Abstract
Objective To evaluate the relative risk of pulmonary disease among patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease treated with methotrexate.
Data sources PubMed, Cochrane central register of controlled trials, and Embase to 9 January 2014.
Study selection Double blind randomised controlled trials of methotrexate versus placebo or active comparator agents in adults with psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis, or inflammatory bowel disease. Studies with fewer than 50 participants or of less than 12 weeks’ duration were excluded.
Data synthesis Two investigators independently searched both databases. All authors reviewed selected studies. We compared relative risk differences using the Mantel-Haenszel random effects method to assess total respiratory adverse events, infectious respiratory adverse events, non-infectious respiratory adverse events, interstitial lung disease, and death.
Results Seven studies met our inclusion criteria, six with placebo as the comparator. Heterogeneity across the studies was not significant (I2=0%), allowing combination of trial results. 504 respiratory adverse events were documented in 1630 participants. Methotrexate was not associated with an increased risk of adverse respiratory events (relative risk 1.03, 95% confidence interval 0.90 to 1.17), respiratory infections (1.02, 0.88 to 1.19), or non-infectious respiratory events (1.07, 0.58 to 1.96). No pulmonary deaths occurred.
Conclusions Findings suggested that there was no increased risk of lung disease in methotrexate treated patients with non-malignant inflammatory diseases. Given the limitations of the study, however, we cannot exclude a small but clinically important risk.
Introduction
Methotrexate is an effective treatment for malignant as well as several non-malignant inflammatory diseases.1 It is recommended as a first line disease modifying treatment for rheumatoid arthritis,2 3 psoriatic arthritis, and psoriasis,4 5 6 and for both the induction and maintenance of remission in Crohn’s disease.7 Methotrexate may be used as monotherapy or in combination with other drugs, including oral agents and newer biologicals.2 3 4 5 6 7 In some disorders methotrexate is not only disease altering but also life saving.8 9
Methotrexate has been implicated as a cause of serious lung toxicity.1 2 3 6 The prevalence of methotrexate related interstitial lung disease remains unknown but has been reported to be as high as 11.6% in rheumatoid arthritis.10 Studies of methotrexate induced lung disease among rheumatoid arthritis populations are confounded by the propensity to develop pulmonary infections and pulmonary manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis itself, concomitant drug use, and a higher rate of pulmonary fatalities.11 12 13 Distinguishing between rheumatoid arthritis related and methotrexate related interstitial lung disease is difficult if not impossible since the clinical and histological features overlap.14 15 16 Aside from case reports, all previous studies of methotrexate related interstitial lung disease have been in rheumatoid arthritis.
A recent meta-analysis of clinical trials of rheumatoid arthritis reported a small but significant increase in infectious respiratory complications but no increase in non-infectious events among participants treated with methotrexate.17 Studies of clinical trials among diseases without pulmonary manifestations provide an opportunity to evaluate this problem more clearly.
We performed a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of 12 weeks or greater duration to evaluate if methotrexate is associated with an increased risk of lung disease in adults with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Methods
Data sources and searches
We carried out a systematic literature search with no date limits using PubMed, the Cochrane central register of controlled trials, and Embase. The search was performed to 9 January 2014 (see supplementary file for keywords used in search strategy). We also searched for previously published meta-analyses and systematic literature reviews. The reference lists of relevant articles were also reviewed.
Study selection
Two authors (CL and RC) independently performed the literature search, with discrepancies resolved by consensus.
The inclusion criteria for study selection were: double blind randomised controlled trials; patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or inflammatory bowel disease; studies in English; studies consisting of a minimum of two arms, at least one receiving methotrexate and at least one not receiving methotrexate; studies including only adults (≥18 years); trials of 12 weeks or more duration; studies of 50 patients or more; and studies reporting respiratory side effects for methotrexate and comparator groups separately. In the case of multiple publications of one randomised controlled trial we included the publication most relevant to our inclusion criteria, in terms of detailed reporting of respiratory side effects. If the results of a study were reported at multiple time points, we included the publication of greatest duration provided it remained a double blind randomised controlled trial and fully reported respiratory adverse events. If required we reviewed previous publications of the same trial to fully assess the trial protocol and risk of bias. This approach was taken to avoid including participants more than once in the meta-analysis.
We selected relevant articles using a two step approach. Firstly, we screened the titles and abstracts of identified references to exclude articles that did not deal with the topic of interest. Secondly, we reviewed the full text of relevant articles.
Data extraction and quality assessment
For each included study two authors (CL and RC) independently extracted data and resolved discrepancies by discussion. One author (CL) entered the data into a database, and the remaining authors checked these entries.
We extracted several variables: authors, year of publication, population studied, number of patients, mean age and range, sex, disease duration, percentage methotrexate naive, previous immunosuppressive drug use, steroid use at baseline, folic acid or folinic acid usage, study design and duration, comparator drug, and adverse events. Adverse events were extracted as both total respiratory adverse events and individual adverse events in each category reported in any individual trial. The terminology used to describe respiratory adverse events varied widely in the included studies; to overcome the lack of standardisation in terminology used, we classified adverse events into two subgroups: infectious adverse events and non-infectious adverse events.
Data synthesis and analysis
We meta-analysed data using RevMan Version 5.1 software,18 expressed as relative risk for dichotomous variables. Throughout we used random effects meta-analysis using the Mantel-Haenszel method. Results are expressed as relative risks with 95% confidence intervals.
Assessment of bias
To assess for trial level risk of bias in included studies we used the criteria described in the Cochrane handbook.19 Two authors (CL and RC) independently assessed studies for risk of bias. Discrepancies were resolved by discussion and consensus. A risk of bias graph and summary were generated. We generated funnel plots to assess for publication bias.
Sensitivity analysis
We performed sensitivity analysis to assess the effect of trial size (<250 participants versus ≥250 participants), disease (psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or inflammatory bowel disease), comparator drug (placebo versus active comparator), folic acid use (documented versus none or unclear use), methotrexate naivety, drop-out rates, and effect of including studies with fewer than 50 patients.
Results
Literature search
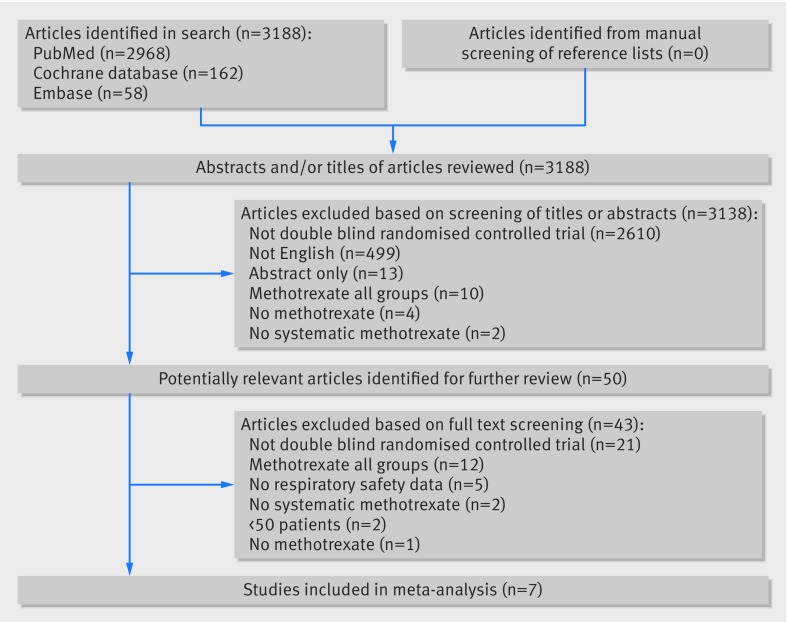
From the literature search 3188 citations were identified: 2968 from PubMed, 162 from the Cochrane central register of controlled trials, and 58 from Embase. Of the 3188 studies, only seven articles met the predefined inclusion criteria and were included in the meta-analysis (fig 1).
Fig 1 Flow of studies through review
Study characteristics
The seven included studies comprised 1640 patients, 818 of whom received methotrexate and 812 comparator treatments (table 1). The study durations ranged from 16 to 52 weeks and the number of patients from 76 to 478. The studies reported a total of 946 patient years of exposure. Five studies involved placebo comparators only, one a monoclonal antibody alone, and one placebo and monoclonal antibody comparator groups.20 21 22 23 24 25 26
Table 1.
Characteristics of studies included in meta-analysis
| Study | Year | Comparator drug | Methotrexate (No) | Comparator (No) | Study duration (weeks) | Age (years)* | Female (%) | Disease duration, (years)* | Methotrexate naïve (%) | Methotrexate dose, weekly (median) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feagan et al20 | 2014 | Placebo | 63 | 63 | 50 | 39 | 44 | 10 | NA | 25 mg subcutaneous |
| Gottlieb et al21 | 2012 | Placebo | 239 | 239 | 24 | 44 | 33 | 17 | 83 | 15 mg oral |
| Kingsley et al22 | 2012 | Placebo | 109 |
112 | 24 | 49 | 44 | 1 | 100 | 15 mg oral |
| Reich et al23 | 2011 | Briakinumab | 163 | 154 | 52 | 44 | 30 | 19 | 100 | 25 mg oral |
| Saurat et al24 | 2008 | Adalimumab/placebo | 110 | 161 | 16 | 42 | 34 | 19 | 100 | 15 mg oral |
| Feagan et al25 | 2000 | Placebo | 40 | 36 | 40 | 33 | 50 | 7 | 0 | 15 mg intramuscular |
| Feagan et al26 | 1995 | Placebo | 94 | 47 | 16 | 35 | 46 | 8 | NA | 25 mg intramuscular |
NA=not available.
*Age and duration of disease expressed as mean as reported by individual studies.
Findings
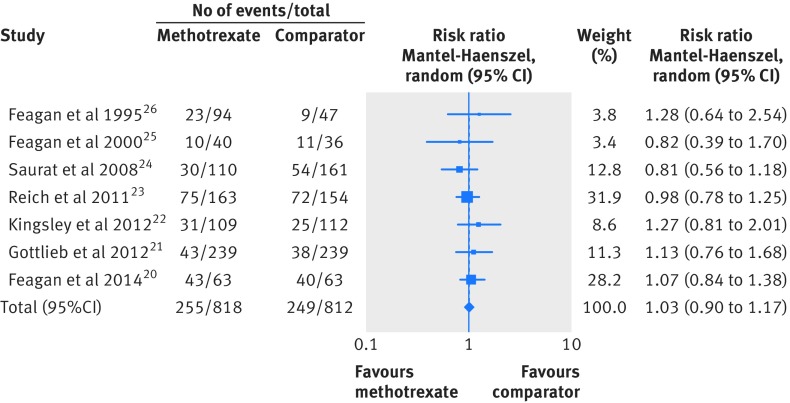
Overall, 504 respiratory adverse events were documented (table 2). Although the I2 index was low (0%), the type and number of respiratory adverse events reported varied considerably between the studies so we chose a random effects model for our analyses. Overall, methotrexate was not associated with an increased risk of total adverse respiratory events compared with comparator agents (relative risk 1.03, 95% confidence interval 0.90 to 1.17, I2=0%, fig 2). In addition we found no increased risk in infectious respiratory events (1.02, 0.88 to 1.19, I2=0%) nor non-infectious respiratory adverse events (1.07, 0.58 to 1.96, I2=0%) (see supplementary figures 1 and 2). No pulmonary deaths occurred. A single case of pneumonitis was reported in a patient treated with methotrexate in one study, but no definitive diagnostic features or additional information were reported.20
Table 2.
Respiratory adverse events reported in individual studies
| Author | Year | Cough | Pneumonitis | Urinary tract infection | Pneumonia | Respiratory tract infection | Asthma | Pulmonary embolism | Nasopharyngitis | Sinusitis | Rhinitis | Rhinorrhoea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feagan et al20 | 2014 | 15 | 1 | — | — | 55 | — | 1 | — | 11 | — | — |
| Gottlieb et al21 | 2012 | — | — | 32 | 1 | — | 1 | — | 49 | — | — | — |
| Kingsley et al22 | 2012 | — | — | — | — | 56 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Reich et al23 | 2011 | 21 | — | 23 | — | — | — | — | 89 | — | 14 | — |
| Saurat et al24 | 2008 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 67 | — | 11 | 6 |
| Feagan et al25 | 2000 | — | — | 20 | — | 1 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Feagan et al26 | 1995 | — | — | 31 | 1 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
Respiratory adverse events reported for each study for methotrexate and comparator groups combined.
Fig 2 Forest plot of relative risk for total adverse respiratory events for methotrexate compared with comparator agents
Risk of bias in included studies
A risk of bias graph, risk of bias summary, and funnel plot suggested a low risk of bias (see supplementary figures 3-5). Three of the studies provided inadequate information to assess the risk of selection bias.
Sensitivity analysis
Additional subgroup analyses showed no effect of study size, disease under study, comparator treatment, study drop-out rate, use of folic acid supplementation, or difference between methotrexate naive patients and those who had previously received methotrexate (table 3). Two additional studies with fewer than 50 patients were identified; they reported no additional respiratory adverse events and their inclusion did not change the results of the analyses (relative risk 1.03, 95% confidence interval 0.90 to 1.17, I2=0%) (see supplementary figure 6).
Table 3.
Sensitivity analysis for total respiratory adverse events
| Outcome | No of studies | No of participants | Relative risk (95% CI)* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study size: | |||
| <250 patients | 4 | 564 | 1.10 (0.90 to 1.35) |
| ≥250 patients | 3 | 1066 | 0.97 (0.81 to 1.16) |
| Disease: | |||
| Psoriatic arthritis | 1 | 221 | 1.27 (0.81 to 2.01) |
| Psoriasis | 3 | 1066 | 0.97 (0.81 to 1.16) |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 3 | 343 | 1.07 (0.85 to 1.34) |
| Comparator: | |||
| Placebo | 6* | 1205 | 1.07 (0.90 to 1.26) |
| Active comparator | 2* | 534 | 0.94 (0.76 to 1.15) |
| Folic acid use: | |||
| Documented | 4 | 935 | 1.01 (0.87 to 1.17) |
| None or unclear | 3 | 695 | 1.09 (0.80 to 1.49) |
| Methotrexate naïve: | |||
| Yes | 3 | 809 | 0.98 (0.80 to 1.20) |
| No | 4 | 821 | 1.08 (0.89 to 1.32) |
| Study drop-out rate: | |||
| ≥30% | 3 | 614 | 1.02 (0.83 to 1.25) |
| <30% | 4 | 1016 | 1.03 (0.86 to 1.23) |
| Inclusion of studies <50 patients | 9 | 1691 | 1.03 (0.90 to 1.17) |
*One study contained placebo and active comparator arms, these have been analysed separately for subgroup analysis.
Discussion
In this study we did not find an increase in the risk of pulmonary adverse events among patients treated with methotrexate for psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or inflammatory bowel disease. Although methotrexate is reported to cause lung disease, we did not find an increase in the risk of infectious or non-infectious lung disease. These results support the findings of a previous study among patients with rheumatoid arthritis, showing that the risk of non-infectious lung disease is rare, if it exists at all.17
Comparison with other studies
Studies of respiratory adverse events in rheumatoid arthritis are confounded by the propensity for patients to develop pulmonary complications of their underlying disease, including interstitial lung disease, pleural effusions, pulmonary nodules, and infections.12 13 While cases of interstitial lung disease in psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis have been reported, these are uncommon.20 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 Some occurred in patients who were not receiving methotrexate at the onset of their lung disease,27 32 33 whereas others were reported as being due to methotrexate or leflunomide, or both.20 28 29 30 31 The inclusion of only double blind randomised controlled trials reduces the potential ascertainment bias resulting from the existing perception that methotrexate causes interstitial lung disease. A single case of pneumonitis due to methotrexate was reported in one paper without further details as to how this conclusion was reached. Our study has a large number of patients who used methotrexate, and the lack of other cases suggests this could also be a chance occurrence.
Interestingly methotrexate did not seem to increase the risk of infectious respiratory events in this study. Methotrexate suppresses the immune system, increasing the risk of infections, and all three diseases have an increased propensity to develop infections, related to both the underlying disease process and immunosuppressive treatment.34 35 We did not find this to be the case in our current study, in contrast with a study among patients with rheumatoid arthritis.17 Most studies included used placebo comparators, reducing the risk that an increased risk of respiratory adverse events in methotrexate treated patients would be masked by a corresponding increase in the comparator group.
Limitations of this study
Our study has some important limitations. Randomised controlled trials have high internal validity but may lack generalisability and are often of shorter duration than observational studies.36 The generalisation of our results to all patient populations is limited by the inclusion and exclusion criteria of the original randomised controlled trials. Their relevance for other patient populations, especially those with important comorbidities or other diseases, warrants due consideration. Rare events require large patient numbers for conclusive evidence. While we have attempted to tackle this problem with our current study, the number of high quality studies in the final analysis was small, a trade-off between quality and power. Robust analyses of observational patient registries would complement our findings and better deal with some of these issues, although the lack of blinding and perceptions of methotrexate and lung disease would be of some concern.36 37 Under-reporting of unexpected outcomes or adverse events is possible, and there were differences between studies in both the terminology and the frequency of respiratory events reported. Detailed information on all respiratory events was not available from all publications, and we did not have access to the unpublished data. Included studies were of relatively short duration, ranging from 16 to 52 weeks; however, reports suggest methotrexate related interstitial lung disease may develop at any time during treatment and occurs in 48% of affected patients within 32 weeks of starting methotrexate.14 A relatively low number of studies met our inclusion criteria, but these strict criteria enabled us to focus on large scale high quality studies to minimise bias.
Conclusions and policy implications
Our study has important clinical implications. Concern among doctors and patients over the potential side effects of methotrexate has led to an ongoing reluctance to initiate or continue an effective drug in situations where it is clinically indicated.1 2 3 Interstitial lung disease is one of the most feared complications of methotrexate treatment, with a reported mortality of 17%.14 Guidelines for the use of methotrexate recommend treatment cessation when pulmonary symptoms occur, and in some instances not restarting it.1 2 This is problematic because methotrexate is often effective, safe, and much cheaper than many alternative treatments. In the current study we found no increased risk of lung disease in methotrexate treated patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or inflammatory bowel disease. These findings, coupled with those of a previous study in rheumatoid arthritis, suggest that methotrexate related lung disease is rare, if it exists at all.
In conclusion the results of our meta-analysis found no significant increase in respiratory adverse events in patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or inflammatory bowel disease prescribed methotrexate. We cannot exclude a rare but important increase in pulmonary adverse events because of the limitations outlined. Our findings have important implications for methotrexate use in clinical practice.
What is already known on this topic
Numerous case reports and observational studies have suggested a link between methotrexate and pulmonary disease
A recent meta-analysis in rheumatoid arthritis found that methotrexate was associated with an increased risk of infectious but not non-infectious pulmonary disease
What this study adds
Methotrexate did not increase the risk of respiratory adverse events in the diseases studies
These results should give doctors and patients the confidence to consider the use of this effective treatment as part of the shared decision making process
Contributors: CL and RC contributed equally: conceived the study, performed the review, and drafted the manuscript. RC, RJC, and MJO’D contributed to data quality assessment and outcomes classification and reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content. RC performed the data analysis. He is the guarantor.
Funding: This research received no specific funding.
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/coi_disclosure.pdf and declare: no support from any organisation for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work. All authors, external and internal, had full access to all of the data (including statistical reports and tables) in the study and can take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Ethical approval: Not required.
Data sharing: No additional data available.
Transparency: The lead author (RC) affirms that the manuscript is an honest, accurate, and transparent account of the review being reported; that no important aspects of the review have been omitted; and that any discrepancies from the review as planned have been explained.
Cite this as: BMJ 2015;350:h1269
Web Extra. Extra material supplied by the author
Supplementary material
References
- 1.Food and Drug Administration. Methotrexate prescribing information. 2014. www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/011719s117lbl.pdf.
- 2.Saag KG, Teng GG, Patkar NM, Anuntiyo J, Finney C, Curtis JR, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2008 recommendations for the use of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2008;59:762-84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Smolen JS, Landewé R, Breedveld FC, Buch M, Burmester G, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:492-509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gossec L, Smolen JS, Gaujoux-Viala C, Ash Z, Marzo-Ortega H, van der Heijde D, et al. European League Against Rheumatism recommendations for the management of psoriatic arthritis with pharmacological therapies. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:4-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gottlieb A, Korman NJ, Gordon KB, Feldman SR, Lebwohl M, Koo JY, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 2. Psoriatic arthritis: overview and guidelines of care for treatment with an emphasis on the biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol 2008;58:851-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, Feldman SR, Gelfand JM, Gordon KB, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 4. Guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with traditional systemic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol 2009;61:451-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dignass A, Van Assche G, Lindsay JO, Lémann M, Söderholm J, Colombel JF, et al. The second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease: Current management. J Crohns Colitis 2010;4:28-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wasko MC, Dasgupta A, Hubert H, Fries JF, Ward MM. Propensity-adjusted association of methotrexate with overall survival in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2013;65:334-42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Choi HK, Hernan MA, Seeger JD, Robins JM, Wolfe F. Methotrexate and mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study. Lancet 2002;359:1173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Barrera P, Laan RF, van Riel PL, Dekhuijzen PN, Boerbooms AM, van de Putte LB. Methotrexate-related pulmonary complications in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1994;53:434-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sokka T, Abelson B, Pincus T. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: 2008 update. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2008;26(5 Suppl 51):S35-61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bongartz T, Nannini C, Medina-Velasquez YF, Achenbach SJ, Crowson CS, Ryu JH, et al. Incidence and mortality of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum 2010;62:1583-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Doran MF, Crowson CS, Pond GR, O’Fallon WM, Gabriel SE. Frequency of infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with controls: a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46:2287-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kremer JM, Alarcón GS, Weinblatt ME, Kaymakcian MV, Macaluso M, Cannon GW, et al. Clinical, laboratory, radiographic, and histopathologic features of methotrexate-associated lung injury in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a multicenter study with literature review. Arthritis Rheum 1997;40:1829-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gabbay E, Tarala R, Will R, Carroll G, Adler B, Cameron D, et al. Interstitial lung disease in recent onset rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1997;156(2 Pt 1):528-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chikura B, Sathi N, Lane S, Dawson JK. Variation of immunological response in methotrexate-induced pneumonitis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47:1647-50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Conway R, Low C, Coughlan RJ, O’Donnell MJ, Carey JJ. Methotrexate and lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014;66:803-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Nordic Cochrane Centre, Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
- 19.Higgins JPT, Green S, eds. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane-handbook.org.
- 20.Feagan BG, McDonald JW, Panaccione R, Enns RA, Bernstein CN, Ponich TP, et al. Methotrexate in combination with infliximab is no more effective than infliximab alone in patients with Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 2014;146:681-8.e1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gottlieb AB, Langley RG, Strober BE, Papp KA, Klekotka P, Creamer K, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the addition of methotrexate to etanercept in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 2012;167:649-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kingsley GH, Kowalczyk A, Taylor H, Ibrahim F, Packham JC, McHugh NJ, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of methotrexate in psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012;51:1368-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Reich K, Langley RG, Papp KA, Ortonne JP, Unnebrink K, Kaul M, et al. A 52-week trial comparing briakinumab with methotrexate in patients with psoriasis. N Engl J Med 2011;365:1586-96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Saurat JH, Stingl G, Dubertret L, Papp K, Langley RG, Ortonne JP, et al. Efficacy and safety results from the randomized controlled comparative study of adalimumab vs. methotrexate vs. placebo in patients with psoriasis (CHAMPION). Br J Dermatol 2008;158:558-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Feagan BG, Fedorak RN, Irvine EJ, Wild G, Sutherland L, Steinhart AH, et al. A comparison of methotrexate with placebo for the maintenance of remission in Crohn’s disease. North American Crohn’s Study Group Investigators. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1627-32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Feagan BG, Rochon J, Fedorak RN, Irvine EJ, Wild G, Sutherland L, et al. Methotrexate for the treatment of Crohn’s disease. The North American Crohn’s Study Group Investigators. N Engl J Med 1995;332:292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kluger N, Bessis D, Guillot B, Girard C. Acute respiratory distress syndrome complicating generalized pustular psoriasis (psoriasis-associated aseptic pneumonitis). J Am Acad Dermatol 2011;64:1154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Salaffi F, Manganelli P, Carotti M, Subiaco S, Lamanna G, Cervini C. Methotrexate-induced pneumonitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis: report of five cases and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol 1997;16:296-304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ameen M, Taylor DA, Williams IP, Wells AU, Barkert JN. Pneumonitis complicating methotrexate therapy for pustular psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2001;15:247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lee MA, Hutchinson DG. HRCT-proven leflunomide pneumonitis in a patient with psoriatic arthritis and normal lung function tests and chest radiography. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2010;49:1206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Margagnoni G, Papi V, Aratari A, Triolo L, Papi C. Methotrexate-induced pneumonitis in a patient with Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis 2010;4:211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hotermans G, Benard A, Guenanen H, Demarcq-Delerue G, Malart T, Wallaert B. Nongranulomatous interstitial lung disease in Crohn’s disease. Eur Respir J 1996;9:380-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Balestra DJ, Balestra ST, Wasson JH. Ulcerative colitis and steroid-responsive, diffuse interstitial lung disease. JAMA 1988;260:62-4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ananthakrishnan AN, McGinley EL. Infection-related hospitalizations are associated with increased mortality in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. J Crohns Colitis 2013;7:107-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wakkee M, de Vries E, van den Haak P, Nijsten T. Increased risk of infectious disease requiring hospitalization among patients with psoriasis: a population-based cohort. J Am Acad Dermatol 2011;65:1135-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.McKee M, Britton A, Black N, McPherson K, Sanderson C, Bain C. Methods in health services research: interpreting the evidence: choosing between randomised and non-randomised studies. BMJ 1999;319:312-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Concato J, Shah N, Horwitz RI. Randomised, controlled trials, observational studies, and the hierarchy of research designs. New Engl J Med 2000;343:1887-92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material