Abstract
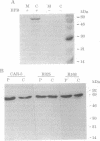
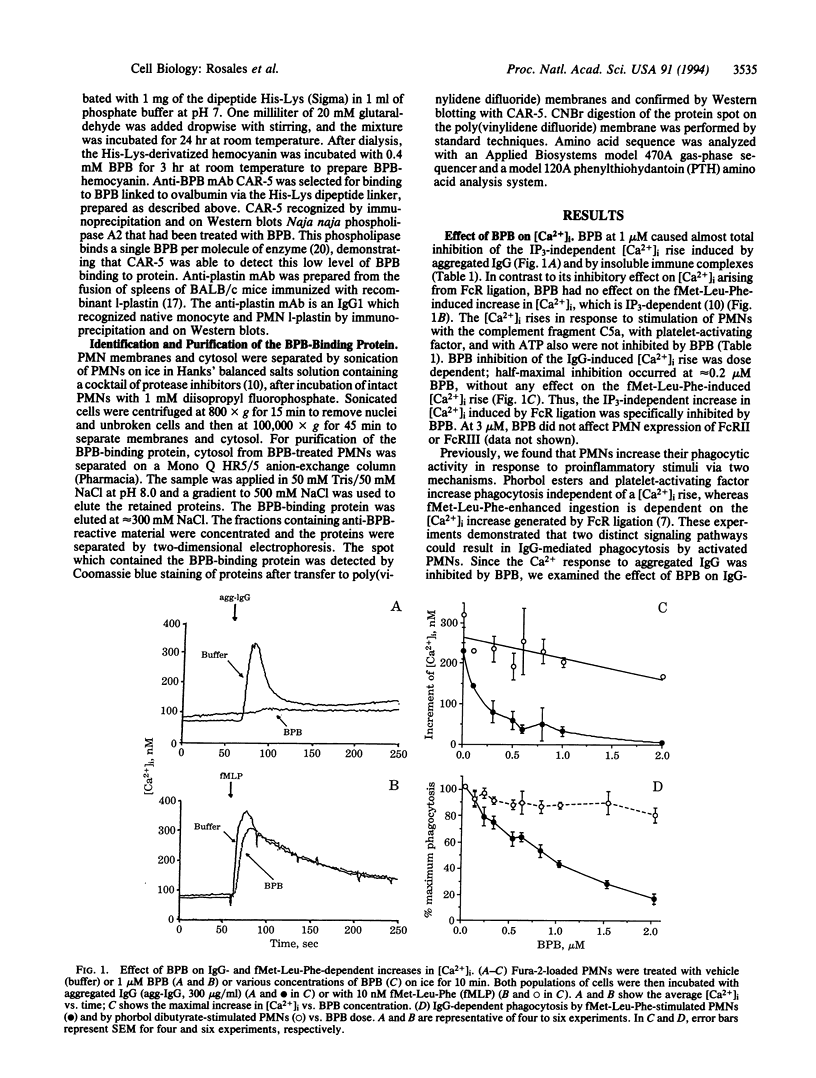
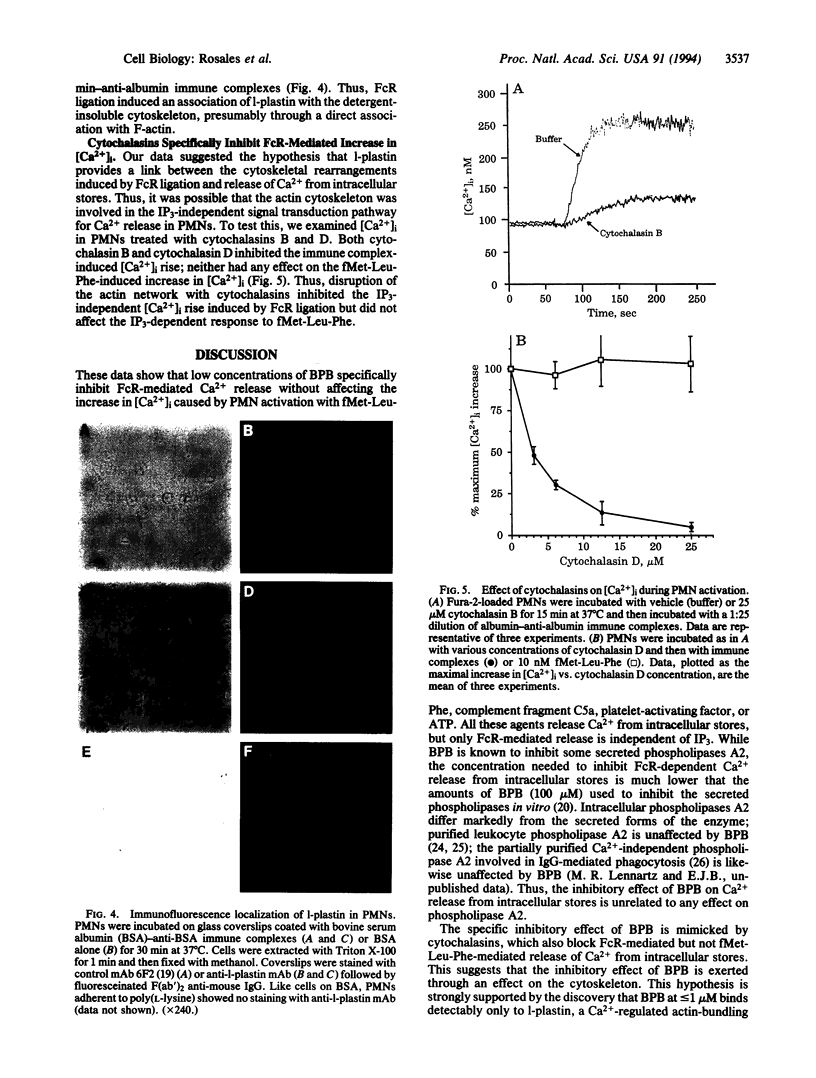
Ligation of IgG Fc receptors on polymorphonuclear leukocytes causes an increase in the concentration of free intracytoplasmic Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) which arises from release of intracellular stores but is independent of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. We found that bromophenacyl bromide (BPB), an alkylating agent which inhibits leukocyte degranulation, adherence, and phagocytosis, inhibited IgG-stimulated increases in [Ca2+]i with an IC50 of 0.2 microM. In contrast, BPB had no effect on inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent [Ca2+]i increases induced by fMet-Leu-Phe, complement fragment C5a, ATP, or platelet-activating factor. Using a monoclonal antibody specific for BPB, we identified in polymorphonuclear leukocytes a single cytosolic protein of 66 kDa and isoelectric point pH 5.6 which bound BPB when intact cells were treated with the alkylating agent. This BPB-binding protein was identified as l-plastin, a Ca(2+)-regulated actin-bundling protein. l-Plastin was found associated with the Triton X-100-insoluble cytoskeleton in polymorphonuclear leukocytes adherent to immune complexes, suggesting that BPB affects Fc receptor-mediated signal transduction by altering the actin cytoskeleton. Consistent with this hypothesis, both cytochalasin B and cytochalasin D inhibited the IgG-dependent increase in [Ca2+]i, without any effect on fMet-Leu-Phe-induced Ca2+ release. These data suggest that the actin cytoskeleton is essential for signal transduction from plasma membrane Fc receptors and that l-plastin has a critical role in activation of this pathway.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderem A. The MARCKS brothers: a family of protein kinase C substrates. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):713–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90546-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal A., Salem P., Robbins K. C. Involvement of p72syk, a protein-tyrosine kinase, in Fc gamma receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15900–15905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M., Birx D. L., Wetzler E. M., O'Shea J. J., Brown E. J., Cross A. S. Calcium requirements for increased complement receptor expression during neutrophil activation. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1342–1348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borregaard N., Kjeldsen L., Lollike K., Sengeløv H. Ca(2+)-dependent translocation of cytosolic proteins to isolated granule subpopulations and plasma membrane from human neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 15;304(2-3):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80617-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon L. Y., Iida N., Jin H. The involvement of the cytoskeleton in regulating IP3 receptor-mediated internal Ca2+ release in human blood platelets. Cell Biol Int. 1993 Aug;17(8):751–758. doi: 10.1006/cbir.1993.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon L. Y., Jin H., Iida N., Brandt N. R., Zhang S. H. The involvement of ankyrin in the regulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-mediated internal Ca2+ release from Ca2+ storage vesicles in mouse T-lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7290–7297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Fath K. Focal contacts: transmembrane links between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Bioessays. 1989 Apr;10(4):104–108. doi: 10.1002/bies.950100403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway C. A., Carvajal M. E., Li Y., Carraway K. L. Association of p185neu with microfilaments via a large glycoprotein complex in mammary carcinoma microvilli. Evidence for a microfilament-associated signal transduction particle. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5582–5587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly P. A., Farrell C. A., Merenda J. M., Conklyn M. J., Showell H. J. Tyrosine phosphorylation is an early signaling event common to Fc receptor crosslinking in human neutrophils and rat basophilic leukemia cells (RBL-2H3). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 31;177(1):192–201. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91967-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser K. B., Lister M. D., Ulevitch R. J., Dennis E. A. Macrophage phospholipase A2 activity and eicosanoid production: studies with phospholipase A2 inhibitors in P388D1 cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1990;275:1–16. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5805-3_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendey B., Maxfield F. R. Regulation of neutrophil motility and adhesion by intracellular calcium transients. Blood Cells. 1993;19(1):143–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaconi M. E., Lew D. P., Carpentier J. L., Magnusson K. E., Sjögren M., Stendahl O. Cytosolic free calcium elevation mediates the phagosome-lysosome fusion during phagocytosis in human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1555–1564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberly R. P., Ahlstrom J. W., Click M. E., Edberg J. C. The glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-linked Fc gamma RIIIPMN mediates transmembrane signaling events distinct from Fc gamma RII. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1239–1255. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowith J. B., Lennartz M. R., Rogers M., Morrison A. R., Brown E. J. Phospholipase activation during monocyte adherence and spreading. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 1;149(5):1729–1735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowith J. B., Rogers M., Lennartz M. R., Brown E. J. Essential fatty acid deficiency impairs macrophage spreading and adherence. Role of arachidonate in cell adhesion. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1071–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennartz M. R., Brown E. J. Arachidonic acid is essential for IgG Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis by human monocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):621–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennartz M. R., Lefkowith J. B., Bromley F. A., Brown E. J. Immunoglobulin G-mediated phagocytosis activates a calcium-independent, phosphatidylethanolamine-specific phospholipase. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Nov;54(5):389–398. doi: 10.1002/jlb.54.5.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. S., Aebersold R. H., Kent S. B., Varma M., Leavitt J. Molecular cloning and characterization of plastin, a human leukocyte protein expressed in transformed human fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4659–4668. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. S., Aebersold R. H., Leavitt J. Correction of the N-terminal sequences of the human plastin isoforms by using anchored polymerase chain reaction: identification of a potential calcium-binding domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1818–1821. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. S., Park T., Chen Z. P., Leavitt J. Human plastin genes. Comparative gene structure, chromosome location, and differential expression in normal and neoplastic cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2781–2792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F. P., Gresham H. D., Schwarz E., Brown E. J. Molecular cloning of integrin-associated protein: an immunoglobulin family member with multiple membrane-spanning domains implicated in alpha v beta 3-dependent ligand binding. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(2):485–496. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lister M. D., Glaser K. B., Ulevitch R. J., Dennis E. A. Inhibition studies on the membrane-associated phospholipase A2 in vitro and prostaglandin E2 production in vivo of the macrophage-like P388D1 cell. Effects of manoalide, 7,7-dimethyl-5,8-eicosadienoic acid, and p-bromophenacyl bromide. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8520–8528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lokeshwar V. B., Bourguignon L. Y. Tyrosine phosphatase activity of lymphoma CD45 (GP180) is regulated by a direct interaction with the cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21551–21557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. W., Hendey B., Maxfield F. R. Attachment to fibronectin or vitronectin makes human neutrophil migration sensitive to alterations in cytosolic free calcium concentration. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(1):149–158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.1.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Shiroo M., Kung H. F., Copeland T. D. Purification and characterization of a cytosolic 65-kilodalton phosphoprotein in human leukocytes whose phosphorylation is augmented by stimulation with interleukin 1. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3765–3770. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba Y., Ito M., Zu Y., Shigesada K., Maruyama K. Human T cell L-plastin bundles actin filaments in a calcium-dependent manner. J Biochem. 1992 Oct;112(4):503–507. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odin J. A., Edberg J. C., Painter C. J., Kimberly R. P., Unkeless J. C. Regulation of phagocytosis and [Ca2+]i flux by distinct regions of an Fc receptor. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1785–1788. doi: 10.1126/science.1837175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud M., Derancourt J. Purification and further characterization of macrophage 70-kDa protein, a calcium-regulated, actin-binding protein identical to L-plastin. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3448–3455. doi: 10.1021/bi00064a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. F., Deems R. A., Mincey T. C., Dennis E. A. Chemical modification of the histidine residue in phospholipase A2 (Naja naja naja). A case of half-site reactivity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2405–2411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romer L. H., Burridge K., Turner C. E. Signaling between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton: tyrosine phosphorylation and focal adhesion assembly. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1992;57:193–202. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1992.057.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales C., Brown E. J. Calcium channel blockers nifedipine and diltiazem inhibit Ca2+ release from intracellular stores in neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1443–1448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales C., Brown E. J. Signal transduction by neutrophil immunoglobulin G Fc receptors. Dissociation of intracytoplasmic calcium concentration rise from inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5265–5271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales C., Brown E. J. Two mechanisms for IgG Fc-receptor-mediated phagocytosis by human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3937–3944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Lechene C. Adhesion is required for protein kinase C-dependent activation of the Na+/H+ antiporter by platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6138–6141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A. Signaling by integrins: implications for tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 1;53(7):1503–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Stoehr S. J. Micromolar concentrations of free calcium provoke secretion of lysozyme from human neutrophils permeabilized with saponin. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1859–1865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toll J. B., Andersson R. G. Effects of mepacrine and p-bromophenacyl bromide on anti-IgE and phospholipase A2-induced histamine release from human basophils. Agents Actions. 1986 Aug;18(5-6):518–523. doi: 10.1007/BF01964957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zu Y., Kohno M., Kubota I., Nishida E., Hanaoka M., Namba Y. Characterization of interleukin 2 stimulated 65-kilodalton phosphoprotein in human T cells. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 30;29(4):1055–1062. doi: 10.1021/bi00456a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Arruda M. V., Watson S., Lin C. S., Leavitt J., Matsudaira P. Fimbrin is a homologue of the cytoplasmic phosphoprotein plastin and has domains homologous with calmodulin and actin gelation proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1069–1079. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]