Abstract
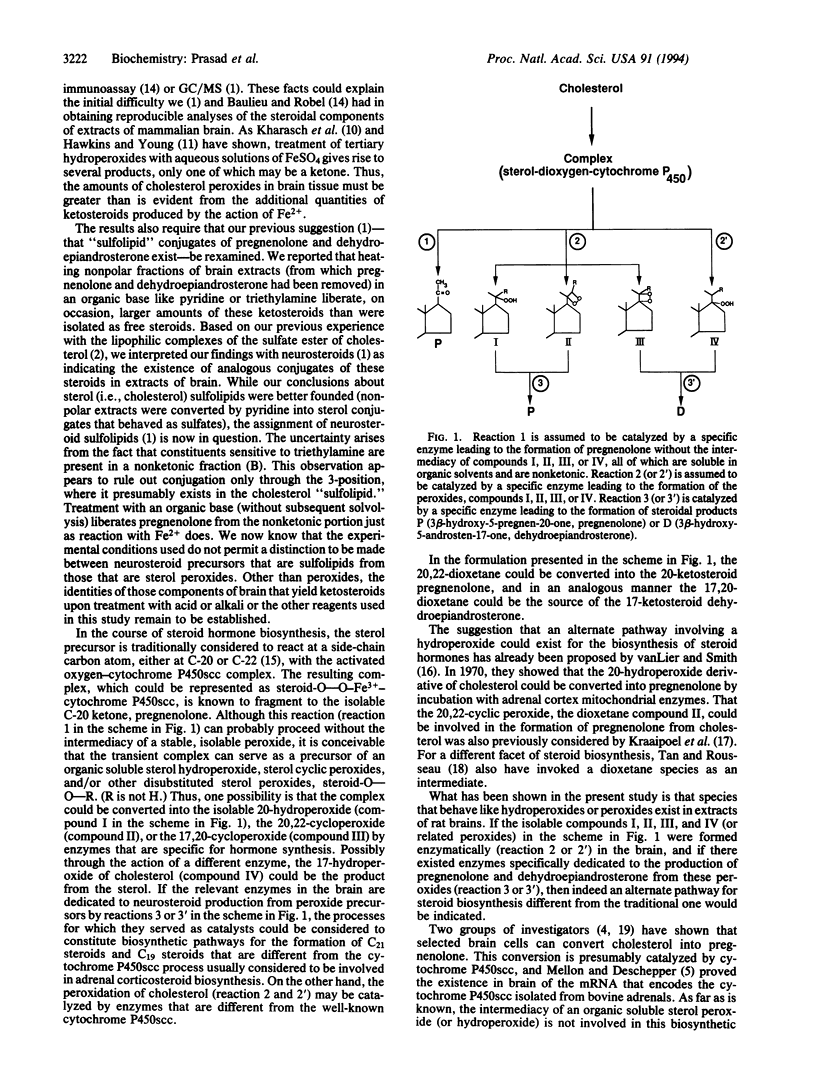
In addition to the neurosteroids pregnenolone and dehydroepiandrosterone, organic solvent extracts of rat brains contain related compounds that react with various reagents to yield additional amounts of these ketosteroids. Among the chemicals producing these increments are triethylamine, HCl, FeCl3, and Pb(OAc)4. Most revealing is the action of FeSO4 on these extracts. This reducing agent also converts components of the extract into the two neurosteroids, suggesting the presence of sterol hydroperoxides or peroxides in brain. The clues provided by this study indicate that the chemical nature of the steroidal constituents existing in extracts of mammalian brains remains to be determined. It is likely that their association with neurological functions will be better understood when the structures of these substances are established.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baulieu E. E., Robel P. Neurosteroids: a new brain function? J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;37(3):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(90)90490-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein S., Dinh J., Co N., Gut M., Schleyer H., Cooper D. Y., Rosenthal O. Kinetic studies on substrate-enzyme interaction in the adrenal cholesterol side-chain cleavage system. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 18;11(15):2883–2891. doi: 10.1021/bi00765a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein S., Zamoscianyk H., Co N., Adelson M., Prasad D. S., Greenberg A., Gut M. Side-chain cleavage of cholesterol to C6 and C8 compounds by adrenal and testis tissue preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;231(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochberg R. B., Mickan H., Lieberman S. Are C19 androgens formed by cleavage of a C8 fragment from cholesterol? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;231(1):208–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Z. Y., Bourreau E., Jung-Testas I., Robel P., Baulieu E. E. Neurosteroids: oligodendrocyte mitochondria convert cholesterol to pregnenolone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8215–8219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung-Testas I., Hu Z. Y., Baulieu E. E., Robel P. Neurosteroids: biosynthesis of pregnenolone and progesterone in primary cultures of rat glial cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Oct;125(4):2083–2091. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-4-2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann R. A. Enzymatic cleavage of the cholesterol side chain to dehydroepiandrosterone and 2-methylheptan-6-one. Steroids. 1968 Aug;12(2):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(68)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman S., Bandy L., Lippman V., Roberts K. D. Sterol intermediates in the conversion of cholesterol into pregnenolone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 21;34(4):367–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90389-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luttrell B., Hochberg R. B., Dixon W. R., McDonald P. D., Lieberman S. Studies on the biosynthetic conversion of cholesterol into pregnenolone. Side chain cleavage of a t-butyl analog of 20 -hydroxycholesterol, (20R(-t-butyl-5-pregnene-3 ,20-diol, a compound completely substituted at C-22. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1462–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur C., Prasad V. V., Raju V. S., Welch M., Lieberman S. Steroids and their conjugates in the mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):85–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon S. H., Deschepper C. F. Neurosteroid biosynthesis: genes for adrenal steroidogenic enzymes are expressed in the brain. Brain Res. 1993 Dec 3;629(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91332-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos V., Guarneri P., Kreuger K. E., Guidotti A., Costa E. Pregnenolone biosynthesis in C6-2B glioma cell mitochondria: regulation by a mitochondrial diazepam binding inhibitor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5113–5117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S. M., Purdy R. H. Neuroactive steroids. FASEB J. 1992 Mar;6(6):2311–2322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad V. V., Warne P. A., Lieberman S. Solid-phase reagents for the isolation and protection of carbonyl compounds. J Steroid Biochem. 1983 Mar;18(3):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(83)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad V. V., el-Maraghy E., Ponticorvo L., Lieberman S. Detection in extracts of bovine brain of lipophilic complexes of sulfate esters of cholesterol and beta-sitosterol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2657–2659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts K. D., Bandy L., Lieberman S. The occurrence and metabolism of 20 alpha-hydroxycholesterol in bovine adrenal preparations. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):1259–1270. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K. Formation of 5-[17beta-2H]androstene-3beta,17alpha-diol from 3beta-hydroxy-5-[17,21,21,21-2H]pregnen-20-one by the microsomal fraction of boar testis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4237–4241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan L., Rousseau J. Anaerobic degradation of the progesterone side chain: a possible new pathway for the biosynthesis of androgen hormones. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 18;65(4):1320–1326. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80374-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lier J. E., Smith L. L. Sterol metabolism. XVI. Cholesterol 20-alpha-hydroperoxide as an intermediate in pregnenolone biosynthesis from cholesterol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Aug 11;40(3):510–516. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90931-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



