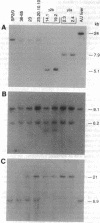
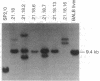
Abstract
As B cells differentiate under the influence of antigen and T cells, they frequently switch from the expression of IgM antibody to the expression of other isotypes. This is accomplished by rearranging the expressed variable region gene to downstream constant region genes and deleting the intervening sequences. Some B-cell lines that represent early stages in development switch constitutively in culture at frequencies that approach those of lipopolysaccharide- or lymphokine-stimulated normal B cells. Hybridoma cells represent a later stage of development and rarely switch in culture. In contrast to early B-cell lines, hybridomas produce large amounts of immunoglobulin, and single cells can be assayed easily for the expression of new isotypes. We have used the ELISA spot assay and fluctuation analysis to determine the rate of switching of two hybridoma cell lines. By identifying subclones that switched more frequently, we have progressively enriched for cells that switch spontaneously at higher rates. These cells, like normal cells, switch by rearrangement and deletion, and the frequency of switched cells in some of the clones is comparable to that which has been observed in less differentiated B-cell lines and in normal B cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., DePinho R. A., Reth M. G., Yancopoulos G. D. Regulation of genome rearrangement events during lymphocyte differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1986 Feb;89:5–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows P. D., Beck G. B., Wabl M. R. Expression of mu and gamma immunoglobulin heavy chains in different cells of a cloned mouse lymphoid line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):564–568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebra J. J., Komisar J. L., Schweitzer P. A. CH isotype 'switching' during normal B-lymphocyte development. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:493–548. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dangl J. L., Parks D. R., Oi V. T., Herzenberg L. A. Rapid isolation of cloned isotype switch variants using fluorescence activated cell sorting. Cytometry. 1982 May;2(6):395–401. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990020607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desaymard C., Giusti A. M., Scharff M. D. Rat anti-T15 monoclonal antibodies with specificity for VH- and VH-VL epitopes. Mol Immunol. 1984 Oct;21(10):961–967. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnick W., Hertz G. Z., Scappino L., Gritzmacher C. DNA sequences at immunoglobulin switch region recombination sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):365–372. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt L. A., Birshtein B. K. Independent immunoglobulin class-switch events occurring in a single myeloma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):856–868. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser C., Radbruch A. Immunoglobulin class switching: molecular and cellular analysis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:717–735. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French D., Kelly T., Buhl S., Scharff M. D. Somatic cell genetic analysis of myelomas and hybridomas. Methods Enzymol. 1987;151:50–66. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)51008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G., Hodous J., Dintzis R. Z., Dintzis H. M. Modification, optimization and simplification of the spot ELISA technique for the enumeration of cells secreting anti-hapten antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1990 May 25;129(2):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90438-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illges H., Radbruch A. DNA binding sites 5' of the IgG1 switch region comprising IL4 inducibility and B cell specificity. Mol Immunol. 1992 Oct;29(10):1265–1272. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(92)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung S., Rajewsky K., Radbruch A. Shutdown of class switch recombination by deletion of a switch region control element. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):984–987. doi: 10.1126/science.8438159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao F., Giannini S. L., Birshtein B. K. A nuclear DNA-binding protein expressed during early stages of B cell differentiation interacts with diverse segments within and 3' of the Ig H chain gene cluster. J Immunol. 1992 May 1;148(9):2909–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. C., Stavnezer J. Regulation of transcription of the germ-line Ig alpha constant region gene by an ATF element and by novel transforming growth factor-beta 1-responsive elements. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):2914–2925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutzker S., Alt F. W. Structure and expression of germ line immunoglobulin gamma 2b transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1849–1852. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Lang R. B., Stanton L. W., Harris L. J. A model for the molecular requirements of immunoglobulin heavy chain class switching. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):87–89. doi: 10.1038/298087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuta T. R., Fukita Y., Miyoshi T., Shimizu A., Honjo T. Isolation of cDNA encoding a binding protein specific to 5'-phosphorylated single-stranded DNA with G-rich sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1761–1766. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowatt M., Dery C., Dunnick W. Unique sequences are interspersed among tandemly repeated elements in the murine gamma 1 switch segment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 11;13(1):225–237. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee J., Casadevall A., Scharff M. D. Mu switch region deletion is associated with both T cell independent and T cell dependent responses. Mol Immunol. 1993 Aug;30(11):1049–1055. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott D. E., Alt F. W., Marcu K. B. Immunoglobulin heavy chain switch region recombination within a retroviral vector in murine pre-B cells. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):577–584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04793.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'Homme J. L., Birshtein B. K., Scharff M. D. Variants of a mouse myeloma cell line that synthesize immunoglobulin heavy chains having an altered serotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1427–1430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radbruch A., Burger C., Klein S., Müller W. Control of immunoglobulin class switch recombination. Immunol Rev. 1986 Feb;89:69–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman P., Li S. C., Gorham B., Glimcher L., Alt F., Boothby M. Identification of a conserved lipopolysaccharide-plus-interleukin-4-responsive element located at the promoter of germ line epsilon transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5551–5561. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein T. L., Gefter M. L. Affinity analysis of idiotype-positive and idiotype-negative Ars-binding hybridoma proteins and Ars-immune sera. Mol Immunol. 1983 Feb;20(2):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz C. L., Elenich L. A., Dunnick W. A. Nuclear protein binding to octamer motifs in the immunoglobulin gamma 1 switch region. Int Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(2):109–116. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.2.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockett P., Stavnezer J. Effect of cytokines on switching to IgA and alpha germline transcripts in the B lymphoma I.29 mu. Transforming growth factor-beta activates transcription of the unrearranged C alpha gene. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4374–4383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Mond J. J. Towards a comprehensive view of immunoglobulin class switching. Immunol Today. 1993 Jan;14(1):15–17. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90318-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira G., Bargellesi A., Teillaud J. L., Scharff M. D. The identification of monoclonal class switch variants by sib selection and an ELISA assay. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Nov 30;74(2):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira G., Scharff M. D. Identification of rare immunoglobulin switch variants using the ELISA spot assay. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Apr 8;148(1-2):121–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90165-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavnezer J., Radcliffe G., Lin Y. C., Nietupski J., Berggren L., Sitia R., Severinson E. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain switching may be directed by prior induction of transcripts from constant-region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7704–7708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavnezer J., Sirlin S., Abbott J. Induction of immunoglobulin isotype switching in cultured I.29 B lymphoma cells. Characterization of the accompanying rearrangements of heavy chain genes. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):577–601. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters S. H., Saikh K. U., Stavnezer J. A B-cell-specific nuclear protein that binds to DNA sites 5' to immunoglobulin S alpha tandem repeats is regulated during differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5594–5601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmore A. C., Prowse D. M., Arnold L. W., Haughton G. Ig isotype switching in B lymphocytes. A method for estimating isotype switch frequency in cloned B cell lymphomas. Int Immunol. 1989;1(5):532–539. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.5.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M., Maizels N. LR1, a lipopolysaccharide-responsive factor with binding sites in the immunoglobulin switch regions and heavy-chain enhancer. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2353–2361. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuerffel R. A., Nathan A. T., Kenter A. L. Detection of an immunoglobulin switch region-specific DNA-binding protein in mitogen-stimulated mouse splenic B cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1714–1718. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu L., Kim M. G., Marcu K. B. Properties of B cell stage specific and ubiquitous nuclear factors binding to immunoglobulin heavy chain gene switch regions. Int Immunol. 1992 Aug;4(8):875–887. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.8.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Bottaro A., Li S., Stewart V., Alt F. W. A selective defect in IgG2b switching as a result of targeted mutation of the I gamma 2b promoter and exon. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3529–3537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]