Abstract
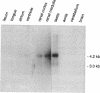
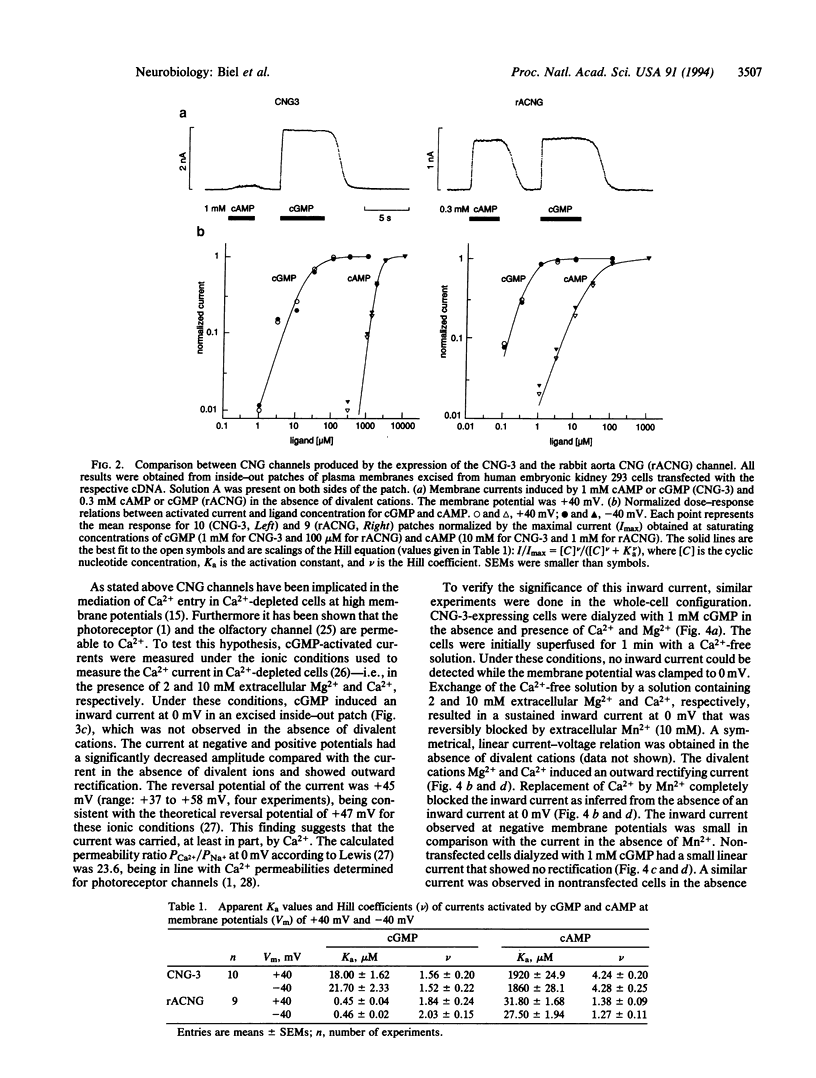
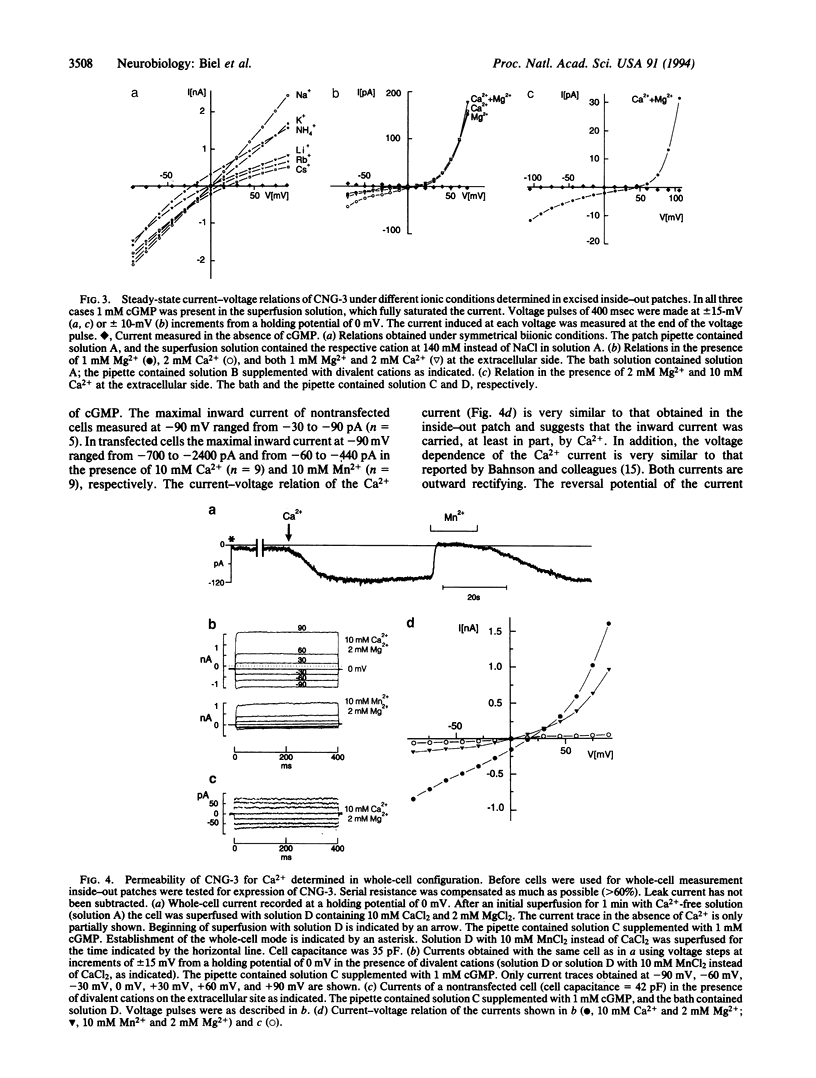
Cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels are essential in visual and olfactory signal transduction. An additional member of the cGMP-gated channel family, termed CNG-3, has been cloned from bovine kidney. Its deduced amino acid sequence is 60% and 62% identical with the CNG-channel proteins from bovine rod outer segment and bovine olfactory epithelium, respectively. Northern analysis and sequences amplified by the PCR showed that the CNG-3 mRNA is present in testis, kidney, and heart. Calcium permeated the expressed channel in the presence of extracellular Mg2+ and Na+ at membrane potentials from -100 to +45 mV. It is likely that CNG-3 protein is responsible for cGMP-induced Ca2+ entry in cells other than sensory cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlner J., Andersson R. G., Torfgård K., Axelsson K. L. Organic nitrate esters: clinical use and mechanisms of actions. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Sep;43(3):351–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad I., Korbmacher C., Segal A. S., Cheung P., Boulpaep E. L., Barnstable C. J. Mouse cortical collecting duct cells show nonselective cation channel activity and express a gene related to the cGMP-gated rod photoreceptor channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10262–10266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenhofen W., Ludwig J., Eismann E., Kraus W., Bönigk W., Kaupp U. B. Control of ligand specificity in cyclic nucleotide-gated channels from rod photoreceptors and olfactory epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9868–9872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahnson T. D., Pandol S. J., Dionne V. E. Cyclic GMP modulates depletion-activated Ca2+ entry in pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10808–10812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballermann B. J., Brenner B. M. George E. Brown memorial lecture. Role of atrial peptides in body fluid homeostasis. Circ Res. 1986 May;58(5):619–630. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.5.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Reifsnyder D. H. Primary sequence of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes and the design of selective inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Apr;11(4):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90066-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biel M., Altenhofen W., Hullin R., Ludwig J., Freichel M., Flockerzi V., Dascal N., Kaupp U. B., Hofmann F. Primary structure and functional expression of a cyclic nucleotide-gated channel from rabbit aorta. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 23;329(1-2):134–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80209-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. Y., Peng Y. W., Dhallan R. S., Ahamed B., Reed R. R., Yau K. W. A new subunit of the cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel in retinal rods. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):764–767. doi: 10.1038/362764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhallan R. S., Yau K. W., Schrader K. A., Reed R. R. Primary structure and functional expression of a cyclic nucleotide-activated channel from olfactory neurons. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):184–187. doi: 10.1038/347184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein S. Electrical signals in olfactory transduction. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Aug;2(4):444–448. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90178-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frings S., Lynch J. W., Lindemann B. Properties of cyclic nucleotide-gated channels mediating olfactory transduction. Activation, selectivity, and blockage. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Jul;100(1):45–67. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbers D. L. Molecular basis of fertilization. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:719–742. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Durell S. R., Warmke J., Drysdale R., Ganetzky B. Similarities in amino acid sequences of Drosophila eag and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):730–730. doi: 10.1126/science.1658932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Dostmann W., Keilbach A., Landgraf W., Ruth P. Structure and physiological role of cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 30;1135(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoth M., Penner R. Depletion of intracellular calcium stores activates a calcium current in mast cells. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):353–356. doi: 10.1038/355353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hullin R., Singer-Lahat D., Freichel M., Biel M., Dascal N., Hofmann F., Flockerzi V. Calcium channel beta subunit heterogeneity: functional expression of cloned cDNA from heart, aorta and brain. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):885–890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaupp U. B., Koch K. W. Role of cGMP and Ca2+ in vertebrate photoreceptor excitation and adaptation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:153–175. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaupp U. B., Niidome T., Tanabe T., Terada S., Bönigk W., Stühmer W., Cook N. J., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Hirose T. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of the rod photoreceptor cyclic GMP-gated channel. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):762–766. doi: 10.1038/342762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanese D. M., Yuan B. H., Falk S. A., Conger J. D. Effects of atriopeptin III on isolated rat afferent and efferent arterioles. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 2):F1102–F1109. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.6.F1102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. A. Ion-concentration dependence of the reversal potential and the single channel conductance of ion channels at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:417–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln T. M., Cornwell T. L. Intracellular cyclic GMP receptor proteins. FASEB J. 1993 Feb 1;7(2):328–338. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.2.7680013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig J., Margalit T., Eismann E., Lancet D., Kaupp U. B. Primary structure of cAMP-gated channel from bovine olfactory epithelium. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):24–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81226-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin-Grez M., Fleming J. T., Steinhausen M. Atrial natriuretic peptide causes pre-glomerular vasodilatation and post-glomerular vasoconstriction in rat kidney. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):473–476. doi: 10.1038/324473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marunaka Y., Ohara A., Matsumoto P., Eaton D. C. Cyclic GMP-activated channel activity in renal epithelial cells (A6). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 18;1070(1):152–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menini A., Rispoli G., Torre V. The ionic selectivity of the light-sensitive current in isolated rods of the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:279–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh A. B., Terlau H., Stühmer W. Depletion of InsP3 stores activates a Ca2+ and K+ current by means of a phosphatase and a diffusible messenger. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):814–818. doi: 10.1038/364814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmentier M., Libert F., Schurmans S., Schiffmann S., Lefort A., Eggerickx D., Ledent C., Mollereau C., Gérard C., Perret J. Expression of members of the putative olfactory receptor gene family in mammalian germ cells. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):453–455. doi: 10.1038/355453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Fasolato C., Hoth M. Calcium influx and its control by calcium release. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993 Jun;3(3):368–374. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(93)90130-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randriamampita C., Tsien R. Y. Emptying of intracellular Ca2+ stores releases a novel small messenger that stimulates Ca2+ influx. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):809–814. doi: 10.1038/364809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. C., Field M. Enterotoxins and ion transport. Biochem Soc Trans. 1984 Apr;12(2):177–180. doi: 10.1042/bst0120177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U. Physiological role of cGMP and cGMP-dependent protein kinase in the cardiovascular system. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1989;113:41–88. doi: 10.1007/BFb0032675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Baylor D. A. Cyclic GMP-activated conductance of retinal photoreceptor cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:289–327. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zufall F., Firestein S. Divalent cations block the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel of olfactory receptor neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1993 May;69(5):1758–1768. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.69.5.1758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]