Abstract
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), the primary inhibitor of urokinase-and tissue-type plasminogen activators (uPA and tPA), is an injury-response gene implicated in the development of tissue fibrosis and cardiovascular disease. PAI-1 mRNA and protein levels were elevated in the balloon catheter-injured carotid and in the vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC)-enriched neointima of ligated arteries. PAI-1/uPA complex formation and PAI-1 antiproteolytic activity can be inhibited, via proteolytic cleavage, by the small molecule antagonist tiplaxtinin which effectively increased the VSMC apoptotic index in vitro and attenuated carotid artery neointimal formation in vivo. In contrast to the active full-length serine protease inhibitor (SERPIN), elastase-cleaved PAI-1 (similar to tiplaxtinin) also promoted VSMC apoptosis in vitro and similarly reduced neointimal formation in vivo. The mechanism through which cleaved PAI-1 (CL-PAI-1) stimulates apoptosis appears to involve the TNF-α family member TWEAK (TNF-α weak inducer of apoptosis) and it’s cognate receptor, fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-inducible 14 (FN14). CL-PAI-1 sensitizes cells to TWEAK-stimulated apoptosis while full-length PAI-1 did not, presumably due to its ability to down-regulate FN14 in a low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1)-dependent mechanism. It appears that prolonged exposure of VSMCs to CL-PAI-1 induces apoptosis by augmenting TWEAK/FN14 pro-apoptotic signaling. This work identifies a critical, anti-stenotic, role for a functionally-inactive (at least with regard to its protease inhibitory function) cleaved SERPIN. Therapies that promote the conversion of full-length to cleaved PAI-1 may have translational implications.
Keywords: Apoptosis, carotid stenosis, SERPIN, vascular injury, PAI-1
1. Introduction
Vascular restenosis, or blood vessel re-narrowing after percutaneous coronary intervention, is a combinatorial pathological consequence of increased vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) migration and proliferation combined with decreased apoptosis [1,2]. Few treatment options for vascular restenosis exist aside from additional catheterization. Among several factors implicated in the vascular response to injury, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), a member of the serine protease inhibitor (SERPIN) superfamily and the major physiologic regulator of the plasmin-based pericellular proteolytic cascade, is perhaps the most prominent.
PAI-1 exists in three distinct conformations [3,4]. While initially synthesized as an active SERPIN, PAI-1 spontaneously converts to a latent form (active half-life ~2 h at 37°C, pH 7.4) which is unable to inhibit uPA or tPA catalysis. This rather short half-life can be extended 2-to-10 fold, however, upon binding of PAI-1 to the somatomedin B domain of vitronectin where it also impacts integrin-matrix interactions and downstream signaling pathways [5–8]. During engagement of PAI-1 with its target proteases, the sissile bond in the reactive center loop (RCL) is cleaved to form a covalent ester bond between a serine hydroxyl group of the enzyme and a PAI-1 carboxyl group. Upon cleavage, the RCL N-terminus inserts into β-sheet A, while the C-terminus of the RCL forms strand s1C in β-sheet C producing a 70Å separation of the P1 and P1′ residues, thereby deforming the complexed protease and rendering it inactive. A substrate form of PAI-1 exists as well in which PAI-1 is cleaved by its target proteases without formation of a covalent PAI-1:protease complex [3,9–11].
Due to the complexity of PAI-1 structure/function, several low-molecular weight antagonists of PAI-1 were developed to evaluate specific contributions of this SERPIN to disease pathology (12). Tiplaxtinin (PAI-039), a well-studied PAI-1 small-molecule inhibitor, attenuates asthmatic episodes, reduces hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia and suppresses tumor angiogenesis [12–19]. The mechanism by which tiplaxtinin antagonizes the anti-fibrinolytic activity of PAI-1 appears to involve promotion of a substrate-like conformation resulting in PAI-1 cleavage and impaired uPA and tPA inhibition [20,21].
This paper reports that PAI-1 levels are elevated in injured VSMCs in vivo. Tiplaxtinin, which promotes PAI-1 cleavage, and elastase-cleaved PAI-1 (CL-PAI-1) both attenuate neointima formation in response to carotid artery ligation and stimulate plasmin-dependent, terminal VSMC apoptosis. CL-PAI-1, but not the functionally-stable full-length recombinant PAI-1 mutant 14-1b (FL-PAI-1), sensitizes VSMCs to TWEAK (TNF-α weak inducer of apoptosis)-induced apoptosis, a likely consequence of full-length PAI-1/LRP1-mediated down-regulation of FN14 receptor expression. This work identifies a novel, anti-stenotic, role for cleaved PAI-1 in the tissue response to arterial injury. Therapies that promote the conversion of full-length to cleaved PAI-1 may have translational implications in the therapy of cardiovascular pathologies.
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1 Cell culture
Newborn rat arterial smooth muscle cells (RASMCs; gift from Dr. Peter A. Jones) were cultured in DMEM with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C. Human carotid artery SMCs (HuCASMCs; Cell Applications Inc., San Diego, CA) were grown in Smooth Muscle Cell Growth Medium containing 5% FBS, 1% penicillin/streptomycin and 0.5% each hEGF, insulin and bFGF/heparin, conditions which maintain VSMC in the de-differentiated, synthetic phenotype.
2.2 Recombinant proteins
Endotoxin levels in full-length, stabilized recombinant 14-1b PAI-1 (FL-PAI-1), R76E-PAI-1 (LRP1-binding deficient mutant; Molecular Innovations, Novi, MI), human neutrophil elastase (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) and high-molecular weight two chain uPA (Seiksui Diagnostics, LLC, Lexington, MA) preparations were measured using the Limulus Amebocyte Lysate kit QCL-1000 (Lonza, Basel, Switzerland) and all found to be <0.14 EU/ml, the acceptable threshold [22]. Recombinant Human TWEAK/TNFSF12 was obtained from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN).
2.3 RNA interference
siRNA designed against human PAI-1 mRNA (5′-AAGGATGAGATCAGCACCACA-3′) and a scrambled control (sc) siRNA (5′-AATTCTCCGAACGTGTCACGT-3′) [23] were obtained from QIAGEN Inc. (Valencia, CA). HuCASMCs were transfected with 20 nM of PAI-1 siRNA or sc siRNA using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen).
2.4 Balloon Catheter Denudation and Carotid Artery Ligation
All animal protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Albany Medical College (IACUC approved protocol #13-09001) and conducted in accord with the EU Directive 2010/63/EU for animal experimentation. Rodents were housed in the College Animal Resource Facility, licensed by the USDA and New York State Department of Health, Division of Laboratories and Research. Male Sprague-Dawley rats (400~450 g, Taconic Farms, Germantown, NY) were anesthetized by i.p. injection of ketamine (0.1 mg/gm) and xylazine (0.01 mg/gm), the left common carotid artery exposed by a midline cervical incision and blunt dissection performed alongside the artery with dull forceps to expose the carotid bifurcation into the internal/external branches. After blood flow cessation by arterial clamping, a 2F Fogarty balloon catheter (Edwards) was introduced via a small arteriotomy in the external carotid and advanced to the common carotid artery [24]. The balloon was inflated by 1.6 atm pressure, inserted and withdrawn three times. For carotid ligation, FVB/NJ mice (Jackson Labs) were anesthetized by i.p. injection of ketamine (0.1 mg/gm) and xylazine (0.01 mg/gm). Following site preparation, the left carotid artery was exposed with a small 8–10 mm midline incision in the neck and blunt dissected to free the left common carotid and branches from surrounding tissue. The common carotid artery was ligated just proximal to the internal and external carotid bifurcation with a 6-0 sterile silk suture. Animals were treated with tiplaxtinin (3 mg/kg; oral gavage), full-length (FL-PAI-1; 3 mg/kg; i.p. injection), and cleaved PAI-1 (CL-PAI-1; 3 mg/kg; i.p. injection), or vehicle control once daily for 14 days following ligation.
2.5 Northern Blotting
Total RNA (10 μg) from the left (denuded) and (right) uninjured carotid arteries was separated on 1.2% agarose/formaldehyde gels, transferred to Nytran membranes by capillary action in 10x SSC (3 M NaCl, 0.3 M Na citrate, pH 7.0) and immobilized by UV crosslinking prior to incubation for 2 h at 42°C in prehybridization buffer (50% formamide, 5X Denhardt’s reagent, 1% SDS, 100 μg/ml sheared/heat-denatured salmon sperm DNA [ssDNA], 5X SSC). RNA blots were incubated with random-primed 32P-dCTP-labeled cDNA probes (5 × 106 cpm) to rat PAI-1 or A50 (loading control) for 16 h at 42°C in hybridization buffer (50% formamide, 2.5x Denhardt’s reagent, 1% SDS, 100 μg/ml ssDNA, 5x SSC, and 10% dextran sulfate). Membranes were washed in 0.1X SSC/0.1% SDS at 42°C, followed by three 15 min washes in 0.1 x SSC/0.1% SDS at 55°C and exposed to X-OMAT AR-5 film using intensifying screens. Probe was removed from blots by washing in 55% formamide, 2X SSC, 1% SDS for 1 h at 65°C and rinsed in 0.1 x SSC/0.1% SDS prior to rehybridization with A50.
2.6 Immunohistochemistry
Paraffin-embedded tissue sections (5 μm) were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). For immunohistochemistry, sections were incubated with primary antibodies to smooth muscle α-actin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO; 1:6,400 dilution) and PAI-1 (Affinity Bioreagents, Waltham, MA; 1:1,000 dilution), washed, incubated with biotinylated anti-rabbit IgG and avidin D horseradish peroxidase (1:1,000 dilution) and color reactions developed using an ABC kit prior to mounting coverslips in Vectashield medium (Vector Labs, Burlingame, CA). Isotype IgG controls were included. Sections were analyzed using Nanozoomer 2.0RS digital microscope equipped with NDP 2.2.1 software (Hamamatsu Photonics, Hamamatsu, Japan).
2.7 Flow Cytometry
Fluorescence intensity was measured using a FACS LSRII (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). Ten thousand events were counted for each sample and experiments analyzed using FlowJo software (Tree Star Inc., Ashland, OR).
Cell Cycle Analysis
After treatment, RASMCs and HuCASMCs were harvested by trypsinization, centrifugation, washed twice with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and fixed in 70% ethanol for 1 h. Fixed cells were washed twice with ice-cold PBS and incubated for 2 h in the dark in PBS containing 0.1% Triton-X100, 20 μg/ml Propidium Iodide (PI; Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) and 10 μg/ml RNase A.
Annexin-V
RASMCs, treated as indicated in the text, were trypsinized, collected and stained with FITC-conjugated Annexin-V (Calbiochem, Darmstadt, Germany).
Cleaved Caspase-3
Treated RASMCs were harvested by trypsinization, collected by centrifugation, washed with 0.2% BSA in PBS and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min. Cells were permeabilized in 90% cold methanol for 30 min, followed by two washes and incubated with antibodies to cleaved caspase-3 (1:200 dilution, Asp175; Cell Signaling, a, MA) followed by Alexa-Fluor 488-tagged IgG (1:1000 dilution) for 60 min each. Cells were washed prior to fluorescence measurements as described above.
FN14 surface expression
After treatment, RASMCs and HuCASMCs were harvested by trypsinization, collected and incubated 10% FBS/phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 15 min. Cells were pelleted and washed in 0.1% BSA/PBS, followed by incubation with FN14 antibody or mouse IgG (5 μg/ml in 0.1% BSA/PBS; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, Texas) followed by Alexa-Fluor 488-tagged IgG (1:1000 dilution for 1 h each). Cells were washed, resuspended in 2% paraformaldehyde/PBS and fluorescence measurements assessed as described above.
2.8 PAI-1-GFP chimera expression construct
Human PAI-1 promoter sequences (−800 to +71) were PCR-amplified for 30 cycles using the p800-Luc reporter plasmid as a template and Platinum Taq polymerase. This fragment was gel-purified for subsequent cloning into the SacI/KpnI sites of the promoter-less GFP expression vector pEGFP-1 (Clontech, Palo Alto, CA). For preparation of a PAI-1-GFP chimeric expression construct, the full-length human PAI-1 coding sequence (approximately 1.3 kb) was derived by RT-PCR from total RNA isolated from human foreskin fibroblasts, amplified by PCR, gel-purified and expressed as a GFP fusion protein by T4 ligase insertion into the BamHI/AgeI site of the PAI-1 promoter-derived pEGFP-1 vector. All constructs were sequence verified. RASMCs were seeded into 35 mm dishes and allowed to reach a density of 1×105 cells/cm2 prior to transfection with 1–2 μg DNA using Lipofectamine-Plus.
2.9 Apoptosis Assay
Annexin-V
RASMCs cultured in 96-well plates were treated with the indicated concentrations of tiplaxtinin in complete media for 24 h. Cells were stained with FITC-conjugated Annexin-V and apoptosis measured using a Biotek Synergy 2 fluorescent microplate reader and Biotek Gen5 software. The vehicle control (DMSO) did not induce apoptosis.
Caspase-3 activity assay
Asynchronously growing HuCASMCs were treated as indicated in complete media for 6 h. Cells were harvested, lysed, and centrifuged to remove cellular debris. Aminomethylcoumarin (AMC)-derived substrate Z-DEVD-AMC was added to cell lysates and incubated for 30 minutes according to manufacturer’s instructions (EnzChek® Caspase-3 Assay Kit #1, Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA). Fluorescent emission (excitation/emission maxima ~342/441 nm) was read every hour using a Biotek Synergy 2 fluorescent microplate reader and Biotek Gen5 software.
Live/Dead assay
Asynchronously growing HuCASMCs were treated as indicated in complete media for 24 hrs. Cell-permeant calcein AM which produces green fluorescence (ex/em ~495/~515 nm) in live cells and ethidium homodimer which only enters damaged membranes and produces a red fluorescence (ex/em ~495 nm/~635 nm; Live/Dead Viability/Cytotoxicity assay for mammalian cells, Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) were added directly in complete media at final concentrations of 2 μM and 4 μM, respectively. Cells were incubated with the Live/Dead reagents for 30 minutes, then counted. Cells positive for ethidium homodimer were scored as apoptotic and normalized against calcein AM (total cells).
2.10 Generation of Elastase-Cleaved PAI-1
Full-length (FL-PAI-1,14-1b stable PAI-1 mutant; Molecular Innovations, Novi, MI) was incubated with a 0.1 molar equivalent of human neutrophil elastase (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) in 100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, buffer containing 500 mM NaCl as described previously [3] to generate cleaved PAI-1 (CL-PAI-1). For each reaction time point, an aliquot was withdrawn and treated with 10 mM PMSF prior to SDS-PAGE and silver staining to confirm cleavage. Reaction products, without added PMSF, were stored at -80°C. CL-PAI-1 was also generated by incubation with Sepharose bead-immobilized porcine pancreatic elastase (Molecular Innovations, Novi, MI).
2.11 Tiplaxtinin:PAI-1:uPA Interactions
FL-PAI-1 (500 nmol/L) was incubated with tiplaxtinin or vehicle alone in 10 mM HEPES, pH=7.4, 150 mM NaCl and 0.5% Tween-20 buffer for 15 min before addition of 500 nM high-molecular weight uPA for a 5 min incubation at 37°C [20]. Enzymatic activity was stopped using 10 mM (final concentration) PMSF and reaction products separated by SDS-PAGE.
2.12 Western Analysis
Cells were washed with PBS and lysates prepared in 60 mM Tris HCl, pH=6.8, and 2% SDS. Protein concentration was determined using BCA Assay (Pierce Scientific, Rockford, IL) and 40 μg protein loaded for each sample. Western blotting was as described [4]. Blot analysis used the ChemiDoc MP System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA). Antibodies were: caspase-8 (1C12), caspase-3, pAkt S473 (D9E), pan Akt (11E7), PARP (from Cell Signaling, Beverly, MA), plasminogen (#364R, Seiksui Diagnostics, LLC, Lexington, MA) and FN14 (ITEM-4), TWEAK (S-20), GAPDH, ERK2 (C-14), actin (I-19) (Santa Cruz, Dallas, TX).
2.13 Statistics
Values are represented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Student’s T-tests were used to determine significance for experiments containing two experimental conditions. One-way ANOVAs with a Tukey’s post-hoc analysis were used for analysis of experiments containing three or more conditions. Experiments that monitored dependent variables over time were analyzed using repeated-measures ANOVA. P-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1 PAI-1 expression is induced in vessel injury in vivo
To examine the relationship between PAI-1 expression and the pathogenesis of neointimal hyperplasia, PAI-1 mRNA levels were assessed in rats in which stenosis was induced in response to balloon catheterization. PAI-1 transcripts were markedly elevated in the catheter-denuded carotid artery as compared to the contralateral control vessel (Fig. 1A). The well-accepted carotid ligation model of arterial injury was used to establish the specific topographic localization of PAI-1 in stenotic lesions. The PAI-1-positive neointima region co-localized with smooth muscle cell α-actin-expressing cells (Fig. 1B) suggesting that the pathological response to vascular injury in vivo is associated with increased PAI-1 in the expanded VSMC cohort.
Figure 1. PAI-1 expression is elevated in smooth muscle cells of the neointimal compartment of injured vessels.
(A) RNA was extracted from balloon catheter-denuded and contralateral control carotid arteries one week following injury. Northern blots were hybridized using 32P-labeled cDNA probes to PAI-1 and A50 (loading control). (B) Paraffin sections (5 μm) of ligated (i–iii) and contralateral control (iv–vi) carotids were stained with H&E (i, iv) or processed for immunohistochemical detection of smooth muscle cell α-actin (ii, v) or PAI-1 (iii, vi) 14 days after common carotid artery ligation. Scale bar=100 μm.
3.2 Tiplaxtinin initiates a two-step inhibition of PAI-1 antiproteolysis and stimulation of VSMC apoptosis
Tipaxtinin, a small molecule inhibitor of PAI-1 function, blocks PAI-1 anti-proteolytic activity in a two-step process. In an in vitro cell-free analysis, tiplaxtinin interferes with uPA::PAI-1 complex formation (Fig. 2A, upper bands) while stimulating (presumably a substrate-like) PAI-1 cleavage (Fig. 2A, middle bands). Compared to control untreated cells in which only one PAI-1 band was detected at 47 kDa, a low molecular weight (43 kDa) PAI-1 species was also evident indicating that tiplaxtinin stimulated PAI-1 cleavage by cultured cells as well (Fig. 2B).
Figure 2. Tiplaxtinin inhibits PAI-1/uPA complex formation and promotes PAI-1 cleavage.

(A) Human uPA was incubated with FL-PAI-1 and the indicated concentration of tiplaxtinin. Solid arrow indicates full-length PAI-1; dashed arrow denotes cleaved PAI-1. (B) RASMCs were treated with tiplaxtinin or vehicle control in complete media for 24 h. PAI-1 and GAPDH (loading control) in cell lysates were identified by western blotting. Full-length and cleaved PAI-1 are highlighted by solid and dashed arrows, respectively. TPX=tiplaxtinin.
Tiplaxtinin-induced cleavage, which generates a non-functional SERPIN (at least with regard to its anti-proteolytic activity), may have significant physiologic consequences. Indeed, PAI-1 is a pro-survival factor in several cell types and both engineered over-expression of wild-type full-length PAI-1 (Fig. 3A,B) and exogenous addition of a stable recombinant PAI-1 mutant (14-1b; FL-PAI-1) (Fig. 3C,D) increased pAKT levels in VSMCs. Since tiplaxtinin significantly blocked the pAKT response to FL-PAI-1 (Fig. 4A), and whereas CL-PAI-1 was markedly deficient (by 50% relative to FL-PAI-1) in pAKT inducibility, these data suggested that a catalytically intact SERPIN was required for Akt activation. It was important, therefore, to evaluate the effect of this small molecule inhibitor of PAI-1 function on VSMC survival. Annexin-V measurements indicated that tiplaxtinin dose-dependently induced RASMC apoptosis (Fig. 4B). Previous reports indicated, moreover, that the tiplaxtinin-binding site on PAI-1 approximates the vitronectin recognition site [20]. Despite the fact that the majority of circulating PAI-1 is bound to vitronectin, which prolongs the active half-life and stabilizes the bioavailability of this SERPIN, RASMCs plated on vitronectin-coated plates remained susceptible to tiplaxtinin-stimulated apoptosis (Fig. 4C).
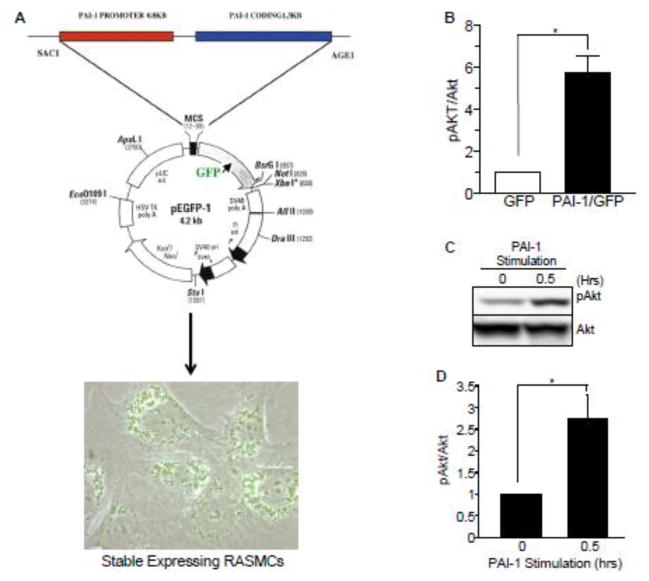
Figure 3. Vector-driven expression and exogenous addition of full-length PAI-1 stimulates Akt phosphorylation.
(A) Schematic of a pEGFP-1-based vector in which a chimeric transcript consisting of 1.3 kb of PAI-1 coding sequences and GFP is expressed under the control of a 0.8 kb PAI-1 promoter. RASMCs were transfected with this PAI-1 coding sequence-GFP fusion construct under control of the PAI-1 promoter and stable expressing clones selected. (B) PAI-1 overexpression by 6- to 8-fold relative to GFP in RASMCs results in elevated pAkt levels. (C) PAI-1 addition induces a rapid and transient Akt activation in RASMCs. At confluence, RASMCs were serum-starved for 48 hours followed by stimulation with full-length PAI-1 (40 nM) for 30 minutes and cellular lysates analyzed by western blot. (D) pAkt levels were normalized to total Akt levels; histogram illustrates mean ± SEM; asterisk=p<0.05; n=3.
Figure 4. Tiplaxtinin inhibits PAI-1-induced Akt phosphorylation and promotes VSMC apoptosis.
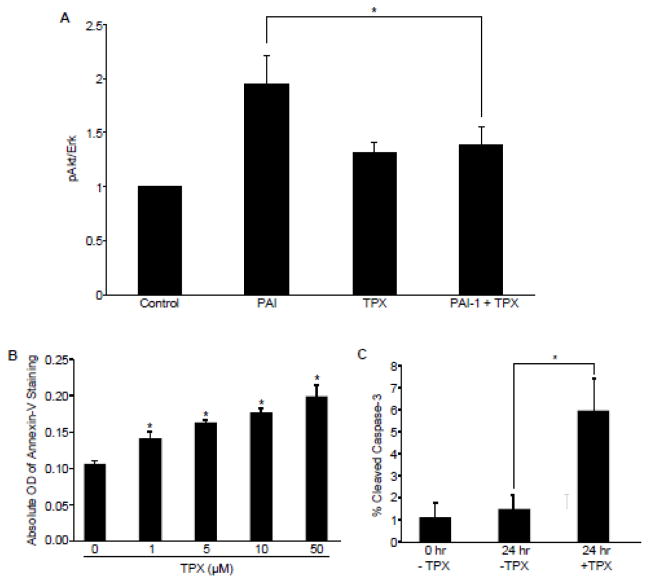
(A) RASMCs were serum-starved for 48 hours then treated with 40 nM PAI-1 with or without 10 nM tiplaxtinin. Cells were lysed, western blots probed for pAkt and normalized to Erk1. Data represent mean ± SEM, N=3. Asterisk=p ≤ 0.05; n=3. (B) RASMCs, cultured in 96-well plates, were treated with various concentrations of tiplaxtinin in complete media for 24 h prior to incubation of FITC-conjugated Annexin-V antibodies; apoptosis was measured using a fluorescence microplate reader. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; asterisks=p<0.05, n=3. (C) RASMCs were plated under reduced-serum conditions on tissue culture dishes pre-incubated with vitronectin and allowed to adhere and spread for 24 h. Cells were then either collected and fixed for immunocytochemical analysis of cleaved caspase-3 expression or treated with 10 μM tiplaxtinin or vehicle control for 24 h prior to fixation. Cleaved caspase-3-positive cells were scored as apoptotic and normalized to total cells (as assessed using DAPI staining). Data plotted are the percent mean ± SEM; asterisk=p<0.05, n=3. TPX=tiplaxtinin.
3.3 Tiplaxtinin induces VSMC apoptosis by promoting a switch from full-length to cleaved PAI-1
Since tiplaxtinin stimulates PAI-1 cleavage as well as VSMC apoptosis (Fig. 4B), it was necessary to determine if cleaved PAI-1 mimicked the tiplaxtinin-induced apoptotic response. Advantage was taken of the time-dependent cleavage of PAI-1 by elastase, a well-established model to evaluate the impact of cleaved PAI-1(CL-PAI-1) [25] (Fig. 4A, compare shift in total PAI-1 [solid arrow] to cleaved PAI-1 [dotted arrow]). Incubation of HuCASMC with CL-PAI-1 but not full-length (FL-PAI-1) resulted in a dramatic increase in apoptosis; the extent of the apoptotic response was dependent on the efficacy of PAI-1 cleavage (Fig. 5B). Identical results were obtained using Sepharose bead-immobilized elastase to generate PAI-1 cleavage (not shown). CL-PAI-1, moreover, significantly increased the level staurosporine-induced active caspase-3 (Fig. 5C). In contrast to FL-PAI-1-treated and control mice, i.p.-injected CL-PAI-1 and gavage-delivered tiplaxtinin (used separately) decreased neointimal thickening in response to carotid artery ligation (Fig. 5D–F). These data suggest that conversion of full-length to cleaved PAI-1 attenuates intimal hyperplasia by stimulating VSMC apoptosis.
Figure 5. Elastase-cleaved PAI-1 promotes VSMC apoptosis while tiplaxtinin and CL-PAI-1 attenuate neointima formation.
(A) Generation of CL-PAI-1 by incubation with human neutrophil elastase. Solid arrow indicates FL-PAI-1; dashed arrow denotes CL-PAI-1. (B) HuCASMCs treated with a final concentration of 10 nM FL-PAI-1 or CL-PAI-1 and a molar equivalent of elastase (as control) for 24 h were stained with ethidium homodimer and calcein AM to determine apoptotic index. Cells positive for ethidium homodimer were scored as apoptotic and normalized against calcein AM (total cells). Data are presented as mean ± SEM; asterisks=p<0.05, n=3. (C) HuCASMCs were treated with CL-PAI-1 (40 nM) and/or staruosporine (5 μM) as indicated for 24 h. Caspase-3 and actin (loading control) were assessed in whole cell lysates by western blot. (D) H&E stained cross-sections of contralateral control and ligated carotid arteries isolated from mice treated once daily with vehicle control (Con), 3 mg/kg tiplaxtinin (via oral gavage), 2 mg/kg FL-PAI-1 or CL-PAI-1 (both by intraperitoneal injection) for 14 days following ligation. Arrowheads indicate the internal elastic lamina. (E) Quantitation of the intima-to-media ration for the indicated ligated carotid artery groups. Data plotted represent the mean ± SEM; asterisks=p<0.05, n=4. (F) Time line of carotid ligation experiments; arrows indicate days of treatment with the indicated reagents.
3.4 Cleaved PAI-1 promotes plasmin-dependent VSMC apoptosis
As plasmin activation stimulates apoptosis [26], it was important to determine if CL-PAI-1 induces a plasmin-dependent apoptotic response. Addition of either tiplaxtinin or CL-PAI-1 increased the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin (Fig. 6A, left) to approximately the same level of plasmin activation as a result of PAI-1 knockdown (Fig. 6A, right). Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage, a down-stream effector of caspase-3, was also up-regulated in response to CL-PAI-1 while Tranexamic Acid, a potent inhibitor of plasmin generation, attenuated the apoptotic response suggesting that CL-PAI-1 stimulates apoptosis through plasmin-dependent caspase-3 activation (Fig. 6B). These data are consistent with additional findings that another plasmin inhibitor (aprotinin), a uPA inhibitor (amelioride), and the pan-MMP inhibitor (prinomastat) also reduced cleaved PAI-1-stimulated apoptosis (not shown). Plasminogen alone had no effect on cell viability; however, in the presence of tiplaxtinin, the increase in VSMC apoptosis was likely a consequence of decreased uPA inhibition and increased plasmin activation (Fig. 6C). These data confirm that CL-PAI-1 stimulates VSMC apoptosis in a plasmin-dependent manner.
Figure 6. Cleaved PAI-1 promotes VSMC apoptosis in a plasmin-dependent manner.
(A) HuCASMCs were treated with tiplaxtinin or CL-PAI-1 for 6 h (left) or with the indicated siRNAs for 48 h (right). Plasminogen, plasmin, PAI-1 and GAPDH (loading control) were evaluated in cell lysates by western blotting. (B) HuCASMCs were incubated with 100 μM tranexamic acid for 30 min prior to the addition of 40 nM CL-PAI-1. Cleaved PARP and actin (loading control) were assessed in cell lysates. (C) RASMCs were pretreated with 1.25 μM plasminogen for 30 min prior to addition of tiplaxtinin (10 μM, final concentration) for 24 h. Cells were collected, stained with Annexin-V and analysed by FACS. TPX=tiplaxtinin; CL-PAI-1=cleaved PAI-1
3.5 Cleaved PAI-1 upregulates FN14 and TWEAK expression while Full-length PAI-1 down-regulates FN14 surface expression via LRP1 and prevents TWEAK stimulated apoptosis
To determine the signaling intermediates involved in cleaved PAI-1-induced apoptosis, the activation of caspase-8 in response to CL-PAI-1 and tiplaxtinin (used separately) suggest the potential involvement of death receptors (Fig. 7A). One pathway recently identified to regulate PAI-1 in atherosclerotic lesions is the fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 (FN14) receptor and its cognate ligand, TNF-α weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) [47]. FN14 and soluble TWEAK levels were up-regulated in response to both CL-PAI-1 and tiplaxtinin while neither had any effect on total cell-associated TWEAK (Fig. 7B). Importantly, decreased circulating soluble TWEAK levels have been associated with poor prognostic outcomes in patients with cardiovascular and chronic kidney diseases [50] and based on these findings, it was necessary to determine if PAI-1 (cleaved or full-length) might modulate surface FN14 levels and signaling. HuCASMCs exhibited a significant down-regulation of FN14 in response to FL-PAI-1, but not CL-PAI-1 (Fig. 8A). PAI-1 recognizes the endocytic low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1) in a multimeric complex that includes uPA/tPA and integrins as binding partners inducing their internalization and lysosomal degradation [28]. Since PAI-1-dependent activation of Akt was inhibited by RAP (Fig. 8B) and LRP1−/− cells were not inducible for PAI-1-initiated pAkt induction (Fig. 8C), it was necessary to determine if LRP1-binding activity was required for FN14 down-regulation. Unlike incubation of VSMCs with FL-PAI-1 which reduced FN14 immunoreactivity, addition of the R76E-PAI-1 mutant (which cannot bind LRP1 [29]) failed to down-regulate surface FN14 levels (Fig. 8D). HuCASMCs were treated with both TWEAK and either FL-PAI, CL-PAI-1, or R76E-PAI-1 to directly test if PAI-1 impacts TWEAK-mediated apoptosis. While TWEAK alone and in combination with FL- PAI-1 had no effect on apoptosis, both CL-PAI-1 and R76E-PAI-1 in addition to TWEAK significantly stimulated an apoptotic response (Fig. 8E). These data suggest that FL-PAI-1, but not CL-PAI-1, down-regulates FN14 via LRP1-mediated endocytosis preventing TWEAK-stimulated apoptosis.
Figure 7. Upregulation of caspase-8 activation, FN14 and soluble TWEAK in response to cleaved PAI-1 and tiplaxtinin.
(A) HuCASMCs were incubated with tiplaxtinin or CL-PAI-1 in the concentrations indicated for 24 h. Whole cell extracts were separated by gel electrophoresis and blots probed with antibodies to caspase-8 and actin (loading control). Bands: 56 kDa=full-length caspase-8; 43, 41 kDa= cleaved caspase-8; 18 kDa= cleaved cleaved caspase-8; ns=non-specific band. (B) HuCASMCs were treated with 40 nM FL-PAI-1, 40 nM CL-PAI-1 or 10 μM tiplaxtinin for 24 hours, extracted and western blots developed using antibodies to TWEAK (depicted in table in B as mean ± SEM normalized to Erk2 expression, n=3) and FN14 using Erk2 as a loading control; NS=not significant. (C) Histogram is a plot of the mean ± SEM of the conditioned media levels of soluble TWEAK (relative to Ponceau S-stained total protein), n=4. TPX=tiplaxtinin; FL-PAI-1=full length PAI-1; CL-PAI-1=cleaved PAI-1
Figure 8. Full-length PAI-1 down-regulates FN14 in an LRP1-dependent manner and protects against TWEAK-stimulated apoptosis.
(A) HuCASMCs were treated with 40 nM FL- PAI-1 or CL-PAI-1 for 24 h. Surface FN14 expression was assessed by FACS. Graphed in (A) is a plot of the mean ± SEM; asterisks=p<0.05, n=4. Below the graph is a representative FACS histogram. n/s indicates no statistical significance. (B) PAI-1 induction of pAkt is LRP1-dependent. RASMCs were serum-starved for 48 hours before a 5 minute pretreatment with 5 μg/ml RAP prior to PAI-1 stimulation for 30 minutes. Cells were lysed and pAkt/Erk levels assessed by western blot analysis; pAkt levels were normalized to Erk1 and represented as a mean ± SEM, n=3. (C) LRP1−/− cells were treated with vehicle alone or 40 nM PAI-1 for 30 minutes; lysates were analyzed by western blot analysis. pAkt levels were normalized to total Erk1 levels. Data is represented as the mean ± SEM, n=3. Asterisks = p <0.05. n/s indicates no statistical significance. (D) RASMCs were incubated with 40 nM R76E-PAI-1 for 24 h, a recombinant PAI-1 mutant deficient in LRP1-binding. FACS was used to quantify surface FN14 expression. Graphed in (D) is a plot of the mean ± SEM; asterisks=p<0.05, n=4. n/s indicates no statistical significance. Below the graph is a representative FACS histogram. (E) HuCASMC were treated with 40 nM FL- PAI-1, CL-PAI-1 or 40 nM R76E-PAI-1 and 250 ng/ml soluble TWEAK, or TWEAK alone, for 6 h. Cells were collected, lysed and an aminomethylcoumarin (AMC)-tagged caspase-3 target (Z-DEVD) added. Fluorescence emission was monitored using a microplate reader every hour for 24 h. Data plotted represents the mean fluorescent intensity over a 24-h period ± SEM; asterisks=p<0.05 using a repeated-measures ANOVA. TPX=tiplaxtinin; FL-PAI-1=full length PAI-1; CL-PAI-1=cleaved PAI-1; R76E-PAI-1=LRP1-binding deficient mutant recombinant PAI-1 protein
4. Discussion
The relative abundance of the different conformational pools of PAI-1 may dictate whether VSMCs migrate or undergo apoptosis in response to injury. Indeed, in the context of cardiovascular disease, it appears that PAI-1 is both pro- and anti-restenotic [reviewed in 30] depending on the specific wound model, level of PAI-1 induction and vessel TGF-β1 expression. Global PAI-1 deletion, over-reliance on application of only the full-length, active form of PAI-1 to assess vascular remodeling, and uncertainties as to the role of PAI-1 conformation-dependent processes, however, are major confounders.
It is increasingly evident that beyond its anti-proteolytic role, PAI-1 also functions as a multifunctional signaling “ligand” where it impacts cellular responses, including the migratory, proliferative and survival programs, at the site of injury [22,28]. The ability of active PAI-1 to inhibit apoptosis, however, is not due to its ability to bind uPA or signal through uPAR [31]. Consistent with the present findings that FL-PAI-1 activates Akt and that CL-PAI-1 induces VSMC apoptosis, a truncated PAI-1 (PAI-123) mutant, deleted in much of the heparin binding-domain and the RCL, also stimulated endothelial cell apoptosis [32,33]. It appears that an intact RCL is required for the pro-survival function of PAI-1. Indeed, application of CL-PAI-1 results in an apoptotic resposne, both with and without additional death stimuli, while tiplaxtinin (10 μM), in the presence of FL-PAI-1 (40 nM), promotes apoptosis to a greater extent than tiplaxtinin alone. Since 20 μM tiplaxtinin generates the complete cleavage of 400 nM PAI-1 in 30 min, it is likely that under more prolonged exposure (24 h) tiplaxtinin effectively stimulates the cleavage of both exogenous recombinant and endogenous PAI-1 pools. Importantly, VSMCs show robust expression of tPA and uPA (not shown), a prerequisite for tiplaxtinin-mediated PAI-1 proteolytic cleavage.
Interestingly, elastase levels increase immediately after balloon-angioplasty, peak at one week and then decline [34] suggesting that lowered elastase activity levels, in the latter stages of vessel “repair” may contribute to a decrease in PAI-1 cleavage at the injury site resulting in reduced apoptosis and increased neointima expansion through both VSMC proliferation and migration. As elastase cleaves PAI-1 at the peptide bond between Val343-Ser344 (P4-P3) [25] and, whereas, tiplaxtinin promotes substrate behavior of PAI-1 allowing for a uPA/tPA protease attack at Arg346-Met347 (P1-P1′) [35], cleavage at either of these sites may be sufficient for promotion of apoptosis. Indeed, ligation-induced neointima formation was significantly attenuated by treatment with both tiplaxtinin and CL-PAI-1. Tiplaxtinin could be a useful therapeutic option in the context of elevated uPA and PAI-1 as it promotes a substrate-like conversion of PAI-1 [36–42].
Assessment of the mechanisms underlying the apoptotic response of VSMCs to CL-PAI-1 and tiplaxtinin implicated the extrinsic death receptor cascade since caspase-8 activation was a common event upon exposure to both. In the context of PAI-1 deficiency, the increase in active plasmin releases a pro-apoptotic soluble Fas ligand that stimulates endothelial cells apoptosis [43]. VSMCs, however, are relatively resistant to Fas ligand-stimulated death [44] and an antagonizing antibody to Fas ligand was unable to rescue VSMCs from tiplaxtinin or cleaved PAI-1-induced apoptosis (not shown). One candidate extrinsic apoptosis signaling pathway involved was the TWEAK/FN14 signaling axis since PAI-1 expression in atherosclerotic lesions appears responsive to exogenous TWEAK application [47]. TWEAK can activate its cognate receptor, FN14, either as a membrane-bound or solubilized ligand. The down-stream signaling and biological repercussions are tissue-type and context-dependent but have been implicated in apoptotic, proliferative and migratory processes [48].
The three forms of PAI-1 (full-length, latent and cleaved) interact with the endocytic low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) and stimulate JAK/STAT1-mediated VSMC migration [22]. Unlike FL-PAI-1 which down-regulates surface FN14, a full-length PAI-1 mutant unable to bind LRP1 (R76E-PAI-1) [49], failed to reduce FN14 levels. Furthermore, addition of soluble, recombinant TWEAK sensitized VSMC to apoptosis in the presence of CL-PAI-1 and R76E-PAI-1, but not in cells exposed to FL-PAI-1. This is significant since, within the context of cardiovascular disease, it appears that circulating soluble TWEAK levels are negatively correlated with disease incidence [50] and tiplaxtinin and CL-PAI-1, but not FL-PAI-1, both up-regulate membrane-bound and soluble TWEAK levels. How CL-PAI-1 promotes TWEAK solubility is unknown. The protease furin, an inhibitory target of PAI-1, cleaves TWEAK; the involvement of other protease systems (e.g. plasmin) in TWEAK bioactivity are unknown, however it appears that CL-PAI-1 versus FL-PAI-1 differentially regulate several components of the FN14:TWEAK signaling axis to impact VSMC survival.
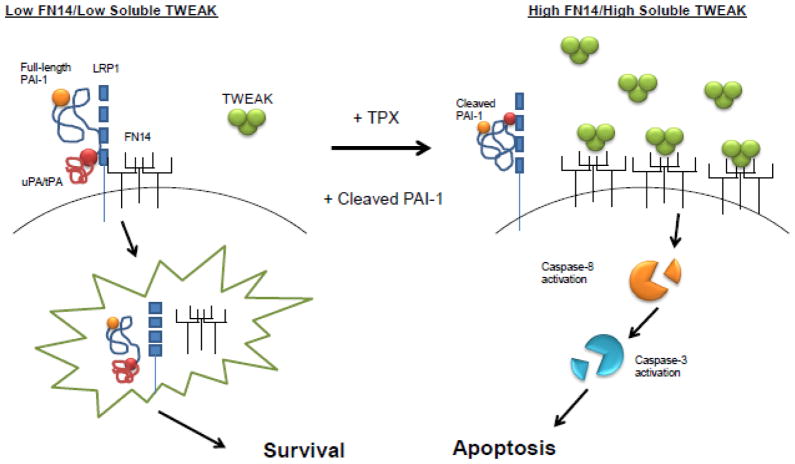
Collectively, these data are consistent with the hypothesis that PAI-1 regulates VSMC survival (Fig. 8). Full-length PAI-1 binds, and inhibits, uPA attenuating the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin while simultaneously down-regulating surface FN14 receptor expression via LRP1-mediated endocytosis. However, when the conformational pools of PAI-1 shift to increased levels of cleaved PAI-1 (either by tiplaxtinin or exogenous addition), conversion of plasminogen to plasmin is amplified. Both membrane-bound and soluble TWEAK expression is potentiated thereby stimulating FN14-TWEAK signaling leading to significant apoptosis. Since tiplaxtinin and CL-PAI-1 reduced neointimal lesion formation, therapies directed at manipulation of PAI-1 conformation may have applicability as a treatment option for restenosis
Figure 9. Hypothetical model.
Current findings suggest that PAI-1 regulates VSMC survival and potentiates neointimal formation. Full-length PAI-1 binds to, and inhibits, uPA attenuating the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin while simultaneously down-regulating surface FN14 receptor expression through LRP1-mediated endocytosis, promoting a pro-survival, pro-stenotic phenotype. When the conformational pools of PAI-1 shift to increased levels of cleaved PAI-1 (either by tiplaxtinin or exogenous addition), conversion of plasminogen to plasmin is amplified. Membrane-bound and soluble TWEAK expression is increased stimulating, thereby, FN14-TWEAK signaling leading to VSMC apoptosis and reduced neointimal hyperplasia.
Highlights.
PAI-1 expression is increased in the neointima of balloon-catheterized and ligated carotid arteries
The small molecule PAI-1 inhibitor tiplaxtinin inhibits PAI-1/uPA complex formation and stimulates PAI-1 cleavage
Tiplaxtinin and cleaved PAI-1, each independently, attenuate the neointimal response in the ligated carotid
Tiplaxtinin and cleaved PAI-1 both stimulate VSMC apoptosis in vitro
Prolonged exposure of VSMCs to cleaved PAI-1 induces apoptosis by augmenting TWEAK/FN14 pro-apoptotic signaling.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Drs. Anthony Ambesi and Mingzhe Zheng (Albany Medical College) for their technical advice and providing reagents.
7. Declaration of Funding
This work was supported by NIH GM057242 to P.J. Higgins, AHA 14PRE18170012 to T.M. Simone, and NIH HL092510 to H. Singer.
Abbreviations
- CL-PAI-1
cleaved PAI-1
- FL-PAI-1
full-length PAI-1
- HNE
human neutrophil elastase
- HuCASMCs
human carotid artery smooth muscle cells
- LRP1
low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1
- pAkt
phospho-Akt
- PAI-1
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
- PARP
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- Plg
plasminogen
- RASMCs
rat arterial smooth muscle cells
- RCL
reactive center loop
- SERPIN
serine protease inhibitor
- SERPINE1
serine protease inhibitor clade E member 1
- TPX
tiplaxtinin
- uPA
urokinase
- VN
vitronectin
- VSMCs
vascular smooth muscle cells
Footnotes
6. Conflict of Interest
None declared.
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Contributor Information
Tessa M. Simone, Email: simonet@mail.amc.edu.
Stephen P. Higgins, Email: higgins@mail.amc.edu.
Jaclyn Archambeault, Email: archamj@mail.amc.
Craig E. Higgins, Email: higginc@mail.amc.edu.
Roman G. Ginnan, Email: ginnanr@mail.amc.edu.
Harold Singer, Email: singer@mail.amc.edu.
Paul J. Higgins, Email: higginp@mail.amc.edu.
References
- 1.Bochaton-Piallat ML, Gabbiani F, Redard M, Desmouliere A, Gabbiani G. Apoptosis participates in cellularity regulation during rat aortic intimal thickening. Am J Pathol. 1995;146:1059–1064. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schwartz SM. Perspectives series: cell adhesion in vascular biology. Smooth muscle migration in atherosclerosis and restenosis. J Clin Invest. 1997;99:2814–2816. doi: 10.1172/JCI119472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Declerck PJ, De Mol M, Vaughan DE, Collen D. Identification of a conformationally distinct form of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, acting as a noninhibitory substrate for tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:11693–11696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Urano T, Strandberg L, Johansson LB, Ny T. A substrate-like form of plasminogen-activator-inhibitor type 1. Conversions between different forms by sodium dodecyl sulphate. Eur J Biochem. 1992;209:985–992. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dellas C, Loskutoff DJ. Historical analysis of PAI-1 from its discovery to its potential role in cell motility and disease. Thromb Haemost. 2005;93:631–640. doi: 10.1160/TH05-01-0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mottonen J, Strand A, Symersky J, Sweet RM, Danley DE, Geoghegan KF, Gerard RD, Goldsmith EJ. Structural basis of latency in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Nature. 1992;355:270–273. doi: 10.1038/355270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Levin EG, Santell L. Conversion of the active to latent plasminogen activator inhibitor from human endothelial cell. Blood. 1987;70:1090–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lindahl TL, Sigurdardottir O, Wiman B. Stability of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) Thromb Haemost. 1989;62:748–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Patston PA, Gettins P, Beechem J, Schapira M. Mechanism of serpin action: evidence that C1 inhibitor functions as a suicide substrate. Biochemistry. 1991;30:8876–8882. doi: 10.1021/bi00100a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gils A, Declerck PJ. Proteinase specificity and functional diversity in point mutants of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:12662–12666. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.19.12662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Aertgeerts K, De Bondt HL, De Ranter CJ, Declerck PJ. Mechanisms contributing to the conformational and functional flexibility of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Nat Struct Biol. 1995;2:891–897. doi: 10.1038/nsb1095-891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lee SH, Eren M, Vaughan DE, Schleimer RP, Cho SH. A plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibitor reduces airway remodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma. Am J Resp Cell Mol Biol. 2012;46:842–846. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0369OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Krause MP, Moradi J, Nissar AA, Riddell MC, Hawke TJ. Inhibition of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 restores skeletal muscle regeneration in untreated type 1 diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2011;60:1964–1972. doi: 10.2337/db11-0007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lijnen HR, Alessi MC, Frederix L, Collen D, Juhan-Vague I. Tiplaxtinin impairs nutritionally induced obesity in mice. Thromb Haemost. 2006;96:731–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schalkwijk CG, Stehouwer CD. PAI-1 inhibition in obesity and the metabolic syndrome: a promising therapeutic strategy. Thromb Haemost. 2006;96:698–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Leik CE, Su EJ, Nambi P, Crandall DL, Lawrence DA. Effect of pharmacologic plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibition on cell motility and tumor angiogenesis. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:2710–2715. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.02244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Crandall DL, Quinet EM, El Ayachi S, Hreha AL, Leik CE, Savio DA, Juhan-Vague I, Alessi MC. Modulation of adipose tissue development by pharmacological inhibition of PAI-1. Arterioscl Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:2209–2215. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000235605.51400.9d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lijnen HR, Alessi MC, Van Hoef B, Collen D, Juhan-Vague I. On the role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in adipose tissue development and insulin resistance in mice. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3:1174–1179. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Weisberg AD, Albornoz F, Griffin JP, Crandall DL, Elokdah H, Fogo AB, Vaughan DE, Brown NJ. Pharmacological inhibition and genetic deficiency of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 attenuates angiotensin II/salt-induced aortic remodeling. Arterioscl Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:365–371. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000152356.85791.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gorlatova NV, Cale JM, Elokdah H, Li D, Fan K, Warnock M, Crandall DL, Lawrence DA. Mechanism of inactivation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 by a small molecule inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:9288–9296. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611642200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Elokdah H, Abou-Gharbia M, Hennan JK, McFarlane G, Mugford CP, Krishnamurthy G, Crandall DL. Tiplaxtinin, a novel, orally efficacious inhibitor of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1: design, synthesis, and preclinical characterization. J Med Chem. 2004;47:3491–3494. doi: 10.1021/jm049766q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Degryse B, Neels JG, Czekay RP, Aertgeerts K, Kamikubo Y, Loskutoff DJ. The low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein is a motogenic receptor for plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:22595–22604. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313004200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fang H, Placencio VR, Declerck YA. Protumorigenic activity of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 through an antiapoptotic function. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104:1470–1484. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhang W, Halligan KE, Zhang X, Bisaillon JM, Gonzalez-Cobos JC, Motiani RK, Hu G, Vincent PA, Zhou J, Barroso M, Singer HA, Matrougui K, Trebak M. Orai1-mediated I (CRAC) is essential for neointima formation after vascular injury. Circ Res. 2011;109:534–542. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.246777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wu K, Urano T, Ihara H, Takada Y, Fujie M, Shikimori M, Hashimoto K, Takada A. The cleavage and inactivation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 by neutrophil elastase: the evaluation of its physiologic relevance in fibrinolysis. Blood. 1995;86:1056–1061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Horowitz JC, Rogers DS, Simon RH, Sisson TH, Thannickal VJ. Plasminogen activation induced pericellular fibronectin proteolysis promotes fibroblast apoptosis. Am J Resp Cell Molec Biol. 2008;38:78–87. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0174OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Brown SA, Ghosh A, Winkles JA. Full-length, membrane-anchored TWEAK can function as a juxtacrine signaling molecule and activate the NF-κB pathway. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:17432–17441. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.131979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Czekay RP, Wilkins-Port CE, Higgins SP, Freytag J, Overstreet JM, Klein RM, Higgins CE, Samarakoon R, Higgins PJ. PAI-1: An integrator of cell signaling and migration. Intl J Cell Biol. 2011;2011:562481. doi: 10.1155/2011/562481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Stefansson S, Muhammad S, Cheng XF, Battey FD, Strickland DK, Lawrence DA. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 contains a cryptic high affinity binding site for the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:6358–6366. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.11.6358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Diebold I, Kraicun D, Bonello S, Gorlach A. The ‘PAI-1 paradox’ in vascular remodeling. Thromb Haemost. 2008;100:984–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kwaan HC, Wang J, Svoboda K, Declerck PJ. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 may promote tumour growth through inhibition of apoptosis. Brit J Cancer. 2000;82:1702–1708. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.2000.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Drinane M, Walsh J, Mollmark J, Simons M, Mulligan-Kehoe MJ. The anti-angiogenic activity of rPAI-1(23) inhibits fibroblast growth factor-2 functions. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:33336–33344. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607097200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mulligan-Kehoe MJ, Wagner R, Wieland C, Powell R. A truncated plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 protein induces and inhibits angiostatin (kringles 1-3), a plasminogen cleavage product. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:8588–8596. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006434200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Barolet AW, Nili N, Cheema A, Robinson R, Natarajan MK, O’Blenes S, Li J, Eskandarian MR, Sparkes J, Rabinovitch M, Strauss BH. Arterial elastase activity after balloon angioplasty and effects of elafin, an elastase inhibitor. Arterioscl Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001;21:1269–1274. doi: 10.1161/hq0801.093589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lindahl TL, Ohlsson PI, Wiman B. The mechanism of the reaction between human plasminogen-activator inhibitor 1 and tissue plasminogen activator. Biochem J. 1990;265:109–113. doi: 10.1042/bj2650109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lennartz MR, Aggarwal A, Michaud TM, Feustel PJ, Jones DM, Brosnan MJ, Keller RS, Loegering DJ, Kreienberg PB. Ligation of macrophage Fcγ receptors recapitulates the gene expression pattern of vulnerable human carotid plaques. PloS One. 2011;6:e21803. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Falkenberg M, Tom C, DeYoung MB, Wen S, Linnemann R, Dichek DA. Increased expression of urokinase during atherosclerotic lesion development causes arterial constriction and lumen loss, and accelerates lesion growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:10665–10670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.162236599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Peng L, Bhatia N, Parker AC, Zhu Y, Fay WP. Endogenous vitronectin and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promote neointima formation in murine carotid arteries. Arterioscl Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:934–939. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.0000019360.14554.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.DeYoung MB, Tom C, Dichek DA. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 increases neointima formation in balloon-injured rat carotid arteries. Circulation. 2001;104:1972–1971. doi: 10.1161/hc4101.097110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chomiki N, Henry M, Alessi MC, Anfosso F, Juhan-Vague I. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in human liver and healthy or atherosclerotic vessel walls. Thromb Haemost. 1994;72:44–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schneiderman J, Sawdey MS, Keeton MR, Bordin GM, Bernstein EF, Dilley RB, Loskutoff DJ. Increased type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in atherosclerotic human arteries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:6998–7002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Olofsson BO, Dahlen G, Nilsson TK. Evidence for increased levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor and tissue plasminogen activator in plasma of patients with angiographically verified coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J. 1989;10:77–82. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bajou K, Peng H, Laug WE, Maillard C, Noel A, Foidart JM, Martial JA, DeClerck YA. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 protects endothelial cells from FasL-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:324–334. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.08.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sata M, Suhara T, Walsh K. Vascular endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells differ in expression of Fas and Fas ligand and in sensitivity to Fas ligand-induced cell death: implications for vascular disease and therapy. Arterioscl Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20:309–316. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.20.2.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sawdey MS, Loskutoff DJ. Regulation of murine type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in vivo. Tissue specificity and induction by lipopolysaccharide, tumor necrosis factor-α, and transforming growth factor-β. J Clin Invest. 1991;88:1346–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI115440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Schleef RR, Bevilacqua MP, Sawdey M, Gimbrone MA, Jr, Loskutoff DJ. Cytokine activation of vascular endothelium. Effects on tissue-type plasminogen activator and type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:5797–5803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Munoz-Garcia B, Madrigal-Matute J, Moreno JA, Martin-Ventura JL, Lopez-Franco O, Sastre C, Ortega L, Burkly LC, Egido J, Blanco-Colio LM. TWEAK-Fn14 interaction enhances plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and tissue factor expression in atherosclerotic plaques and in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;89:225–233. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Winkles JA. The TWEAK-Fn14 cytokine-receptor axis: discovery, biology and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:411–425. doi: 10.1038/nrd2488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Stefansson S, Muhammad S, Cheng XF, Battey FD, Strickland DK, Lawrence DA. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 contains a cryptic high affinity binding site for the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:6358–6366. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.11.6358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Blanco-Colio LM. TWEAK/Fn14 Axis: A promising target for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Front Immunol. 2014;5(3):1–13. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]