Abstract
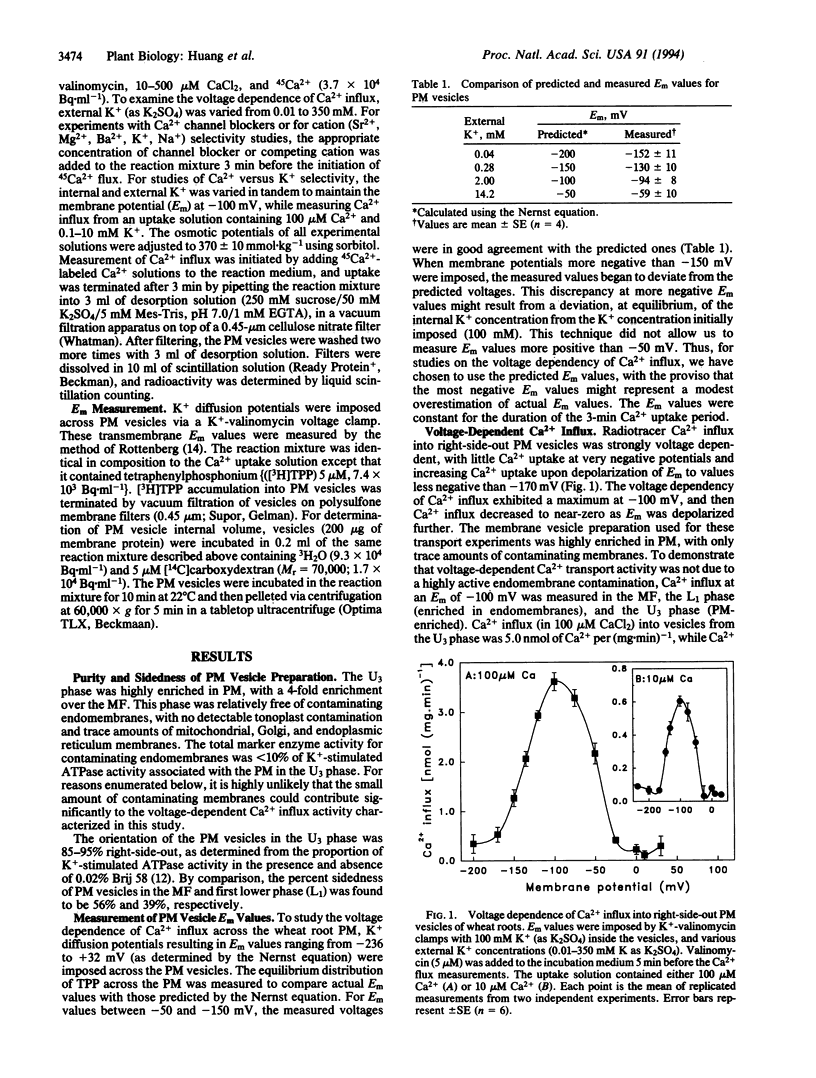
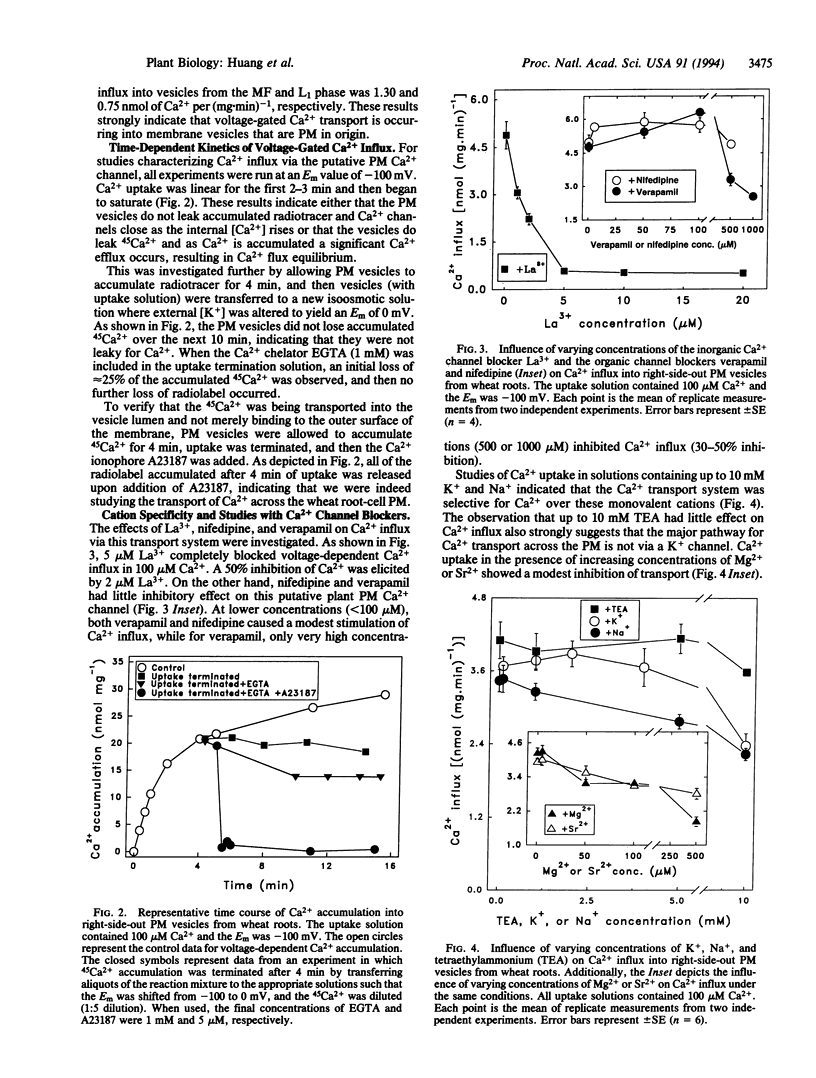
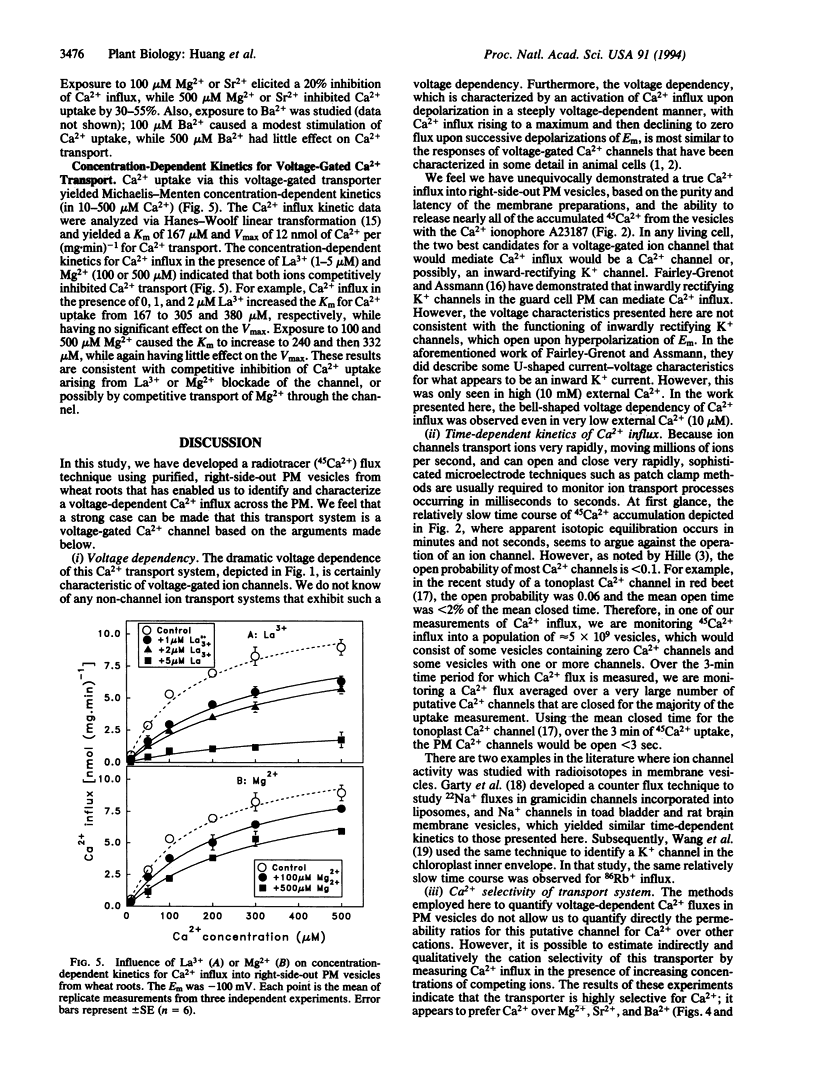
We report on the identification of a voltage-dependent Ca2+ transport system that mediates Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane (PM) of wheat (Triticum aestivum) root cells. The experimental approach involved the imposition of transmembrane electrical potentials (via K+ diffusion potentials) in populations of purified, right-side-out PM vesicles isolated from wheat roots. Using 45Ca2+ to quantify Ca2+ influx into the PM vesicles, the voltage-dependent characteristics of Ca2+ transport were found to be similar to those exhibited by L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in animal cells. The putative PM Ca2+ channel opened upon depolarization of the membrane potential, and Ca2+ flux increased to a maximum upon further depolarization and then decreased back to zero upon further successive depolarizations. This channel was found to be selective for Ca2+ over Mg2+, Sr2+, K+, and Na+; was blocked by very low concentrations of La3+; was unaffected by high concentrations of the K+ channel blocker tetraethylammonium; and exhibited Michaelis-Menten-type transport kinetics. Based on these transport properties, we argue that this transport system is a PM Ca2+ channel. We suggest that the use of radiotracer flux analysis of voltage-clamped PM vesicles derived from plant roots is a straightforward approach for the characterization of certain voltage-gated ion channels functioning in cellular membranes of higher plant cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove D. J., Hedrich R. Stretch-activated chloride, potassium, and calcium channels coexisting in plasma membranes of guard cells of Vicia faba L. Planta. 1991 Dec;186(1):143–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00201510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding J. P., Pickard B. G. Mechanosensory calcium-selective cation channels in epidermal cells. Plant J. 1993 Jan;3(1):83–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairley-Grenot K. A., Assmann S. M. Permeation of Ca2+ through K+ channels in the plasma membrane of Vicia faba guard cells. J Membr Biol. 1992 Jun;128(2):103–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00231883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H., Rudy B., Karlish S. J. A simple and sensitive procedure for measuring isotope fluxes through ion-specific channels in heterogenous populations of membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13094–13099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelli A., Blumwald E. Calcium Retrieval from Vacuolar Pools (Characterization of a Vacuolar Calcium Channel). Plant Physiol. 1993 Aug;102(4):1139–1146. doi: 10.1104/pp.102.4.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmgren M. G., Sommarin M., Ulvskov P., Larsson C. Effect of detergents on the H(+)-ATPase activity of inside-out and right-side-out plant plasma membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jan 29;1021(2):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90025-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelzer D., Pelzer S., McDonald T. F. Properties and regulation of calcium channels in muscle cells. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1990;114:107–207. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid R. J., Smith F. A. Regulation of Calcium Influx in Chara: Effects of K, pH, Metabolic Inhibition, and Calcium Channel Blockers. Plant Physiol. 1992 Oct;100(2):637–643. doi: 10.1104/pp.100.2.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of membrane potential and deltapH in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:547–569. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuleau P., Graziana A., Canut H., Ranjeva R. A 75-kDa polypeptide, located primarily at the plasma membrane of carrot cell-suspension cultures, is photoaffinity labeled by the calcium channel blocker LU 49888. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec 15;87(24):10000–10004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuleau P., Graziana A., Ranjeva R., Schroeder J. I. Solubilized proteins from carrot (Daucus carota L.) membranes bind calcium channel blockers and form calcium-permeable ion channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):765–769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Calcium channels, stores, and oscillations. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:715–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Berkowitz G. A., Peters J. S. K+-conducting ion channel of the chloroplast inner envelope: functional reconstitution into liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):4981–4985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.4981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zernig G. Widening potential for Ca2+ antagonists: non-L-type Ca2+ channel interaction. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jan;11(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90040-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



