Abstract
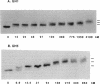
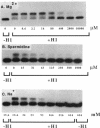
We have compared chicken erythrocyte linker histones H1 and H5 binding to a synthetic four-way DNA junction. Each histone binds to form a single complex, with an affinity which permits competition against a large excess of linear duplex DNA. The affinity of H5 is higher than that of H1. The globular domain from either protein will also bind strongly, but in this case multiple binding occurs. Binding of intact H1 is inhibited by cations: Mg2+ and spermidine are very effective, Na+ much less so. This inhibition is not likely to be a general ion-competition effect, for Mg2+ is much less effective in inhibiting the binding of H1 to linear DNA. Instead, the inhibition of binding may be due to ion-dependent changes in the conformation of the four-way junction, which are known to occur under similar conditions. These results strongly suggest that the angle formed between the arms of the DNA junction could be a major determinant in the interaction of H1 with DNA crossovers.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bianchi M. E., Beltrame M., Paonessa G. Specific recognition of cruciform DNA by nuclear protein HMG1. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2922595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E. Interaction of a protein from rat liver nuclei with cruciform DNA. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):843–849. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02883.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. The organization of histones and DNA in chromatin: evidence for an arginine-rich histone kernel. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):333–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary P. D., Hines M. L., Bradbury E. M., Smith B. J., Johns E. W. Conformation studies of histone H1(0) in comparison with histones H1 and H5. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):371–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg R. M., Murchie A. I., Zechel A., Carlberg C., Diekmann S., Lilley D. M. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer analysis of the structure of the four-way DNA junction. Biochemistry. 1992 May 26;31(20):4846–4856. doi: 10.1021/bi00135a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckett D. R., Murchie A. I., Diekmann S., von Kitzing E., Kemper B., Lilley D. M. The structure of the Holliday junction, and its resolution. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckett D. R., Murchie A. I., Lilley D. M. The role of metal ions in the conformation of the four-way DNA junction. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):583–590. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Ramirez M., Leuba S. H., Ausio J. One-step fractionation method for isolating H1 histones from chromatin under nondenaturing conditions. Protein Expr Purif. 1990 Sep;1(1):40–44. doi: 10.1016/1046-5928(90)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman P. G., Chapman G. E., Moss T., Bradbury E. M. Studies on the role and mode of operation of the very-lysine-rich histone H1 in eukaryote chromatin. The three structural regions of the histone H1 molecule. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 1;77(1):45–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krylov D., Leuba S., van Holde K., Zlatanova J. Histones H1 and H5 interact preferentially with crossovers of double-helical DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5052–5056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. DNA--protein interactions. HMG has DNA wrapped up. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):282–283. doi: 10.1038/357282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki B. L., Neelin J. M. The histones of rainbow trout erythrocytes include an erythrocyte-specific histone. Can J Biochem. 1975 Nov;53(11):1158–1169. doi: 10.1139/o75-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEELIN J. M., CALLAHAN P. X., LAMB D. C., MURRAY K. THE HISTONES OF CHICKEN ERYTHROCYTE NUCLEI. Can J Biochem. 1964 Dec;42:1743–1752. doi: 10.1139/o64-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan V., Finch J. T., Graziano V., Lee P. L., Sweet R. M. Crystal structure of globular domain of histone H5 and its implications for nucleosome binding. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):219–223. doi: 10.1038/362219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D. S., Singer M. F. Studies on the interaction of H1 histone with superhelical DNA: characterization of the recognition and binding regions of H1 histones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2531–2547. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Rees C., Finch J. T. Cooperative binding of the globular domains of histones H1 and H5 to DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):187–194. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga-Weisz P., van Holde K., Zlatanova J. Preferential binding of histone H1 to four-way helical junction DNA. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20699–20700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel T., Singer M. F. Interaction of f1 histone with superhelical DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2597–2600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel T., Singer M. F. The effect of superhelicity on the interaction of histone f1 with closed circular duplex DNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2334–2338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]