Abstract
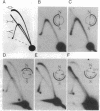
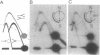
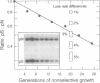
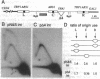
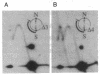
Replication origins in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae are identified as autonomous replication sequence (ARS) elements. To examine the effect of origin density on replication initiation, we have analyzed the replication of a plasmid that contains two copies of the same origin, ARS1. The activation of origins and the direction that replication forks move through flanking sequences can be physically determined by analyzing replication intermediates on two-dimensional agarose gels. We find that only one of the two identical ARSs on the plasmid initiates replication on any given plasmid molecule; that is, this close spacing of ARSs results in an apparent interference between the potential origins. Moreover, in the particular plasmid that we constructed, one of the two identical copies of ARS1 is used four times more frequently than the other one. These results show that the plasmid context is critical for determining the preferred origin. This origin preference is also exhibited when the tandem copies of ARS1 are introduced into a yeast chromosome. The sequences responsible for establishing the origin preference have been identified by deletion analysis and are found to reside in a portion of the yeast URA3 gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell S. P., Stillman B. ATP-dependent recognition of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication by a multiprotein complex. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):128–134. doi: 10.1038/357128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi F., Zatchej M., Thoma F. Species specific protein--DNA interactions may determine the chromatin units of genes in S.cerevisiae and in S.pombe. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1177–1185. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. Initiation at closely spaced replication origins in a yeast chromosome. Science. 1993 Dec 10;262(5140):1728–1731. doi: 10.1126/science.8259517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Lockshon D., Fangman W. L. The arrest of replication forks in the rDNA of yeast occurs independently of transcription. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90355-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B. M., Brewer B. J., Reynolds A. E., Fangman W. L. A yeast origin of replication is activated late in S phase. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90468-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B. M., Fangman W. L. A position effect on the time of replication origin activation in yeast. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90474-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Spotila L. D., Nawotka K. A., el-Assouli S. M., Davis L. R. The in vivo replication origin of the yeast 2 microns plasmid. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90643-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marahrens Y., Stillman B. A yeast chromosomal origin of DNA replication defined by multiple functional elements. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):817–823. doi: 10.1126/science.1536007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marczynski G. T., Jaehning J. A. A transcription map of a yeast centromere plasmid: unexpected transcripts and altered gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8487–8506. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Parras L., Hernández P., Martínez-Robles M. L., Schvartzman J. B. Initiation of DNA replication in ColE1 plasmids containing multiple potential origins of replication. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22496–22505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarroll R. M., Fangman W. L. Time of replication of yeast centromeres and telomeres. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):505–513. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natale D. A., Schubert A. E., Kowalski D. DNA helical stability accounts for mutational defects in a yeast replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2654–2658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natale D. A., Umek R. M., Kowalski D. Ease of DNA unwinding is a conserved property of yeast replication origins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):555–560. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivin C. J., Fangman W. L. Replication fork rate and origin activation during the S phase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1980 Apr;85(1):108–115. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.1.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schvartzman J. B., Adolph S., Martín-Parras L., Schildkraut C. L. Evidence that replication initiates at only some of the potential origins in each oligomeric form of bovine papillomavirus type 1 DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3078–3086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Nucleosome positioning can affect the function of a cis-acting DNA element in vivo. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):387–389. doi: 10.1038/343387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Isolation and characterisation of a yeast chromosomal replicator. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):39–43. doi: 10.1038/282039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A., Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. Replication of each copy of the yeast 2 micron DNA plasmid occurs during the S phase. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):923–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90332-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]