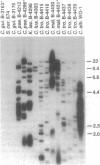
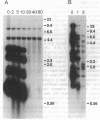
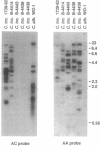
Abstract
Telomeric DNA sequences have generally been found to be remarkably conserved in evolution, typically consisting of repeated, very short sequence units containing clusters of G residues. Recently however the telomeric DNA of the asexual yeast Candida albicans was shown to consist of much longer repeat units. Here we report the identification of seven additional telomeric sequences from sexual and asexual budding yeast species. The telomeric repeat units from this group of relatively closely related species show more phylogenetic diversity in length (8-25 bp), sequence, and composition than has been seen previously throughout a wide phylogenetic range of other eukaryotes. We also show that certain strains of the asexual diploid species Candida tropicalis have two forms of telomeric repeats, which appear to differ by a single base pair. Despite their great diversity, the telomeric repeat units of C. albicans, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and all of the species we have examined in this report share a conserved approximately 6-bp motif of T and G residues resembling more typical telomeric sequences.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barns S. M., Lane D. J., Sogin M. L., Bibeau C., Weisburg W. G. Evolutionary relationships among pathogenic Candida species and relatives. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2250–2255. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2250-2255.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. B., Lewis A. L., Baldwin K. K., Resnick M. A. Lethality induced by a single site-specific double-strand break in a dispensable yeast plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5613–5617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Mason J. M. Genetics and molecular biology of telomeres. Adv Genet. 1992;30:185–249. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Valgeirsdottir K., Lofsky A., Chin C., Ginther B., Levis R. W., Pardue M. L. HeT-A, a transposable element specifically involved in "healing" broken chromosome ends in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3910–3918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Gall J. G. A tandemly repeated sequence at the termini of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):33–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):569–573. doi: 10.1038/350569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:113–129. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. G-strings at chromosome ends. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):777–778. doi: 10.1038/332777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang G., Cech T. R. The beta subunit of Oxytricha telomere-binding protein promotes G-quartet formation by telomeric DNA. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschling D. E., Zakian V. A. Telomere proteins: specific recognition and protection of the natural termini of Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):331–337. doi: 10.1038/337331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E. R., Blackburn E. H. An overhanging 3' terminus is a conserved feature of telomeres. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):345–348. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Hardin C. C., Walk S. K., Tinoco I., Jr, Blackburn E. H. Telomeric DNA oligonucleotides form novel intramolecular structures containing guanine-guanine base pairs. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):899–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Swanton M. T., Donini P., Prescott D. M. All gene-sized DNA molecules in four species of hypotrichs have the same terminal sequence and an unusual 3' terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. D., Spangler E. A., Blackburn E. H. Dynamics of telomere length variation in Tetrahymena thermophila. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90501-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R. W., Ganesan R., Houtchens K., Tolar L. A., Sheen F. M. Transposons in place of telomeric repeats at a Drosophila telomere. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90318-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longtine M. S., Wilson N. M., Petracek M. E., Berman J. A yeast telomere binding activity binds to two related telomere sequence motifs and is indistinguishable from RAP1. Curr Genet. 1989 Oct;16(4):225–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00422108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEachern M. J., Hicks J. B. Unusually large telomeric repeats in the yeast Candida albicans. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):551–560. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B., Cech T. R. Mitochondrial telomeres: surprising diversity of repeated telomeric DNA sequences among six species of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):367–374. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B., Cech T. R. Telomeric repeats of Tetrahymena malaccensis mitochondrial DNA: a multimodal distribution that fluctuates erratically during growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4450–4458. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B. The human telomere terminal transferase enzyme is a ribonucleoprotein that synthesizes TTAGGG repeats. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta A. F., Kaine B. P., Spear B. B. The terminal organization of macronuclear DNA in Oxytricha fallax. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8145–8154. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M., Cech T. R. Telomeric DNA-protein interactions of Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):783–793. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prowse K. R., Avilion A. A., Greider C. W. Identification of a nonprocessive telomerase activity from mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1493–1497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandell L. L., Zakian V. A. Loss of a yeast telomere: arrest, recovery, and chromosome loss. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90493-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shampay J., Szostak J. W., Blackburn E. H. DNA sequences of telomeres maintained in yeast. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):154–157. doi: 10.1038/310154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. S., Zakian V. A. Sequencing of Saccharomyces telomeres cloned using T4 DNA polymerase reveals two domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4415–4419. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellinger R. J., Wolf A. J., Zakian V. A. Saccharomyces telomeres acquire single-strand TG1-3 tails late in S phase. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90049-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R. G-quartets in biology: reprise. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3124–3124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. L., Blackburn E. H. Developmentally programmed healing of chromosomes by telomerase in Tetrahymena. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):823–832. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90077-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. L., Bradley J. D., Attardi L. D., Blackburn E. H. In vivo alteration of telomere sequences and senescence caused by mutated Tetrahymena telomerase RNAs. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):126–132. doi: 10.1038/344126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Prescott D. M. Telomere terminal transferase activity in the hypotrichous ciliate Oxytricha nova and a model for replication of the ends of linear DNA molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6953–6972. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]