Abstract
Background
Although many of the volatile constituents of flavor and aroma in citrus have been identified, the knowledge of molecular mechanisms and regulation of volatile production are very limited. Our aim was to understand mechanisms of flavor volatile production and regulation in mandarin fruit.
Result
Fruits of two mandarin hybrids, Temple and Murcott with contrasting volatile and non- volatile profiles, were collected at three developmental stages. A combination of methods, including the isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification (iTRAQ), quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, gas chromatography, and high-performance liquid chromatography, was used to identify proteins, measure gene expression levels, volatiles, sugars, organic acids and carotenoids. Two thirds of differentially expressed proteins were identified in the pathways of glycolysis, citric acid cycle, amino acid, sugar and starch metabolism. An enzyme encoding valencene synthase gene (Cstps1) was more abundant in Temple than in Murcott. Valencene accounted for 9.4% of total volatile content in Temple, whereas no valencene was detected in Murcott fruit. Murcott expression of Cstps1 is severely reduced.
Conclusion
We showed that the diversion of valencene and other sesquiterpenes into the terpenoid pathway together with high production of apocarotenoid volatiles might have resulted in the lower concentration of carotenoids in Temple fruit.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12870-015-0466-9) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Apocarotenoid volatiles, Carotenoids, Sesquiterpene synthase, Citrus, Gene expression
Background
Fruit volatiles are essential components of fruit flavor, have defense mechanisms against biotic and abiotic stresses, and contribute to various physiological and ecological functions during plant development [1]. Flavor in mandarin fruit is the result of a combination of sugars (glucose, sucrose and fructose), acids (citric and malic), flavonoids, limonoids, and volatile compounds [2]. Volatiles in mandarin fruit belong to several chemical families such as terpenes, hydrocarbons, aldehydes, esters, alcohols, ketones and sulfur compounds [3]. Terpenoids play a central role in generating the chemical diversity, and accounted for 85–95% of volatiles in tangerine fruit [4]. Most volatiles are derived from a diverse set of non-volatile precursors, simple or complex molecules including amino acids, fatty acids, carbohydrates and carotenoids, which can be grouped into four biosynthetic classes: terpenoids, fatty acids, branched-chain amino acids and aromatic amino acids such as phenylalanine [5]. Virtually all of these precursors are essential human nutrients [6].
Breeding for improvement of fruit flavor is a very challenging task when using classical breeding methods due to the difficulty of scoring and quantifying such a complex trait. The presence of a single volatile molecule, even at a relatively high level, does not mean that it contributes to either flavor or liking [7]. To complicate matters further, some volatiles can also impact the perception of sweetness and vice versa [8]. So far, we still do not really understand how all of these volatiles and non-volatiles are integrated into the unique flavor perception of a fruit. For breeding programs, screening for the large range of flavor chemicals is not practically possible. Therefore, it is important to characterize the molecular mechanisms and regulation of flavor in order to understand the complexity of this trait. Knowledge of biosynthetic pathways of fruit flavor compounds and regulatory mechanisms will lead to efficient breeding strategies, such as to identify markers that track flavor-associated chemicals.
Several studies in tomato, peach, strawberry and banana have been performed, identifying and characterizing the most important genes and encoded enzymes involved in aroma-related volatiles [9-14], however, very few studies have been carried out in citrus [15]. Although volatile constituents of flavor and aroma have been identified in tangerine [3,4,16], research on the mechanisms of regulation or modulation, especially in citrus, is very limited. Progress in gene isolation related to volatile production has been impeded by the lack of information concerning plant secondary metabolism, with flavor-associated volatiles [17]. Even for some of the most important metabolites, pathways for synthesis have only recently been established or remain to be established [18]. An integrated approach, including metabolomics, genomics, transcriptomics and proteomics, and determining fundamental metabolism, can make an important contribution toward this goal [2,19-22].
In the present study, we selected contrasting volatile and non-volatile profiles between two mandarin hybrids: Murcott and Temple. The two hybrids have similar genetic backgrounds due to having the same general parentage of mandarin and sweet orange, although their exact origins are unknown [23]. Despite that, both of these cultivars have good fruit flavor, although previous studies indicate that Temple is much richer in volatiles than Murcott, especially in sesquiterpenes and esters [4]. In addition to a comparison of volatile and non-volatile (sugars, acids, and carotenoids) compounds, and the interrelationships of these chemical components, a comparative iTRAQ (isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification) proteome analysis was used to identify qualitative and quantitative differences in the proteome between the two hybrids at three levels of maturity. iTRAQ is a powerful approach, using isotope labeling coupled with multidimensional liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (MS), thereby enabling sensitive assessment and quantification of protein levels [24-26]. This analysis helped to better understand the pathways and genes controlling synthesis of flavor volatiles during mandarin hybrid fruit maturation, and to identify enzymes and genes involved in their biosynthesis pathways, especially concerning the terpenoid biosynthesis pathway.
Results
Differences in sugar, organic acid and carotenoid content between Murcott and Temple
Fruits of Temple and Murcott were different in flesh color (Figure 1). There were differences for sugars, organic acids and carotenoids between Temple and Murcott at the three maturity stages. Among sugars, only sucrose and total sugars were higher in Murcott than Temple at stage 3, and total soluble solids content (SSC) at stage 1 and 3. However, no differences were found in fructose and glucose. Among acids, Temple was higher than Murcott for citric acid at stage1, malic acid and titratable acidity (TA) at stage 1 and 2, and ascorbic acid at all three stages, respectively. The pH values for Temple were significantly lower at stage 2. Overall, ascorbic acid was 21 times higher in Temple than Murcott. SSC/titratable acidity (TA) was lower in Temple at stage 1 and 2. SSC/TA is an indicator of maturity in citrus, and no differences were found between the two cultivars in stage 3. All carotenoids, except α-carotene for stage 2 and 3 and lutein for stage 1, were significantly higher in Murcott than in Temple (Figure 2).
Figure 1.

Cross section of Temple and Murcott mandarin hybrid fruit.
Figure 2.
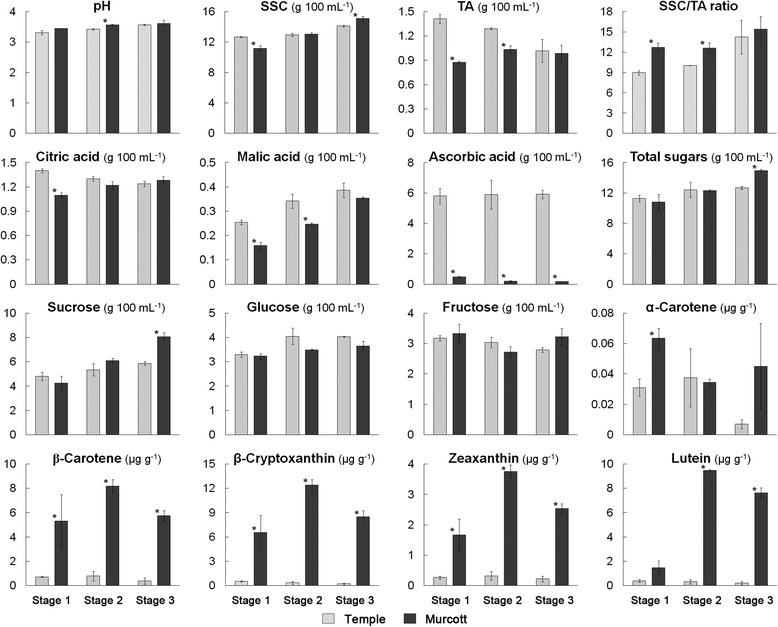
Sugar, organic acid and carotenoid content in Temple and Murcott mandarin hybrid fruit at three developmental stages (stage 1: 22-Dec-2008; stage 2: 30-Jan-2009; and stage 3: 11-Mar-2009). Student’s T-test was used to determine the statistical significance of the differences between mean values for Temple and Murcott at the same developmental stage; standard error bars are provided. *: significant difference (P < 0.05); SSC: soluble solids content; TA: titratable acidity.
Differences in aroma volatiles between Murcott and Temple
A total of 121 volatile compounds were detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), with 108 compounds in Temple and 60 compounds in Murcott, respectively (Additional file 1: Table S1). Only 48 volatiles were found in both Temple and Murcott. There were 46 volatiles unique to Temple, in addition to 14 unknown compounds, whereas 12 volatiles were found only in Murcott (Table 1). The sum of total relative peak areas (peak area of compounds divided by peak area of internal standard) was twice as high in Temple than in Murcott, 21.9 for Temple, 11.5 for Murcott, respectively (Table 2). Terpenoid-related compounds contributed more than 85 and 95% of the total volatiles in Temple and Murcott respectively, also the volatile profile was markedly different. Valencene accounted for 9.4% of the total profile in Temple, whereas no valencene nor nootkatone was detected in Murcott. Sesquiterpenes were 0.15% and 3.10% and esters were 0.38% and 7.16% in Murcott and Temple, respectively. We found seven carotenoid-derived volatiles in Temple: nerol, neral, geranial, neryl acetate, α-ionone, geranyl acetone, and β-ionone. In contrast, only two of these, neryl acetate and geranyl acetone, were found in Murcott. D-limonene was the most abundant volatile compound which accounted for 80.8% and 64.4% of the volatile profile in Murcott and Temple, respectively. Murcott had two branched aldehydes, 3-methyl pentanal and 4-methyl hexanal, which were lacking in Temple. However, Temple had one branched alcohol, 3-methyl-1-butanol, and one branched ester, ethyl 2-methylbutyrate, likely to have been derived from the branched alcohol, whereas Murcott did not have these compounds (Table 2).
Table 1.
Volatiles in Temple and Murcott mandarin hybrid fruit arranged by chemical class
| Temple only | Murcott only | Both |
|---|---|---|
| Monoterpenes | Monoterpenes | Monoterpenes |
| Isoterpinolene | β-Pinene | α-Thujene |
| 3-Carene | (+)-4-Carene | α-Pinene |
| 2-Carene | Aldehydes | Sabinene |
| 3-Methyl-4-methylenebicyclo[3.2.1]oct-2-ene | Butanal | β-Myrcene |
| 3-Methyl pentanal | α-Phellandrene | |
| Sesquiterpenes | 4-Methyl hexanal | γ-Terpinene |
| β-Elemene | ρ-Menth-1-en-9-al | ρ-Cymene |
| β-Cubebene | p-Menth-1-en-9-al isomer | d-Limonene |
| β-Humulene | Ester | β-Phellandrene |
| α-Caryophyllene | Ethyl acetate | γ-Terpiene |
| α-Selinene | Ether | ρ-Mentha-3,8-diene |
| γ-Selinene | Ethyl ether | Terpinolene |
| Valencene | Hydrocarbons | Sesquiterpenes |
| Aromadendrene | (E,E)-2,6-dimethyl-1,3,5,7-octatetraene | α-Cubebene |
| Calamenene | Copaene | |
| (−)-α-Panasinsen | Furans | Caryophyllene |
| Eremophilene | 2-n-Butyl furan | δ-Cadinene |
| Eudesma-3,7-diene | 2-Pentyl furan | Aldehydes |
| 4,11-Selinadiene | Acetaldehyde | |
| Aldehydes | Propanal | |
| (E)-2-Pentenal | Pentanal | |
| Geranial (carotenoid) | Hexanal | |
| Neral (carotenoid) | Heptanal | |
| Ketones | Octanal | |
| Acetone | Nonanal | |
| Nootkatone | Decanal | |
| α-Ionone (carotenoid) | (E)-2-Hexenal | |
| β-Ionone (carotenoid) | (E)-2-Heptenal | |
| Alcohols | (E)-2-Octenal | |
| 1-Hexanol | (E)-2-Nonenal | |
| 3-Methylbutanol | (E)-2-Decenal | |
| (Z)-ρ-Mentha-2,8-dien-1-ol | Perillaldehyde | |
| β-Terpineol | Ketones | |
| Nerol (carotenoid) | 1-Pentene-3-one | |
| Esters | 3-Pentanone | |
| Ethyl butanoate | 4-Heptanone | |
| Ethyl 2-butenoate | d-Carvone | |
| Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate | Dihydrocarvone | |
| Ethyl pentanoate | Geranyl acetone (carotenoid) | |
| Ethyl hexanoate | Alcohols | |
| Ethyl-3-hydroxyhexanoate | Ethyl alcohol | |
| Ethyl octanoate | 1-Penten-3-ol | |
| Propyl butanoate | Linalool | |
| Methyl butanoate | Terpinen-4-ol | |
| Methyl hexanoate | α-Terpineol | |
| Hexyl acetate | Esters | |
| Linalool acetate | Octyl acetate | |
| Terpinyl acetate | Citronellol acetate | |
| Ether | Neryl acetate (carotenoid) | |
| 1,8-Cineole | Hydrocarbons | |
| Hydrocarbons | 1,3-Pentadiene | |
| (E)-2,6-Dimethyl-2,6-octadiene | (Z)-2,6-Dimethyl-2,6-octadiene | |
| 1,5-Dimethyl-cyclooctadiene | (+/−)-4-Acetyl-1-methylcyclohexene | |
| Furan | ||
| 2-Ethyl furan | Furan | |
| 2-Methyl furan |
Carotenoid-derived volatiles are in parentheses.
Table 2.
Content of major volatile classes in Temple and Murcott mandarin hybrid fruit
| Chemical class | Murcott | Temple | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aliphatic alcohols | 0.045 ± 0.021 | 0.094 ± 0.043 | 0.356 |
| Branched alcohols | n. d. | 0.002 ± 0.001 | |
| Aliphatic aldehydes | 0.910 ± 0.257 | 0.755 ± 0.138 | 0.442 |
| Branched aldehydes | 0.005 ± 0.002 | n. d. | |
| Aliphatic esters | 0.044 ± 0.017 | 1.561 ± 0.246 | 0.000 |
| Branched esters | n. d. | 0.006 ± 0.001 | |
| Aliphatic ketones | 0.014 ± 0.001 | 0.019 ± 0.002 | 0.001 |
| d-Limonene | 9.266 ± 1.203 | 14.03 ± 2.317 | 0.110 |
| Monoterpenes except d-Limonene | 0.937 ± 0.141 | 1.323 ± 0.217 | 0.191 |
| Valencene | n. d. | 2.053 ± 0.367 | |
| Sesquiterpenes except Valencene | 0.017 ± 0.004 | 0.677 ± 0.004 | 0.000 |
| Terpene alcohols | 0.123 ± 0.013 | 0.720 ± 0.144 | 0.007 |
| Terpene aldehydes | 0.013 ± 0.003 | 0.026 ± 0.005 | 0.035 |
| Terpene esters | 0.011 ± 0.011 | 0.061 ± 0.010 | 0.004 |
| Terpene ketones | 0.057 ± 0.011 | 0.061 ± 0.010 | 0.764 |
| Ethers | n. d. | 0.348 ± 0.073 | |
| Furans | 0.022 ± 0.004 | n. d. | |
| Other hydrocarbon | n. d. | 0.149 ± 0.031 | |
| Other | 0.005 ± 0.001 | 0.007 ± 0.001 | 0.390 |
| Total | 11.47 ± 1.51 | 21.90 ± 3.000 | 0.030 |
Total ion current of target compound was divided by that of internal standard, 3-hexanone.
Differentially expressed proteins in Temple versus Murcott
We identified 280 differentially expressed proteins in Temple versus Murcott (Additional file 1: Table S2). Of these identified proteins, 92 were significantly differentially expressed in juice sacs at the three ripening stages (fold change > 1.5, P < 0.05) (Table 3). We found 42, 54 and 45 expressed proteins in ripening stage 1, stage 2 and stage 3, respectively. There were 22 proteins in common between stage 1 and 2, 24 between stage 2 and 3, whereas only 9 proteins in common were identified between stage 1 and 3. Five proteins were present across all three stages: hypothetical protein (gi|225442225), superoxide dismutase (SOD) (gi|77417715), phospholipase D alpha (gi|169160465), plastid-lipid-associated protein (gi|62900641), and UDP-glucosyltransferase family 1 protein (gi|242199340). All proteins were more highly expressed in Murcott than Temple in stage 2, whereas most proteins were more highly expressed in Temple than Murcott in stage 1. In stage 3, 13 proteins were up-regulated versus 32 down-regulated in Temple versus Murcott. We found several important proteins involved in volatile production. Phospholipase D alpha (gi|169160465), a key enzyme involved in membrane deterioration which produces precursors to aliphatic alcohols and aldehydes, was up-regulated in Temple versus Murcott at stage 1, but not stage 2 and 3. The Family1 glycotranferases might affect biosynthesis and accumulation of glycosides that bind volatile terpenoids. Isopentenyl diphosphate Delta-isomerase I (gi|6225526) isomerizes isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) to its isomer dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) and was up-regulated in Murcott versus Temple at ripening stage 2. Valencene synthase (gi|33316389) was the protein that was the most different between the two cultivars, being 25 times higher in Temple than in Murcott at ripening stage 3. Several proteins from the glycolysis pathway were identified: triosephosphate isomerase (gi|77540216), a triosphosphate isomerase-like protein (gi|76573375), and pyruvate decarboxylase (gi|17225598). All were only expressed in ripening stage 3, and were higher in Murcott than in Temple. A citrate synthase precursor (gi|624676) was found in ripening stage 1, upregulated in Temple in comparison with Murcott. In addition to citrus synthase, malate dehydrogenase (gi|27462762) and isocitrate dehydrogenase (gi|5764653) of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle were also found and downregulated in Temple versus Murcott. Glutamate decarboxylase (gi|70609690) and aspartate aminotransferase (gi|255551036), involved in glutamate synthesis, were also identified.
Table 3.
Differentially expressed proteins in fruit flesh of Temple (Te) versus Murcott (Mu) mandarin hybrid fruit
| Accession | Name | Species | iTRAQ ratio fold change | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 | ||||||
| Te/Mu | P value | Te/Mu | P value | Te/Mu | P value | |||
| gi|11596186 | cystatin-like protein | Citrus x paradisi | 4.041 | 0.036 | 0.647 | 0.002 | ||
| gi|118061963 | extracellular solute-binding protein, family 5 | Roseiflexus castenholzii DSM 13941 | 0.483 | 0.047 | ||||
| gi|119367477 | putative H-type thioredoxin | Citrus cv. Shiranuhi | 10.782 | 0.001 | 0.404 | 0.001 | ||
| gi|119367479 | putative cyclophilin | Citrus cv. Shiranuhi | 0.588 | 0.037 | 2.347 | 0.002 | ||
| gi|121485004 | cytosolic phosphoglycerate kinase | Helianthus annuus | 5.535 | 0.002 | ||||
| gi|124360080 | Galactose mutarotase-like | Medicago truncatula | 1.724 | 0.003 | ||||
| gi|125546170 | hypothetical protein OsI_14032 | Oryza sativa Indica Group | 0.561 | 0.014 | ||||
| gi|14031067 | dehydrin COR15 | Citrus x paradisi | 2.806 | 0.000 | ||||
| gi|147809484 | hypothetical protein | Vitis vinifera | 0.608 | 0.022 | 0.696 | 0.065 | ||
| gi|147836508 | hypothetical protein | Vitis vinifera | 1.630 | 0.024 | ||||
| gi|147853192 | hypothetical protein | Vitis vinifera | 1.803 | 0.018 | ||||
| gi|15219028 | 26.5 kDa class I small heat shock protein-like | Arabidopsis thaliana | 0.491 | 0.008 | ||||
| gi|15235730 | phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (ATP), putative/PEP carboxykinase, putative/PEPCK, putative | Arabidopsis thaliana | 1.899 | 0.034 | ||||
| gi|159471948 | U2 snRNP auxiliary factor, large subunit | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | 0.255 | 0.044 | ||||
| gi|166850556 | CTRSFT1-like protein | Poncirus trifoliata | 3.261 | 0.011 | 0.237 | 0.005 | ||
| gi|169160465 | phospholipase D alpha | Citrus sinensis | 4.060 | 0.000 | 0.240 | 0.000 | 0.573 | 0.000 |
| gi|17225598 | pyruvate decarboxylase | Fragaria x ananassa | 0.286 | 0.012 | ||||
| gi|183579873 | chitinase | Citrus unshiu | 1.534 | 0.012 | ||||
| gi|192912988 | 40S ribosomal protein S4 | Elaeis guineensis | 1.601 | 0.049 | ||||
| gi|218202932 | 14-3-3 protein | Dimocarpus longan | 0.227 | 0.016 | ||||
| gi|221327587 | ascorbate peroxidase | Citrus maxima | 4.863 | 0.000 | 0.180 | 0.049 | ||
| gi|2213425 | hypothetical protein | Citrus x paradisi | 0.627 | 0.000 | 0.524 | 0.001 | ||
| gi|223949137 | unknown | Zea mays | 5.116 | 0.003 | ||||
| gi|224069008 | predicted protein | Populus trichocarpa | 6.992 | 0.001 | ||||
| gi|224099429 | predicted protein | Populus trichocarpa | 0.587 | 0.014 | 0.316 | 0.002 | ||
| gi|224109966 | predicted protein | Populus trichocarpa | 0.476 | 0.040 | ||||
| gi|224127346 | predicted protein | Populus trichocarpa | 0.156 | 0.007 | 0.641 | 0.043 | ||
| gi|224128794 | predicted protein | Populus trichocarpa | 0.298 | 0.007 | 0.382 | 0.022 | ||
| gi|224135985 | predicted protein | Populus trichocarpa | 0.248 | 0.006 | 0.366 | 0.021 | ||
| gi|225424861 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein isoform 2 | Vitis vinifera | 0.536 | 0.040 | ||||
| gi|225425914 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein | Vitis vinifera | 0.429 | 0.002 | 0.425 | 0.010 | ||
| gi|225439785 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein | Vitis vinifera | 0.441 | 0.007 | 0.658 | 0.023 | ||
| gi|225441981 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein | Vitis vinifera | 0.304 | 0.002 | 0.568 | 0.007 | ||
| gi|225442225 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein | Vitis vinifera | 9.896 | 0.015 | 0.576 | 0.010 | 0.571 | 0.002 |
| gi|225451968 | PREDICTED: similar to mangrin | Vitis vinifera | 4.507 | 0.040 | 0.263 | 0.095 | ||
| gi|231586 | ATP synthase subunit beta | Hevea brasiliensis | 0.134 | 0.004 | 0.555 | 0.007 | ||
| gi|242199340 | UDP-glucosyltransferase family 1 protein | Citrus sinensis | 7.535 | 0.002 | 0.394 | 0.008 | 0.539 | 0.030 |
| gi|255539613 | phosphoglucomutase, putative | Ricinus communis | 0.142 | 0.020 | ||||
| gi|255543156 | conserved hypothetical protein | Ricinus communis | 7.967 | 0.000 | ||||
| gi|255544686 | eukaryotic translation elongation factor, putative | Ricinus communis | 0.424 | 0.006 | 0.323 | 0.008 | ||
| gi|255550111 | heat-shock protein, putative | Ricinus communis | 3.788 | 0.043 | ||||
| gi|255551036 | aspartate aminotransferase, putative | Ricinus communis | 0.599 | 0.037 | ||||
| gi|255561582 | Patellin-3, putative | Ricinus communis | 0.588 | 0.017 | ||||
| gi|255571742 | peptidase, putative | Ricinus communis | 0.275 | 0.004 | ||||
| gi|255586766 | monodehydroascorbate reductase, putative | Ricinus communis | 0.429 | 0.003 | 0.493 | 0.001 | ||
| gi|255641409 | unknown | Glycine max | 0.645 | 0.021 | ||||
| gi|255642211 | unknown | Glycine max | 0.521 | 0.011 | 0.121 | 0.001 | ||
| gi|255644696 | unknown | Glycine max | 5.914 | 0.002 | ||||
| gi|257659867 | unnamed protein product | Linum usitatissimum | 0.329 | 0.235 | 0.368 | 0.047 | ||
| gi|257675725 | unnamed protein product | Zea mays | 3.832 | 0.019 | ||||
| gi|257690969 | unnamed protein product | Citrus sinensis | 0.384 | 0.002 | ||||
| gi|257712573 | unnamed protein product | Brassica napus | 9.086 | 0.011 | 0.664 | 0.006 | ||
| gi|257720002 | unnamed protein product | Glycine max | 0.551 | 0.001 | 0.387 | 0.007 | ||
| gi|257726687 | unnamed protein product | Zea mays | 1.650 | 0.035 | 0.387 | 0.001 | ||
| gi|27462762 | malate dehydrogenase | Lupinus albus | 0.305 | 0.003 | ||||
| gi|29124973 | unknown | Populus tremuloides | 2.039 | 0.031 | ||||
| gi|33316389 | valencene synthase | Citrus sinensis | 25.730 | 0.022 | ||||
| gi|33325127 | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A isoform VI | Hevea brasiliensis | 1.914 | 0.039 | ||||
| gi|33340236 | copper/zinc superoxide dismutase | Citrus limon | 3.706 | 0.001 | 0.638 | 0.004 | ||
| gi|37524017 | COR15 | Citrus clementina x Citrus reticulata | 10.311 | 0.006 | 2.382 | 0.010 | ||
| gi|3790102 | pyrophosphate-dependent phosphofructokinase alpha subunit | Citrus x paradisi | 1.724 | 0.025 | 0.554 | 0.011 | ||
| gi|40646744 | mitochondrial citrate synthase precursor | Citrus junos | 0.201 | 0.032 | 0.553 | 0.018 | ||
| gi|4580920 | vacuole-associated annexin VCaB42 | Nicotiana tabacum | 0.209 | 0.046 | 0.330 | 0.007 | ||
| gi|4704605 | glycine-rich RNA-binding protein | Picea glauca | 4.452 | 0.009 | ||||
| gi|530207 | heat shock protein | Glycine max | 4.177 | 0.045 | ||||
| gi|544437 | Probable phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase | Citrus sinensis | 3.140 | 0.039 | ||||
| gi|5764653 | NADP-isocitrate dehydrogenase | Citrus limon | 0.430 | 0.006 | 0.437 | 0.003 | ||
| gi|6094476 | Thiazole biosynthetic enzyme | Citrus sinensis | 0.228 | 0.007 | ||||
| gi|6166140 | Elongation factor 1-delta 1 | Oryza sativa Japonica Group | 7.427 | 0.045 | 0.654 | 0.028 | ||
| gi|6225526 | Isopentenyl-diphosphate Delta-isomerase I | Clarkia breweri | 0.562 | 0.033 | ||||
| gi|624674 | heat shock protein | Citrus maxima | ||||||
| gi|624676 | citrate synthase precursor | Citrus maxima | 2.731 | 0.020 | ||||
| gi|62900641 | Plastid-lipid-associated protein | Citrus unshiu | 6.082 | 0.002 | 0.289 | 0.000 | 0.662 | 0.022 |
| gi|63333659 | beta-1,3-glucanase class III | Citrus clementina x Citrus reticulata | 0.493 | 0.141 | 2.712 | 0.000 | ||
| gi|6518112 | H + −ATPase catalytic subunit | Citrus unshiu | 4.754 | 0.017 | 0.598 | 0.007 | ||
| gi|6682841 | sucrose synthase | Citrus unshiu | 3.194 | 0.025 | 0.632 | 0.009 | ||
| gi|6682843 | sucrose synthase | Citrus unshiu | 0.144 | 0.008 | 0.575 | 0.024 | ||
| gi|7024451 | glycine-rich RNA-binding protein | Citrus unshiu | 1.886 | 0.531 | ||||
| gi|70609690 | glutamate decarboxylase | Citrus sinensis | 3.588 | 0.025 | 0.643 | 0.043 | ||
| gi|7269241 | UDPglucose 4-epimerase-like protein | Arabidopsis thaliana | 0.424 | 0.011 | 0.158 | 0.004 | ||
| gi|74486744 | translation elongation factor 1A-9 | Gossypium hirsutum | 4.923 | 0.008 | ||||
| gi|76573375 | triosphosphate isomerase-like protein | Solanum tuberosum | 0.311 | 0.000 | ||||
| gi|77417715 | SOD | Citrus maxima | 0.638 | 0.017 | 0.118 | 0.010 | 0.322 | 0.013 |
| gi|77540216 | triosephosphate isomerase | Glycine max | 0.514 | 0.022 | ||||
| gi|77744899 | temperature-induced lipocalin | Citrus sinensis | 4.028 | 0.018 | 0.548 | 0.016 | ||
| gi|82623427 | glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase-like | Solanum tuberosum | 0.661 | 0.297 | ||||
| gi|862480 | valosin-containing protein | Glycine max | 1.510 | 0.029 | 0.374 | 0.010 | ||
| gi|870794 | polyubiquitin | Arabidopsis thaliana | 4.534 | 0.005 | ||||
| gi|90820120 | UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase | Cucumis melo | 7.835 | 0.028 | ||||
| gi|9082317 | actin | Helianthus annuus | 3.959 | 0.051 | 0.527 | 0.001 | ||
| gi|9280626 | UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase | Astragalus membranaceus | 9.821 | 0.002 | 1.626 | 0.022 | ||
| gi|9757974 | polyubiquitin | Arabidopsis thaliana | 0.585 | 0.011 | ||||
The P value was selected from the most significant one among three biological replications. Additional file 1: Table S2 has the result from all three biological replications. Stage 1 was on December 22, 2008, Stage 2 was on January 30, 2009, and Stage 3 was on March 11, 2009.
Gene annotation was conducted using the Blast2GO program for all 92 identified proteins. The biological interpretation was further completed by assigning them to metabolic pathways using Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) annotation. KEGG analysis assigned the 46 differentially expressed proteins to 48 metabolic pathways (Additional file 1: Table S3). Most biosynthetic pathways identified were glycolysis, citric acid cycle, sugar synthesis, amino acid synthesis and terpene synthesis. Additional file 2: Figure S1 shows the distributions of GO terms (2nd level GO terms) according to biological processes, cellular components and molecular function. Most differentially expressed proteins were predicted to be involved in carbohydrate, amino acid, and lipid metabolism as well as in energy production. We found 10 enzymes involved in the glycolysis pathway and 16 enzymes involved in different amino acid pathways (Table 4; Additional file 1: Table S3).
Table 4.
KEGG assigned differentially expressed proteins between Temple and Murcott mandarin hybrid fruit in metabolic pathways
| KEGG pathway | Pathway | Enzyme number |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrate metabolism | Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | ec:2.7.7.9, ec:3.2.1.14, ec:5.1.3.2,ec:5.4.2.2 |
| Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | ec:1.10.3.3, ec:1.11.1.11, ec:1.6.5.4 | |
| Butanoate metabolism | ec:4.1.1.15 | |
| Tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) | ec:1.1.1.37, ec:1.1.1.42, ec:2.3.1.12, ec:2.3.3.1, ec:4.1.1.49 | |
| Fructose and mannose metabolism | ec:2.7.1.11, ec:2.7.1.90, ec:4.1.2.13,ec:5.3.1.1 | |
| Galactose metabolism | ec:2.7.1.11, ec:2.7.7.9, ec:5.1.3.2, ec:5.4.2.2 | |
| Glycerophospholipid metabolism | ec:3.1.4.4 | |
| Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis | ec:1.2.1.12, ec:2.3.1.12, ec:2.7.1.11, ec:2.7.2.3, ec:4.1.1.1, ec:4.1.1.49, ec:4.1.2.13, ec:5.1.3.3, ec:5.3.1.1, ec:5.4.2.2 | |
| Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | ec:1.1.1.37, ec:1.11.1.6, ec:2.3.3.1 | |
| Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | ec:2.7.7.9, ec:3.1.1.11 | |
| Pentose phosphate pathway | ec:1.1.1.49, ec:2.7.1.11, ec:4.1.2.13, ec:5.4.2.2 | |
| Pyruvate metabolism | ec:1.1.1.37, ec:2.3.1.12, ec:4.1.1.49, ec:4.4.1.5 | |
| Amino acid metabolism | Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | ec:2.6.1.1, ec:2.6.1.2, ec:4.1.1.15 |
| Arginine and proline metabolism | ec:2.6.1.1, ec:3.5.3.1 | |
| beta-Alanine metabolism | ec:4.1.1.15 | |
| Cysteine and methionine metabolism | ec:2.6.1.1 | |
| Glutathione metabolism | ec:1.1.1.42, ec:1.1.1.49, ec:1.11.1.11, ec:1.11.1.12, ec:1.11.1.15, ec:1.11.1.9, ec:2.5.1.18 | |
| Phenylalanine metabolism | ec:1.11.1.7,ec:2.6.1.1 | |
| Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | ec:2.6.1.1 | |
| Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | ec:4.1.1.15 | |
| Tryptophan metabolism | ec:1.11.1.6 | |
| Tyrosine metabolism | ec:2.6.1.1 | |
| Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation | ec:2.3.1.168 | |
| Other secondary metabolites | Isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis | ec:2.6.1.1 |
| Novobiocin biosynthesis | ec:2.6.1.1 | |
| Tropane, piperidine and pyridine alkaloid biosynthesis | ec:1.11.1.6 | |
| Streptomycin biosynthesis | ec:5.4.2.2 | |
| Energy metabolism | Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms | ec:1.1.1.37, ec:2.6.1.1, ec:2.6.1.2, ec:2.7.2.3, ec:4.1.1.49, ec:4.1.2.13, ec:5.3.1.1 |
| Carbon fixation pathways in prokaryotes | ec:1.1.1.37, ec:1.1.1.42 | |
| Inositol phosphate metabolism | ec:5.3.1.1 | |
| Methane metabolism | ec:1.1.1.37, ec:1.11.1.6, ec:1.11.1.7, ec:2.7.1.11, ec:4.1.2.13 | |
| Oxidative phosphorylation | ec:3.6.3.6 | |
| Lipid metabolism | alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism | ec:5.3.99.6 |
| Arachidonic acid metabolism | ec:1.11.1.9 | |
| Ether lipid metabolism | ec:3.1.4.4 | |
| Primary bile acid biosynthesis | ec:1.3.1.3 | |
| Steroid degradation | ec:1.1.1.145 | |
| Steroid hormone biosynthesis | ec:1.1.1.145, ec:1.3.1.3 | |
| Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides | Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis | ec:5.3.3.2 |
| Nucleotide metabolism | Arginine and proline metabolism | ec:3.5.3.11 |
| Cysteine and methionine metabolism | ec:4.4.1.14 | |
| Purine metabolism | ec:3.6.1.3, ec:5.4.2.2 | |
| Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism | Chlorocyclohexane and chlorobenzene degradation | ec:3.1.1.45 |
| Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450 | ec:2.5.1.18 | |
| Fluorobenzoate degradation | ec:3.1.1.45 | |
| Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 | ec:2.5.1.18 | |
| Toluene degradation | ec:3.1.1.45 |
Discussion
In this study, two thirds of differentially expressed proteins were identified in the pathways of glycolysis and TCA as well as amino acid, sugar and starch metabolism (Tables 3 and 4). This is understandable, because the upstream precursors for most volatiles come from carbohydrate metabolism, mainly through sugar and starch metabolism through the glycolysis pathway, which is important for providing the carbon skeleton and toward the different branches that lead to the aforementioned volatiles. Most organic acids, amino acids, terpenes and fatty acids are produced from glycolysis and TCA. For amino acids, the carbon skeletons are derived from 3-phosphoglycerate, phosphoenolpyruvate or pyruvate generated in glycolysis, or from 2-oxoglutarate and oxaloacetate generated in TCA [20]. Terpenoids are enzymatically synthesized de novo from acetyl CoA and pyruvate provided by the carbohydrate pools in plastids and the cytoplasm [27].
The differences in protein expression between Temple and Murcott were due to the different ripening patterns of these two hybrids. Temple is a middle-late variety whereas Murcott is a very late variety; however in Florida citrus production conditions, and depending on season, Temple and Murcott maturity times may overlap. These differences in time of maturity might explain proteins being more highly expressed in Temple than Murcott in stage 1, whereas all proteins were more highly expressed in Murcott than Temple in stage 2, and mixed protein expression levels were seen in stage 3. Feng et al. [28] found that glutamate decarboxylase (gi|70609690) was one of two proteins likely associated with carbohydrate and acid metabolism in the ripening fruit. In our study, this protein is expressed more in Temple at stage 1, but less in stage 2 than Murcott. This might also explain the differences in levels of volatiles, sugar, organic acids in different stages between Temple and Murcott.
Sugar, TCA and glycolysis biosynthesis
Sucrose is the major sugar translocated in the plant, the major photo-assimilate stored in the plant, and can be degraded by cell wall sucrose synthase to glucose and fructose. Glucose can be converted into pyruvate, generating small amounts of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced form (NADH) via the glycolysis pathway. Glucose phosphomutase (gi|255539613, EC 5.4.2.2) was down-regulated in Temple in stage 2, and is an enzyme responsible for the conversion of D-glucose 1-phosphate into D-glucose 6-phosphate. Sucrose synthase (gi|6682841/gi|6682843, EC 2.4.1.13) catalyzes the degradation of sucrose into UDP-glucose and fructose, up-regulated in Temple at stage 1 and down-regulated in stage 2 and 3. The high expression of sucrose synthase in Murcott stage 2 might partially explain why Murcott had higher sucrose than Temple (Figure 2). Sucrose, in turn, is derived from hexose phosphates through UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase, (gi|90820120, gi|9280626, EC 2.7.7.9). The glycolysis biosynthesis is a central pathway that produces important precursor metabolites: six-carbon compounds of glucose-6P and fructose-6P and three-carbon compounds of glycerone-P, glyceraldehyde-3P, glycerate-3P, phosphoenolpyruvate, and pyruvate. Acetyl-CoA and another important precursor metabolite are produced by oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate. The reaction, mediated by phosphofructokinase (gi|3790102, EC 2.7.1.11), is one of the key control points of glycolysis in plants. This reaction catalyzes the interconversion of fructose-6-phosphate and fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate.
Citric acid is the main organic acid in citrus fruit juice. Yun et al. [29] found citric acid comprised up to 90% of the total organic acid content throughout the entire postharvest period. Citrate may be utilized by three major metabolic pathways for sugar production, amino acid synthesis, and acetyl-CoA metabolism. 2-Oxoglutarate can be then metabolized to an amino acid such as glutamate. Six enzymes acting in the TCA cycle were identified in our study including: pyruvate decarboxylase (gi|17225598, EC 4.1.1.1), malate dehydrogenase (gi|27462762, EC 1.1.1.37), isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+) (gi|5764653, EC 1.1.1.42), dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase (gi|225442225, EC 2.3.1.12), citrate synthase (gi|624676, EC 2.3.3.1) and phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) carboxykinase (gi|15235730, EC 4.1.1.49). The pyruvate decarboxylase enzyme, down-regulated in Temple, links the TCA cycle to glycolysis. Plant cells can convert PEP to malate via oxaloacetate in reactions catalyzed by PEP carboxykinase (gi|15235730, EC 4.1.1.49) and malate dehydrogenase (gi|27462762, EC 1.1.1.37) [1]. Citrate can be produced by condensation of oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA, catalyzed by citrate synthase which was up-regulated in Temple in stage 2. Citrate synthase is the rate-limiting enzyme of the TCA cycle [29]. The result might explain the higher citric acid content in Temple than Murcott. The oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate into 2-oxoglutarate is mediated by the action of isocitrate dehydrogenase. The last step of the TCA pathway is the interconversion of malate to oxaloacetate utilizing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidized form (NAD+) /NADH and is catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase. In general, however, the changes of enzymes in the TCA cycle and glycolysis cannot fully explain the difference of organic acid and sugar contents in Temple compared to Murcott. Katz et al. [21] indicated that changes in metabolite amounts in fruit do not always correlate well with protein expression levels, reflecting the complication of regulated pathway outputs.
Amino acids, oxidization, ascorbate-glutathione cycle
KEGG pathway analysis conducted by Blast2GO indicated that seven enzymes are involved in the glutathione metabolic pathway (Table 4). In plants, glutathione is crucial for biotic and abiotic stress management. It is a pivotal component of the glutathione-ascorbate cycle, a system that reduces poisonous hydrogen peroxide. Pan et al. [30] found that expression levels of five antioxidative enzymes (catalase, peroxidase, ascorbate peroxidase, glutathione reductase and superoxide dismutase) were altered in a mutant orange “Hong Anliu” which has a high level of lycopene, and implied a regulatory role of oxidative stress on carotenogenesis. In our study, the protein expression of L-ascorbate peroxidase (gi|221327587, EC 1.11.1.11), phospholipid-hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (gi|544437, EC 1.11.1.12), superoxide dismutase (SOD) (gi|77417715), and monodehydroascorbate reductase (gi|255586766, EC 1.6.5.4), were mixed (Table 3). SOD and monodehydroascorbate reductase had lower expression in Temple, whereas, other proteins were higher in stage 1 and 3, and lower in stage 2 (Table 3). We could not define a clear relationship between antioxidative enzyme activity and the amount of carotenoids. The discrepancy is likely due to other regulatory pathways, since there are many steps involved in the biosynthesis pathways that are tightly regulated [31]. Liu et al. [32] found glutamate decarboxylase is an enzyme catalyzing the conversion of L-glutamate to γ-aminobutyric acid, and suggested that it is possible that glutamate decarboxylase (gi|70609690) could participate in regulating the cytosolic pH.
Volatile biosynthesis
All terpenoids derive from the common building units isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and its isomer dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMADP). Both IPP and DMADP are synthesized via two parallel pathways, the mevalonate (MVA) pathway, which is active in the cytosol, and the methylerythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway, which is active in the plastids. In this study, IPP isomerase (gi|6225526) upregulated in Murcott relative to Temple, catalyzes isomerization between IPP and dimethylallyl diphosphate (Table 3). Aharoni et al. [33] found that the pool of IPP in the plastids might affect the formation of sesquiterpenes in the cytosol given that transport of isoprenoid precursors is known to occur from the plastids to the cytosol. A valencene synthase (gi|33316389) expression explains the difference in valencene content between Temple and Murcott. Sharon-Asa et al. [15] isolated and characterized the valencene synthase gene (Cstps1) and reported that valencene accumulates during the ripening of Valencia orange fruits together with Cstps1. Results from the current work agreed with their study (Additional file 2: Figure S2-A). In order to validate the result, real-time PCR showed that the gene expression of Cstps1 was found to be over 217 and 2720 times higher in Temple than in Murcott on Dec 22, 2008 and March 11, 2009, respectively (Figure 3). Murcott expression of Cstps1 gene is very severely reduced.
Figure 3.
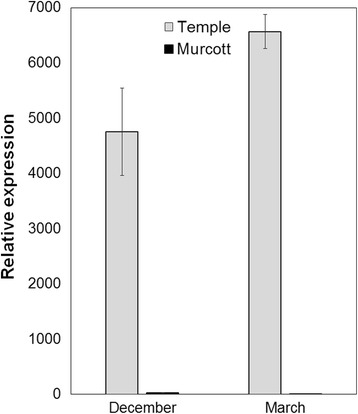
QRT-PCR validation of the expression profiles of Cstsp1 genes at two time points. Results were expressed relative to the value of the expression of Murcott Cstps1 in March.
Non-volatile sugar conjugates constitute a large pool of precursors for many of the important flavor volatiles. Enzymes synthesizing and hydrolyzing these sugar conjugates are likely to influence the volatile profiles. Family 1 glycosyltransferases (gi|242199340), often referred to as UDP glycosyltransferases, is the largest in the plant kingdom [34], which catalyze the transfer of a glycosyl moiety from UDP-sugars to a wide range of acceptor molecules. Glycosyltransferase might affect biosynthesis and accumulation of glycosides of volatile terpenoids. Fan et al. [35] identified three putative terpenoid UDP-glycosyltransferase (UGT) genes in sweet orange. The different expression of glycotranferase family 1 in three stages of fruit ripening in Temple might explain the difference in terpenoid volatile levels compared with Murcott.
Fatty acids play a major role in ester volatile synthesis. We have identified the phospholipid D (gi|169160465, EC 3.1.4.4) in all three ripening stages. Oke et al. [36] found that the transgenic tomato fruits with an antisense phospholipase D (PLD) showed improved red color, lycopene content, and results suggest that a reduction in PLD activity may lead to increased membrane stability and preservation of membrane compartmentalization that can have positive quality impacts for transgenic fruit and their products. We did not find major enzyme differences downstream, such as the lipoxygenase (LOX) pathway, which comprises the action of phospholipase, lipoxygenase, and hydroxyperoxide. The lipid-derived volatiles represent the bulk of aroma volatiles in tomato and are generated by the lipoxygenase (LOX) pathway [37]. In addition, pyruvate decarboxylase (gi|17225598) is believed to be involved in the pathway that provide aldehydes and alcohols for ester synthesis [38].
Correlation between valencene/sesquiterpenes accumulation and total carotenoids
It is generally recognized that the cytosolic MVA pathway is responsible for the synthesis of sesquiterpenes, phytosterols and ubiquinone, whereas monoterpenes, gibberellins, abscisic acid, carotenoids and the prenyl moiety of chlorophylls, plastoquinone and tocopherol are produced in plastids via the MEP pathway [27,39]. Although the subcellular compartmentation of MVA and MEP pathways allows them to operate independently, metabolic “crosstalk” between the two pathways was prevalent, particularly in the direction of plastids to cytosol [5] (Figure 4). Prenyltransferase condenses dimethylallyl diphosphate with two IPP molecules to produce FPP or three IPP to geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP). In this study, Temple, had lower carotenoids but higher number of apocarotenoid volatiles than Murcott (Additional file 1: Table S1). Davidovich-Rikanati et al. [11] indicated that a transgenic tomato expressing a monoterpene synthesis gene resulted in lighter color in comparison with wild type tomatoes. Because GGPP is the precursor of the carotenoids, the activity of valencene synthase (Cstps1) converting FPP to valencene could be one of the limiting steps for carotenoid production in Temple (Figure 4). The important flavor volatile genes are those that encode enzymes responsible for synthesis of the end products and those encoding factors that regulate pathway output [18]. Valencene synthase (Cstps1) is the protein for synthesis of the end product, valencene. Klee et al. [18] indicated that all of the apocarotenoid volatile QTLs identified to date are associated with carotenoid biosynthetic enzymes, and substrate availability rather than enzyme synthesis appears to be limiting apocarotenoid volatiles. Our study indicated that the high concentration of carotenoids in Murcott might be due to its lack of valencene synthase activity (Figure 3; Additional file 2: Figure S2-B) as well as less sesquiterpenes and other carotenoid derived volatiles (Additional file 1: Table S1), compared with Temple. In tomato and watermelon, studies have indicated that carotenoid pigmentation patterns have profound effects on apocarotenoid volatile compositions [40,41]. By comparison with Murcott, our results suggest that the diversion of high valencene and other sesquiterpenes into the terpenoid pathway together with high production of apocarotenoid volatiles might have resulted in the lower concentration of carotenoids in Temple.
Figure 4.
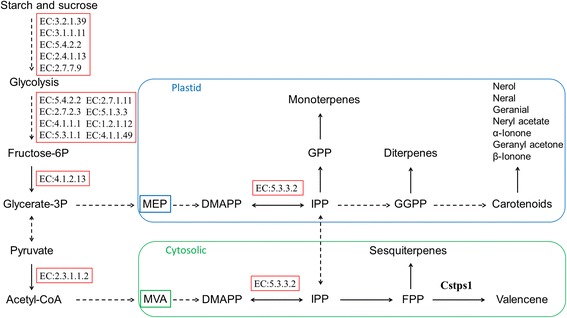
Summary of metabolic pathways leading to terpenoid-associated volatile synthesis. The differently expressed KEGG enzymes between Temple and Murcott mandarin hybrid fruit are in red boxes. The second metabolites are presented in yellow boxes. Pathway names are presented in the blue box. In most cases, arrows indicate multiple enzyme reactions. Abbreviations: MEP, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate; MVA, mevalonate; IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate; DMAPP, dimethyl-allyl diphosphate; GPP, geranyl diphosphate; FPP, farnesyl diphosphate; GGPP, geranylgeranyl diphosphate; Cstps1,valencene synthase.
Conclusions
Two thirds of differently expressed proteins were identified in the pathway of glycolysis and TCA, as well as amino acid, sugar and starch metabolism. This highlights the importance of these metabolic pathways for providing the carbon skeleton of the upstream precursors for most volatiles. Total carotenoids were significantly higher and apocarotenoid volatiles lower in Murcott than in Temple. It appears that high concentrations of apocarotenoid volatile compounds may result in low concentrations of carotenoids in Temple. In addition, we found that valencene synthase (Cstps1) was severely reduced in Murcott, and consequently, no valencene was detected in Murcott fruit during development, while substantial amounts were present in Temple. Further study is needed to confirm if there is a relationship between carotenoid concentrations and apocarotenoid volatile compounds, sesquiterpenes such as valencene, in citrus fruit. Improving fruit flavor is a challenging task using classic breeding methods because of the difficulty in scoring and quantifying such a complex trait. An increased understanding of biosynthetic pathways for fruit flavor compounds and corresponding regulatory mechanisms will lead to more efficient breeding strategies to improve flavor.
Methods
Plant material
Fruit of Murcott and Temple cultivars were collected on three harvest dates (designated as Stage 1, 2, and 3 respectively): 22 December 2008, 30 January 2009, and 11 March 2009 from groves at the University of Florida, Citrus Research and Education Center (UF-CREC) (Figure 1). These trees were grown under the same environmental conditions of soil, irrigation and illumination. Fruit maturity for Murcott and Temple was determined based on previous results [4], and three years of measurements of volatiles and non-volatiles at different stages amoung 14 mandarin hybrids including Temple and Murcott. Sample fruits were also selected based on fruit of similar size, color, and flavor by experienced breeders. Both Temple and Murcott have the same rootstock, Cleopatra mandarin, and are grown in the center part of field. In total, 20 fruits were collected randomly around the tree, 10 fruits for protein and 10 fruits for volatile compound identification, respectively. Three to four fruits were bulked as biological replications for proteome analysis.
Sugars, organic acids and carotenoids analysis
The measurement of sugars and acids was based on the method described by Baldwin et al. [42]. For titratable acidity (TA) and soluble solids content (SSC), TA was determined by titrating to pH8.2 with 0.1 M NaOH using an autotitrator (Mettler Toledo DL50, Columbus, OH) and SSC using a refractometer (Atago PR-101, Tokyo, Japan). Individual sugar and acid analysis was performed via high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Approximately 40 g of juice was extracted using 70 mL of an 80% ethanol/deionized water solution. The mixture was boiled for 15 min, cooled, and filtered (Whatman #4 filter paper, Batavia, IL). The filtered solution was brought to 100 mL with 80% ethanol. A total of 10 mL of the filtered solution was then passed through a C18 Sep-Pak (Waters/Millipore), followed by a 0.45 μm Millipore (Siemens-Millipore, Shrewbury, MA) filter. Individual sugars analysis was performed by HPLC with a refractive index detector (Perkin Elmer, Norwalk, Conn) equipped with a Waters Sugar Pak column [43-45]; The mobile phase was 10−4 M ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium calcium salt (CaEDTA) (0.5 mL min−1 flow rate at 90°C). All results are expressed as g 100 mL−1 juice. Organic acids, including ascorbic acid, were analyzed using a Perkin-Elmer Series 200 auto sampler (Waltham, MA), a Spectra System P4000 pump, and a Spectra System UV 6000 LP detector (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). Acids were separated on an AltechOA1000 Prevail organic acid column with a flow rate of 0.2 mL min−1 at 35°C and a mobile phase of 0.01 N H2SO4 [42,46]. The injection volume was 20 μL.
Carotenoids in the pellet and supernatant were analyzed using HPLC. Juice samples (30 mL) were centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 15 min. The pellet extracts were collected by dissolving pellets in acetone. Both pellet extracts and supernatants were individually filtered through a 0.45 μm filter into amber vials and stored at −20°C until injected into an HPLC (20 μL loop) equipped with an YMC carotenoid column (YMC Co. Ltd., Komatsu City, Japan). Elution conditions included a three-solvent gradient composed initially of water/methanol/methyl tertbutyl ether (4/81/15, v/v/v), and changed to linear gradients of 4/6/90 (v/v/v) by 60 min at a flow rate of 1 mL min−1, at 30°C. Compounds were detected using a photo diode array (PDA) detector scanning 200–700 nm at 5 nm increments, identified using standards (Sigma, Carotenoid Nature) and quantified using absorbance measurements. Values for pellet extracts and supernatants were then added together for each sample.
Volatile compound identification
Sample preparation for volatile and aroma identification used the same methods as previously described [4]. Briefly, Temple and Murcott samples were juice composites of 10 fruits with 2 replications of 5 fruits. The fruit were washed, rinsed and gently juiced manually using a table-top manual juicer (model 3183; Oster, Rye, NY, USA) to avoid potential peel components (peel oil) entering the juice. Juice samples (2.5 mL) were placed in 20 mL glass vials (Gerstel, Inc., Baltimore, MD, USA) along with saturated sodium chloride solution (2.5 mL) to help drive volatiles into the headspace and inhibit any potential enzymatic activity. An internal standard (3-hexanone, 1 ppm) was added to juice samples. The vials were capped and stored at −20°C until analyzed. The extraction of aroma volatiles was performed using solid-phase microextraction (SPME) with an MPS-2 auto sampler (Gerstel). The vials were incubated at 40°C for 30 min and volatile compounds were identified by comparison of their mass spectra with library entries (NIST/EPA/NIH Mass Spectral Library, version 2.0; National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MA, USA), as well as by comparing retention indices (RIs) with published RIs on both columns. Volatiles were semi-quantified by dividing peak area with the peak area of the internal standard.
Statistical analysis of volatile and non-volatile compounds
Two pooled samples from ten fruits were used for each harvesting time. All calculations were based on means of harvesting time. The differences of volatile and non-volatile compounds between Temple and Murcott were examined by an analysis of variance using the PROC GLM procedure of the SAS 9.4 statistical software package (http://www.sas.com).
Protein extraction
Protein extraction was modified based on the following description [21]. Briefly, the juice sacs were ground in homogenization buffer containing 0.5 M MOPS-KOH pH 8.5, 1.5% PVPP, 7.5 mM EDTA, 2 mM DTT, 0.1 mM PMSF, and 0.1% (v/v) protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). The homogenates were filtered through four layers of cheesecloth and centrifuged at 1500 × g for 20 min to eliminate cellular debris and nuclei. The pellet was discarded and the supernatant was centrifuged at 12000 × g for 20 min at 4°C. Soluble protein was precipitated in ammonium sulfate (85%) and collected by centrifugation at 12000 × g. The pellets were resuspended in a buffer containing 10 mM KH2PO4 and 0.5 mM DTT and desalted with a PD-10 column (Amersham Bioscience, GE Healthcare, Piscataway, NJ, USA) according to manufacturer’s instruction. Protein concentration was determined using the Bio-Rad Bradford protein assay (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA. USA). One hundred μg protein from each sample was precipitated in 80% cold acetone at −20°C overnight, centrifuged at 18,000 rpm for 20 min at 4°C, and washed once with 80% cold acetone.
iTRAQ Labeling and data analysis
In total, 18 samples were labeled and analyzed (2 cultivars × 3 maturity levels × 3 replications). Three to four fruits were pooled with 100 μg protein as one replication. iTRAQ labeling and data analysis were performed as a service by the Interdisciplinary Center for Biotechnology Research (ICBR) Proteomic Core facility at the University of Florida (Gainesville, FL, USA). For protein digestion, iTRAQ labeling and cation exchange were done according to the company’s protocols and described by Zhu et al. [47]. Briefly, the MS/MS data were analyzed by a thorough search considering biological modifications against the NCBI subset of green plants fasta database (downloaded on November, 2010) using the Paragon™ Algorithm of PROTEINPILOT v3.0 software suite (Applied Biosystems). For relative quantification of proteins, only MS/MS spectra unique to a particular protein and for which the sum of the signal-to-noise ratio for all of the peak pairs was greater than 9 were used for quantification (Applied Biosystems). To be identified as being differentially expressed, a protein had to be quantified with at least three spectra, a p < 0.05, and a ratio -fold change of at least 2 in more than two independent experiments (i.e. at least six peptides). Protein identities were confirmed using BLAST at the NCBI. Gene ontology analysis of identified proteins was carried out using Blast2GO [48]. The biological interpretation of the differentially expressed proteins was further completed by assigning them to metabolic pathways using Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) annotation. For proteins identified more than once, only the most significant identified protein was selected. In addition, functional classification of total identified proteins was analyzed by Blast2Go with default parameters (https://blast2go.com).
RNA extraction and quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (QRT-PCR)
Total RNA from each sample was extracted using Trizol (Ambion), and contaminating DNA was eliminated using the Turbo DNA-free Kit (Ambion, Austin, TX). The concentration of RNA was measured in a NanoDrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE). Total RNA was diluted as 5 ng/μL−1. QRT-PCR was carried out in the Agilent Mx3005P System (Agilent Technology) using a Brilliant III Ultra-Fast SYBR Green QRT-PCR Master Mix (Agilent Technology). Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as a reference gene to provide relative quantification for the target gene valencene synthase (Cstps1). Primer sequences of Cstps1 were used according to Sharon-Asa et al. [15] (Additional file 2: Table S4). The results represent normalized mean values and standard error of mean analyzed by using the program in the Agilent Mx3005P System.
Availability of supporting data
The data supporting the results of this article are included within the article.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mrs. Misty Holt for collecting fruit samples. This work was partly supported by grants from the New Varieties Development and Management Corporation (NVDMC), and the Citrus Research and Development Foundation Inc. (CRDF), on behalf of the Florida citrus industry.
Abbreviation
- ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
- Cstps1
Valencene synthase
- CaEDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium calcium salt
- DMPP
Isomer dimethylallyl diphosphate
- GC-MS
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry
- GO
Gene ontology
- HPLC
High performance liquid chromatography
- IPP
Isopentenyl diphosphate
- iTRAQ
Isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification
- KEGG
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- MEP
Methylerythritol 4-phosphate
- MVA
Mevalonate
- NAD+
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (oxidized form)
- NAPDH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (reduced form)
- QRT-PCR
Quantitative real-time Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- RIs
Retention indices
- SOD
Superoxide dismutase
- SPME
Solid-phase microextraction
- SSC
Soluble solids content
- TA
Titratable acidity
- TCA
The tricarboxylic acid cycle
Additional files
The excel spread sheet contains 3 tables describing identified volatiles, proteins and results of metabolite pathway analyses in Temple and Murcott. Table S1. Volatiles identified in Temple and Murcott mandarin hybrid fruit. Table S2. Total proteins identified in fruit flesh of Temple and Murcott mandarin hybrid fruits, and ratio of Temple versus Murcott. Table S3. Metabolite pathways containing differentially expressed proteins between Temple and Murcott mandarin hybrid fruits.
Detailed information on primers used for amplifying valencene synthase, gene ontology assignment, valencene and carotenoid content during fruit ripening in Temple and Murcott. Table S4. Primers used for amplifying valencene synthase and control genes for real-time PCR. Figure S1. Gene Ontology (GO) assignment (2nd level GO terms) of differential proteins between Murcott and Temple. The differential proteins were categorized based on GO annotation and the proportion of each category was displayed according to: Biological process (A), Cellular component (B) and Molecular function (C). Because a gene could be assigned to more than one GO term, the sum of genes in a category would be above the total number 92. X axis indicates number of different expressed proteins. Figure S2. (A) Valencene production during fruit ripening in Temple and Murcott; (B) Carotenoid content in Temple and Murcott during ripening.
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
QY, AP, and FGG conceived and designed the study; QY, AP, EAB, JB and YY collected and analyzed the volatile and non-volatile data; QY, MH and HSD collected and analyzed the proteomic data; QY wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
Qibin Yu, submitting author.
Contributor Information
Qibin Yu, Email: qibin@ufl.edu.
Anne Plotto, Email: Anne.Plotto@ars.usda.gov.
Elizabeth A Baldwin, Email: Liz.Baldwin@ars.usda.gov.
Jinhe Bai, Email: Jinhe.Bai@ars.usda.gov.
Ming Huang, Email: minghuang@ufl.edu.
Yuan Yu, Email: ymmzyz@ufl.edu.
Harvinder S Dhaliwal, Email: dhaliwal_mandhali@yahoo.com.
Frederick G Gmitter, Jr, Email: fgmitter@ufl.edu.
References
- 1.Baldwin IT. Plant volatiles. Curr Biol. 2010;20(9):392–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.02.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tietel Z, Plotto A, Fallik E, Lewinsohn E, Porat R. Taste and aroma of fresh and stored mandarins. J Sci Food Agric. 2011;91(1):14–23. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.4146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Miyazaki T, Plotto A, Baldwin EA, Reyes-De-Corcuera JI, Gmitter FG., Jr Aroma characterization of tangerine hybrids by gas-chromatography-olfactometry and sensory evaluation. J Sci Food Agric. 2012;92(4):727–35. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.4663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Miyazaki T, Plotto A, Goodner K, Gmitter FG., Jr Distribution of aroma volatile compounds in tangerine hybrids and proposed inheritance. J Sci Food Agric. 2011;91(3):449–60. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.4205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dudareva N, Klempien A, Muhlemann JK, Kaplan I. Biosynthesis, function and metabolic engineering of plant volatile organic compounds. New Phytol. 2013;198(1):16–32. doi: 10.1111/nph.12145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Goff SA, Klee HJ. Plant volatile compounds: sensory cues for health and nutritional value? Science. 2006;311(5762):815–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1112614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tieman D, Bliss P, McIntyre LM, Blandon-Ubeda A, Bies D, Odabasi AZ, et al. The chemical interactions underlying tomato flavor preferences. Curr Biol. 2012;22(11):1035–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Baldwin EA, Goodner K, Plotto A. Interaction of volatiles, sugars, and acids on perception of tomato aroma and flavor descriptors. J Food Sci. 2008;73(6):S294–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2008.00825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Beekwilder J, Alvarez-Huerta M, Neef E, Verstappen FW, Bouwmeester HJ, Aharoni A. Functional characterization of enzymes forming volatile esters from strawberry and banana. Plant Physiol. 2004;135(4):1865–78. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.042580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Aharoni A, Keizer LCP, Bouwmeester HJ, Sun ZK, Alvarez-Huerta M, Verhoeven HA, et al. Identification of the SAAT gene involved in strawberry flavor biogenesis by use of DNA microarrays. Plant Cell. 2000;12(5):647–61. doi: 10.1105/tpc.12.5.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Davidovich-Rikanati R, Sitrit Y, Tadmor Y, Iijima Y, Bilenko N, Bar E, et al. Enrichment of tomato flavor by diversion of the early plastidial terpenoid pathway. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(8):899–901. doi: 10.1038/nbt1312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gonzalez Aguero M, Troncoso S, Gudenschwager O, Campos Vargas R, Moya Leon MA, Defilippi BG. Differential expression levels of aroma-related genes during ripening of apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) Plant Physiol Bioch. 2009;47(5):435–40. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2009.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhang B, Shen JY, Wei WW, Xi WP, Xu CJ, Ferguson I, et al. Expression of genes associated with aroma formation derived from the fatty acid pathway during peach fruit ripening. J Agric Food Chem. 2010;58(10):6157–65. doi: 10.1021/jf100172e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lucker J, Bowen P, Bohlmann J. Vitis vinifera terpenoid cyclases: functional identification of two sesquiterpene synthase cDNAs encoding (+)-valencene synthase and (−)-germacrene D synthase and expression of mono- and sesquiterpene synthases in grapevine flowers and berries. Phytochemistry. 2004;65(19):2649–59. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sharon-Asa L, Shalit M, Frydman A, Bar E, Holland D, Or E, et al. Citrus fruit flavor and aroma biosynthesis: isolation, functional characterization, and developmental regulation of Cstps1, a key gene in the production of the sesquiterpene aroma compound valencene. Plant J. 2003;36(5):664–74. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tietel Z, Feldmesser E, Lewinsohn E, Fallik E, Porat R. Changes in the transcriptome of 'Mor' mandarin flesh during storage: emphasis on molecular regulation of fruit flavor deterioration. J Agric Food Chem. 2011;59(8):3819–27. doi: 10.1021/jf104614s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Muhlemann JK, Klempien A, Dudareva N. Floral volatiles: from biosynthesis to function. Plant Cell Environ. 2014;37(8):1936–49. doi: 10.1111/pce.12314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Klee HJ. Improving the flavor of fresh fruits: genomics, biochemistry, and biotechnology. New Phytol. 2010;187(1):44–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pan Z, Zeng Y, An J, Ye J, Xu Q, Deng X. An integrative analysis of transcriptome and proteome provides new insights into carotenoid biosynthesis and regulation in sweet orange fruits. J Proteomics. 2012;75(9):2670–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2012.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Katz E, Fon M, Eigenheer RA, Phinney BS, Fass JN, Lin D, et al. A label-free differential quantitative mass spectrometry method for the characterization and identification of protein changes during citrus fruit development. Proteome Sci. 2010;8:68. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-8-68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Katz E, Fon M, Lee YJ, Phinney BS, Sadka A, Blumwald E. The citrus fruit proteome: insights into citrus fruit metabolism. Planta. 2007;226(4):989–1005. doi: 10.1007/s00425-007-0545-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Guillaumie S, Fouquet R, Kappel C, Camps C, Terrier N, Moncomble D et al. Transcriptional analysis of late ripening stages of grapevine berry. BMC Plant Biol. 2011;11:165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Saunt J. Citrus Varieties of the World: an Illustrated Guide. Norwich, England: Sinclair international Limited; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Chen S, Harmon AC. Advances in plant proteomics. Proteomics. 2006;6(20):5504–16. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200600143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gan CS, Chong PK, Pham TK, Wright PC. Technical, experimental, and biological variations in isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) J Proteome Res. 2007;6(2):821–7. doi: 10.1021/pr060474i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pierce A, Unwin RD, Evans CA, Griffiths S, Carney L, Zhang L, et al. Eight-channel iTRAQ enables comparison of the activity of six leukemogenic tyrosine kinases. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008;7(5):853–63. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M700251-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schwab W, Davidovich-Rikanati R, Lewinsohn E. Biosynthesis of plant-derived flavor compounds. Plant J. 2008;54(4):712–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Feng C, Chen M, Xu CJ, Bai L, Yin XR, Li X, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra) fruit development and ripening using RNA-Seq. BMC Genomics. 2012;13:19. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yun Z, Li WY, Pan ZY, Xu J, Cheng YJ, Deng XX. Comparative proteomics analysis of differentially accumulated proteins in juice sacs of ponkan (Citrus reticulata) fruit during postharvest cold storage. Postharvest Biol Tec. 2010;56(3):189–201. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2010.01.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pan ZY, Liu Q, Yun Z, Guan R, Zeng WF, Xu Q, et al. Comparative proteomics of a lycopene-accumulating mutant reveals the important role of oxidative stress on carotenogenesis in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis [L.] osbeck) Proteomics. 2009;9(24):5455–70. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200900092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Trindade H. Molecular biology of aromatic plants and spices. A Rev Flavour Frag J. 2010;25(5):272–81. doi: 10.1002/ffj.1974. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liu Q, Zhu A, Chai L, Zhou W, Yu K, Ding J, et al. Transcriptome analysis of a spontaneous mutant in sweet orange [Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck] during fruit development. J Exp Bot. 2009;60(3):801–13. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Aharoni A, Jongsma MA, Bouwmeester HJ. Volatile science? Metabolic engineering of terpenoids in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2005;10(12):594–602. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2005.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Hanada K. An evolutionary view of functional diversity in family 1 glycosyltransferases. Plant J. 2011;66(1):182–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fan J, Chen C, Yu Q, Li ZG, Gmitter FG., Jr Characterization of three terpenoid glycosyltransferase genes in 'Valencia' sweet orange (Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck) Genome. 2010;53(10):816–23. doi: 10.1139/G10-068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Oke M, Pinhero RG, Paliyath G. The effects of genetic transformation of tomato with antisense phospholipase D cDNA on the quality characteristics of fruits and their processed products. Food Biotechnol. 2003;17(3):163–82. doi: 10.1081/FBT-120026338. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Pirrello J, Regad F, Latche A, Pech JC, Bouzayen M. Regulation of tomato fruit ripening. CAB Reviews. 2009;4(051):1–14. doi: 10.1079/PAVSNNR20094051. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Song J, Forney CF. Flavour volatile production and regulation in fruit. Canadian J Plant Sci. 2008;88(3):537–50. doi: 10.4141/CJPS07170. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dudareva N, Negre F, Nagegowda DA, Orlova I. Plant volatiles: recent advances and future perspectives. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2006;25(5):417–40. doi: 10.1080/07352680600899973. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lewinsohn E, Sitrit Y, Bar E, Azulay Y, Ibdah M, Meir A, et al. Not just colors – carotenoid degradation as a link between pigmentation and aroma in tomato and watermelon fruit. Trends Food Sci Tech. 2005;16(9):407–15. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2005.04.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lewinsohn E, Sitrit Y, Bar E, Azulay Y, Meir A, Zamir D, et al. Carotenoid pigmentation affects the volatile composition of tomato and watermelon fruits, as revealed by comparative genetic analyses. J Agric Food Chem. 2005;53(8):3142–8. doi: 10.1021/jf047927t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Baldwin E, Plotto A, Manthey J, McCollum G, Bai J, Irey M, et al. Effect of Liberibacter infection (huanglongbing disease) of citrus on orange fruit physiology and fruit/fruit juice quality: chemical and physical analyses. J Agric Food Chem. 2010;58(2):1247–62. doi: 10.1021/jf9031958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Baldwin EA, Nisperos-Carriedo MO, Baker R, Scott JW. Quantitative analysis of flavor parameters in six Florida tomato cultivars (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) J Agric Food Chem. 1991;39(6):1135–40. doi: 10.1021/jf00006a029. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Baldwin EA, Scott JW, Einstein MA, Malundo TMM, Carr BT, Shewfelt RL, et al. Relationship between sensory and instrumental analysis for tomato flavor. J Am Soc Hortic Sci. 1998;123(5):906–15. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Baldwin EA, Goodner K, Plotto A, Pritchett K, Einstein M. Effect of volatiles and their concentration on perception of tomato descriptors. J Food Sci. 2004;69(8):S310–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2004.tb18023.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Baldwin EA, Bai J, Plotto A, Cameron R, Luzio G, Narciso J, et al. Effect of extraction method on quality of orange juice: hand-squeezed, commercial-fresh squeezed and processed. J Sci Food Agric. 2012;92(10):2029–42. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.5587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zhu M, Dai S, McClung S, Yan X, Chen S. Functional differentiation of Brassica napus guard cells and mesophyll cells revealed by comparative proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009;8(4):752–66. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M800343-MCP200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Conesa A, Gotz S, Garcia-Gomez JM, Terol J, Talon M, Robles M. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics. 2005;21(18):3674–6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


