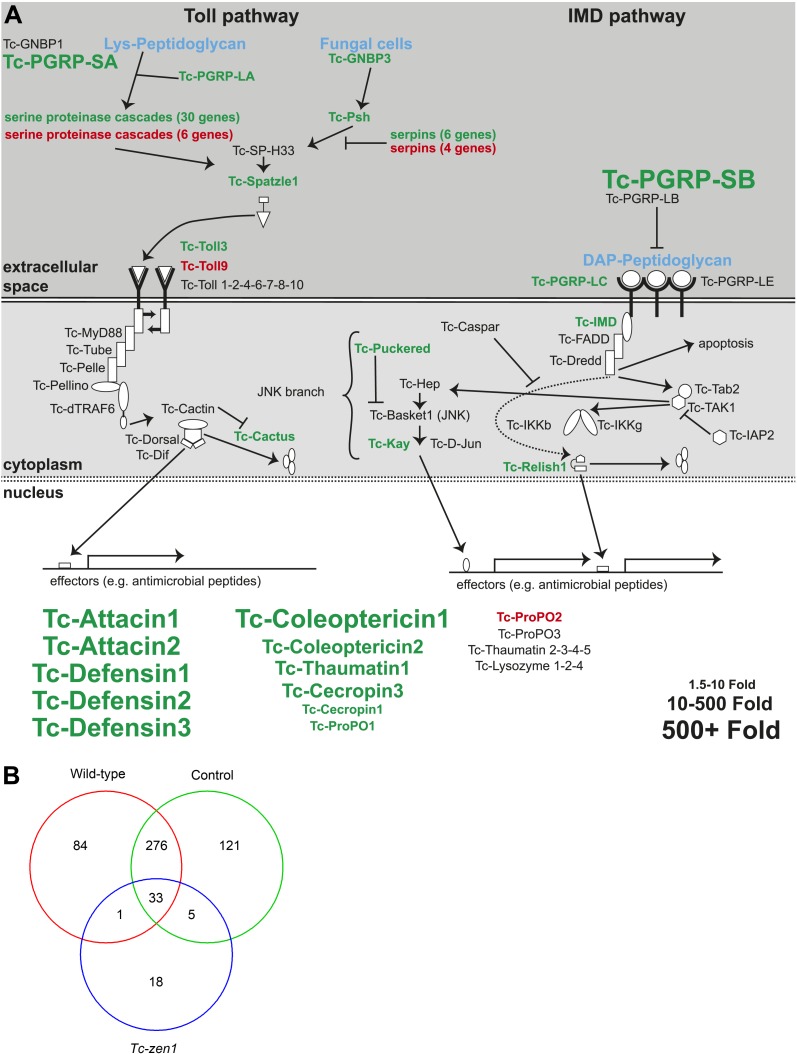
Figure 4. Immune-responsive genes in wild-type, control, and Tc-zen1 RNAi eggs.
(A) Schematic representation of the immune signaling pathways in Tribolium as described in Zou et al. (2007). Significantly induced genes after septic injury in wild-type or control RNAi eggs are indicated in green; significantly repressed genes after septic injury in wild-type or control RNAi eggs are indicated in red. Genes not differentially expressed are black. The size of the gene names represents the fold change (small = 1.5- to 10-fold, medium = 10- to 500-fold, large = 500 + fold expression). (B) Venn diagram showing the number of differentially expressed genes in septically injured eggs as compared to naive eggs (FDR < 0.01). In total, 538 genes are differentially expressed upon infection, of which 394 in wild-type eggs, 435 in control RNAi eggs, and only 57 in Tc-zen1 RNAi eggs. This means that Tribolium eggs display an extensive transcriptional response upon infection and that this response is largely abolished in eggs without a serosa.