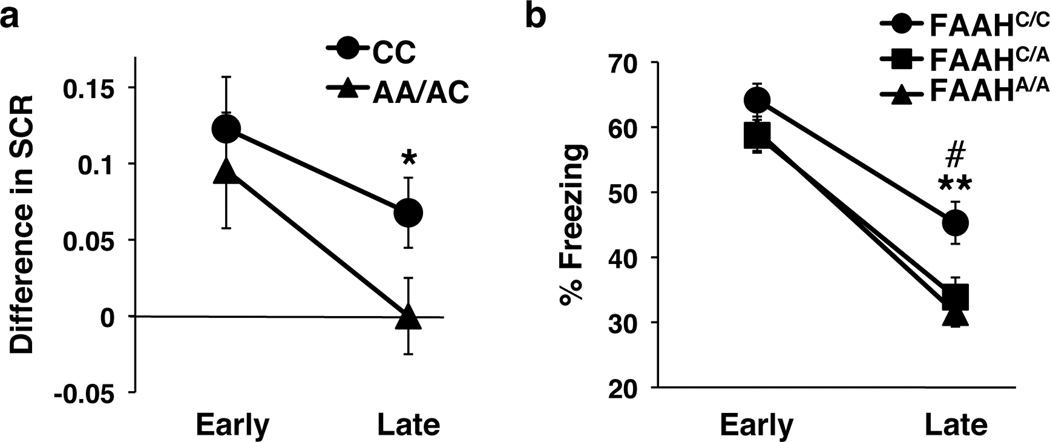
Building on our biochemical and circuit-level genotypic differences in mice and humans, we tested for behavioral effects of this variation across species in parallel fear extinction experiments. The selective increase in connectivity within an established fear regulatory circuit (IL-BLA projection) in the mouse and the homologous vmPFC-amygdala circuit in human, led to the a priori prediction that A-allele carriers would show improved fear extinction learning but no difference in fear acquisition. These predictions are consistent with reported effects of pharmacological and genetic knockout manipulations of FAAH expression in mice2, 27, 28. We tested humans (22 CC-alleles, 18 A-allele carriers; Supplementary Table 2) and mice using cued fear conditioning with extinction on the following day. In humans, there was no main effect of FAAH genotype on fear acquisition (Supplementary Fig. 7a) but there was an effect of genotype on fear extinction. Namely, human A-allele carriers exhibited facilitated fear extinction learning, as indexed by decreased galvanic skin responses during late trials of extinction training [F(1,36)=4.35, P = 0.044], controlling for age and gender effects between genotypic groups (Fig. 3a; Supplementary Fig. 4b; Bayesian statistical analysis in Supplementary Fig. 5b). Parallel findings in mice showed a significant effect of genotype on freezing behavior during extinction (ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni test [F(2,116)=6.8, P < 0.01]) (Fig. 3b), with heterozygous [P < 0.05] and homozygous [P < 0.01] FAAH C385A mice showing less freezing behavior compared to wild types in late trials, but no difference in early trials (Fig. 3b) or in fear acquisition (Supplementary Fig. 7b). These parallel effects of enhanced fear extinction in FAAH A-allele carriers have not previously been established for both mice and humans.
Figure 3. Enhanced cued fear extinction in humans and mice with FAAH C385A.
(a) Extinction, indexed by differential skin conductance response (SCR) [(CS+) – (CS−)], in 18 A-allele carriers and 22 C homozygotes. Trials were binned into early (average of the first 5 trials) and late (average of the following 6 trials). (b) Fear extinction, time spent freezing to cue, was tested in wild type (FAAHC/C; n = 21), heterozygous (FAAHC/A; n = 20) and homozygous knock-in mice (FAAHA/A; n = 20). Extinction trials were binned into early (average of extinction day 1) and late trials (average of extinction day 4). Means ± SEM presented. *P < 0.05, #P < 0.05 heterozygous knock-in mice vs wild-type controls, **P < 0.01 homozygous knock-in mice vs wild-type controls
Decreased anxiety levels in humans and mice
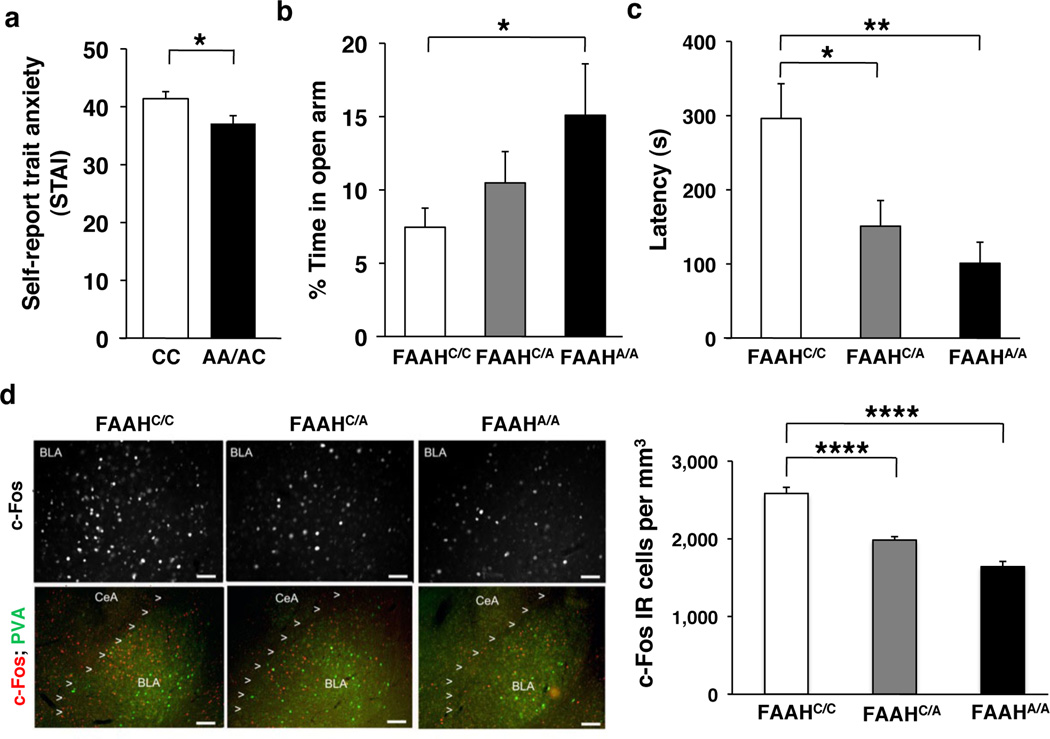
We further characterized the anxiolytic phenotype of the FAAH variant A allele in both mice and humans using standard measures of anxiety-related behaviors. Given that our results demonstrated enhanced fear extinction in human and mouse FAAH A-allele carriers, we predicted they would also show reduced anxiety1, 2, 10, 27, 28,29. In 137 humans (Supplementary Table 3), A-allele carriers reported reduced levels of trait anxiety [t(135)=2.30, P = 0.019] (Fig. 4a; Supplementary Fig. 4c; Bayesian statistical analysis in Supplementary Fig. 5c); this effect was replicated in our separate fear extinction cohort (Supplementary Table 2; Supplementary Fig. 8). In mice, we performed two standard measures of anxiety-like behaviors that involve placing subjects in conflict situations. In the elevated plus maze (EPM) test, homozygous mutant mice spent a higher percentage of time in the open arms than wild-type controls (ANOVA with post-hoc Dunnett’s test [F(2,37)=2.89, P < 0.04]), indicative of reduced anxiety-like behavior (Fig. 4b). There was no significant difference in total distance traveled (Supplementary Fig. 9). In the novelty-induced hypophagia (NIH) task, mice were trained to approach a reward (sweetened milk) in their home cage and then tested in a novel, brightly lit environment. For this task, the latency to approach and drink the sweetened milk in the novel environment is a measure of anxiety-related behavior30. FAAH C385A mice showed decreased latency to drink milk in the NIH task, suggesting decreased anxiety phenotype (ANOVA with post-hoc Dunnett’s test [F(2,44)=5.83, P < 0.01]) (Fig. 4c). To investigate the neural correlates of the observed anxiolytic effects, we examined neural activity, as indicated by expression of the early immediate gene c-Fos31, in the BLA following the NIH task. We found a main effect of genotype on BLA c-Fos expression in mutant knock-in mice (ANOVA with post-hoc Dunnett’s test [F(2,15)=53.92, P < 0.0001]) in a dose-dependent pattern, suggesting decreased engagement of the BLA in these mice during a stressful experience (Fig. 4d). This reduced activation of the amygdala in response to stressful situations is consistent with reductions in amygdala activity in response to threat in human FAAH A-allele carriers1.
Figure 4. Decreased anxiety in humans and mice with FAAH C385A.
(a) Trait anxiety levels in A-allele carriers (n = 57) and C homozygotes (n = 80). Anxiety-related behavior in FAAH C385A mice in (b) elevated plus maze (FAAHC/C, n = 17; FAAHC/A, n = 11; FAAHA/A, n = 12) and (c) novelty induced hypophagia (NIH) (FAAHC/C, n = 16; FAAHC/A, n = 21; FAAHA/A, n = 10). (d) Photomicrographs of NIH-induced c-Fos (red) labeling in the BLA (parvalbumin (green)) in FAAH C385A mice. Density of c-Fos immunoreactive (IR) cells in BLA, n = 5 per group. (Scale bars: 50µm upper row, 100µm lower row) Means ± SEM presented. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001
Discussion
Using a vertically integrated approach with parallel studies in humans and mice, we have identified the relevance and impact of the FAAH C385A polymorphism on brain biochemistry, neurocircuitry, behavior and symptoms. We validate our mouse model by showing that the FAAH variant allele leads to reductions in FAAH protein and enzymatic activity and increases in AEA levels in the brain. Our subsequent analyses in humans and mice elucidated circuit level and behavioral phenotypes not previously established in human carriers of this variant. We found enhanced fear extinction in both humans and mice with the C385A mutation. In addition, our finding of selectively enhanced fronto-amygdala connectivity in both mouse and human A-allele carriers provides a mechanistic explanation for these behavioral effects through enhanced regulation of BLA responses to threat by the IL. Non-replication of candidate gene association studies has been a major problem within the field of behavioral genetics. Here, we have used a parallel mouse-human experimental approach which enables greater control for environmental and genetic confounds. The convergent findings reported here establish that effects of genetic variation in FAAH are evident at neural and behavioral levels in both the mouse and in humans, providing a persuasive cross-species validation. Thus, this variant SNP may represent a gain-of-function in the domain of anxiety-related behaviors and may prove valuable in determining for whom and for what symptoms FAAH inhibitors or exposure-based therapies that build on basic principles of extinction learning will be most efficacious. In this way, therapeutics might be tailored to an individual to move from standard care to more precise personalized care. A persistent problem identified in animal models of disease is a failure of the findings to translate to the human in clinical trials. Our studies translate mouse behavioral and brain findings to show their human relevance using parallel paradigms and imaging tools across species. Thus, the present results obtained using this integrated approach bridge a large translational gap from mouse to human.
Methods
Generation of FAAH C385A Mice
The replacement targeting vector consisted of a 9.53kb mouse genomic fragment containing exons 2–9 FAAH-coding sequence. In a 1.6kb fragment containing the FAAH coding region, the C385A mutation was introduced and put back into the targeting vector. The FRT-Neo cassette was introduced via homologous recombination as a positive selection marker. A pGK-thymidine kinase cassette was used as a negative selection marker. The targeting vector was comprised of a 1.88kb short arm, a 5.52kb long arm, a 9.53kb targeted sequence carrying the C385A mutation, and the Neo cassette flanked by two FRT sites. Linearalized targeting vectors were electroporated into iTL BA1 (C57BL/6N × 129/SvEv) hybrid embryonic stem cells. DNA derived by G418-resistant ES clones were screened using a diagnostic SspI and BamHI restriction enzyme digestions. Recombinant clones containing the predicted 8.6 and 10.4kb rearranged bands were obtained at a frequency of 5 in 100. Two positive ES clones were injected into C57BL/6 blastocysts, which were then introduced into pseudopregnant females. Chimeric animals were mated with C57BL/6 to produce heterozygous animals, and these mice were subsequently crossed with C57LB/6 mice expressing FLP recombinase in germ cells to excise the neo cassette. Upon weaning, all genotypes were housed together and randomly assigned to experimental groups. Sample size was chosen based on previous literature for each experimental procedure. All analyses were performed on mice back-crossed at least 7 generations onto the C57BL/6 genetic background.
Western Blot Analysis
Samples of brain lysates were prepared as described previously32. Briefly, brain tissue was incubated in RIPA lysis buffer (150mM NaCl, 50mM Tris pH 8, 5mM EDTA, 1% Triton X-100, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulphate) with protease and phosphatase inhibitors (1:100, Calbiochem #539131 and #524625, respectively). Samples were triturated, rotated at 4°C for 30 minutes then spun down at 14,000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C. The supernatant was collected and cell debris discarded. Protein concentration was measured using a BCA kit. To measure FAAH levels, 10mg of forebrain lysate was resolved by SDS/PAGE electrophoresis (NuPAGE 10% Bis-Tris gel; Invitrogen #NP0315) and probed with antibodies: mouse monoclonal anti-FAAH (Abcam, ab54615; 1:500) and goat polyclonal anti-actin (Santa Cruz, sc-1616HRP; 1:5000) were used. As a positive control, 293T cells purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) were transfected with 1mg mouse FAAH cDNA clone (Origene, NM_010173), and lysates were processed in parallel. Forebrain lysate from FAAH knockout mice5 were used as a negative control.
FAAH Activity Assay
FAAH activity from forebrain lysates was measured as the conversion of AEA labeled with [3H] in the ethanolamine portion of the molecule ([3H]AEA) to [3H]ethanolamine as reported previously33. Membranes were incubated in a final volume of 0.5 ml of TME buffer (50mM Tris-HCl, 3.0mM MgCl2, and 1.0mM EDTA, pH 7.4) containing 1.0mg/ml fatty acid-free bovine serum albumin and 0.2nM [3H]AEA. Isotherms were constructed using eight concentrations of AEA at concentrations between 10nM and 10µM. Incubations were carried out at 37°C and were stopped with the addition of 2ml of chloroform/methanol (1:2). After standing at ambient temperature for 30 minutes, 0.67ml of chloroform and 0.6ml of water were added. Aqueous and organic phases were separated by centrifugation at 1,000rpm for 10 minutes. The amount of [3H] in 1ml of the aqueous phase was determined by liquid scintillation counting and the conversion of [3H]AEA to [3H]ethanolamine was calculated. The Vmax values for this conversion were determined by fitting the data to a single site competition equation using Prism.
Lipid Extraction from Tissue for eCB Levels
For analysis of endocannabinoid content, brain regions were subjected to a lipid extraction process. Forebrain tissue samples were weighed and placed into borosilicate glass culture tubes containing 2ml of acetonitrile with 5pmol of [2H8]anandamide and 5nmol of [2H8]2-arachidonoylglycerol for extraction. Tissue was homogenized with a glass rod and sonicated for 30 minutes on ice. Samples were incubated overnight at −20°C to precipitate proteins then centrifuged at 1,500g to remove particulates. The supernatants were removed to a new glass tube and evaporated to dryness under N2 gas. The samples were resuspended in 300µl of acetonitrile to recapture any lipids adhering to the glass tube, and dried again under N2 gas. Finally, lipid extracts were suspended in 20µl of acetonitrile, and stored at −80°C until analysis.
Mass Spectrometrical Detection of eCBs
Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analyses were carried out on an Eksigent ekspert™ micro LC 200 coupled with an AB Sciex Qtrap™ 5500 mass spectrometer, installed with a Turbo V™ Spray ion source (AB Sciex, Canada). The LC was equipped with a temperature-controlled CTC autosampler. An Eksigent HALO C18 HPLC column (1 × 50mm, 2.7µm particle diameter, 90Å pore size) was used. Samples were analyzed isocratically, at a flow rate of 30µl/minute and a solvent composition of 15% mobile phase A (10mM ammonium acetate in water), and 85% mobile phase B (acetonitrile). After 3.25 minutes, the column was regenerated with 100% B. Before each injection, the column was re-equilibrated at the initial mobile phase condition for 2 minutes. Following each LC-MS/MS run, a blank was run. The sample injection loop (5µL loop size) was rinsed with 40µL of methanol, and the column purged for 5 minutes with 100% B for 4.5 minutes and followed by 85% B for 0.5 minutes. This was intended to mitigate cross contaminations due to carryover from preceding sample injections. The LC column was maintained at 25°C, and the samples at 10°C.
The mass spectrometer was operated in positive ion mode, with the ion-spray voltage set at 5500V, curtain gas at 20 (arbitrary units), source gas 1 and gas 2 both at 40 (arbitrary units), and source temperature at 300°C. Protonated molecular ions of AEA (m/z 348) and AEA-d8 (m/z 356), and ammonium adduct ions of 2-AG (m/z 396) and 2-AG-d8, (m/z 404) were selected as the respective precursor ions for CID. MRM scan modes were used with Q1 and Q3 both at unit resolution. Optimized collision energies for the transitions were as follows: AEA (348 to 62) CE 22V, AEA-d8 (356 to 62) CE 22V, 2-AG (396 to 287) CE 15V; and 2-AG-d8 (404 to 294) CE 17V.
Each brain tissue extract sample was further diluted in ACN to yield a 100-fold diluted sample, for the LC-MS/MS quantification of 2-AG, while the undiluted extract sample was analyzed directly for quantification of AEA. It has been reported that 2-AG undergoes spontaneous isomerization converting to 1-AG by acyl group migration during tissue extraction and reconstitution procedures. We also observed that 1-AG was present in authentic standard solutions of 2-AG, as well as brain tissue extracts. Peak areas of 1-AG and 2-AG were combined to establish a standard calibration curve for 2-AG. The data processing was accomplished using Analyst® 1.5.2 software (AB Sciex). Linear regressions of relative peak areas (analyte to IS ratios) were performed over analyte concentrations from 0.00025 to 0.25pmol/µl (AEA), and 0.0025 to 2.5pmol/µl (2-AG). Analyte levels were normalized to tissue weight.
CB1 Receptor Binding Assay
CB1 receptor agonist binding parameters were determined using radioligand binding using a Multiscreen Filtration System with Durapore 1.2-lM filters in 96-well filter plates (Millipore, USA) through a protocol previously described34. Incubations (total volume=0.2mL) were carried out using TME buffer containing 1mg/ml bovine serum albumin (TME/BSA). Membranes (10µg protein per incubate) were added in triplicate to wells containing 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 or 2.5nM [3H]CP 55,940 (American Radiochemicals, USA), a cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonist, and incubated for 1hr at room temperature on an orbital shaker. Ten micromolar AM251 (Tocris Biosciences, USA) was used to determine non-specific binding. Bmax (maximal binding site density) values were determined by nonlinear curve fitting of specific binding data to the single site binding equation using GraphPad Prism (GraphPad, USA).
Behavioral Overview
In order to reduce experimental variability, age-matched littermate pairs resulting from heterozygous crossings were randomly assigned to experimental groups. Only adult male mice were used for all experiments. All behavioral measurements were performed by observers blind to genotype. All animals were kept on a 12:12 light-dark cycle at 18°C~22°C with food and water available ad libitum unless noted otherwise. All procedures were in accordance with the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Weill Cornell Medical College.
Cued Fear Conditioning and Extinction Procedure
The task was conducted as described previously35. Briefly, the fear conditioning apparatus consisted of a mouse shock-chamber (Coulbourn Instruments, USA) placed in a sound-attenuated box. On day 1 (acquisition), after a 2 minute acclimation period to the conditioning chamber (scented with 0.1% peppermint in 70% EtOH), mice were fear conditioned with three tone-shock pairings, consisting of a 30-second presentation of a tone (conditioned stimulus; 5 kHz, 70 dB) that coterminated with a 0.7mA foot shock (unconditioned stimulus) during the last 1.0s of the tone with an intertrial interval (ITI) of 30 seconds. Mice remained in the conditioning chamber for 1 minute before being returned to their home cages. Twenty-four hours after fear acquisition, mice were exposed to 5 presentations of the tone in the absence of shock (extinction). To eliminate any confounding interactions of contextual fear, tones were presented in a novel context, consisting of a white cylindrical arena (scented with 0.1% lemon in 70% EtOH). Tone presentations lasted for 30 seconds with an ITI of 30 seconds. After the final tone presentation, mice remained in the conditioning chamber for 1 minute before being returned to their home cages. Fear extinction trials were repeated daily for a total of 4 days of extinction training. Graphic State 3.02 software was used to control experiments. Mice were videotaped for subsequent analysis. Freezing was defined as the absence of visible movement except that required for respiration36. The percentage time spent freezing was calculated by dividing the amount of time spent freezing during the 30-second tone presentations by the duration of the tone.
Elevated Plus Maze (EPM) Procedure
The EPM task was conducted as described previously37. The maze was constructed of grey Plexiglas, raised 70 cm above the floor, and consisted of two opposite closed arms with 14cm high opaque walls and two opposite open arms of the same size (29cm × 6cm). The maze was set up under a digital camera connected to a video recorder and computer under the control of Ethovision XT 5.0 software (Noldus, USA) to live track subject movements. A single testing session of 10 minutes was carried out under dim light (~6 Lux in center of maze). To begin a trial, the animal was placed in the center of the maze facing an open arm. The maze was cleaned with a 70% ethanol solution between trials to eliminate possible odor cues left by previous subjects. Measures of anxiety-like behavior were assessed by calculating the percentage time spent in the open arms by dividing the amount of time spent in the open arms by the duration of the trial (10 minutes).
Novelty Induced Hypophagia (NIH) Procedure
The task was conducted as described previously38. Briefly, mice received 3 consecutive days of training (Day1–3) prior to testing in a room with dim lighting in order to acclimate to the milk and the manner in which it is administered (metal nozzle). Training consisted of presenting the mice with a standard dual bearing sipper tube (5oz. bottle) inserted between the wire bars of the home cage lid containing 90% sweetened condensed milk diluted in tap water. On day 4, mice underwent home cage testing in which all mice were placed into a holding cage and then returned to the home cage one at a time for testing in dim lighting. The latency to drink was recorded over a 10-minute period. Mice that did not approach the sipper bottle during the home cage test were excluded from the study (4 mice total). There were no baseline differences in latency to drink between groups in the home cage test. On day 5, novel cage testing was conducted by placing a single mouse into a clean cage with no bedding of the same dimensions as their home cage, but under bright conditions and with a white piece of paper under the cage. Excess light was focused specifically on the sipper bottle. Mice were again presented with a sipper tube containing 90% sweetened milk and the latency to drink over a 10-minute period was reported as a measure of anxiety-like behavior.
c-Fos Immunohistochemistry
All experiments were carried out at room temperature, as previously described38, unless otherwise specified. 90 minutes after exposure to experimental factors, mice were sacrificed by intraperitoneal injection of Euthasol and perfused through the heart with 30ml of saline followed by 90ml of 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1M sodium phosphate (pH 7.4) at flow rate of 30ml/min. Brains were removed and post-fixed overnight in 4% paraformaldehyde before transferred to 30% sucrose in 0.1M sodium phosphate (pH 7.4) for 48 hours at 4°C. Brains were frozen in powdered dry ice and stored at −20°C until sectioning. Coronal sections (40µm) of whole brain were cut by using sliding microtome frozen by powdered dry ice. Six sets of serial sections were collected in Ependoff tubes each containing 2ml cryoprotectant (30% glycerol and 30% Ethylene glycol in 0.1 M sodium phosphate, pH 7.4) and stored at −20°C. Free-floating serial sections (take 1 every third) were washed (3 times for 10 minutes each) in TBS, incubated for 30 minutes in a blocking solution containing 4% normal horse serum (NHS) and 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in TBS with 0.2% Triton X-100 (TBS-Tx), and incubated overnight at 4°C with rabbit anti-c-Fos primary antibody (c-Fos sc-52, Lot# F2209, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, USA; sc-52 antibody was raised against amino acids 3–16 of human c-Fos: SGFNADYEASSSRC) diluted 1:1000 mixed with goat anti-parvalbumin primary antibody (1:2000, Lot# PVG 214, Swant, Switzerland) in the blocking solution mentioned above. Sections were then washed in TBS and incubated for 2 hours with Alexa Fluor labeled donkey anti-rabbit and anti-goat IgG secondary antibodies (Alexa Fluor 555 and 488) diluted 1:500 in TBS-Tx. Sections were again washed, mounted on chromalum/gelatin-coated slides, and air-dried for 2 hours in dark. Slides were cover slipped by water-soluble glycerol based mounting medium containing DAPI, and sealed with nail polish. Estimation of cell density of c-Fos positive neurons in amygdala was performed with StereoInvestigator 9.0 (Microbrightfield, USA). Briefly, serial sections (every third section - 120µm were numbered by rostra-caudal order, and contours of BLA was traced by referring to the Allen Brain Map (Allen Co., USA). For the boundaries of the amygdala, we used parvalbumin counter-stain combined with DAPI to yield a clear boundary for sub-nuclei or layers. All cells across all sections per animal were counted. Individual cell density was calculated for each mouse by dividing the total sampled cell numbers by the total volume of the region.
Stereotaxic Injections of Tracers
Mice were microinjected with 10nl of 4% fluorogold (FG) (Fluorochrome, USA) retrograde tracer in neutral saline or 50nl of adeno-associated virus 2 expressing enhanced green fluorescent protein (AAV2-eGFP) (CMV promoter, 5×1011 VG/ml, Vector Biolabs, USA) into the prelimbic (PL) (anterior-posterior =1.9mm, medial-lateral=0.4mm, dorsal-ventral=1.98mm) or infralimbic (IL) (anterior-posterior=2.0mm, medial-lateral=0.3mm, dorsal-ventral=2.0mm) prefrontal cortex. Mice were anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of ketamine and xylazine cocktail at 0.1ml/10g body weight and mounted on a stereotaxic alignment system (David Kopf Instruments, USA). After surgical exposure of skull, 3% of H2O2 solution was applied to enhance sutures and bregma. Stereotaxic coordination was performed by using an electrical drill mounted on a manipulator (David Kopf Instruments, USA) and microinjection was performed by Nanoject II (Drummond Scientific Nanoject II, Fisher Scientific, USA). Small deposits of FG or AAV2-eGFP tracers were pressure-injected 3 times over 2 minutes each into IL or PL using glass micropipette (tip diameter 25µm). The needle was left in place for additional 10 minutes to prevent leakage up the needle track and then slowly withdrawn.
Following a survival time of 7 days after FG injections or 10 days after AAV2-eGFP injections, animals were deeply anesthetized with Euthasol 0.1ml/10g body weight and perfused through the heart with 30ml of 0.9% saline followed by 120ml of cold 4% paraformaldehyde in a 0.01M sodium phosphate buffer (25ml/min) using Perfusion Two automated pressure perfusion system (Leica Microsystems, USA). Brains were removed and post-fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in a 0.01M sodium phosphate buffer at 4°C overnight then transferred to a sucrose solution (30% sucrose in 0.1M PB) at 4°C for 48 hours. Coronal sections were cut on a freezing microtome (40µm). One section in every three was immediately mounted. The remaining sections were stored in cryoprotectant solution (30% Glycerol, 30% ethylene glycol and 40% 0.25M PB) at −20°C. The mounted sections were air dried for at least 3 hours and cover-slipped by using a FG-enhancing solution (10% SiO2, 0.1M Tris, pH 11).
Injection sites were confirmed by referring to Allen Mouse Brain Map (Allen Co., USA). Sections were observed under Nikon 80i fluorescent microscope with a DAPI/FITC/Rhodamine Tri-color filter. Digital photography was performed using a MicroFire camera and FireFrame software (Optronics, USA) and stereological estimation of cell density was performed using StereoInvestigator software (MicroBrightfeild, USA). Contours of the basolateral amygdala (BLA) were drawn and random sampling was applied to contours. Total volume of BLA was estimated using Cavalieri method. Total cell numbers were estimated by Fractionator with counting frame size 25×25×40µm and sampling grid size 100×100µm. Cell density was calculated by total cell number divided by total volume. Detection of fiber density was performed using a stereological method39. Briefly, sections were traced under 4× lens then perimetrics probe analysis was done under a 40× lens. Counting frame was set to 25×25µm and radius of Merz coherent test system was set to 5µm. Total length of all sampling sites was automatically calculated. For each animal, fiber density is obtained from the sum of the lengths divided by the sum of the areas for all sections.
Human Participants
All participants reported no past, present, or first-degree family history of a psychiatric or neurologic disorder and no history of head trauma. Imaging participants were also all right-handed and pre-screened for MRI contraindications (e.g. metal plates or implants, braces). All participants submitted written informed consent approved by the Institutional Review Board prior to the study. Compensation was provided as described in their written consent form. In total, 240 participants took part in this study. Each experiment was conducted on an independent cohort of subjects (Supplementary Table 1–3).
Human Genotyping
Human subjects provided saliva samples (Oragene, DNA Genotek Inc., Canada) from which we extracted genomic DNA according to the manufacturer’s standard protocol. Genotyping for the FAAH C385A polymorphism (rs324420) was performed using a Taqman 5’ exonuclease assay (assay C___1897306_10, Applied Biosystems, USA) run on an Applied Biosystems 7900HT real time thermal cycler. Genotypes were called using Sequence Detection System software version 2.3. All samples that did not result in automated genotype calls were re-run in duplicate and those samples that provided concordant genotypes called by visual inspection on re-run were used for analysis.
Image Acquisition
All subject MRI data were collected with a Siemens MAGNETOM TrioTim MRI scanner (Siemens Medical Solutions, Germany). From each subject, we acquired a high-resolution, T1-weighted anatomical scan (256×192 in-plane resolution, 240mm field of view, 160 1.2mm slices) for normalization to a standard template40. Functional imaging data were pooled from multiple studies, resulting in slight differences in functional acquisition parameters. All functional data were collected using echo-planar imaging with interleaved acquisition. A representative example of specific acquisition parameters is: TR=3000ms echo time=30ms, field of view=240mm, flip angle=90°, 46 slices of 3.8×3.8×3.5mm voxels. During each resting state run, subjects were presented with a white visual fixation crosshair on a black background. They were asked to stay awake and refrain from movement during the task. Subjects completed either 1 run of 128 TRs or 2 runs of 150 TRs (see Imaging Data Preprocessing and Analysis showing similar genotypic effects regardless of number of acquisitions).
Imaging Data Preprocessing and Analysis
All subject’s resting state data underwent identical preprocessing steps. Imaging data were processed using Analysis of Functional Neuroimages (AFNI) software tools41. Scans were slice-time corrected for temporal alignment to this first slice of each volume. Calculations were then performed for rigid-body alignment of all functional volumes to the first series functional volume, rigid-body alignment of the subject’s anatomical scan to their first functional volume, and nonlinear transformation of the subject anatomical to the standard template. These three transformation matrices were combined and applied in a single step to minimize interpolation error. Functional scans were blurred to a target FWHM of 4.0mm.
To minimize effects of motion on resting state fMRI data, we followed recent recommendations for motion artifact correction42. Functional volumes exceeding a 0.2mm framewise displacement, along with the preceding volume, were censored and excluded from all further preprocessing steps. A general linear model (GLM) was used to compute the effects of 27 parameters: 6-motion parameters and their 6 first-derivatives, as well as average time courses from an eroded white-matter mask, and eroded grey-matter mask, and global signal. In addition, band-pass filtering (0.01 to 0.1Hz) and regression were applied concurrently on sub-motion-threshold TRs only to avoid reintroduction of noise from unfiltered regressors43. The error term of this GLM was used for subsequent analysis.
We compared connectivity between a priori cortical areas of interest and the amygdala. First, time series were extracted from subgenual vmPFC and dorsal ACC seed regions of interest (ROIs). We drew 4mm spherical ROIs around the center of activation of these two brain regions areas as defined in previous studies presenting convergent functional or structural evidence of a role for these regions in fear expression (dorsal ACC) or regulation (subgenual vmPFC)18, 19. These seeds overlap with regions of activation correlating with fear regulation and expression from several other fear conditioning studies44, 45, 46. A target ROI was constructed using a standard-based atlas, forming a bilateral mask of the amygdala. We calculated the mean correlation coefficient between each seed ROI and the target ROI. These values were Fischer-transformed then compared between subject groupings based on FAAH C385A genotype.
Due to the potential of temporal and frontal lobe signal dropout, we manually checked each subject for coverage of ROIs before including them in the final analysis. Only subjects with complete coverage of both seed ROIs and the target ROI were selected. We observed no volumetric structural differences between genotypic groups in either of our cortical ROIs (data not shown). These data were analyzed including covariates of age, gender, ethnicity, and number of resting state scans. The main effect of genotype remained significant for subgenual vmPFC – amygdala connectivity [F(8,26)=4.88, P = 0.036] and there was no effect of dorsal ACC – amygdala connectivity [F(8,26)=0.68, P = 0.080].
Human Fear Conditioning and Extinction Procedure
We utilized a two-day fear conditioning/extinction paradigm. Acquisition occurred on experimental day 1 and extinction occurred 24 hours later on experimental day 2. Acquisition and extinction took place in different visual contexts consisting of pictures of rooms presented on the computer screen (Contexts A & B47). Cues were two colored windows (blue and yellow) that were otherwise black, embedded within each visual context. The unconditioned stimulus (US) was a hybrid consisting of auditory and visual components. The visual component was derived from a set of validated aversive pictures from the International Affective Picture Series48. The auditory component was a validated custom-designed hybrid of white noise and a 1000Hz tone with duration of one second, intensity tiered for smooth onset and offset. It was created using the software Audacity 1.2.6 and was rated as aversive in multiple independent experiments (http://audacity.sourceforge.net)35, 49, 50. Fear acquisition took place in Context A. One cue was paired with the US at a 50% reinforcement rate (CS+). Each presentation of the US consisted of the same sound and a different picture. The other cue (CS−) was never followed by the US. Participants were presented 32 trials during acquisition (8 CS+US, 8 CS+ and 16 CS−). Twenty-four hours later, participants returned for experimental day 2, which took place in Context B and consisted of a 32-trial extinction session (16 CS+, 16 CS−). Stimuli were presented in a pseudo-randomized order, defined by non-consecutive CS+USs during conditioning and no more than three consecutive squares of the same color in any session. Visual contexts, stimuli and script orders were counterbalanced across subjects. Fear response was measured by skin conductance response (SCR), an index of autonomic nervous system activity51. Differential fear responding was calculated by subtracting normalized and scaled SCR to the CS− from corresponding CS+ responses. Only subjects who showed fear acquisition (magnitude of SCR to the CS+ was greater than to the CS− during acquisition) were included in the analyses.
In this experiment, half the participants were randomly assigned to either a reconsolidation update or extinction only condition. Participants who were assigned to the reconsolidation update condition received a single presentation of the CS+, unpaired with the aversive stimulus, prior to a 10-minute rest period followed immediately by the extinction session. Controlling for the effects of this experimental condition together with age, sex and ethnicity results in a similar main effect of genotype for late trials [F(1,32)=3.09, P < 0.09]. Genotypic differences in fear extinction learning diminished with 5 additional extinction trials [main effect of genotype: [F(1,32)=0.04, P = 0.83, CC: −0.031±0.028; AC/AA: −0.044±0.028].
Physiological Response Measurement and Analysis
Throughout fear conditioning and extinction, participant skin conductance response (SCR) was recorded via disposable electrodes attached to the distal phalanx of the second and third digits of the left hand. Electrodes came pre-filled with isotonic gel. All stimuli were presented using E-prime software (Psychology Software Tools, USA). This software sent time markers to the skin conductance recording system (MP35; Biopac, USA), which recorded and amplified SCR in combination with AcqKnowledge software (Biopac, USA).
SCR was recorded at a sampling frequency of 200Hz with a 1Hz filter and manually smoothed. After each stimulus presentation, the first SCR peak occurring within 0.5–4.5s was considered the subject’s response to that stimulus. Responses, as estimated by the difference between trough and peak, were only included in analysis when greater than 0.02µS52. Responses smaller than this threshold were replaced with zeros during analysis. During analysis, individual SCR responses were square root transformed and scaled to that participant’s largest CS+US acquisition response. Normalized SCR scores were averaged separately by stimulus type (CS+, CS−, CS+US). All presented responses were calculated as the difference between CS+ and CS− responses.
Anxiety Self-Report
A subset of participants (Supplementary Table 3) completed the State Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI-S; STAI-T) self-report questionnaires separately assessing current and general levels of anxiety53. These results remained significant after co-varying the effects of age, sex, and ethnicity [main effect of genotype: F(7,129)=5.22, P < 0.024]
Statistics
When two groups were compared, data were analyzed using a Student’s t-test. For multiple comparisons, a one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post-hoc test or a two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test was used. A value of P ≤ 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Alternative Statistical Analyses
To examine the robustness of the human findings given uncertainty about the true distribution of this data, we tested our main hypotheses using a Bayesian statistical framework. Statistical analysis was performed within the R statistical software package, version 2.15.154. Bayesian statistical analyses were implemented using the “Bayesian estimation” (BEST) software package for R55.
STAI Replication Analysis
We examined the effect of the rs324420 allele in our fear extinction cohort to determine if this behavioral genetic finding was replicable. We examined the correlation between number of mutant C385A alleles and normalized STAI-trait anxiety scores.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the resources and staff at the Biomedical Imaging Core Facility of the Citigroup Biomedical Imaging Center at Weill Cornell Medical College, a generous gift by the Dr. Mortimer D. Sackler family. We acknowledge support from NIH grants MH079513 (B.J.C., F.S.L., C.E.G.), MH060478 (B.J.C.), NS052819 (F.S.L.), GM07739 (A.D.), EY007138 (D.C.J), DA017259 (B.F.C.), and the Pritzker Neuropsychiatric Disorders Research Consortium (F.S.L., C.E.G.), the NewYork Presbyterian Hospital Youth Anxiety Center (F.S.L., B.J.C.), Brain and Behavior Research Foundation (F.S.L., D.Q.J.), DeWitt-Wallace Fund of the New York Community Trust (F.S.L., B.J.C., C.E.G.), and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (M.N.H) and Alberta Innovates Health Solutions (J.M.G). The authors would also like to acknowledge the Southern Alberta Mass Spectrometry (SAMS) Centre, located in and supported by the Cumming School of Medicine, University of Calgary for their services in targeted LC-MS-MS. We acknowledge Dr. Jack Barchas for extensive discussions on the design and implementation of these studies.
Footnotes
Author Contributions I.D. and A.T.D. collected and analyzed mouse extinction and human anxiety data, respectively, and were involved in manuscript preparation. K.A.H. was involved in study design. D.C.J. collected and analyzed human extinction data. I.D., A.T.D., K.A.H., and D.C.J. contributed equally to this work. D.Q.J. performed stereotaxic injections and along with R.Y. performed immunohistochemitry studies. E.C.K. performed Western blot analysis and along with S.R. collected mouse anxiety data. A.M.D. generated the FAAH mouse knock-in line. J.M.G. and M.N.H. performed enzymatic activity, endocannabinoid content and receptor binding assays. B.F.C. provided the FAAH−/− mouse line, and was involved in study design. M.N.H. was also involved in study design and manuscript preparation. C.H. maintained mouse colony and genotyping. C.E.G. performed human genotyping and was involved in manuscript preparation. B.J.C. and F.S.L. designed the study and were involved in data analysis and manuscript preparation. All authors discussed the results and comments of the manuscript.
Competing Financial Interests
M. N. H. is a consultant for Pfizer. All other authors declare no competing financial or other interest.
References
- 1.Hariri AR, et al. Divergent effects of genetic variation in endocannabinoid signaling on human threat- and reward-related brain function. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;66:9–16. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.10.047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gunduz-Cinar O, et al. Convergent translational evidence of a role for anandamide in amygdala-mediated fear extinction, threat processing and stress-reactivity. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;18:813–823. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hill MN, Miller GE, Ho WS, Gorzalka BB, Hillard CJ. Serum endocannabinoid content is altered in females with depressive disorders: a preliminary report. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2008;41:48–53. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-993211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gunduz-Cinar O, Hill MN, McEwen BS, Holmes A. Amygdala FAAH and anandamide: mediating protection and recovery from stress. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013;34:637–644. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.08.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cravatt BF, et al. Supersensitivity to anandamide and enhanced endogenous cannabinoid signaling in mice lacking fatty acid amide hydrolase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:9371–9376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.161191698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Abecasis GR, et al. An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature. 2012;491:56–65. doi: 10.1038/nature11632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sipe JC, Chiang K, Gerber AL, Beutler E, Cravatt BF. A missense mutation in human fatty acid amide hydrolase associated with problem drug use. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:8394–8399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.082235799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sipe JC, et al. Biomarkers of endocannabinoid system activation in severe obesity. PLoS One. 2010;5:e8792. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chiang KP, Gerber AL, Sipe JC, Cravatt BF. Reduced cellular expression and activity of the P129T mutant of human fatty acid amide hydrolase: evidence for a link between defects in the endocannabinoid system and problem drug use. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13:2113–2119. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kathuria S, et al. Modulation of anxiety through blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Nat Med. 2003;9:76–81. doi: 10.1038/nm803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chhatwal JP, Davis M, Maguschak KA, Ressler KJ. Enhancing cannabinoid neurotransmission augments the extinction of conditioned fear. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30:516–524. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vidal-Gonzalez I, Vidal-Gonzalez B, Rauch SL, Quirk GJ. Microstimulation reveals opposing influences of prelimbic and infralimbic cortex on the expression of conditioned fear. Learn Mem. 2006;13:728–733. doi: 10.1101/lm.306106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Laurent V, Westbrook RF. Inactivation of the infralimbic but not the prelimbic cortex impairs consolidation and retrieval of fear extinction. Learn Mem. 2009;16:520–529. doi: 10.1101/lm.1474609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sierra-Mercado D, Padilla-Coreano N, Quirk GJ. Dissociable roles of prelimbic and infralimbic cortices, ventral hippocampus, and basolateral amygdala in the expression and extinction of conditioned fear. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36:529–538. doi: 10.1038/npp.2010.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Phelps EA, LeDoux JE. Contributions of the amygdala to emotion processing: from animal models to human behavior. Neuron. 2005;48:175–187. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.09.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hartley CA, Phelps EA. Changing fear: the neurocircuitry of emotion regulation. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35:136–146. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Phelps EA, Delgado MR, Nearing KI, LeDoux JE. Extinction learning in humans: role of the amygdala and vmPFC. Neuron. 2004;43:897–905. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.08.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Milad MR, Quirk GJ, Pitman RK, Orr SP, Fischl B, Rauch SL. A role for the human dorsal anterior cingulate cortex in fear expression. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;62:1191–1194. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.04.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schiller D, Delgado MR. Overlapping neural systems mediating extinction, reversal and regulation of fear. Trends Cogn Sci. 2010;14:268–276. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2010.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kim H, et al. Contextual modulation of amygdala responsivity to surprised faces. J Cogn Neurosci. 2004;16:1730–1745. doi: 10.1162/0898929042947865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Urry HL, et al. Amygdala and ventromedial prefrontal cortex are inversely coupled during regulation of negative affect and predict the diurnal pattern of cortisol secretion among older adults. J Neurosci. 2006;26:4415–4425. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3215-05.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hare TA, Tottenham N, Galvan A, Voss HU, Glover GH, Casey BJ. Biological substrates of emotional reactivity and regulation in adolescence during an emotional go-nogo task. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;63:927–934. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.03.015015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kim MJ, Gee DG, Loucks RA, Davis FC, Whalen PJ. Anxiety dissociates dorsal and ventral medial prefrontal cortex functional connectivity with the amygdala at rest. Cereb Cortex. 2011;21:1667–1673. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhq237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Burghy CA, et al. Developmental pathways to amygdala-prefrontal function and internalizing symptoms in adolescence. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15:1736–1741. doi: 10.1038/nn.3257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hahn A, et al. Reduced resting-state functional connectivity between amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex in social anxiety disorder. Neuroimage. 2011;56:881–889. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.02.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kim MJ, et al. The structural and functional connectivity of the amygdala: from normal emotion to pathological anxiety. Behav Brain Res. 2011;223:403–410. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.04.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Moreira FA, Kaiser N, Monory K, Lutz B. Reduced anxiety-like behaviour induced by genetic and pharmacological inhibition of the endocannabinoid-degrading enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) is mediated by CB1 receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2008;54:141–150. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chhatwal JP, Ressler KJ. Modulation of fear and anxiety by the endogenous cannabinoid system. CNS Spectr. 2007;12:211–220. doi: 10.1017/s1092852900020939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Conzelmann A, et al. A polymorphism in the gene of the endocannabinoid-degrading enzyme FAAH (FAAH C385A) is associated with emotional-motivational reactivity. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2012;224:573–579. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2785-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dulawa SC, Hen R. Recent advances in animal models of chronic antidepressant effects: the novelty-induced hypophagia test. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2005;29:771–783. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dragunow M, Faull R. The use of c-fos as a metabolic marker in neuronal pathway tracing. J Neurosci Methods. 1989;29:261–265. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(89)90150-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yang J, et al. Neuronal release of proBDNF. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:113–115. doi: 10.1038/nn.2244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lee TT, Hill MN, Hillard CJ, Gorzalka BB. Temporal changes in N-acylethanolamine content and metabolism throughout the peri-adolescent period. Synapse. 2013;67:4–10. doi: 10.1002/syn.21609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lee TT, Hill MN. Age of stress exposure modulates the immediate and sustained effects of repeated stress on corticolimbic cannabinoid CB(1) receptor binding in male rats. Neuroscience. 2013;249:106–114. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.11.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pattwell SS, et al. Altered fear learning across development in both mouse and human. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:16318–16323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206834109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fanselow MS. Conditioned and unconditional components of post-shock freezing. Pavlov J Biol Sci. 1980;15:177–182. doi: 10.1007/BF03001163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chen ZY, et al. Genetic variant BDNF (Val66Met) polymorphism alters anxiety-related behavior. Science. 2006;314:140–143. doi: 10.1126/science.1129663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Malter Cohen M, Jing D, Yang RR, Tottenham N, Lee FS, Casey BJ. Early-life stress has persistent effects on amygdala function and development in mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:18274–18278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1310163110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Howard CV, Reed MG. Unbiased stereology. New York: Garland Science; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Talairach J, Tournoux P. Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain : 3-dimensional proportional system : an approach to cerebral imaging. Georg Thieme; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Cox RW. AFNI: software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput Biomed Res. 1996;29:162–173. doi: 10.1006/cbmr.1996.0014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Power JD, Mitra A, Laumann TO, Snyder AZ, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE. Methods to detect, characterize, and remove motion artifact in resting state fMRI. Neuroimage. 2014;84:320–341. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.08.048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hallquist MN, Hwang K, Luna B. The nuisance of nuisance regression: spectral misspecification in a common approach to resting-state fMRI preprocessing reintroduces noise and obscures functional connectivity. Neuroimage. 2013;82:208–225. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Etkin A, Egner T, Kalisch R. Emotional processing in anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex. Trends Cogn Sci. 2011;15:85–93. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2010.11.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mechias ML, Etkin A, Kalisch R. A meta-analysis of instructed fear studies: implications for conscious appraisal of threat. Neuroimage. 2010;49:1760–1768. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.09.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Klucken T, Kagerer S, Schweckendiek J, Tabbert K, Vaitl D, Stark R. Neural, electrodermal and behavioral response patterns in contingency aware and unaware subjects during a picture-picture conditioning paradigm. Neuroscience. 2009;158:721–731. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.09.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Milad MR, Orr SP, Pitman RK, Rauch SL. Context modulation of memory for fear extinction in humans. Psychophysiology. 2005;42:456–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2005.00302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lang PJ. University of Florida; 2005. International Affective Picture System (IAPS): Affective ratings of pictures and instruction manual. (ed^(eds). [Google Scholar]
- 49.Soliman F, et al. A genetic variant BDNF polymorphism alters extinction learning in both mouse and human. Science. 2010;327:863–866. doi: 10.1126/science.1181886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Levita L, Hare TA, Voss HU, Glover G, Ballon DJ, Casey BJ. The bivalent side of the nucleus accumbens. Neuroimage. 2009;44:1178–1187. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.09.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.LaBar KS, Gatenby JC, Gore JC, LeDoux JE, Phelps EA. Human amygdala activation during conditioned fear acquisition and extinction: a mixed-trial fMRI study. Neuron. 1998;20:937–945. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80475-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Schiller D, Monfils MH, Raio CM, Johnson DC, Ledoux JE, Phelps EA. Preventing the return of fear in humans using reconsolidation update mechanisms. Nature. 2010;463:49–53. doi: 10.1038/nature08637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.CD S. STAI: manual for the State Trait Anxiety Inventory. 3 edn. Consulting Psychologists Press; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Team RC. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2012 http://www.R-project.org/ [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kruschke JK. BEST: Bayesian Estimation Supersedes the t-Test. 2013 doi: 10.1037/a0029146. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=BEST. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.