Abstract
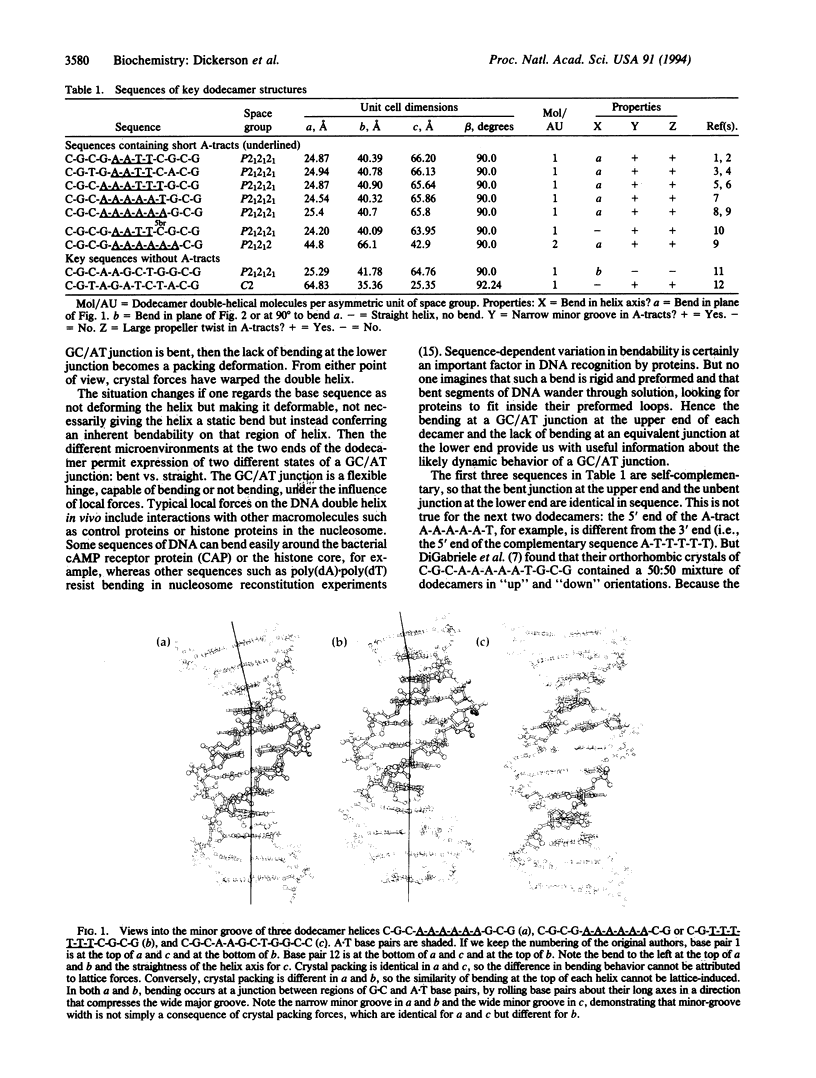
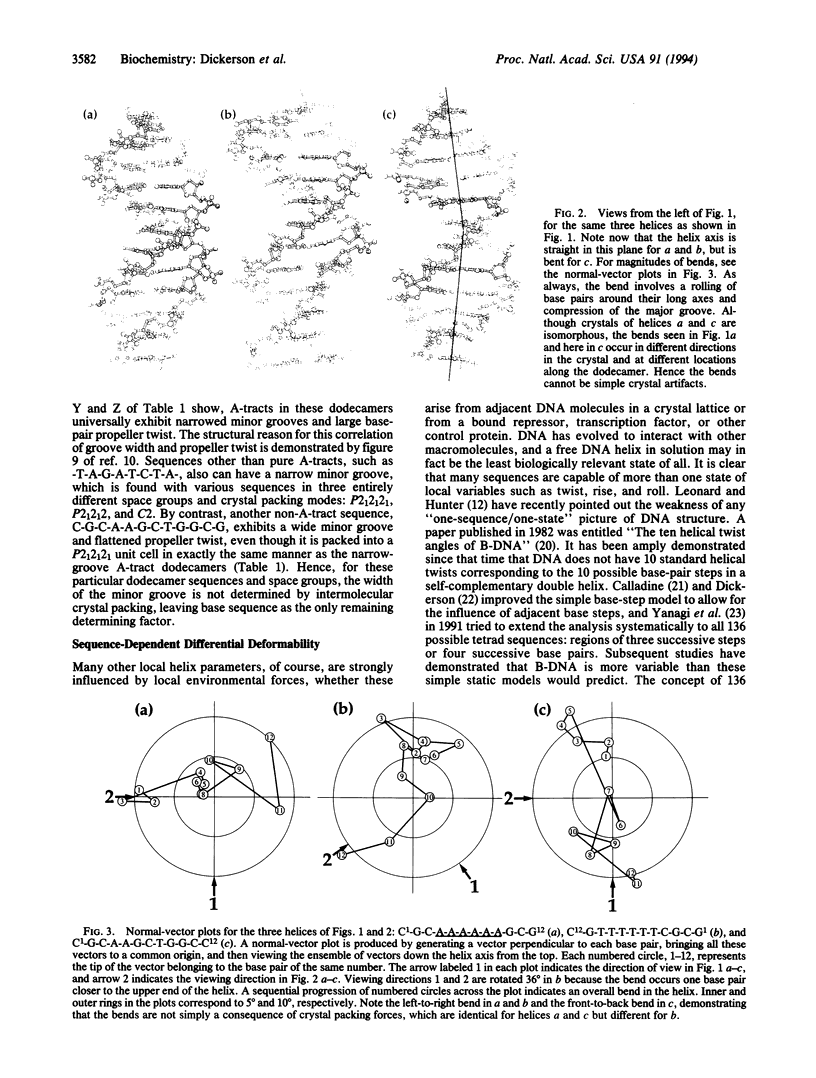
A systematic comparison of crystal structures of nine different B-DNA dodecamers, in three different space groups, with and without A-tracts, shows that crystal packing or lattice forces are of secondary importance for helix axis bending, minor-groove width, and propeller twist. While other local helix parameters may be influenced or even established by crystal packing, the properties just enumerated are determined primarily by base sequence. One and the same crystal packing scheme can accommodate a bend in one of two different directions, or no bend at all. A-tract regions of B-DNA are inherently straight and unbent, with base-pair inclination no different from that of general-sequence B-DNA. Where bends are observed at junctions between G.C and A.T regions, they always involve a roll about base-pair long axes in a direction that compresses the wide major groove and, hence, are 90 degrees away from that necessary for the correctness of the junction model of A-tract bending. The G.C/A.T junction appears to be a flexible hinge, capable of adopting either a straight or a bent conformation under the local influence of weak crystal packing forces. Such forces therefore are a source of information about DNA deformability and not a curse to be deplored. But as an indication of the weakness of crystal packing forces, introduction of a single bromine atom in the major groove is sufficient to eliminate a bend, although brominated and unbrominated crystals are isomorphous.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calladine C. R. Mechanics of sequence-dependent stacking of bases in B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 25;161(2):343–352. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll M., Frederick C. A., Wang A. H., Rich A. A bifurcated hydrogen-bonded conformation in the d(A.T) base pairs of the DNA dodecamer d(CGCAAATTTGCG) and its complex with distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8385–8389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Drak J. Global features of DNA structure by comparative gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:46–71. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12005-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Drak J., Kahn J. D., Levene S. D. DNA bending, flexibility, and helical repeat by cyclization kinetics. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:3–29. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGabriele A. D., Sanderson M. R., Steitz T. A. Crystal lattice packing is important in determining the bend of a DNA dodecamer containing an adenine tract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1816–1820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGabriele A. D., Steitz T. A. A DNA dodecamer containing an adenine tract crystallizes in a unique lattice and exhibits a new bend. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jun 20;231(4):1024–1039. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Base sequence and helix structure variation in B and A DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):419–441. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Goodsell D. S., Kopka M. L., Pjura P. E. The effect of crystal packing on oligonucleotide double helix structure. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Dec;5(3):557–579. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10506413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards K. J., Brown D. G., Spink N., Skelly J. V., Neidle S. Molecular structure of the B-DNA dodecamer d(CGCAAATTTGCG)2. An examination of propeller twist and minor-groove water structure at 2.2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 20;226(4):1161–1173. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratini A. V., Kopka M. L., Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Reversible bending and helix geometry in a B-DNA dodecamer: CGCGAATTBrCGCG. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14686–14707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodsell D. S., Kopka M. L., Cascio D., Dickerson R. E. Crystal structure of CATGGCCATG and its implications for A-tract bending models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2930–2934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzeskowiak K., Goodsell D. S., Kaczor-Grzeskowiak M., Cascio D., Dickerson R. E. Crystallographic analysis of C-C-A-A-G-C-T-T-G-G and its implications for bending in B-DNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 31;32(34):8923–8931. doi: 10.1021/bi00085a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Sander C., Trifonov E. N. The ten helical twist angles of B-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):1097–1104. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Drak J., Rice J. A., Crothers D. M. Determination of the extent of DNA bending by an adenine-thymine tract. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4227–4234. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Martinson H. G. Nucleosomes will not form on double-stranded RNa or over poly(dA).poly(dT) tracts in recombinant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6869–6888. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen T. A., Kopka M. L., Dickerson R. E. Crystal structure analysis of the B-DNA dodecamer CGTGAATTCACG. Biochemistry. 1991 May 7;30(18):4443–4449. doi: 10.1021/bi00232a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard G. A., Hunter W. N. Crystal and molecular structure of d(CGTAGATCTACG) at 2.25 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1993 Nov 5;234(1):198–208. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayana N., Ginell S. L., Russu I. M., Berman H. M. Crystal and molecular structure of a DNA fragment: d(CGTGAATTCACG). Biochemistry. 1991 May 7;30(18):4449–4455. doi: 10.1021/bi00232a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H. C., Finch J. T., Luisi B. F., Klug A. The structure of an oligo(dA).oligo(dT) tract and its biological implications. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):221–226. doi: 10.1038/330221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster G. D., Sanderson M. R., Skelly J. V., Neidle S., Swann P. F., Li B. F., Tickle I. J. Crystal structure and sequence-dependent conformation of the A.G mispaired oligonucleotide d(CGCAAGCTGGCG). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6693–6697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing R., Drew H., Takano T., Broka C., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. Crystal structure analysis of a complete turn of B-DNA. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):755–758. doi: 10.1038/287755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi K., Privé G. G., Dickerson R. E. Analysis of local helix geometry in three B-DNA decamers and eight dodecamers. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jan 5;217(1):201–214. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90620-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





