Abstract
Blindness due to retinal degeneration affects millions of people worldwide, but many disease-causing mutations remain unknown. PNPLA6 encodes the patatin-like phospholipase domain containing protein 6, also known as neuropathy target esterase (NTE), which is the target of toxic organophosphates that induce human paralysis due to severe axonopathy of large neurons. Mutations in PNPLA6 also cause human spastic paraplegia characterized by motor neuron degeneration. Here we identify PNPLA6 mutations in childhood blindness in seven families with retinal degeneration, including Leber congenital amaurosis and Oliver McFarlane syndrome. PNPLA6 localizes mostly at the inner segment plasma membrane in photo-receptors and mutations in Drosophila PNPLA6 lead to photoreceptor cell death. We also report that lysophosphatidylcholine and lysophosphatidic acid levels are elevated in mutant Drosophila. These findings show a role for PNPLA6 in photoreceptor survival and identify phospholipid metabolism as a potential therapeutic target for some forms of blindness.
PNPLA6 (also previously referred to as neuropathy target esterase (NTE)) is a highly conserved lysophospholipase anchored to the cytoplasmic face of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). It is the primary target of toxic organophosphorous compounds (found in agricultural pesticides and agents of chemical warfare) that cause axonal degeneration in large neurons. Human organophosphorous-induced delayed neuropathy (OPIDN) occurs when PNPLA6 becomes phosphorylated by these organophosphates, followed by dealkylation of the phosphoryl enzyme, inhibiting the catalytic domain4,5. Patients with mutations in the catalytic domain of PNPLA6 develop a Mendelian motor neuron disease called spastic paraplegia (SPG39), which is characterized by distal degeneration of motor axons surprisingly similar to OPIDN6,7. The exact mechanism of PNPLA6 function in both OPIDN and SPG39 remains unknown8.
PNPLA6 is expressed in the brain, where it deacetylates phosphatidylcholine (PC) to lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) and LPC to glycerophosphocholine1,9. In Drosophila, the Swiss cheese protein (sws; the orthologue of vertebrate PNPLA6) is involved in the regulation of membrane lipid homeostasis and in the survival of both neurons and glia as well10. In mice, Pnpla6-deficient animals are embryonic lethal11 but brain-specific mutants show neurodegeneration12, and there is much evidence that PNPLA6 is involved in maintaining nervous system integrity13,14. Interestingly, mice expressing a single copy of Pnpla6 are viable but show increased sensitivity to organophosphorous toxins11.
In this work, we identified biallelic PNLPA6 mutations in patients with childhood blindness due to severe photoreceptor death and clinical features of Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA) and, interestingly, also of the rare Oliver McFarlane syndrome (OMS; OMIM 275400). OMS patients have a complex phenotype characterized by blindness due to severe photoreceptor degeneration, dwarfism due to pituitary growth hormone deficiency, trichomegaly and progressive alopecia. Occasionally, OMS is associated with mental retardation, distal muscle weakness/wasting and ataxia, due to axonal peripheral neuropathy. We document PNPLA6 expression in mouse and Drosophila retina, and test phenotypic and metabolic consequences (phospholipids) of PNLPA6 and SWS mutations in humans and Drosophila, respectively. We show that PNPLA6 has a role in photoreceptor survival and identify phospholipid metabolism as a potential therapeutic target for some forms of blindness.
Results
Identification of PNPLA6 mutations in OMS
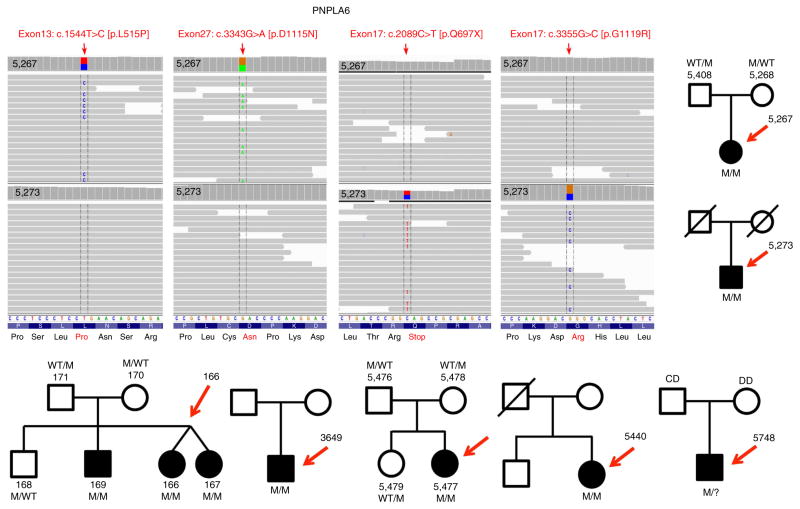
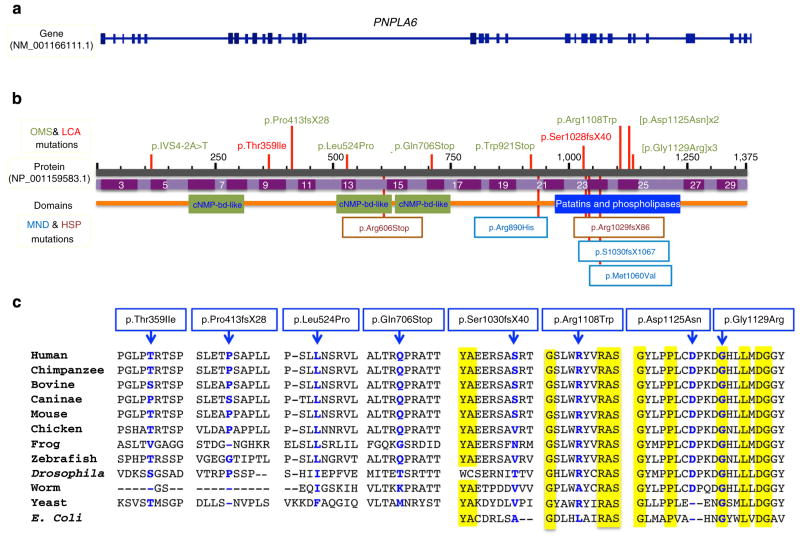
Our initial goal was to discover the causal genetic mutations for two sporadic cases (5,267 and 5,273) in two Canadian families and three affected siblings (166, 167 and 169), in a third OMS family from the Czech Republic (Fig. 1). Although most OMS cases seem to be sporadic, segregation patterns of the phenotype support the recessive mode of inheritance. We therefore hypothesized that we could identify the unknown causal gene by excluding all genomic variants, except those biallelic variants that we would find in the same gene in the five affected OMS patients (assuming one gene for OMS). Whole exome sequencing (WES) first excluded such mutations in the currently known 210 retinal disease genes. We then sifted through thousands of variants and identified that all five patients harboured and shared biallelic variants in PNPLA6 and not in any other gene (Fig. 1). We identified six missense mutations in these three OMS families in PNPLA6 (NM 001166111.1). With Sanger sequencing, we confirmed co-segregation in two out of the three families (one family was deceased) and excluded the variants from 100 normal controls. We then recruited five more OMS families from around the world (Fig. 1), and overall we identified ten novel PNPLA6 mutations (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Fig. 1) in a total of seven families. Only one OMS family did not harbour PNPLA6 mutations, suggesting allelic heterogeneity and thus a second OMS-causing gene. We then searched for PNPLA6 mutations in 200 cases with LCA that had undergone WES and found one patient with significant autism and two PNPLA6 mutations. We discovered a total of five missense, two nonsense, two frameshift and one splice site mutation(s) in PNPLA6 (Figs 1 and 2). One of the mutations, that is, p. Gly1129Arg was found three times, while another mutation, that is, p. Asp1125Asn was identified twice, affecting residues in the evolutionarily highly conserved patatin domain (down to Escherichia coli; Fig. 2c). In five out of seven patients, we found compound heterozygous missense mutations in both the regulatory (amino-terminal) and in the catalytic domain (carboxy-terminal). The missense mutations are all in residues that are very well conserved (Fig. 2c). Targeted DNA screening revealed that the mutations found in the affected individuals are rare, as they were absent from >1,000 WES samples in our in-house databases of which at least 200 patients were genetically unsettled LCA.
Figure 1. PNPLA6 mutations in individuals from seven families with childhood blindness.
Sequencing reads are aligned against positive strand of hg19. Vertical arrows represent the 100 paired-end reads in 5,267 and 5,273 patients, respectively. Both patients carry heterozygous mutations in PNPLA6: 5,267 has 2 missense mutations c.1571T>C (leucine to proline substitution at codon 524) and c.3373G>A (aspartic acid to asparagine at codon 1125). Patient 5,273 has a nonsense mutation c.2116C>T, which result in a glutamine to stop codon at codon 706, leading to loss of the last 669 amino acids of the protein and a missense mutation c.3385G>C glycine to arginine at codon 1129. All of the complementary DNA positions are based on PNPLA6 NM_001166111.1. Moreover, shown are seven families/pedigrees with various forms of childhood blindness due to photoreceptor degeneration in OMS and LCA. Chromatograms of the PNPLA6 mutations, pedigrees and co-segregation of the mutations are shown for each family (Supplementary Fig. 1).
Figure 2. Mutations identified in PNPLA6 patients.
Shown here is the genetic structure (a) and the protein structure (b) with all the mutations (ten) identified in the current study indicated above the PNPLA6 protein. Previously reported mutations causing the paraplegia syndrome (SPG39) are shown below the protein. A line-up of the affected protein regions from various species (from E. coli to man) is shown in c, showing the marked and significant evolutionary conservation of the residues, some down to E. coli.
Genotype/phenotype correlations in the cohort
All except one patient had OMS, as per standard clinical diagnostic criteria, with some patients exhibiting ataxia, mental retardation, or peripheral neuropathy. Detailed phenotypes are described in Table 1. All our OMS patients had significant retinal degeneration with photo-receptor death and blindness, long lashes and dwarfism. The retinal degeneration is severe and early onset, with photoreceptor death, but also with inner retinal changes and retinal thinning accompanied by lipofuscin metabolism abnormalities (Fig. 3).
Table 1.
Complex phenotypes associated with PNPLA6 mutations.
| Patient MOGL study |
5,267 | 5,273 | 166 | 167 | 169 | 3,649 | 5,477 | 5,440 | 5,748 |
| Gender | F | M | F | F | M | M | F | F | M |
| Age at first exam (years) |
9 | 29 | 3 | 3 | 16 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Birth weight (kg) |
2 kg | NA | 3 kg | 3.3 kg | 1.9 kg | NA | 2.5 kg | 2.5 kg | 2.4 kg |
| Height | Short | Short | Short | Short | Short | Normal | Short/ Dwarfism |
Short | Short |
| Bone age | Delayed | NA | NA | NA | Normal | None | Delayed | Delayed | Delayed |
| Trichomegaly | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | NA | Normal | NA |
| Hair | Normal | Sparse | Alopecia | Normal | Alopecia | Normal | Alopecia | Alopecia | NA |
| Retinal degeneration |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| GH deficiency | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | None | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Hypothyroidism | Yes | Yes | None | None | None | None | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Hypogonadism | None | None | Yes | Yes | Yes | None | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Mental retardation |
None | None | None | None | None | Autism | Mild | None | Yes |
| Peripheral neuropathy and/or ataxia |
None | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | None | Yes | Motor neuropathy |
Yes |
| Inheritance | Sporadic | Sporadic | AR | AR | AR | Sporadic | NA | Sporadic | Sporadic |
| Chromosome | NA | 46 XY | 46 XX | 46 XX | 46 XY | NA | NA | 46 XY | NA |
| Age when last seen (years) |
9 | 30 | 22 | 22 | 31 | 20 | 23 | 54 | 20 |
| VA | 20/400 OD 20/400 OS |
Light perception with projection in both eyes |
NA | NA | NA | Counting fingers |
Lower than 20/400 |
Light perception only |
20/200 OD 20/80 OS |
| GVF | No measurable field |
No measurable visual field |
NA | NA | NA | No measurable field |
No measurable field |
No measurable field |
Peripheral constriction |
| ERG | No recordable responses |
No recordable responses |
NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | No recordable responses |
NA |
| Retinal appearance |
Severe degeneration |
Severe degeneration |
Severe degeneration |
Severe degeneration |
Severe degeneration |
Severe degeneration |
Severe degeneration |
Severe degeneration |
Severe degeneration |
| Cancer | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | None |
| Dental history | None | Chalky white teeth, numerous cavities |
tooth development abnormalities |
tooth development abnormalities |
tooth development abnormalities |
None | None | Delay in dentition |
None |
| Comments | None | None | Severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia |
Severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia |
Severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia |
Nystagmus | Retinal sparing around the optic disc. Optic disc normal appearance |
Mild elevation of LFTs |
Thoracic lumbar scoliosis |
ERG, electroretinograms; F, female; GH, growth hormone; GVF, Goldmann visual field; LFT, liver function tests; M, male; NA, not available; OD, oculus dexter; OS, oculus sinister; VA, Snellen visual acuity.
Figure 3. Retinal phenotypes of children with PNPLA6 mutations.
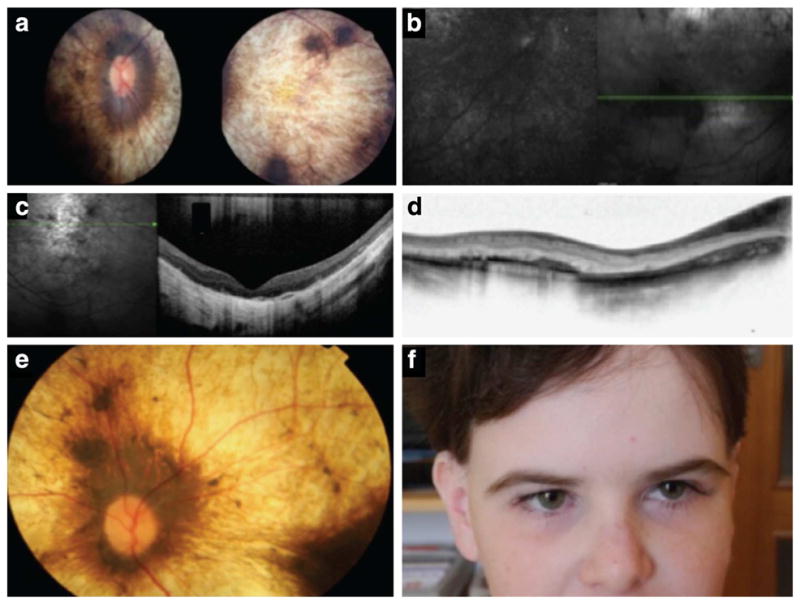
(a) A retinal photo shows severe choroidal and retinal atrophy ‘choroideremia like’ in patient 5,267. (b) Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) shows severely abnormal and grossly absent lipofuscin metabolism. (c) Optical coherence tomography reveals severe photoreceptor loss, retinal thinning and retinal remodelling. (d) Using optical coherence tomography, we found that the inner retinal layers are also abnormal. (e) Another child (167) with mutations in PNPLA6 shows a strikingly similar retinal appearance as shown in a, again illustrating the ‘choroideremia-like’ retinal changes. (f) Full-face photo of a child with PNPLA6 mutations, illustrating the extremely long lashes.
In proband 5,267 from family 1, we found two missense mutations (Figs 1 and 2b and Supplementary Fig. 1) One of the missense mutations resides in a residue in the regulatory region and the second in the catalytic region (patatin domain) (Fig. 2). Briefly, this affected French–Canadian child with OMS developed nyctalopia (significant nightblindness) at the age of 2 years. At age 9 years, she had 20/1,200 visual acuities from severe retinal and choroidal degeneration (Fig. 3a), with diffuse photoreceptor loss (Fig. 3b), growth retardation and long lashes, but high intelligence. In proband 5,273 from family 2 with OMS, we found a nonsense mutation in the regulatory region and a missense mutation in the patatin domain of PNPLA6 (Figs 1, 2b and Supplementary Fig. 1). This 30-year-old Scottish male had light perception vision photoreceptor loss, dwarfism, peripheral neuropathy and ataxia. In cases 166, 167 and 169 from the Czech OMS family 3 we found a splice site mutation in the regulatory region and a missense mutation in the patatin domain (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Fig. 1). The three affected members had severe photoreceptor degeneration, dwarfism, long lashes, normal intelligence, ataxia and peripheral neuropathy. Proband 3,649 from family 4 with LCA was found to have a frameshift in the catalytic region and a missense mutation in the regulatory region of PNPLA6 (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Fig. 1). This Caucasian child had congenital visual loss and significant autism but no other systemic disease. Proband 5,477 from family 5 with OMS was found to have two missense mutations, both in the catalytic region, which co-segregate through this Brazilian family (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Fig. 1). The affected child has severe visual loss (counting fingers vision) from photoreceptor degeneration, long lashes, short stature, mild mental handicap and neuropathy with ataxia. Proband 5,440 from family 6 with OMS from Scotland carried a frameshift mutation in the regulatory region and a missense mutation in the catalytic region of PNPLA6, which co-segregated in the family (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Fig. 1). The affected child was noted to have congenital nystagmus from photoreceptor degeneration, normal mentation and lashes, but short stature and a motor neuropathy. Proband 5,748 from family 7 with OMS from Great Britain was found to harbour a nonsense mutation in the regulatory region of PNPLA6, shared by the father of the affected child, but we could not identify the maternal mutation (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Fig. 1).
PNPLA6 is expressed in mouse and fly photoreceptors
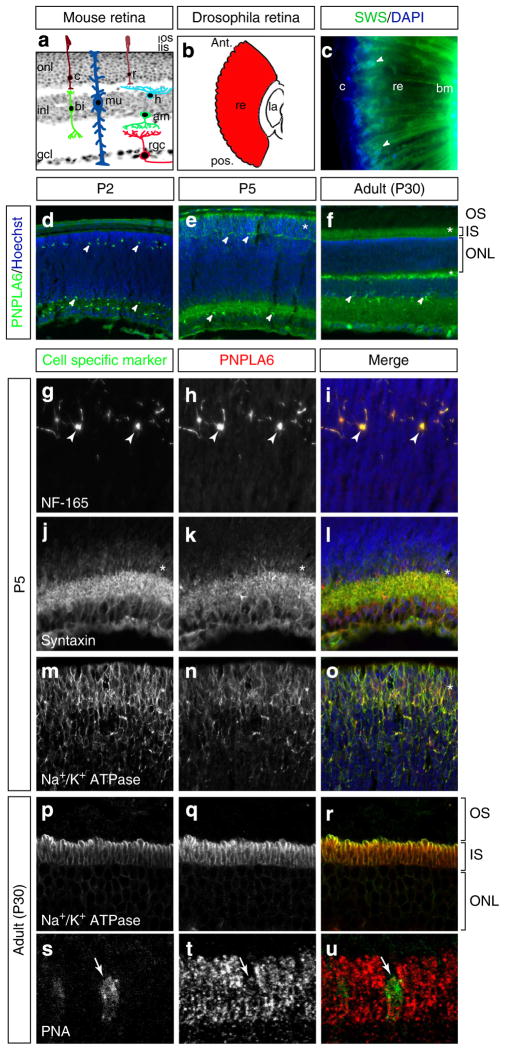
All our subjects with PNPLA6 mutations have photoreceptor degeneration resulting in blindness. However, PNPLA6 mutations associated with SPG39 and OPIDN diseases are not known to cause retinal degeneration or blindness. As it was previously not known whether PNPLA6 is expressed in retinal tissue, we investigated the spatiotemporal retinal expression pattern of the PNPLA6 orthologues in Drosophila (SWS) and in mouse retina (Fig. 4a,b). Using an anti-serum against fly SWS, we found expression around photoreceptor nuclei and along the entire photoreceptor (Fig. 4c). Performing co-stainings with the plasma membrane marker anti-horseradish peroxidase, we found that some of the SWS is associated with the plasma membrane, but that it can also be found in the cytoplasm (Supplementary Fig. 2). This is in agreement with our previous results in central nervous system neurons, which showed that SWS can be detected in the ER10. In the mouse, we found PNPLA6-expressing cells in both developing and adult retinas (Fig. 4d–f). Co-staining of PNPLA6 with cell-type-specific markers showed restricted expression in horizontal, amacrine and photoreceptor cells (Fig. 4g–o), but not in ganglion cells (not shown). To determine the subcellular localization of PNPLA6 in photoreceptors, we co-stained adult mouse retinal sections with PNPLA6 and the inner segment (IS) plasma membrane marker Na+/K+ ATPase. Three-dimensional confocal imaging revealed clear co-labelling (Fig. 4p–r), indicating primarily IS plasma membrane localization in adult photoreceptors, although some intracellular staining was also observed (Fig. 4q). Interestingly, PNPLA6 was not found in the outer segments (OS). Peanut agglutinin co-staining in adult mice showed that PNPLA6 is also expressed in cones (Fig. 4s–u).
Figure 4. PNPLA6 expression in the mouse and Drosophila retina.
(a) Section of a mouse retina superimposed with illustrations of the cell types found in the three different layers. onl, outer nuclear layer; inl, inner nuclear layer; gcl, ganglion cell layer; os, outer segment; is, inner segment; r, rod; c, cone; mu, Müller cell; rgc, retinal ganglion cell; bi, bipolar cell; h, horizontal cell; am, amacrine cell. (b) Illustration of a Drosophila retina along the longitudinal axis. ant, anterior; pos, posterior; re, retina; la, lamina. (c) Immunostaining for SWS in longitudinal sections of fly retina. SWS is expressed surrounding the nuclei and along the entire length of the photoreceptor (arrowheads). bm, basement membrane; c, cornea; re, retina. (d–f) Time course of PNPLA6 expression in the mouse retina, as indicated. PNPLA6 is expressed in cells of the inner and outer retina at all stages examined (arrowheads), as well as in the photoreceptor inner segment area (asterisk). Co-immunostaining of mouse retinal sections at P5 with PNPLA6 and the horizontal cell marker neurofilament-165 (NF-165; g–i), amacrine cell marker syntaxin (j–l) and the photoreceptor cell marker Na+/K+-ATPase (m–o). Arrowheads point to positive cells and asterisks point to area of positive staining. (p–r) Confocal z-stack projection of an adult mouse retinal sections (P30) co-immunostained with PNPLA6 and the photoreceptor inner segment plasma membrane marker Na+/K+-ATPase. PNPLA6 localizes mostly to the plasma membrane, although some staining is detected inside the inner segment. (s–u) Co-immunostaining of PNPLA6 with the cone photoreceptor marker peanut agglutinin (PNA) showing expression of PNPLA6 in cones (arrow). Sections were counterstained with Hoechst (blue) to reveal nuclei.
PNPLA6 is required for photoreceptor survival in Drosophila
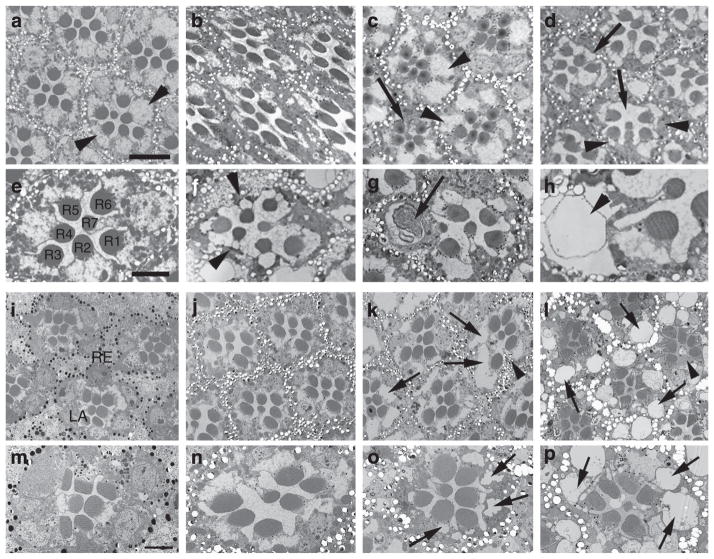
To study the consequences of PNPLA6 loss, we analysed the recessive sws1-null mutant in Drosophila, which shows severe age-dependent neurodegeneration15 starting around day five of adulthood, but no overt eye phenotype. Electron microscopic studies from sws1 flies shortly before eclosion revealed that the eye developed normally with all photoreceptors present (Fig. 5b). Whereas 14-day-old flies still had mostly intact ommatidia (occasionally one photoreceptor was lost, arrow, Fig. 5c), at 23 days the photoreceptors were either lost (arrows, Fig. 5d) or showed degenerative signs such as condensed cell bodies (arrowheads, Fig. 5d,f), intracellular membranous bodies (arrow, Fig. 5g), or vacuoles (arrowhead, Fig. 5h). Thirty-day-old wild-type flies did not reveal any of these phenotypes (Fig. 5a,e). To exclude that the photoreceptor degeneration is a secondary effect of the brain degeneration in sws1, we also analysed an eye-specific knockdown of SWS using GMR-GAL4. Again, the photoreceptors developed normally (Fig. 5i,m) and still appeared unaffected in 7-day-old flies (Fig. 5j,n), but when 30 days old flies showed obvious signs of degeneration (Fig. 5k,o, arrows) and some photoreceptors were lost (Fig. 5k, arrowhead). To determine whether the degeneration was activity dependent, we raised the flies in the dark. As seen in Fig. 5l,p, this did not prevent the degeneration, showing that neuronal activity is not affecting the degeneration. To further assess a connection between degeneration and photoreceptor activity, we directly measured activity using electroretinograms (ERGs). Again, we could not detect any defects neither in young flies (1–3 days old) nor in aged ones (28–30 days old, Supplementary Fig. 3), which strongly suggests that phototransduction is not affected by the loss of SWS.
Figure 5. Loss of SWS causes photoreceptor degeneration in Drosophila.
Electron microscopy studies from a 3-week-old wild-type fly show intact ommatidia with seven photoreceptor cells (R1–7) present (a,e; arrowheads in a point to the photoreceptor cell somata). Performing sections from the retina of a sws1 mutant fly shortly before eclosion (pharate adult) shows that photoreceptors develop normally (b) and persist during the first 2 weeks of adulthood (c, 14 days), although occasionally ommatidia missing a single photoreceptor can be found (arrow). However, after 23 days of ageing (which, due to the reduced live span of sws1, is shortly before these flies die), photoreceptor degeneration is evident in all ommatidia by the loss of photoreceptors (arrows in d), and in the condensed and darkly stained cell somata of the photoreceptors that are still present (arrowheads). In addition, vacuoles can be found in the somata (arrowheads in f,h) and the rhabdomeres are shrunken. In some photoreceptors, membranous structures can be found (arrow in g). Knocking down SWS specifically in the eye using an RNA interference (RNAi) construct expressed by GMR-GAL4 showed that newly enclosed flies look normal with all the seven photoreceptors R1–7 present (i,m). At 7 days of age the ommatidia still look wild type (j,n), but at 4 weeks the photoreceptors clearly show degeneration with vacuoles forming in the photoreceptor somata (arrows in k,o) and loss of some photoreceptors (arrowhead in k). Raising the flies in the dark resulted in a comparable photoreceptor degeneration in 30-day-old flies (l,p). Scale bar, 4 μm (a), 2 μm (e).
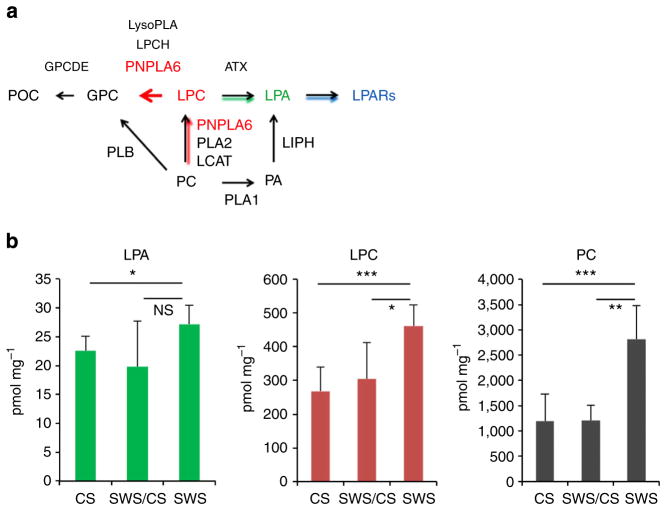
Mutations in PNPLA6 alters phospholipid levels
Loss of SWS/PNPLA6 results in increased PC levels in flies and mice10,13. We therefore predicted that sws1 Drosophila as well as our OMS patients may show abnormalities in phospholipid levels due to lower PNPLA6 enzymatic activity. If true, this may then provide a tool for clinical diagnoses and potentially provide a therapeutic target. Based on the phospholipid metabolism showed in Fig. 6a, we predicted that mutant PNPLA6 (NTE) would result in elevated PC, LPC and LPA levels. This was confirmed using mass spectrometry analysis of these phospholipids in extracts from whole wild-type and mutant Drosophila (Fig. 6b). We also measured phospholipid levels in serum from family 1 (5,267) and family 3 (166–171) members. We found on average 10–15% increased levels of PC, LPA and LCA in patients and mutation carriers compared with controls (data not shown). However, as levels of these phospholipids are found to vary about two- to sixfold in normal human plasma/serum samples, with limited sample size and no opportunity to replicate these measurements in additional patients, the detected changes did not reach statistical significance.
Figure 6. Phospholipid metabolism is altered in SWS mutant flies.
(a) PNPLA6 (NTE)-related metabolic pathway. POC, phosphorylcholine; GPC, glycerolphosphocholine; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPARs, lysophosphatidic acid receptors; PCH, phosphatidylcholine; PA, phosphatidic acid; GPCDE, glycerolphosphocholinediesterase; NTE, neuropathy target esterase; LCAT, lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase; PLA1, phospholipase A1; PLA2, phospholipase A1; PLB, phospholipase B; LPCH, lysophosphatidylcholine hydrolase; LIPH, lipase H; ATX, autotaxin. (b) Elevated PC, LPC and LPA levels in SWS mutant flies. Wild-type Drosophila (CS), (n = 8); mutant heterozygotes (SWS/CS), n = 4; sws1-null mutants (SWS), n = 5. PC, LPC and LPA levels (y axis) are expressed in pmol of individual compounds per mg of protein. The means±s.d. for individual groups and P-values (t-test) are indicated; *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001; n.s., not significant. Experiments were repeated twice.
Discussion
Our results suggest that PNPLA6 is essential for vision and photoreceptor biology, and that mutations in PNPLA6 cause photoreceptor neuron death and blindness in children with OMS and LCA. Moreover, this report documents the first gene for OMS and the 20th gene for LCA. Finding PNPLA6 mutations in various forms of childhood blindness was unexpected, because mutations and organophosphate-induced changes in PNPLA6 are observed in two neurological disorders with large motor neuron disease, spastic paraplegia (SPG39) and organophosphate-induced neuropathy (OPIDN). SPG39 and OPIDN are severe diseases but do not present with photoreceptor degeneration. Why do the mutations in PNPLA6 described here cause photoreceptor cell death, while patients with SPG39 and OPIDN do not? One explanation is that the PNPLA6 mutations in five out of seven of our families were compound heterozygotes, with one mutation in the regulatory and one mutation in the catalytic domain (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Fig. 1). SPG39 patients have homozygous mutations in the catalytic (patatin) domain12,16. In OPIDN patients, the organophosphates bind to and inhibit only the catalytic domain and the N-terminal functions may not be affected. Having mutations in both domains may cause a more severe overall impairment of PNPLA6 function, leading to photoreceptor death. Alternatively, the mutations in the N-terminal regulatory domain might induce specific phenotypes. It is also possible that the harmful effects of organophosphates are not strong enough to affect retinal photoreceptors but only large neurons, such as motor neurons. It will be possible to test this hypothesis in future experiments.
PNPLA6 has been known for over 45 years and despite intense investigations (600 + publications), its various functions have not been fully elucidated13. Previously, PNPLA6 was found to be expressed in the brain, most prominently in large (motor) neurons, but not in the retinal tissue2,17. We now show (Fig. 4) that PNPLA6 is expressed in the developing and mature mouse retina in horizontal, amacrine and photoreceptors cells, and in Drosophila photoreceptors. Unlike mouse neurons, where PNPLA6 localizes to the ER12,18, we show here that PNPLA6 is mostly localized to the IS plasma membrane of mouse photoreceptors, suggesting a possible role for PNPLA6 in the formation of distinct plasma membrane domains in the IS and in the OS, or in the development/renewal of OS disc membranes, which are essential for maintaining the integrity of the photoreceptors and vision16,19,20. Previous studies indeed support a role for PNPLA6 in membrane growth, as knockdowns of Pnpla6 in zebrafish caused axonal truncation and abnormal branching in addition to small eyes17. Furthermore, it was proposed that altered membrane trafficking in neuronal-specific Pnpla6 knockout mice causes axonal degeneration in spinal neurons13.
Similar to vertebrates, SWS is expressed in photoreceptor cells in flies. Although the photoreceptors develop normally in mutants, the eye-specific knockdown of SWS shows severe photoreceptor degeneration when aged, revealing that SWS is crucial for photoreceptor maintenance but not development. In addition, the degeneration is not dependent on light input, showing that the degeneration is not activity dependent. This suggests that the degeneration is caused by a failure to maintain the integrity of the photoreceptor cells and not by deleterious effects due to alterations in photoreception. This is also in agreement with the fact that the loss of SWS in other neurons also causes a progressive degeneration.
In agreement with the role of PNPLA6 as a phospholipase, we found alterations in phospholipid composition (LPC, LPA and PC) in Drosophila. We carefully examined the wild type, sws mutants and heterozygotes. Interestingly and importantly, we show a significant accumulation of all, LPA, LPC and LC, which may explain some of the clinical features of OMS. Indeed, elevated concentrations of LPA are known to be cytotoxic to neuronal cells, including photoreceptors21, and defects in the LPC acyltransferase-1, an enzyme catalysing the conversion of LPC to PC, cause photoreceptor degeneration in mice22. LPA also promotes hair growth23 and defects either in LPA production24,25 or LPA signalling26,27 are associated with hair growth abnormalities, as observed in our OMS patients. It is therefore possible that elevations in LPA lead to the trichomegaly, wooly hair and progressive alopecia in our OMS patients. Altered LPA signalling may also be responsible for the abnormalities in bone and tooth development28, and growth hormone deficiency25, also seen in our OMS patients (Table 1). Interestingly, transient juvenile trichomegaly and progressive alopecia, as well as a strong family history of different early-onset cancers29 were also found in some of our families (data not shown). However, this link needs to be further explored.
Most of the identified mutations in OMS are in highly conserved residues, supporting their functional importance and potential use for rapid clinical testing of OMS and LCA patients. Our studies have opened a new avenue in investigating functions of PNPLA6, including whether single PNPLA6 mutations increase photoreceptor susceptibility to environmental toxins. In the near future, it will be interesting to generate and characterize a photoreceptor-specific Pnpla6 mouse knockout to study the fundamental mechanism of action of PNPLA6 and evaluate the potential therapeutic benefits of lowering LPC and LPA.
Methods
Patient information
Patients were phenotyped at several international centres, after informed consents were obtained, approved by the ethical and scientific review boards. Detailed ophthalmological evaluations were followed by medical and clinical genetics consultations. All patients underwent a detailed history and pedigree analysis and detailed eye examinations, including best-corrected visual acuities by projected Snellen charts, near vision, slitlamp biomicroscopy and dilated retinal exams. In vivo retinal imaging was performed by the Heidelberg OCT (Heidelberg Engineering), followed by fundus autofluorescence. Kinetic fields were measured by Goldmann perimetry. In selected patients, we performed International Society for Clinical Electrophysiology of Vision (ISCEV) standard ERGs and multifocal ERGs (Diagnosys, Boston, USA). Peripheral blood was collected in lavender top (EDTA) tubes for DNA extraction.
Animals
All animal work was carried out in accordance with the Canadian Council on Animal Care guidelines and was approved by the Institut de recherches cliniques de Montréal Animal Care Committee. CD1 and C57/Bl6 mice of either sex were used in this study.
WES analysis
DNA was extracted from whole blood using the FlexiGene kit or the QIAamp DNA blood kit according to the manufacturer’s protocol. DNA quantity and quality were verified by using NanoDrop. The exomes of two sporadic cases (5,273 and 5,267) and all individuals from the Czech family 3 (166–171) with childhood blindness and OMS were captured by the Sure Select Human Exome Kit version 4 (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA), using 3 μg of genomic DNA of each. Exon-enriched DNA libraries were then sequenced either on Illumine HiSeq2000 that generate 100 bp paired-end reads or on SOLiD 4 that generate 50 bp reads. The details of bioinformatics analysis have been reported previously30–33. Briefly, the high-quality trimmed reads from Illumina HiSeq2000 were aligned to the positive strand of human genome (hg19) by BWA version 0.5.9 (ref. 29) and a mean coverage of 128 × (5,273) and 131 × (5,267) was obtained for the targeted coding regions (consensus coding sequence). Reads from SOLiD 4 were aligned using Novoalign version 2.08.03. Quality score recalibration was performed during alignment and reads that aligned to multiple locations were discarded. Following alignment PCR, duplicate reads were removed using Picard tools version 1.84. Variant calling and annotation were performed by SAMtools version 0.1.7 (ref. 34) and ANNOVAR35, respectively. Filtering steps were carried out with public (dbsnp135, 1,000 genome project and NHLBI exomes) and our in-house exome (contains more than 800 samples) databases. Subsequently, variants that were predicted to be protein-altering (that is, missense, nonsense, frameshift, or canonical splice site changes) were prioritized and were manually examined in IGV36. Variants identified in individuals from Czech family 3 were also used for homozygosity mapping, linkage analysis and detection of copy-number variants.
Sanger sequencing and co-segregation
The selected variants were confirmed by Sanger sequencing in the patients and co-segregation was tested in their family members on an ABI 3730xl capillary sequencers. The Sanger sequencing results were analysed with the Sequencher software. Mutations were excluded from normal controls (at least 100 normal controls) and co-segregation in the family was studied. All mutations were studied by in silico analysis (Pmut, Blossum62, SIFT and Polyphen). All patients had two mutations, either homozygous or compound heterozygous. To ensure the completeness and quality of the sequences, primers were designed from intron sequences so that the entire exon and at least 50 bp of intron DNA on each side of each exon were amplified. Primers for the PCRs were designed by primer3 (http://frodo.wi.mit.edu/primer3/).
Drosophila PNPLA6 localization and knockout experiments
The 50-μm vibratome head sections from white-eyed flies (w1118, to avoid interference by the autofluorescence from the eye pigment) were performed as described in Bolkan et al.37 and stained with our anti-SWS serum at a dilution of 1:100. Detection was done with a biotinylated secondary antibody (1:200; Vector Laboratories) and a Cy5-conjugated streptavidin (1:100; Jackson ImmunoResearch). Sections were counterstained with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; Invitrogen). Optical images (0.5 μm thick) were taken on an Olympus FW1000 confocal microscope. Semi-thin and ultra-thin Epon plastic sections were prepared as described in ref. 15. Semi-thin sections (1 μm) were stained with 1% toluidine blue and 1% borax, and analysed by light microscopy. Ultra-thin sections were analysed with a FEI Morgagni 268 electron microscope. sws1 is described in Kretzschmar et al.15 ΔTM-SWS was created by deleting aa1–55, which includes the N terminus and the first transmembrane domain. The eye-specific knockdown was achieved by inducing the JF03428 RNA interference construct with GMR-GAL4 (both from the Bloomington Stock Center). Flies were raised and aged under standard conditions at 25 °C.
Mouse PNPLA6 immunostaining
Eyes were enucleated and fixed by immersion in freshly prepared 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 3 h on ice. For adult eyes, a small incision was made along the ora serrata after 10 min in paraformaldehyde, to allow better access to the fixative. The eyes were then rinsed in PBS and cryo-protected in sucrose 20% overnight, frozen and embedded in a sucrose:optimal cutting temperature (O.C.T.) compound (1:1) mix. For immunofluorescence, retinas were sectioned and processed for staining on the same day. Slides were preincubated for 1 h in blocking buffer (20% goat serum in 0.2% Triton) and then incubated 48 h at 4 °C with primary antibodies diluted in PBS. Primary antibodies used were PNPLA6 (NTE; 1/100, Abcam), Na2+K+-ATPase (1/100, Thermo Scientific), Syntaxin (1/500, Sigma), NF-165 (1/200, gift from B. Barres, Stanford U.) and Brn3b (1/100, Santa-Cruz). Bound antibodies were detected using appropriate secondary antibodies conjugated with Alexa 488, 555, 594 or 647 (1:1,000; Invitrogen) diluted in antibody buffer at room temperature for 1 h. In all cases, nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342 (Molecular Probes).
Extraction of Drosophila phospoholipids for flow injection-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry analysis
Whole flies were homogenized in MilliQ water to acquired concentration 80 mg ml−1. Homogenization was performed with Branson Digital Sonifier 450 working as cup horn set to pulse mode (1 s pulse/1 s pause) with amplitude maximum at 100watt each sample was total homogenization time was 2 × 30 s. The 250 μl of fly homogenates was extracted by modified method of Natomi38. Fly homogenates (250 μl) corresponding to 20 mg was extracted by 2 ml of mixture of chloroform:methanol:water (20:10:1 v/v/v). Extraction mixture was repeatedly vortexed in 15-min steps during 2 h and then left at −20 °C overnight. Supernatant was filtered through glass filter to a glass tube. Sediment was re-extracted with 2 ml of mixture of chloroform:methanol:water (10:10:1 v/v/v). Extraction mixture was vortexed for 1 h and then filtered through glass filter and combined with the first extract. Final re-extraction step was with 2 ml mixture of chloroform:methanol:water (10:20:1 v/v/v). The mixture was vortexed for 1 h and then filtered through glass filter and combined with previous extracts. The combined supernatants were dried under a stream of nitrogen. Aliquot corresponding to 1 mg of flies was mixed with 50 pmol of internal standards: C17:0 LPC, C17:0 LPA and C10:0PC (Avanti Polar Lipids Inc., Alabaster, Alabama, USA) and reconstituted in 1 ml of methanol with 5 mM NH4COOH (to generate [M + H] + ions) or in pure methanol in the case of LPA (to generate [M−H]− ions). Samples were introduced by flow injection with tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS).
Phospholipids analysis by FIA-ESI-MS/MS
Mass spectra were obtained on an ABI/MDS SCIEX API 4000 tandem mass spectrometer equipped with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source and coupled to an Agilent HPLC 1290 series.
PC and LPC were analysed by multiple reaction monitoring scans using common product ion with 184.1 m/z (phosphocholine) in the positive ion mode. Transition pairs were monitored for 100 ms and their m/z were as follows: LPC—494.3→184.1 (C16:1); 496.5→184.1 (C16:0); 520.4→184.1 (C18:2); 522.5→184.1 (C18:1); 524.5→184.1 (C18:0); 510.4→184.1 (C17:0 IST); PC: 732.6→184.1 (C32:3); 734.6→184.1 (C32:2); 742.6→184.1 (C33:3); 744.6→184.1 (C33:2); 746.6→184.1 (C33:1); 758.6→184.1 (C34:2); 760.6→184.1 (C34:1); 762.6→184.1 (C34:0); 780.6→184.1 (C36:3); 782.6→184.1 (C36:2); 784.6→184.1 (C36:1); 786.6→184.1 (C36:0); 794.7→184.1(C37:3); 796.7→184.1 (C37:2); 806.6→184.1 (C38:4); 808.6→184.1 (C38:3); 810.6→184.1 (C38:2); 812.7→184.1 (C38:1); 814.7→184.1 (C38:0); 426.6→184.1 (C10:0 IST). The ESI condition were as follows: curtain gas (N2), 14 psi; collision gas (N2), 7 psi; source gas 1 (N2), 20 psi; source gas 2 (N2), 50 psi; nebulizing gas (N2) temperature, 200 °C; the capillary spray voltage was 5.5 kV, interface heater, ON. The ion optics settings for PC and LPC measurements were: 98 V for the declustering potential and 3 V for the entrance potential. The collision energy was set to 35 V, with a collision cell exit potential of 11 V. LPA was analysed by negative multiple reaction monitoring using 152.8 m/z product ion for LPA (glycerolphosphate): LPA 409.2→152.8 (C16:); 433.3→152.8 (C18:2); 435.4→152.8 (C18:1); 437.3→152.8 (C18:0); 457.2→152.8 (C20:4); 423.3→152.8 (C17:0 IST), and scan times for each transition pair was 500 ms. The ESI condition were as follows: curtain gas (N2), 14 psi; collision gas (N2), 12 psi; source gas 1 (N2), 5 psi; source gas 2 (N2), 25 psi; nebulizing gas (N2) temperature, 200 °C; the capillary spray voltage was −4.5 kV, interface heater, ON. The ion optics settings for LPA measurement were: −118 V for the declustering potential and −10.7 V for the entrance potential. The collision energy was set to −35 V with a collision cell exit potential of −5 V.
PC, LPC and LPA concentrations were calculated using known amount (50 pmol) of internal standard added to samples. Final concentrations were expressed as pmol of lipids per mg of Drosophila. The Analyst 1.5 software was used to operate the instruments and process the data.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the children and parents involved in this study. We acknowledge the crucial support from the Foundation Fighting Blindness Canada (to I.M.M., M.C. and R.K.K.). Further funding came from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (M.C. and R.K.K.) and NIH (EY022356-01, EY018571-05 and NS047663-09 to R.K.K., R.C. and D.K.). M.C. is a Senior Fellow of the Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé/Fondation Antoine-Turmel. S.K. is supported by the Charles University institutional programmes PRVOUK-P24/LF1/3, UNCE 204011 and SVV2013/266504, and by BIOCEV—Biotechnology and Biomedicine Centre of the Academy of Sciences and Charles University (CZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0109), from the European Regional Development Fund. Specific support was provided by grant NT13116-4/2012 and NT14015-3/2013 from the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic. R.G. was supported by the Graduate School of Life Sciences (University of Wuerzburg). We gratefully acknowledge the indispensible work of Xia Wang, Hui Wang, Ms Eunice Esteban, Leah Wood MSc, Jonas Tapia RN and Renee Pigeon. We sincerely thank the Care4Rare Canada Steering Committee: Kym Boycott (leader; University of Ottawa), Jan Friedman (co-lead; University of British Columbia), Jacques Michaud (co-lead; Université de Montréal), Francois Bernier (University of Calgary), Michael Brudno (University of Toronto), Bridget Fernandez (Memorial University), Bartha Knoppers (McGill University), Mark Samuels (Université de Montréal) and Steve Scherer (University of Toronto). This work was funded in part by the Government of Canada through Genome Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Ontario Genomics Institute (OGI-049). Additional funding was provided by Genome Quebec, Genome British Columbia and the McLaughlin Centre. We thank Janet Marcadier (Clinical Coordinator) and Chandree Beaulieu (Project Manager) for their contribution to the infrastructure of the FORGE Canada Consortium. We acknowledge the contribution of the high-throughput sequencing platform of the McGill University and Génome Québec Innovation Centre, Montréal, Canada.
Footnotes
Accession codes: Sequence data has been deposited at the European Genome-phenome Archive (EGA, http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ega/), which is hosted by the EBI, under accession number EGAS00001001013.
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper at http://www.nature.com/naturecommunications
Competing financial interests: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author contributions
J.M. and S.F. designed, oversaw and interpreted the genome experiments. S.C., H.R., I.L., V.S., V.K., A.K., E.B. and D.S. performed the genetic studies. V.R. performed and interpreted immunohistochemical characterization in mouse retina. D.S. performed the fly genetic studies, and R.G. and C.H.F. performed the electroretinograms. V.S. and A.P. analysed exome-sequencing data, performed linkage analysis and provided bioinformatic support; H.H., K.H. and L.P. performed exome sequencing and mutation segregation studies; L.K. performed phospholipid analysis; A.B. was responsible for biosampling, clinical evaluation and genetic counselling of the Czech family. I.M.M., R.C., O.G.P.B., A.P., H.G., M.S., J.R.S., J.L.T., J.S., P.C., Care4Rare, E.B., R.G., C.H.F. and J.L.P. collected family data and provided DNA material. S.K., J.M., V.R., D.K., M.C. and R.K.K. interpreted results. D.K., M.C. and R.K.K. designed and oversaw the study. S.K., D.K., M.C. and R.K.K. wrote the manuscript, which was reviewed and approved by all co-authors.
References
- 1.Dudek BR, Richardson RJ. Evidence for the existence of neurotoxic esterase in neural and lymphatic tissue of the adult hen. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982;31:1117–1121. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Johnson MK. Initiation of organophosphate-induced delayed neuropathy. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1982;4:759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Glynn P. Neuropathy target esterase and phospholipid deacylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1736:87–93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2005.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Johnson MK. The delayed neurotoxic effect of some organophosphorus compounds. Identification of the phosphorylation site as an esterase. Biochem J. 1969;114:711–717. doi: 10.1042/bj1140711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Glynn P. NTE: one target protein for different toxic syndromes with distinct mechanisms? Bioessays. 2003;25:742–745. doi: 10.1002/bies.10322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hein ND, Rainier SR, Richardson RJ, Fink JK. Motor neuron disease due to neuropathy target esterase mutation: enzyme analysis of fibroblasts from human subjects yields insights into pathogenesis. Toxicol Lett. 2010;199:1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.06.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rainier S, et al. Motor neuron disease due to neuropathy target esterase gene mutation: clinical features of the index families. Muscle Nerve. 2011;43:19–25. doi: 10.1002/mus.21777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Richardson RJ, Hein ND, Wijeyesakere SJ, Fink JK, Makhaeva GF. Neuropathy target esterase (NTE): overview and future. Chem Biol Interact. 2013;203:238–244. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2012.10.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chang PA, Wu YJ. Neuropathy target esterase: an essential enzyme for neural development and axonal maintenance. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42:573–575. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Muhlig-Versen M, et al. Loss of Swiss cheese/neuropathy target esterase activity causes disruption of phosphatidylcholine homeostasis and neuronal and glial death in adult Drosophila. J Neurosci. 2005;25:2865–2873. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5097-04.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Winrow CJ, et al. Loss of neuropathy target esterase in mice links organophosphate exposure to hyperactivity. Nat Genet. 2003;33:477–485. doi: 10.1038/ng1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Akassoglou K, et al. Brain-specific deletion of neuropathy target esterase/swisscheese results in neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:5075–5080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401030101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Read DJ, Li Y, Chao MV, Cavanagh JB, Glynn P. Neuropathy target esterase is required for adult vertebrate axon maintenance. J Neurosci. 2009;29:11594–11600. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3007-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Read DJ, Li Y, Chao MV, Cavanagh JB, Glynn P. Organophosphates induce distal axonal damage, but not brain oedema, by inactivating neuropathy target esterase. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;245:108–115. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2010.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kretzschmar D, Hasan G, Sharma S, Heisenberg M, Benzer S. The swiss cheese mutant causes glial hyperwrapping and brain degeneration in Drosophila. J Neurosci. 1997;17:7425–7432. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-19-07425.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nilsson SE. Receptor cell outer segment development and ultrastructure of the disk membranes in the retina of the tadpole (Rana pipiens) J Ultrastruct Res. 1964;11:581–602. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(64)80084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Song Y, et al. Knockdown of Pnpla6 protein results in motor neuron defects in zebrafish. Dis Model Mech. 2013;6:404–413. doi: 10.1242/dmm.009688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zaccheo O, Dinsdale D, Meacock PA, Glynn P. Neuropathy target esterase and its yeast homologue degrade phosphatidylcholine to glycerophosphocholine in living cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:24024–24033. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400830200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sahly I, et al. Localization of Usher 1 proteins to the photoreceptor calyceal processes, which are absent from mice. J Cell Biol. 2012;199:381–399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201202012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Anderson DH, Fisher SK, Steinberg RH. Mammalian cones: disc shedding, phagocytosis, and renewal. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1978;17:117–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Barth C, Stark G. Radiation inactivation of ion channels formed by gramicidin A. Protection by lipid double bonds and by alpha-tocopherol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1066:54–58. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90249-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Friedman JS, et al. Loss of lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 1 leads to photoreceptor degeneration in rd11 mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:15523–15528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1002897107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Takahashi T, Kamimura A, Hamazono-Matsuoka T, Honda S. Phosphatidic acid has a potential to promote hair growth in vitro and in vivo, and activates mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase in hair epithelial cells. J Invest Dermatol. 2003;121:448–456. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kazantseva A, et al. Human hair growth deficiency is linked to a genetic defect in the phospholipase gene LIPH. Science. 2006;314:982–985. doi: 10.1126/science.1133276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rui L, Archer SF, Argetsinger LS, Carter-Su C. Platelet-derived growth factor and lysophosphatidic acid inhibit growth hormone binding and signaling via a protein kinase C-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:2885–2892. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.4.2885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pasternack SM, et al. G protein-coupled receptor P2Y5 and its ligand LPA are involved in maintenance of human hair growth. Nat Genet. 2008;40:329–334. doi: 10.1038/ng.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shimomura Y, et al. Disruption of P2RY5, an orphan G protein-coupled receptor, underlies autosomal recessive woolly hair. Nat Genet. 2008;40:335–339. doi: 10.1038/ng.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Blackburn J, Mansell JP. The emerging role of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) in skeletal biology. Bone. 2012;50:756–762. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2011.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1754–1760. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fahiminiya S, et al. Whole-exome sequencing reveals a heterozygous LRP5 mutation in a 6-year-old boy with vertebral compression fractures and low trabecular bone density. Bone. 2013;57:41–46. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2013.07.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fahiminiya S, et al. Mutations in WNT1 are a cause of osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet. 2013;50:345–348. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2013-101567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hartmannova H, et al. Isolated X-linked hypertrophic cardiomyopathy caused by a novel mutation of the four-and-a-half LIM domain 1 gene. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2013;6:543–551. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.113.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Stranecky V, et al. Mutations in ANTXR1 cause GAPO syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2013;92:792–799. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.03.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Li H, et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:2078–2079. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H. ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:e164. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Robinson JT, et al. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29:24–26. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bolkan BJ, Triphan T, Kretzschmar D. Beta-secretase cleavage of the fly amyloid precursor protein is required for glial survival. J Neurosci. 2012;32:16181–16192. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0228-12.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Natomi H, Sugano K, Iwamori M, Takaku F, Nagai Y. Region-specific distribution of glycosphingolipids in the rabbit gastrointestinal tract: preferential enrichment of sulfoglycolipids in the mucosal regions exposed to acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988;961:213–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.