Background: Nav1.7 mutations are associated with pain syndromes including erythromelalgia.
Results: Disulfide locking experiments and three-dimensional modeling show close proximity of residues Gln-875 and the gating charge Arg-214.
Conclusion: The erythromelalgia mutation Q875E introduces a salt bridge that stabilizes the domain I voltage sensor in the activated position.
Significance: An inter-domain interaction is the structural basis for a novel mechanism underlying this pain disorder.
Keywords: Electrophysiology, Molecular Modeling, Neurophysiology, Pain, Patch Clamp, Disulfide Locking
Abstract
The human voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7 plays a crucial role in transmission of noxious stimuli. The inherited pain disorder erythromelalgia (IEM) has been linked to Nav1.7 gain-of-function mutations. Here we show that the IEM-associated Q875E mutation located on the pore module of Nav1.7 produces a large hyperpolarizing shift (−18 mV) in the voltage dependence of activation. Three-dimensional homology modeling indicates that the side chains of Gln-875 and the gating charge Arg-214 of the domain I voltage sensor are spatially close in the activated conformation of the channel. We verified this proximity by using an engineered disulfide bridge approach. The Q875E mutation introduces a negative charge that may modify the local electrical field experienced by the voltage sensor and, upon activation, interact directly via a salt bridge with the Arg-214 gating charge residue. Together these processes could promote transition to, and stabilization of, the domain I voltage sensor in the activated conformation and thus produce the observed gain of function. In support of this hypothesis, an increase in the extracellular concentration of Ca2+ or Mg2+ reverted the voltage dependence of activation of the IEM mutant to near WT values, suggesting a cation-mediated electrostatic screening of the proposed interaction between Q875E and Arg-214.
Introduction
The voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7 is mainly expressed in peripheral sensory neurons (1) and is linked to pain perception (2). Patients suffering from chronic inherited neuropathic pain syndromes such as inherited erythromelalgia (IEM)2 or paroxysmal extreme pain disorder were found to carry single amino acid mutations in the Nav1.7-encoding gene SCN9A (3–5). In contrast, loss of functional Nav1.7 due to truncation mutations is associated with congenital insensitivity to pain (6, 7). Nav channels are formed of four homologous domains (DI–DIV for domains I–IV) linked by intracellular loops and containing six transmembrane spanning helices (S1–S6) per domain (8). S5 and S6 helices form the ion-conducting pore module, and their extracellular linker forms the selectivity filter. S1–S4 form the voltage-sensing domains (VSDs), and positive gating charge residues on the S4 helix enable this segment to move in response to a changing transmembrane potential. This motion is coupled with gating of the pore (9). Crystal structures of homo-tetrameric ion channels show that, in addition to a covalent connection through the S4–S5 linker, each VSD also makes contact with the pore module via interactions between the S4 section and the S5 helix of an adjacent domain (10, 11). Cysteine disulfide locking or histidine metal bridge studies with voltage-gated potassium and bacterial sodium channels have proved valuable in investigating how interactions within the VSD (12, 13) and between VSD and pore module (14–16) change during transitions between channel functional states.
Electrophysiological characterization of more than 20 IEM-linked single point mutations of Nav1.7 reveals a shift of the voltage dependence of activation to more negative potentials in almost all cases, which is likely to underlie increased nociceptor excitability (7, 17). The IEM mutations are not clustered in any specific area (2), suggesting that different molecular mechanisms may be responsible for producing the gain-of-function phenotype. For example, the addition of an extra positive charge (L832R) on the DII S4 helix was proposed to increase sensitivity of this VSD to changes in membrane potential (18). In the case of F1449V, a combinatorial molecular modeling and electrophysiology approach showed that this mutation disrupted the cytoplasmic gate of the channel (19).
The Q875E mutation of Nav1.7 was discovered in a 15-year-old girl suffering from typical progressive symptoms of IEM (20): burning pain in the lower extremities as well as redness and swelling of the feet and lower legs triggered by mild warmth or walking on rough surfaces. We determined, using voltage-clamp electrophysiology studies, that Q875E induces gating changes in Nav1.7 typical for IEM mutations; activation is shifted to more hyperpolarized potentials, deactivation is slowed, and time to maximum peak of inward current is shortened. Our three-dimensional modeling studies suggest the formation of a salt bridge between the introduced glutamate in position 875 in the pore module and DI voltage sensor. Using the engineered disulfide bridge approach, we find support for this structural hypothesis, which is likely to be the molecular basis for the gain of function of this IEM-linked Q875E mutation.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Mutagenesis
hNav1.7 pcDNA cloned into pHCMV was provided by Norbert Klugbauer (21), and the Q875E mutant was generated using QuikChange XL site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene). Phusion polymerase (New England Biolabs) was used to generate the mutations R214C, Q875C, Q875A, R214C/Q875C, and R214C/Q875E. Plasmid DNA was amplified with XL1-Blue MRF′ ultracompetent cells (Agilent Technologies).
Cell Culture and Transfection
HEK293 were cultured in DMEM (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (PAA Laboratories GmbH). Cells were grown at 37 °C and 5% CO2. JetPEI transfection reagent (Polyplus Transfection) was used with 1 μg of Nav1.7 WT or mutant cDNA and 0.15 μg of GFP (Clontech laboratories, Inc.). Cells were used for experiments 24 h after transfection.
Electrophysiology
Extracellular recording solution contained 140 mm NaCl, 3 mm KCl, 2 mm MgCl2, 2 mm CaCl2, 10 mm HEPES, 20 mm glucose, pH 7.38, adjusted with NaOH (328 mosm). All chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich unless stated otherwise. To test for changes in channel activation under reducing conditions, cells were incubated with bath solution containing 10 mm DTT for a minimum of 5 min. Only green fluorescent cells were patched using patch pipettes with a resistance of 1.3–2.2 megaohms, pulled from borosilicate glass fibers with a DMZ puller (Zeitz Instruments GmbH, Martinsried, Germany). Intracellular solution contained 140 mm CsF, 10 mm NaCl, 10 mm HEPES, 1 mm EGTA, 10 mm glucose, pH 7.4, adjusted with CsOH (321 mosm).
A HEKA EPC10-USB amplifier operated by PatchMaster (HEKA Elektronik, Lambrecht/Pfalz, Germany) was used for recordings, data were filtered with a 10-kHz Bessel filter (except for deactivation protocols, which were filtered at 30 kHz), and a p/4 leak subtraction and Rs compensation (at least 50% at 10 μs, Rs <4 megaohms) were applied. Data were analyzed using FitMaster, Origin 8.6 (OriginLab) and Excel (Microsoft Corp.). For current-voltage relations, cells were held at −120 mV and depolarized to potentials ranging from −110 mV to +60 mV in +10-mV steps lasting for 100 ms every 10 s.
Conductance Gm was calculated as Gm = Im/(Vm − Erev) (Im, recorded maximum peak inward current; Vm, transmembrane potential; Erev, reversal potential, determined for each cell individually) and normalized to the absolute conductance. Single normalized conductance-voltage relationships were fitted with a Boltzmann equation, which yielded Vhalf and k (half-maximal activation potential and the slope of the fitted curve). Current density was calculated as maximum conductance divided by capacitance as a measure for cell size.
Steady-state fast inactivation was assessed using 500-ms prepulses ranging from −150 mV to 10 mV followed by a test pulse to +20 mV. Peak currents were normalized to the maximal inward current obtained at this voltage step. Deactivation time constants were determined by fitting the currents recorded during hyperpolarizing voltage steps following a short 0.5-ms test pulse to +20 mV with a single exponential function. Slow inactivation properties were measured with a three-pulse protocol starting with a 10-ms pulse to +20 mV (I1) for normalization followed by a test pulse of 30 s in length ranging from −120 mV to +10 mV in increments of 10 mV to induce slow inactivation, a short hyperpolarizing step to −120 mV to let channels recover from fast inactivation, and a test pulse of 40 ms to +20 mV (I2). Currents evoked by the last depolarizing pulse (I2) were normalized to those at the first test pulse (I1) and fitted with a single Boltzmann equation.
Normality was tested using a Shapiro-Wilk test followed by one-way analysis of variance and a two-sample t test. For comparing non-normally distributed data, a Mann-Whitney-test was applied.
Modeling
A three-dimensional homology model of hNav1.7 was generated based on the NavAb crystal structure as described (22). The model was mutated to Q875E and energy-minimized using Swiss-PdbViewer software (23). The atomic coordinates of Arg-214 and either Gln-875 or Q875E were extracted to separate Protein Data Bank (PDB) files, and different side chain conformations for each residue were generated using the rotamer library of Swiss-PdbViewer. The PISA program (24) was used to determine whether a hydrogen bond or salt bridge was present between each generated pair of rotamers. Figures were produced using PyMOL (Schrödinger, LLC).
RESULTS
Q875E Is a Gain-of-function Mutation
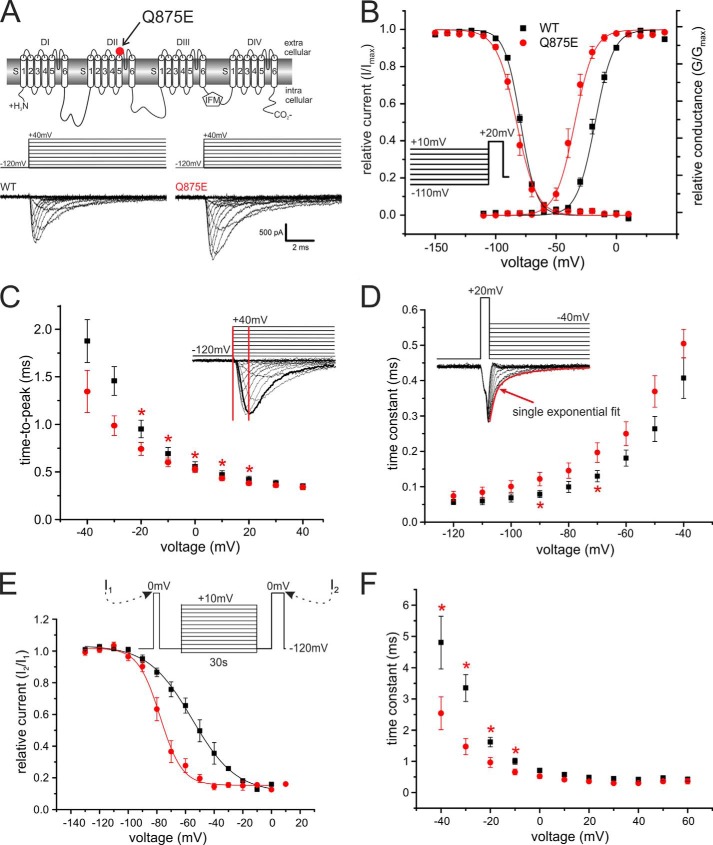
We used whole-cell patch clamp recordings to determine the functional effects of the IEM-associated Q875E mutation in Nav1.7. The Q875E mutant and WT Nav1.7 expressed robustly in transiently transfected HEK293 cells (Fig. 1A). The voltage of half-maximal activation (Vhalf) was dramatically shifted to more hyperpolarized potentials for the Q875E mutant when compared with WT (Fig. 1B). Boltzmann fits reveal a Vhalf of −18.5 mV ± 1.1 mV for WT and −36.0 mV ± 2.1 mV for the Q875E mutant (ΔVhalf = −17.5 mV; Table 1). The Vhalf of steady-state fast inactivation remained unaltered (WT, −79.0 mV ± 0.5 mV, n = 9; Q875E, −82.9 mV ± 1.6 mV, n = 16).
FIGURE 1.
The IEM-associated Q875E mutation shifts activation to more hyperpolarized potentials. A, transmembrane map of Nav1.7 indicating the position of the Q875E mutation. Shown are representative current traces obtained with the displayed voltage protocol. B, relative conductance-voltage relationship and their corresponding Boltzmann fits (solid lines) for activation of WT (black squares, n = 13) and Q875E (red points, n = 10) and steady-state fast inactivation (WT, n = 9; Q875E, n = 16). Voltage protocol for measuring fast inactivation is shown as the inset. The Vhalf of activation for Q875E is shifted from WT by −17.5 mV, whereas the Vhalf of fast inactivation remains unchanged. C, time to peak calculated from pulse onset to maximum peak inward current, as shown schematically in the inset. Q875E mutation accelerates time to peak significantly between voltages −20 mV and +20 mV (*, p < 0.05). D, deactivation time constants at voltages between −120 mV and −40 mV (WT, n = 9; Q875E, n = 7). The mutant shows delayed deactivation. Asterisks indicate significant difference between Q875E and WT (p < 0.05). Inset, representative current traces obtained with the shown voltage protocol for WT. The red curve denotes an example of a single exponential fit that was used to obtain deactivation time constants. E, voltage dependence of slow inactivation. Solid lines show Boltzmann fits for WT (n = 4) and Q875E mutant (n = 6). Slow inactivation for the IEM mutant is enhanced as the midpoint is shifting by 22.8 mV. F, fast inactivation time constants as determined by a single exponential fit at potentials between −40 mV and +60 mV. The IEM mutant has significantly smaller time constants at potentials between −40 mV and −10 mV. Asterisks indicate significant difference between Q875E and WT (p < 0.05). All data are represented as mean ± S.E.
TABLE 1.
Summary of changes of activation kinetics of the generated mutants, ΔVhalf and time-to-peak: change relative to WT values
All Vhalf values were tested as significantly different (p < 0.05) from WT except for WT + DTT. p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. NS, not significant.
| Channel | Vhalf ± S.E. | ΔVhalf compared with WT | ΔVhalf with DTT | Slope ± S.E. | Time to peak | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mV | mV | mV | ||||
| WT | −18.5 ± 1.1 | 7.4 ± 0.3 | 13 | |||
| WT + DTT | −20.0 ± 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 6.8 ± 0.3 | NS | 8 |
| Q875E | −36.0 ± 2.1 | −17.5*** | 6.3 ± 0.5 | Faster | 10 | |
| R214C/Q875C | −43.6 ± 1.0 | −25.0*** | 12.9*** ± 0.4 | Faster | 16 | |
| R214C/Q875C + DTT | −34.6 ± 1.2 | −16.1*** | 9.0*** | 12.9*** ± 0.4 | Faster | 12 |
| R214C | −34.7 ± 2.6 | −16.2*** | 7.7 ± 0.6 | Faster | 5 | |
| R214C + DTT | −30.9 ± 1.5 | −12.3*** | 3.9 | 8.5 ± 0.6 | Faster | 11 |
| Q875C | −29.0 ± 2.4 | −10.5*** | 7.6 ± 0.4 | Faster | 10 | |
| Q875C + DTT | −28.9 ± 2.0 | −10.3*** | 0.2 | 7.5 ± 0.3 | Faster | 12 |
| Q875A | −26.3 ± 2.0 | −7.7** | 7.1 ± 0.4 | Faster | 13 | |
| R214C/Q875E | −30.3 ± 2.2 | −11.7*** | 10.5*** ± 0.5 | Faster | 6 | |
| R214C/Q875E + DTT | −32.6 ± 1.2 | −14.0*** | −2.3 | 9.3** ± 0.4 | Faster | 8 |
| WT + Ca2+ | −7.8 ± 1.0 | 9.5*** | 7.6 ± 0.5 | NS | 8 | |
| Q875E + Ca2+ | −16.5 ± 1.3 | 0.8 | 8.4 ± 0.2 | Faster | 11 | |
| WT + Mg2+ | −5.1 ± 2.5 | 12.2*** | 8.7 ± 0.8 | NS | 4 | |
| Q875E + Mg2+ | −16.5 ± 1.1 | 0.7 | 8.4 ± 0.2 | Faster | 7 |
The time interval from pulse onset until maximum inward current (time to peak) was significantly accelerated for voltages between −20 mV and +20 mV for the Q875E mutant when compared with WT (Fig. 1C). Deactivation time constants, determined by fitting a single exponential curve to the decaying current following a brief 0.5 ms depolarizing pulse, were slowed for the Q875E mutant at two tested voltages (−90 mV and −70 mV; Fig. 1D), whereas inactivation kinetics were faster at negative potentials (Fig. 1F). The latter is likely to be due to the left shift of voltage dependence of activation of Q875E when compared with WT. The voltage dependence of slow inactivation was strongly shifted to more hyperpolarized potentials for the Q875E mutant (ΔVhalf = −22.8 mV; WT, 54.5 mV ± 8.0 mV, n = 4; Q875E, 77.3 mV ± 7.0 mV, n = 6; Fig. 1E), as commonly reported for IEM mutations (7). Overall, we showed that the Q875E mutation induces a negative shift in the voltage dependence of activation, which is likely to induce the pain symptoms experienced by the patient.
Three-dimensional Homology Modeling Predicts That Q875E Introduces a Novel Interaction
We modeled the Nav1.7 channel to examine the environment around the Gln-875 residue and to explore the structural consequences of introducing the Q875E mutation. The crystal structure of the NavAb bacterial sodium channel (11) provided the template for homology modeling of the Nav1.7 transmembrane domain (22). It was proposed that NavAb was crystallized with voltage sensors adopting the activated conformation, based in part on the observation that the side chain of the first gating charge arginine of the S4 helix is oriented toward the extracellular surface. In the resting-state conformation of voltage-gated channels, this arginine is predicted to instead interact with a negative countercharge on the S2 helix (25).
We found in the three-dimensional model of Nav1.7 with activated VSDs that the side chains of Gln-875 and Arg-214 are located in close proximity (Fig. 2). The Arg-214 residue is the outermost S4 gating charge of the DI voltage sensor. Generating the Q875E mutation substitutes the polar moiety of the glutamine side chain with a negatively charged carboxylate group, which introduces the potential for a salt bridge interaction with the Arg-214 side chain (Fig. 2). To further analyze potential interactions between the 214 and 875 positions, different side chain conformations were generated; 26 rotamers of Arg-214 were combined with 14 rotamers of either Gln-875 or Q875E to produce two sets of 364 rotamer pairs. An inter-side chain salt bridge was found with 100 of the Arg-214 and Q875E rotamer pairs, whereas a hydrogen bond was present in only 12 of the Arg-214 and Gln-875 rotamer pairs. Visual inspection of the models revealed the structural basis for this difference. Formation of a hydrogen bond with Arg-214 required suitable positioning and orientation of the oxygen atom of the Gln-875 amide moiety. In contrast, there are two oxygens on the carboxylate group of Q875E that are available to form a salt bridge with Arg-214. Therefore both the introduction of a negative charge at the 875 position and the less stringent geometrical constraints required for this side chain to form a favorable interaction with Arg-214 may be the molecular bases for the gain of function observed with the mutant channel.
FIGURE 2.

The side chain of residue Gln-875 is likely to interact with the gating charge Arg-214 in the activated state. Top and bottom panels, a homology model of Nav1.7 in ribbon format showing pore module (gold) and VSDs of DI and DIII (green) viewed from the membrane (top panels) or extracellular side (bottom panels). Boxed areas show residues Arg-214 and either Gln-875 or Q875E as sticks and transparent surface.
Q875E Interacts with the Gating Charge Arg-214
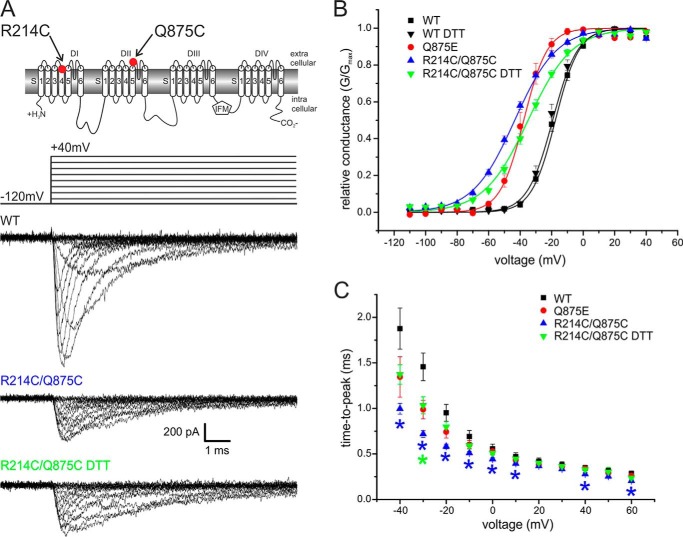
We introduced the double mutation R214C/Q875C into Nav1.7 to assess whether these two residues indeed move close enough to form a disulfide bridge. This mutant was successfully expressed, albeit producing smaller inward currents when compared with the WT channel (Fig. 3A).
FIGURE 3.
Activation of the R214C/Q875C double mutant is shifted to more hyperpolarized potentials. A, two-dimensional scheme of Nav1.7 indicating positions of the mutations. Shown are representative current traces obtained with the displayed protocol for WT, R214C/Q875C, and R214C/Q875C with 10 mm DTT present in the extracellular bath solution. B, relative conductance-voltage relationship and their Boltzmann fits (solid lines) for WT (n = 13), Q875E mutant (n = 10), R214C/Q875C (n = 16), and R214C/Q875C + DTT (n = 12). The Vhalf of R214C/Q875C is shifted from WT by −25.0 mV. In the presence of DTT, this shift is less pronounced (−16 mV from WT). C, time to peak calculated from pulse onset to maximum peak inward current for each potential. Asterisks denote significant difference from WT (p < 0.05) and are colored according to mutant tested. Data for WT and Q875E are reproduced from Fig. 1 for comparison. All data are represented as mean ± S.E.
The Vhalf of R214C/Q875C was −43.6 mV ± 1.0 mV, which corresponds to a hyperpolarizing shift of 25.0 mV when compared with WT. The slope of the voltage dependence of activation of the R214C/Q875C mutant was less steep (7.4 ± 0.3 for WT and 12.9 ± 0.4 for the mutant; Fig. 3B, Table 1). We observed a decrease of time to peak for the R214C/Q875C double mutant in the range of −40 mV to +10 mV, +40 mV, and +60 mV (Fig. 3C).
To assess whether breaking the putative disulfide bridge would reverse the observed hyperpolarizing shift, we recorded R214C/Q875C currents with 10 mm DTT present in the external bath solution (see Fig. 5B). This reducing condition resulted in a reversal of the hyperpolarizing shift of R214C/Q875C by +9.0 mV toward WT values. DTT in the external bath solution did not affect activation of WT Nav1.7 channels (Fig. 3B). Slope of activation curves were not altered by the addition of DTT, but time to peak of R214C/Q875C was significantly slower with DTT (Fig. 3C), supporting our hypothesis of an interaction between the VSD of DI and the DII pore region in the activated conformation.
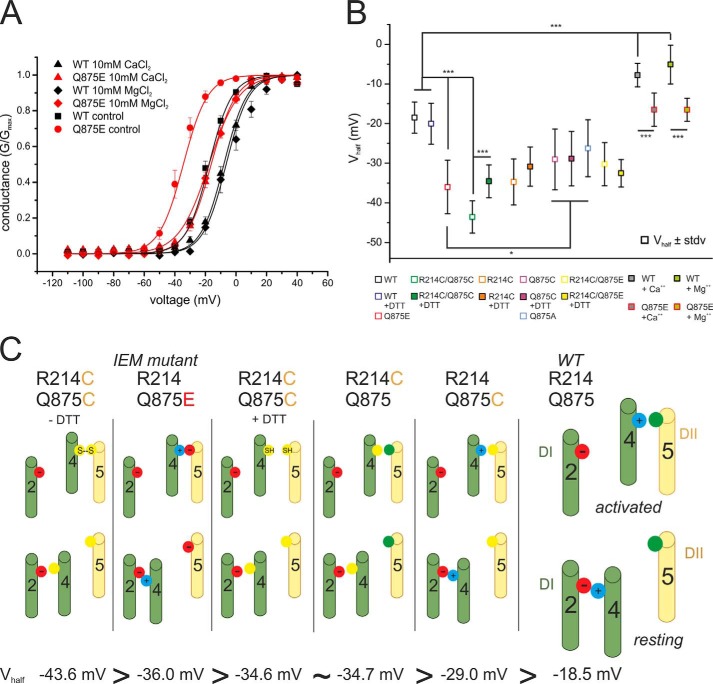
FIGURE 5.
Voltage dependence of the IEM mutation is more sensitive to increased extracellular concentrations of MgCl2 and CaCl2 than WT. A, relative conductance-voltage relationship and their corresponding Boltzmann fits (solid lines) for activation in the presence of 2 mm CaCl2 and MgCl2 for WT (black squares, n = 21, Vhalf = −17.3 mV ± 4.4 mV) and Q875E (red points, n = 15, Vhalf = −34.8 mV ± 6.6 mV, for other Vhalf values, see Table 1) and in the presence of 10 mm CaCl2 (upper triangles, WT, n = 8; Q875E, n = 11) and 10 mm MgCl2 (diamonds, WT, n = 4; Q875E, n = 7). Increasing the extracellular concentration of the divalent cations shifts activation to more depolarized potentials for both WT and the Q875E mutant and reduces the ΔVhalf between WT and Q875E. B, summary of mean Vhalf values and statistical differences between means (*, p < 0.05, ***, p < 0.001). All data are represented as mean ± S.E. C, schematic summary of the proposed interactions between the DI voltage sensor and pore module in activated and resting conformations. The channels are arranged according to the leftward shift of their activation. The IEM-causing Nav1.7 mutation Q875E (second from left) introduces an activated state-stabilizing salt bridge between two oppositely charged residues. R214C/Q875C (first on the left) mimics this electrostatic interaction with a disulfide bridge. DTT prevents disulfide bond formation in the open activated conformation (third from the left). An electrostatic interaction within the voltage sensor is disrupted by the R214C mutant to produce resting-state destabilization (third from the right). Substitution of Gln-875 with cysteine (second from the right) leads to reduced steric hindrance to movement of DI S4 in response to depolarizing stimuli. Green cylinders, S2 and S4 of VSD of DI; yellow cylinders, S5 of pore domain of DII. Cysteine residues are represented as yellow filled circles, and negative and positive charges are represented as red and blue filled circles, respectively. Glutamine residues are represented as green filled circles.
To distinguish between INa mediated by endogenously expressed Nav channels in HEK293 cells (26) and heterologously expressed mutant R214C/Q875C channels, only cells with a minimal current amplitude of −200 pA were included for analysis. In addition, sodium currents from mock transfected HEK293 cells were recorded, and current density was distinctly smaller than that of R214C/Q875C transfected cells (mock transfected, 0.3 ± 0.1 picosiemens/picofarads; R214C/Q875C, 0.8 ± 0.1 and 0.5 ± 0.1 picosiemens/picofarads without and with DTT, respectively).
The effect of the IEM mutation in producing a major hyperpolarizing shift of activation was recapitulated by disulfide locking of the DI VSD and pore module. However, although DTT partially reversed the leftward shift, reducing conditions did not completely re-establish WT behavior for the R214C/Q875C double mutant.
Mutagenesis Studies Reveal Potential Interaction of Arg-214 within the VSD
The substitution or addition of voltage-sensing charges in Nav channels can cause severe alterations of channel gating and behavior (18, 27, 28). R214C neutralizes a gating charge in the VSD of DI and therefore may have an effect on activation by itself. To test for this, we expressed the single mutant R214C in HEK cells and investigated activation characteristics.
Voltage dependence of activation of R214C was shifted to more hyperpolarized potentials when compared with WT, but slope was not affected by the mutation (Fig. 4B, Table 1). The addition of DTT induced no modification of half-maximal activation, suggesting that there was no spontaneous disulfide bond formation for this mutant, in contrast to R214C/Q875C. Time to peak of R214C was accelerated (Fig. 4C). Thus, Arg-214 may form closed state stabilizing interactions that we may have disrupted by the R214C mutation.
FIGURE 4.
The single point mutations R214C, Q875C, and Q875A shift activation in a hyperpolarizing direction. A, transmembrane map of Nav1.7 indicating the positions of mutated residues and representative current traces obtained with the shown protocol for R214C ± DTT and Q875C/A. B, relative conductance-voltage relationship and corresponding Boltzmann fits (solid lines) for WT (n = 13), R214C (n = 5) and R214C +DTT (n = 11). The Vhalf of R214C is shifted by −16.2 mV when compared with WT, and DTT does not affect this shift. C and F, time to peak measured from pulse onset to maximum peak inward current for each potential. Asterisks denote significant difference from WT (p < 0.05) and are colored according to mutant. D, relative conductance-voltage relationship and their Boltzmann fits (solid lines) for WT (n = 13), R214C/Q875E (n = 6) and R214C/Q875E + DTT (n = 8), and R214C/Q875C (n = 16) and R214C/Q875C + DTT (n = 12). E, relative conductance-voltage relationship and corresponding Boltzmann fits for WT (n = 13), Q875E (n = 10), Q875C (n = 10), Q875C + DTT (n = 12), and Q875A (n = 13). The Q875C and Q875A mutants show a hyperpolarizing shift in activation with a Δ Vhalf of −10.5 mV and −7.7 mV, respectively. The addition of DTT to the external bath solution does not significantly alter midpoint of activation of Q875C. Data for WT and Q875E are reproduced from Fig. 1 for comparison. All data are represented as mean ± S.E.
To test for the effect of the IEM mutation on the R214C substitution, we generated the R214C/Q875E double mutant. Boltzmann fits of the voltage dependence of activation in the presence and absence of DTT revealed a mean activation midpoint of −30.3 mV ± 2.2 mV and −32.6 mV ± 1.2 mV, respectively (Fig. 4D, Table 1), demonstrating that, as with the R214C mutant, DTT showed no marked change in mean half-maximal activation of R214C/Q875E.
As found for the R214C/Q875C double cysteine mutation, the slope of the activation curve of R214C/Q875E was significantly reduced when compared with WT (Fig. 4D, Table 1), and maximum peak inward current was reached faster for R214C/Q875E when compared with Nav1.7 WT at more negative potentials. Thus, the R214C/Q875E mutant induced a shift of activation that was not sensitive to the application of a reducing agent.
As mutations in the pore may affect activation (19), we tested the effects of the Q875C single mutation on channel activation. Q875C did induce a hyperpolarizing shift, although it was much smaller than that of the IEM mutant Q875E or the double mutant R214C/Q875C (Fig. 4E, Table 1). Q875C decreased time to peak over a wide range of voltages (Fig. 4F). The addition of DTT did not influence the observed half-maximal activation of Q875C mutant channels, suggesting that the Q875C mutation did not introduce a disulfide bond.
To assess whether the cysteine in position 875 is interacting with other residues in its vicinity, we introduced the small-chain, non-polar alanine residue into position 875. Voltage dependence of activation of the Q875A mutant was found to be shifted in the hyperpolarized direction (ΔVhalf = −7.7 mV when compared with WT; Fig. 4E, Table 1), and time to peak was decreased (Fig. 4F). Shift of midpoint of activation was proportionally small, and statistical testing confirmed that mean half-maximal activation of Q875A and Q875C ±DTT was not significantly different (see Fig. 5B). This finding indicates that Q875C does not form disulfide bridges within this mutant.
Extracellular Divalent Cations Shift Activation of the IEM Mutation Strongly to More Depolarized Potentials
To better distinguish between the effects deriving from the direct interaction of Q875E with Arg-214 versus the effects relating to an altered local electrical field by the introduced Q875E negative charge, we determined the voltage dependence of activation for Nav1.7 WT and Q875E in the presence of an elevated extracellular concentration of either Ca2+ or Mg2+ divalent cations. Increased CaCl2 and MgCl2 concentrations (10 mm when compared with 2 mm under control condition) shifted the activation of both Q875E and WT to more depolarized potentials (Fig. 5A). However, the effect on Q875E was larger than on WT (Table 1). The difference in the shift between Q875E and WT was thus reduced to −8.7 mV in the presence of 10 mm Ca2+ and to −11.4 mV with 10 mm Mg2+ (when compared with −17.5 mV under control conditions (Table 1)). Interestingly, the cations shifted the voltage dependence of activation of the IEM mutant toward WT values: −16.5 mV when compared with −18.5 mV for the WT control in the absence of elevated Ca2+ or Mg2+ (Table 1).
DISCUSSION
In this study, we show that the hyperpolarizing shift of activation found with the IEM mutation Q875E may be due to a strengthening of a direct interaction between the VSD and the pore region in the open state conformation of Nav1.7. Q875E introduces a negative charge in the pore module, and our data suggest that it forms a salt bridge with the gating charge Arg-214 of DI VSD.
For most IEM mutations, a prominent leftward shift of channel activation is described, enhancing the probability of channel opening at more hyperpolarized potentials (for review, see e.g. Refs. 7 and 29). The marked shift of activation of the Q875E mutation by −17.5 mV when compared with Nav1.7 WT is very likely to induce hyperexcitability (17, 22, 30), as are a faster time to peak and slower channel deactivation (Fig. 1). Conversely, there was a −22.8-mV hyperpolarizing shift of slow inactivation for the mutant (Fig. 1D), which could act to countervail and limit the extent of gain-of-function effects (31). Enhanced slow inactivation is a common property of IEM-associated mutant Nav1.7 channels, and the biophysical changes observed for the Q875E mutation are consistent with the effects produced by other IEM mutants (e.g. Refs. 18 and 32–35).
Our homology model indicates that in the channel three-dimensional structure, the side chains of residues Arg-214 and Gln-875 are located in close proximity in the activated state. Q875E introduces a negatively charged side chain that could interact directly with Arg-214 via a salt bridge (Figs. 2 and 5C) and thus stabilize the activated conformation of the DI VSD. Hence, by inhibiting the return of the VSD to its resting state, the channel may be rendered partially activated and primed to gate in response to a more limited depolarization pulse. Mechanistically, this is analogous to the voltage sensor trapping effect of β-scorpion toxins, which bind with and stabilize the activated conformation of the DII VSD to produce a hyperpolarizing shift of activation (36).
Indeed, there is a correlation between the magnitude of the shift of activation and the proposed strength of the interaction between residues occupying the 214 and 875 positions (Fig. 5C). The greatest shift (−25.0 mV) was observed when these two residues were covalently coupled by a disulfide bridge (R214C/Q875C). The next greatest shift (−17.5 mV) was found when a salt bridge formed the putative interaction between Arg-214 and Q875E. In contrast, a comparatively weaker hydrogen bond interaction is feasible between the Arg-214 guanidinium group and Gln-875 amide oxygen in the WT channel (Fig. 5C).
Our disulfide locking studies verified the proximity of 214 and 875 (Figs. 2 and 3) and also demonstrated that, in the presence of the reducing agent DTT, the R214C/Q875C double mutant produces a hyperpolarizing shift of activation (−16.1 mV) that is equal in effect to that of the R214C single mutation (−16.2 mV, Fig. 5, B and C, and Table 1). In VSDs, the outermost gating charge is proposed to interact with a negative counter charge on the S2 helix in the resting state conformation (25, 37). The R214C mutation would eliminate such an intra-VSD salt bridge. It therefore appears that two different processes, resting state destabilization versus activated state stabilization of the DI VSD, can produce an equivalent functional outcome, namely shifting the voltage dependence of activation to more hyperpolarized potentials.
The Q875C and Q875A mutants exhibit the smallest changes of activation from WT values with shifts of −10.5 mV and −7.7 mV, respectively (Fig. 5, B and C, and Table 1). Introducing a small side chain at this position may result in reduced steric hindrance to movement of the Arg-214 side chain, thus facilitating transition from resting to activated states. This mechanism is not applicable in the case of the Q875E mutation, however, which involves substitution of a side chain of equivalent shape and size. Here, the newly introduced negative charge, as opposed to a steric factor, accounts for the potency of this mutation.
Reduced voltage dependence of channel activation indicated by the increased slope factors of the two double mutants R214C/Q875C and R214C/Q875E (Table 1) may be due to the synergistic effects of electrostatic and steric changes that arise when two sites of the channel protein are altered simultaneously, particularly if the mutations affect both stabilization of the closed state and S4 movement. In contrast, the R214C single substitution did not change the slope factor in our experiments, possibly because cysteine may still function adequately as a gating charge substitute by interacting with a negative counter charge in the voltage sensor via a hydrogen bond. Nevertheless, this interaction would be weaker than the inter-VSD salt bridge found in the WT channel, and so a shift in the midpoint of voltage dependence of activation is still observed.
It is possible that the negative charge introduced by Q875E perturbs the local electrical field experienced by the DI VSD even in its resting state conformation. The Q875E side chain may be mimicking the effect of the negatively charged sialic acid carbohydrate that is N-linked to the channel. Glycosylation is proposed to exert an attractive electrostatic force to promote S4 movement and therefore VSD activation; deglycosylated Nav channels are associated with a +10-mV depolarizing shift of activation (38). Although the Q875E mutation represents only a single extra negative charge, in contrast with the 110–130 negative charges added extracellularly by glycosylation (39), the close proximity of Q875E to the DI S4 helix may have a major effect on making transition from resting to activated state more energetically favorable for the VSD, thereby contributing to the hyperpolarizing shift of activation for this mutation.
The electric surface potential can be altered by the addition of extracellular divalent cations such as Ca2+ or Mg2+. Both shift the midpoint of activation to more depolarized potentials (Fig. 5B), but this shift is more pronounced for Q875E than for WT. This indicates that shielding of the negative charge introduced by the Q875E mutation partially cancels a Q875E specific effect, which we propose involves the interaction with Arg-214. From a therapeutic perspective, our results suggest that elevation of extracellular Mg2+ may help to curb the attacks of the patient, and this option may be worth investigating further in clinics.
In summary, our characterization of the biophysical properties of the IEM-linked Q875E mutation shows that it produces a gain-of-function phenotype. We propose that the molecular basis for the effects of this mutation involves an introduced negative charge modulating the electrical field experienced by the DI VSD and directly interacting via a salt bridge with the Arg-214 outermost gating charge upon activation. By investigating this naturally occurring Q875E mutation, we discovered a gating-relevant interaction between the DII pore region and the VSD of DI. Our results suggest that diverse and mutation-specific molecular mechanisms can produce equivalent functional modifications of Nav1.7, notably a shift of the voltage dependence of activation, that fit a paradigm of biophysical changes associated with this pain disorder.
Acknowledgments
We thank Michaela Hellwig and Iwona Izydorczyk for excellent technical assistance and Benjamin Häberle for performing preliminary experiments.
This work was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) Grant LA2740/2-1 (to A. L.), German Israeli Foundation (GIF) Grant 1091-27.1/2010 (to A. L.), Marie-Curie Fellowship FP7-PEOPLE-2010-IEF, Number 275768 (to A. O. R.), and a fellowship from the Studienstiftung des deutschen Volkes (to T. S.).
- IEM
- inherited erythromelalgia
- VSD
- voltage-sensing domain.
REFERENCES
- 1. Toledo-Aral J. J., Moss B. L., He Z. J., Koszowski A. G., Whisenand T., Levinson S. R., Wolf J. J., Silos-Santiago I., Halegoua S., Mandel G. (1997) Identification of PN1, a predominant voltage-dependent sodium channel expressed principally in peripheral neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94, 1527–1532 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Lampert A., O'Reilly A. O., Reeh P., Leffler A. (2010) Sodium channelopathies and pain. Pflugers Arch. 460, 249–263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Yang Y., Wang Y., Li S., Xu Z., Li H., Ma L., Fan J., Bu D., Liu B., Fan Z., Wu G., Jin J., Ding B., Zhu X., Shen Y. (2004) Mutations in SCN9A, encoding a sodium channel α subunit, in patients with primary erythermalgia. J. Med. Genet. 41, 171–174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Fertleman C. R., Ferrie C. D., Aicardi J., Bednarek N. A., Eeg-Olofsson O., Elmslie F. V., Griesemer D. A., Goutières F., Kirkpatrick M., Malmros I. N., Pollitzer M., Rossiter M., Roulet-Perez E., Schubert R., Smith V. V., Testard H., Wong V., Stephenson J. B. (2007) Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder (previously familial rectal pain syndrome). Neurology 69, 586–595 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Drenth J. P., te Morsche R. H., Guillet G., Taieb A., Kirby R. L., Jansen J. B. (2005) SCN9A mutations define primary erythermalgia as a neuropathic disorder of voltage gated sodium channels. J. Invest. Dermatol. 124, 1333–1338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Cox J. J., Reimann F., Nicholas A. K., Thornton G., Roberts E., Springell K., Karbani G., Jafri H., Mannan J., Raashid Y., Al-Gazali L., Hamamy H., Valente E. M., Gorman S., Williams R., McHale D. P., Wood J. N., Gribble F. M., Woods C. G. (2006) An SCN9A channelopathy causes congenital inability to experience pain. Nature 444, 894–898 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Lampert A., Eberhardt M., Waxman S. G. (2014) Altered sodium channel gating as molecular basis for pain: contribution of activation, inactivation, and resurgent currents. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 221, 91–110 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Catterall W. A., Goldin A. L., Waxman S. G. (2005) International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 57, 397–409 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Catterall W. A. (2010) Ion channel voltage sensors: structure, function, and pathophysiology. Neuron 67, 915–928 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Long S. B., Campbell E. B., Mackinnon R. (2005) Crystal structure of a mammalian voltage-dependent Shaker family K+ channel. Science 309, 897–903 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Payandeh J., Scheuer T., Zheng N., Catterall W. A. (2011) The crystal structure of a voltage-gated sodium channel. Nature 475, 353–358 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. DeCaen P. G., Yarov-Yarovoy V., Zhao Y., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. (2008) Disulfide locking a sodium channel voltage sensor reveals ion pair formation during activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 15142–15147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. DeCaen P. G., Yarov-Yarovoy V., Sharp E. M., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. (2009) Sequential formation of ion pairs during activation of a sodium channel voltage sensor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 22498–22503 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Lewis A., Jogini V., Blachowicz L., Lainé M., Roux B. (2008) Atomic constraints between the voltage sensor and the pore domain in a voltage-gated K+ channel of known structure. J. Gen. Physiol. 131, 549–561 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Lainé M., Lin M. C., Bannister J. P., Silverman W. R., Mock A. F., Roux B., Papazian D. M. (2003) Atomic proximity between S4 segment and pore domain in Shaker potassium channels. Neuron 39, 467–481 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Phillips L. R., Swartz K. J. (2010) Position and motions of the S4 helix during opening of the Shaker potassium channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 136, 629–644 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Dib-Hajj S. D., Rush A. M., Cummins T. R., Hisama F. M., Novella S., Tyrrell L., Marshall L., Waxman S. G. (2005) Gain-of-function mutation in Nav1.7 in familial erythromelalgia induces bursting of sensory neurons. Brain 128, 1847–1854 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Lampert A., Dib-Hajj S. D., Eastman E. M., Tyrrell L., Lin Z., Yang Y., Waxman S. G. (2009) Erythromelalgia mutation L823R shifts activation and inactivation of threshold sodium channel Nav1.7 to hyperpolarized potentials. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 390, 319–324 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Lampert A., O'Reilly A. O., Dib-Hajj S. D., Tyrrell L., Wallace B. A., Waxman S. G. (2008) A pore-blocking hydrophobic motif at the cytoplasmic aperture of the closed-state Nav1.7 channel is disrupted by the erythromelalgia-associated F1449V mutation. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 24118–24127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Skeik N., Rooke T. W., Davis M. D., Davis D. M., Kalsi H., Kurth I., Richardson R. C. (2012) Severe case and literature review of primary erythromelalgia: novel SCN9A gene mutation. Vasc. Med. 17, 44–49 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Klugbauer N., Lacinova L., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. (1995) Structure and functional expression of a new member of the tetrodotoxin-sensitive voltage-activated sodium channel family from human neuroendocrine cells. EMBO J. 14, 1084–1090 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Eberhardt M., Nakajima J., Klinger A. B., Neacsu C., Hühne K., O'Reilly A. O., Kist A. M., Lampe A. K., Fischer K., Gibson J., Nau C., Winterpacht A., Lampert A. (2014) Inherited pain: sodium channel Nav1.7 A1632T mutation causes erythromelalgia due to a shift of fast inactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 1971–1980 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Guex N., Diemand A., Peitsch M. C. (1999) Protein modelling for all. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24, 364–367 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Krissinel E., Henrick K. (2007) Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J. Mol. Biol. 372, 774–797 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Vargas E., Bezanilla F., Roux B. (2011) In search of a consensus model of the resting state of a voltage-sensing domain. Neuron 72, 713–720 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. He B., Soderlund D. M. (2010) Human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells express endogenous voltage-gated sodium currents and Nav1.7 sodium channels. Neurosci. Lett. 469, 268–272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Stühmer W., Conti F., Suzuki H., Wang X. D., Noda M., Yahagi N., Kubo H., Numa S. (1989) Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel. Nature 339, 597–603 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Kontis K. J., Rounaghi A., Goldin A. L. (1997) Sodium channel activation gating is affected by substitutions of voltage sensor positive charges in all four domains. J. Gen. Physiol. 110, 391–401 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Waxman S. G. (2013) Painful Na-channelopathies: an expanding universe. Trends Mol. Med. 19, 406–409 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Sheets P. L., Jackson J. O., 2nd, Waxman S. G., Dib-Hajj S. D., Cummins T. R. (2007) A Nav1.7 channel mutation associated with hereditary erythromelalgia contributes to neuronal hyperexcitability and displays reduced lidocaine sensitivity. J. Physiol. 581, 1019–1031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Han C., Dib-Hajj S. D., Lin Z., Li Y., Eastman E. M., Tyrrell L., Cao X., Yang Y., Waxman S. G. (2009) Early- and late-onset inherited erythromelalgia: genotype-phenotype correlation. Brain 132, 1711–1722 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Choi J. S., Dib-Hajj S. D., Waxman S. G. (2006) Inherited erythermalgia: limb pain from an S4 charge-neutral Na channelopathy. Neurology 67, 1563–1567 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Cheng X., Dib-Hajj S. D., Tyrrell L., Waxman S. G. (2008) Mutation I136V alters electrophysiological properties of the Nav1.7 channel in a family with onset of erythromelalgia in the second decade. Mol. Pain 4, 1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Estacion M., Dib-Hajj S. D., Benke P. J., Te Morsche R. H., Eastman E. M., Macala L. J., Drenth J. P., Waxman S. G. (2008) Nav1.7 gain-of-function mutations as a continuum: A1632E displays physiological changes associated with erythromelalgia and paroxysmal extreme pain disorder mutations and produces symptoms of both disorders. J. Neurosci. 28, 11079–11088 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Cregg R., Laguda B., Werdehausen R., Cox J. J., Linley J. E., Ramirez J. D., Bodi I., Markiewicz M., Howell K. J., Chen Y. C., Agnew K., Houlden H., Lunn M. P., Bennett D. L., Wood J. N., Kinali M. (2013) Novel mutations mapping to the fourth sodium channel domain of Nav1.7 result in variable clinical manifestations of primary erythromelalgia. Neuromolecular Med. 15, 265–278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Cestèle S., Qu Y., Rogers J. C., Rochat H., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. (1998) Voltage sensor-trapping: enhanced activation of sodium channels by β-scorpion toxin bound to the S3–S4 loop in domain II. Neuron 21, 919–931 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Takeshita K., Sakata S., Yamashita E., Fujiwara Y., Kawanabe A., Kurokawa T., Okochi Y., Matsuda M., Narita H., Okamura Y., Nakagawa A. (2014) X-ray crystal structure of voltage-gated proton channel. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 21, 352–357 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Bennett E., Urcan M. S., Tinkle S. S., Koszowski A. G., Levinson S. R. (1997) Contribution of sialic acid to the voltage dependence of sodium channel gating. A possible electrostatic mechanism. J. Gen. Physiol. 109, 327–343 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Miller J. A., Agnew W. S., Levinson S. R. (1983) Principal glycopeptide of the tetrodotoxin/saxitoxin binding protein from Electrophorus electricus: isolation and partial chemical and physical characterization. Biochemistry 22, 462–470 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]